2.4 - Organic Compounds
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
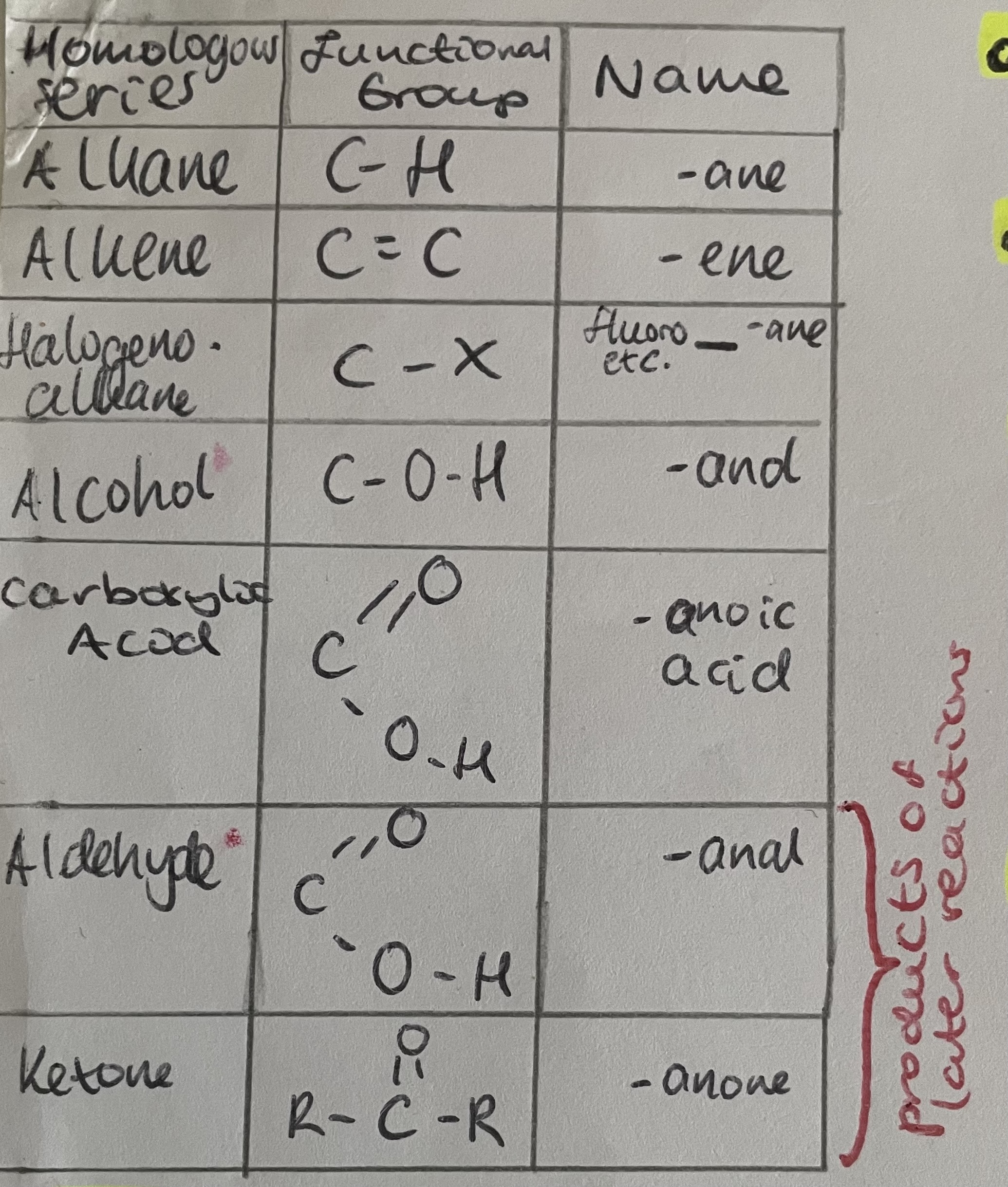
Functional group
Atom/group which gives the compound its characteristic properties
Homologous series
A series of compounds with the same functional group and general formula
Hydrocarbon
A compound containing carbon and hydrogen onkt
Saturated compound
A compound in which all the C to C bonds are single bonds
Unsaturated compound
A compound that contains C to C multiple bonds
Molecular formula
Shows the number of atoms presents in a compound
Structural formula
Shows which atoms are bonded to which
Shortened formula
Shows the functional group and structure in sufficient detail so that the compound is unambiguous. Cannot be used if details of the bonds needed
Skeletal formula
Shows the C/H backbone of the molecule as a series of bonds with any functional groups attached. Does not show interactive chains
Displayed formula
Shows all of the atoms and bonds in the molecule. Used for mechanisms
Nomenclature rules
Find the longest hc chain → stem of name
Name C atoms, starting from side which gives smallest number
Identify side chains and functional groups and add to name as prefixes
List prefixes in alphabetical order
Commas between numbers
Hyphens between letters and numbers
Effect of chain length on melting + boiling temperatures
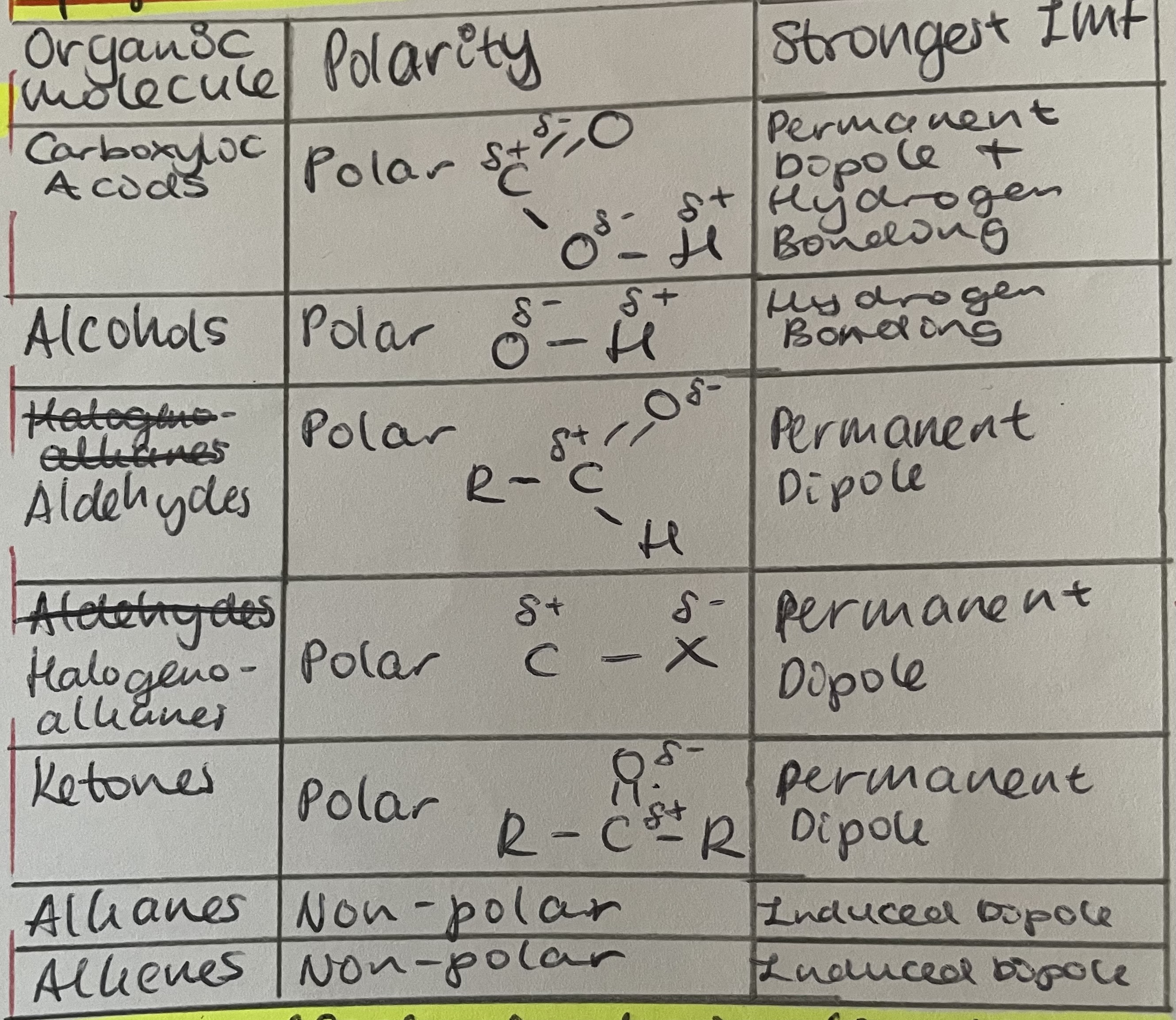
Hydrocarbons contain only td-td VdW present between the molecules (WEAK IMFs)
Weak IMFs act between surfaces of the molecules
The more surface in contact, the stronger the forces so more energy needed to overcome forces
Small hc = (g) At room temp
Larger = liquid or solid at room temp
Effect of branching on boiling temperatures
more branches → more spherical molecules
Small SA available for contact
→ less SA for contact between molecules
→ weaker VdW forces between molecules → less energy needed to separate them → lower Tb
Effect of functional groups on boiling temperatures
Increases chain length and branching
Molecules that form H-bonds have higher Tb than those of a similar size that cannot H-bond
Effect of functional groups on solubility
Molecules that cannot H-bond/those that can only form dp or VdW are not able to form significant attractions with the polar water molecules and therefore cannot dissolve
Smaller alcohols/carboxylic acids/molecules which can H bond = soluble in water
Solubility decreases as chain length increases
As size of hc part of molecule increases, it exerts such a large hydrophobic effect on that compound is no longer soluble
Structural isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but with different structural formula
Types of structural isomerism
Chain isomerism
Position isomerism
Functional group isomerism
Chain isomerism
Carbon chain of molecule is arranged different differently
One straight chained and other isomers are branched chains
Position isomers
Functional group is in a different position in the molecule
Functional group isomerism
Functional group in the compounds is different
Cyclical molecules
General formula = CnH2n
Each C atom in the ring is bonded to 2 H atoms
Table of homologous series
Polarity of organic molecules