INB 373 Exam 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Tundra
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ polar (canda, greenland, russia)
temperature→ cold
precipitation→ wet or dry
vegetation→ no trees, small woody plants
diversity→ low
fire→ rare
human uses/threats→ climate change thawing permafrost— oil and gas extraction
Boreal Forests
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ above 50 deg N but south of Tundra
temperature→ cold (freezing half year)
precipitation→ wet or dry (permafrost maintains high water availb)
vegetation→ coniferous trees
diversity→ low
fire→ common
human uses/threats→ lumber, thaw permaforst GW
Temperate evergreen forest
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ 30-40 degrees N,S (western WA, OR, SE, Australia)
temperature→ cold winter and warm summers
precipitation→ variable (characterized by low nutrient status
vegetation→ coniferous trees
diversity→ low
fire→ common
human uses/threats→ beautiful hiking
Temperate deciduous forest
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ 30-50 deg from equator (mostly N hemisphere)
temperature→ cold winter, warm summers
precipitation→ year round percp, more than grasslands
vegetation→ cold-deciduous broad-leaved trees
diversity→ moderate
fire→ rare (higher moisture)
human uses/threats→ logging, urbanization, agriculture
Temprate Scrubland and Woodland
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ California and mediterranean
temperature→ seasonal
precipitation→ wet in winter
vegetation→ shrubs, grasses, trees (no multilayer forest)
diversity→ moderate to high
fire→ common
human uses/threats→ grazing, agriculture, urbanization
Temperate grassland
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ 30-50 deg from equator (OK, TX, Australia)
temperature→ intermediate
precipitation→ intermediate
vegetation→ grasses and herbs (forbs), very few woody plants
diversity→ moderate
fire→ common
human uses/threats→ agriculture !!
Desert
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ 30 deg N/S (Australia, Sahara, Arizona)
temperature→ hot
precipitation→ little
vegetation→ succulents, annual herbaceous plants
diversity→ low to moderate
fire→ rare (not enough vegetation to keep fire going)
human uses/threats→ grazing, recreation, urbanization
Tropical seasonal forest + Savanna
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ 20 deg N/s (close to edge of tropics— Costa Rica, South Africa)
temperature→ hot
precipitation→ seasonal, heavy rains when ITCZ passes overhead
vegetation→ drought-deciduous trees, savanna-continuous grass layer with trees
diversity→ moderate to high
fire→ common
human uses/threats→ grazing and agriculture
Tropical rainforest
geographical location
temperature
precipitation
vegetation
diversity
fire
human uses/threats
geographical location→ near the equator
temperature→ hot
precipitation→ lots
vegetation→ broadleaf evergreen trees
diversity→ high
fire→ rare (high humidity)
human uses/threats→ logging, agriculture, grazing
define nitrification and denitrification
nitrification→ biological process where ammonia is converted to nitrate
ammonium converted to nitrite then to nitrate all by bacteria
provides nitrate for plant uptake
denitrification→ biological process where nitrate reduced to nitrogen bass or nit-oxide
removed nitrogen from ecosystem by bacteria
permafrost
→ permanently frozen ground for 2+ years, mainly in polar regions
thawing permafrost releases GHG from decomposing organic matter
stores tons of carbon
maintains ecosystem water flow
eutrophication
→ the excess of enrichment of water bodies with nutrients
nitrogen and phosphorus abundance
leads to oxygen depletion
how? agriculture runoffs, sewage, industrial waste, detergents
**a natural process but still influenced by humans
State 3 Micro-evolution forces critical to ecology
Genetic drift: random changes in allele frequencies in populations
Larger effect on smaller populations→ fixation of bad alleles
Gene flow: introduction of new alleles through movement of organisms
Ex. 1980s Africa mosquitos became immune to pesticides and resistance spread
Natural selection: ecological selective pressures and adapting to new environments
Ex. pocket mice and volcanic eruption
positive feedback loop of global temperature rise
increased GHG’s like CO2 increased global temps
polar ice caps melting
less ice reflecting sunlight
less heat back to atm/space
more uptake of radiation by darker ground and water→ Earth temp increased
Freshwater zones
photic (light) zone→ upper layer where sunlight penetrates so supports photosynthesis
aphotic (dark) zone→ deeper layer without sunlight, so low light and low oxygen (organic sinking)
benthic zone→ bottom sediment layer, home to decomposers like bacteria
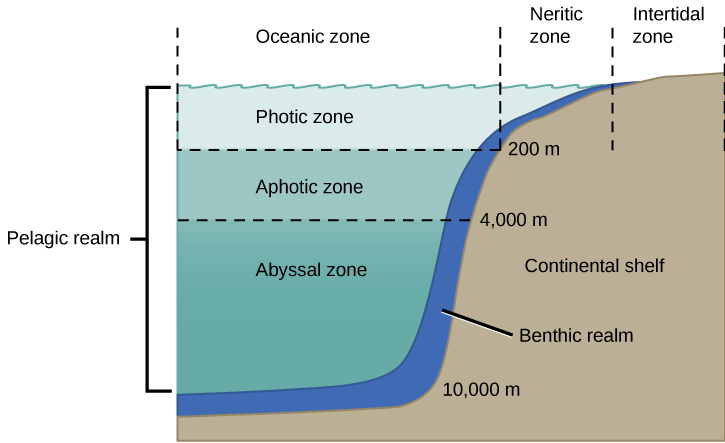
Marine Zones
nearshore (coastal)→ shallow water, rich in biodiversity (nursery) so high productivity w/ nutrient flow from inland
benthic (seafloor)→ shoreline to ocean trenches, home of coral, crab, deep-sea-fish, critical for decomp
pelagic (open water)→ supports free-swimming organisms (fish, jellyfish, whales)
photic and aphotic zones
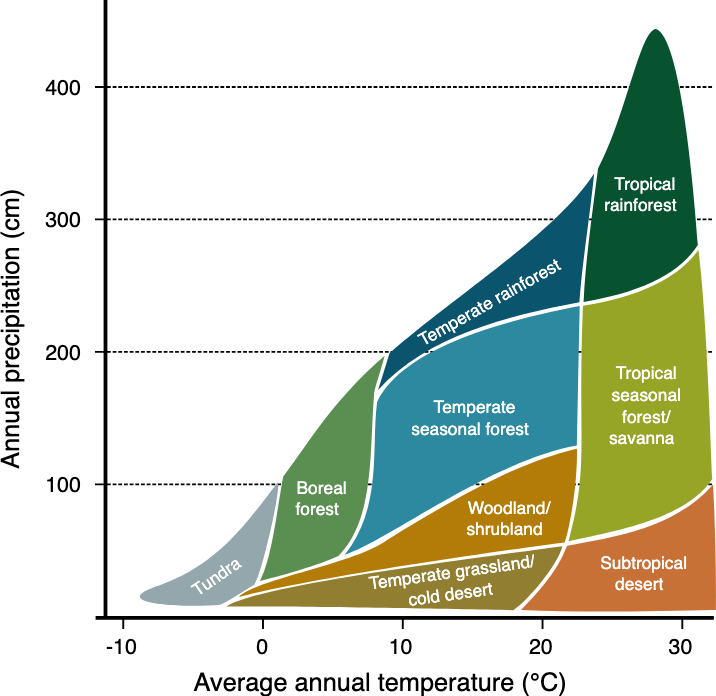
identify a temperature and precipitation graph of biomes
identify pools of carbon in organic and inorganic matter
organic
living organisms (macromolecules)
detritus (dead living matter)
fossil fuels
inorganic
CO2 in air/water
bicarbonate ion and carbonate ions is water
nitrogen cycle
nitrogen in air becomes fixed in bacteria/frankia and used by plants
lightening can also introduce nitrogen to soil
herbivores eat plants→ carnivores eat herbivores
detrivores eat nitrogen from soil and are also eaten by carnivores
detritus take in nitrogen by death, waste, decomp, and nitrification
denitrification and burning fossil fuels relased nitrogen back into air
Guilds vs Functional group
guild→ species with similar roles in an ecosystem but different morphology
ex. nectar-feeders like hummingbirds and butterflies
functional group→ species that have a similar function in an ecosystem and same morphology (look alike)
ex. grassland grasses all perform photosynthesis
keystone vs foundation species
keystone→ disproportionate impact on ecosystem compared to abundance
fewer in # but sig control
ex. sea otters (control urchin pop)
foundation→ important species in food web bc of high number
lots in # so usually primary producers
ex. grass eaten by bison
**keystone species CANNOT be a foundation species and vice versa
types of food chain controls
bottom-up: amount of biomass is controlled by limited resources
GPP/NPP dependent
top-down: top predators control food web
more common
ex. sea otter, urchins, and kelp relationship
Trophic Cascade
→ change in the population of a top predator in a food web indirectly impacts the abundance of species at lower trophic levels
ex. sea otters
Pools vs. Fluxes
pools of matter→ compounds for a certain area
flux→ how pools move from one form to another
carbon pools and fluxes
pools→ atm, oceans, fossil fuels, biomass, soils
fluxes→ photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, ocean exchange
nitrogen pools and fluxes
pools→ atm (largest), soil, biomass, water
fluxes→ nitrogen fixation, decomp, denitrification
phosphorus pools and fluxes
pools→ rocks (largest), soil, water, organisms
fluxes→ volcanic eruptions, fossil fuel combustion, decomp
GPP & NPP
GPP→ total photosynthesis area/unit time
NPP→ energy available to herbivores and detrivores/unit time (left over after plant uses E)
Global Circulation cells (3)
hadley cells→ transports warm air from equator to 30o latitude, air rising to poles cools creating trade winds
ferrel cells→ 30o-60o movies air in the opposite direction to transfer heat poleward
polar cells→ circulate cold air from poles toward lower latitudes to complete global winds system
coriolis effect
→ phenomenon due to Earth’s (axis) rotation impacting ocean currents, atm circulation, weather systems, migration, climate
define ecology
→ scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environment
outline the levels of ecology (7)
environment→ abiotic factors (air, water, detritus/waste, minerals)
organismal→ single biotic
population→ group of same species interact with each other
community→ two species interacting (all biotic)
ecosystem→ at least two biotic and one abiotic factor interact
landscape→ multiple ecosystems
global→ all ecosystems in planet
detrivores
→ eat detritus (waste) for energy
ex. earthworm