measurement of energy transfer Pt 1 - 4
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what are two ways we can measure energy expenditure and the aerobic system
Direct Calorimetry: Directly measures energy expenditure via heat production.
- Limited practical applications with humans.
INdirect Calorimetry:
1. Open circuit spirometry •O2 consumption, •CO2 production
2. Nitrogen balance- not rlly abt energy *Doubly labeled water
what is open spirometry
“Metabolic Cart” (most common)
EXPIRED AIR is measured with a high speed
1. O2 sensor
2. CO2 sensor
3. Pneumotach (pressure-volume sensor)
“Bag or Tank Method” (less common)
EXPIRED AIR is collected in parcels then volume is calculated and VO2 and VCO2 are measured separately
Does not fully mirror the macronutrient mixture catabolized for energy (non-protein, steady state)
what does the quality of indirect calorimetry depend on
The quality of the indirect calorimetry depends on the quality of the calibration.
• Calibrate the pneumotach (volume sensor).
• Calibrate O2 and CO2 sensors with a known concentration of gas.
• Adjust all calibrations for the ambient temperature and humidity
what is respiratory exchange ratio RER
VCO2 produced / VO2 consumed
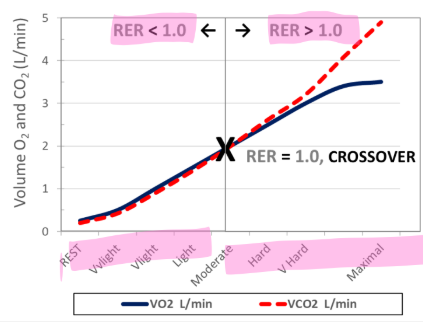
what is the criteria for steady state
RER is less than 1 (usually 0.7 - 1)
Accurate caloric estimates from gas exchange Exercise must be at steady state if we are going to get an accurate measurement of energy expenditure for a given power output.
Criteria for steady state for measuring the aerobic system:
1. VO2 < 100 ml/min change.
2. VCO2 < 100 ml/min change.
3. HR < 5 bpm.
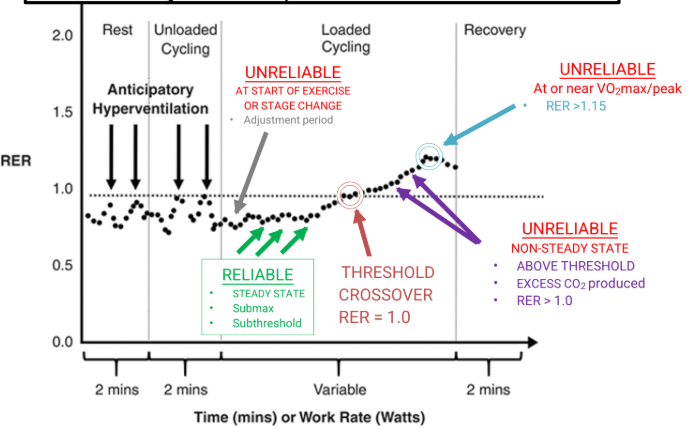
when is RER unreliable when measuring the aerobic system
• RER unreliable at onset of exercise or stage it can be high, low or dropping
• RER unreliable >1.00 indicates excess CO2 production in relation to O2 uptake.
- Buffering in plasma during intense exercise adds “excess” CO2 to blood and exhaled air resulting in Hyperventilation which increases VCO2 expired.
• RER unreliable <0.7 following intense exercise - min that it can be
- this can occur because cells and bodily fluids retain CO2 to replenish bicarbonate.
RER vs RQ for measuring aerobic system
RER (at the lung) and RQ (at the cell) are often used interchangeably but there are limitations
RQ = #CO2 produced / #O2 consumed # = the number of moles
RQ ≠ RER because that assumes that gas exchange at the lung = cell metabolism
• VO2/VCO2 at the lungs only reflects what is happening at the cellular level during light to moderate activity. RER above 1.00 CAN’T be attributed to food oxidation because of buffering reactions in cells and the blood
• During high intensity exercise RER can exceed 1.0 because bicarbonate must buffer excess H+ ion accumulating in blood
see slide 14
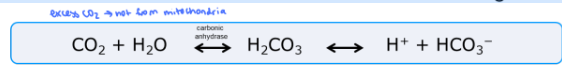
what is a mole
a mole is defined as the amount of a chemical substance that contains
exactly Avogadro’s number (6.02214076 × 10^23) constitutive particles.
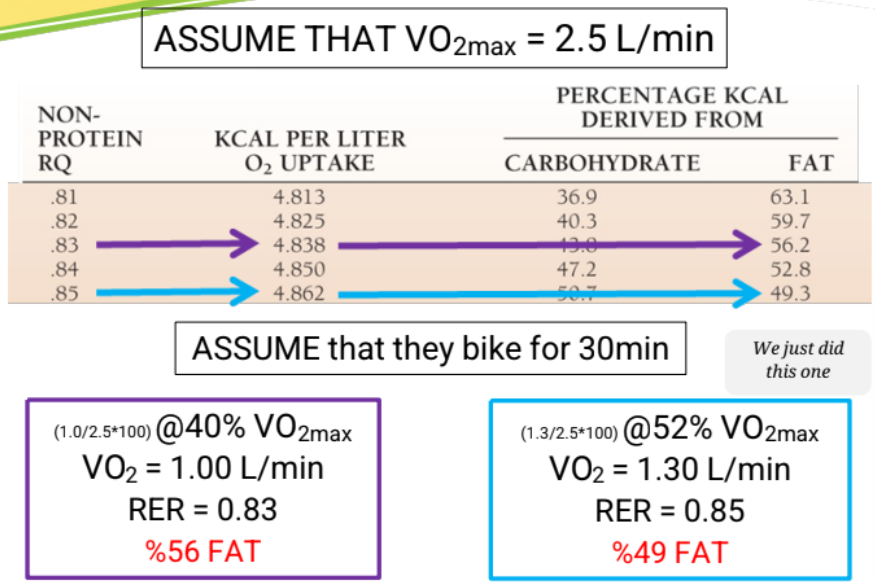
what does the mixed diet look like with RER and RQ
the RQ or RER = 0.82
The body rarely oxidizes just one macronutrient
• When a typical mix of carbohydrate, lipid and protein burns in 1L of oxygen, 4.82 kcal is released every minute.
• 5.00 kcal/LO2 is a good rule of thumb
• RQ has a range of 0.7-1.0 or 4.96 to 5.05 kcal/LO2
• RER can range from 0.7 - > 1.0 if there is non metabolic CO2
Protein oxidation is NOT included in the RER calculations because it is not measured PRO contribution can be adjusted for...theoretically Protein RQ = 0.82
how can we change RER to kcal/min
check the RER table
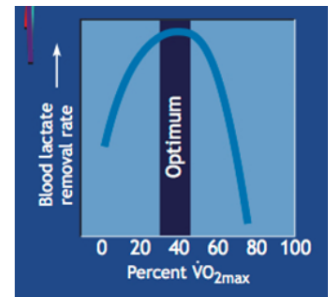
what is fat max
the exercise intensity at which fat oxidation peaks, at moderate intensity
its low when intensity is low or too high
rate of energy generated by fat is half as fast as carbohydrates
large variation in max fat oxidation between individuals
how do we use gross efficiency for measuring the aerobic system
GE = work in joules or kcal from ergometer / total energy in joules or kcal from open circuit spirometry and RER table x100
how do we use net efficiency to measure aerobic system
NE = work in joules from ergometer / (total energy in joules from open circuiit spirometry and RER table - resting energy in joules from open circuit spirometry and RER table) x100
NE is always more than GE
how do we measure the VO2 kinetics
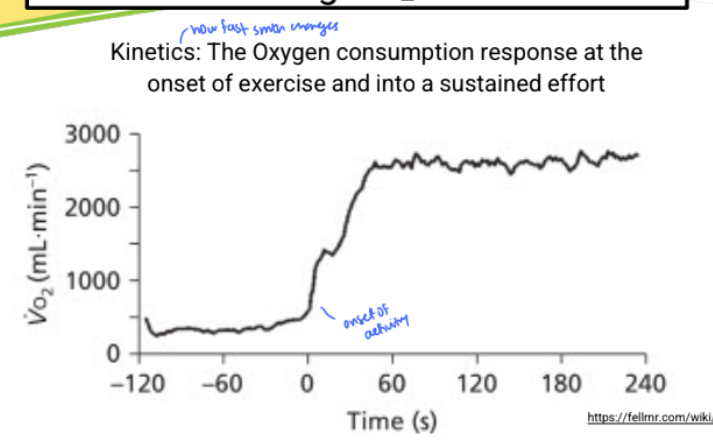
what is the oxygen deficit in VO2 kinetics
O2 deficit represents the difference between total VO2 during activity and additional amount that would have been consumed had steady- rate aerobic metabolism occurred immediately at start - a warm up can help
if its too big youre burning sugars when you shouldnt be
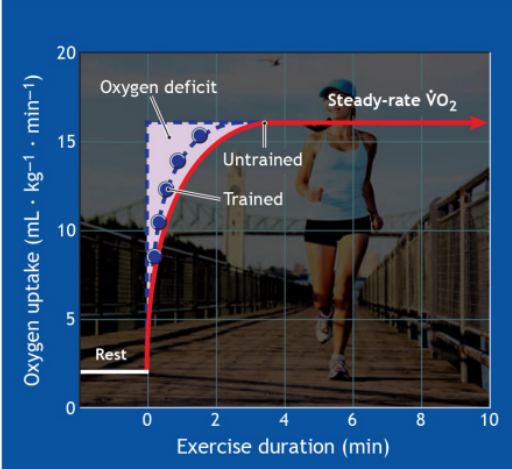
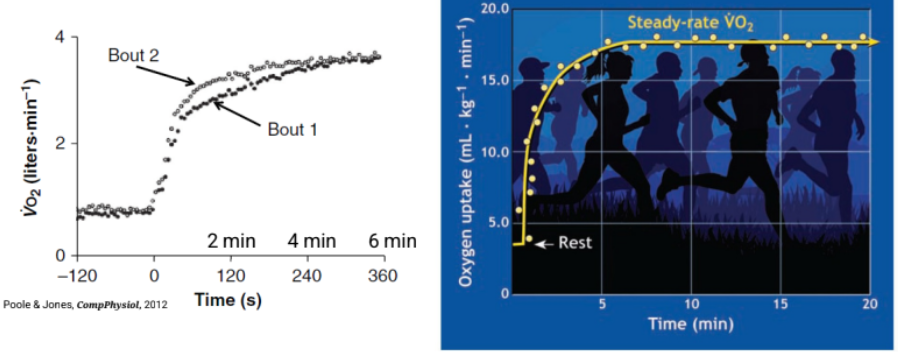
what does VO2 kinetics and steady state look like
Aerobic metabolic contributions are not instantaneous and Anaerobic systems must support the energy demand at the onset of exercise
Aerobic metabolic reactions provide the greatest portion of energy transfer when exercise duration exceeds 2 to 3 min.
warmup can help you reach steady state faster
what is oxygen drift
Exercise VO2 increases under any of these 3 conditions:
1. Intensity > ~70% VO2max
2. Longer duration exercise >30 minutes
3. Exercise in hot, humid environments
unsteady VO2
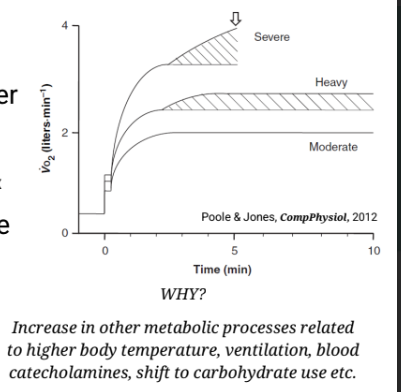
what are the VO2 intensity zones
• At severe/extreme intensities VO2 will climb until exhaustion even if the external power output remains constant
• Exercise at heavy and severe VO2 intensities is not very sustainable.
• Exercise at low and moderate VO2 intensities will be sustainable and physiological responses will be relatively stable
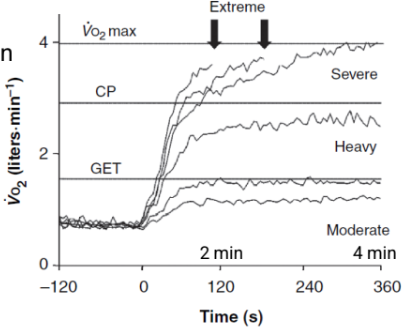
how much PA leads to a depletion of ATP
Physical activity that generates about 3 to 4 LO2 deficit significantly depletes intramuscular high- energy phosphates (ATP-PC)
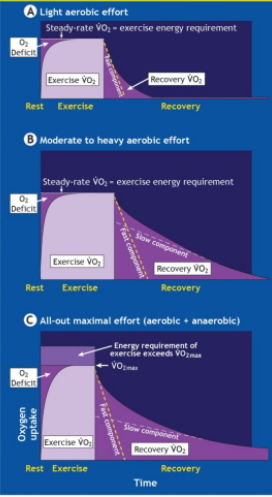
What does post exercise oxygen recovery (EPOC) look like
• Recovery VO2 defines excess VO2 above resting level in recovery in excess of pre-activity baseline levels.
• Recovery VO2 is intensity dependent - A. Light, B. Mod-Heavy, C. All-out
• Recovery VO2 returns to rest at different rates depending on what is being observed:
1. Fast component
2. Slow component
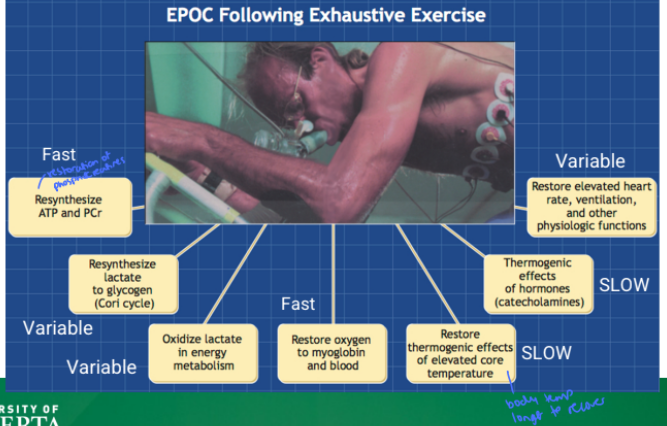
what are factors that contribute to EPOC after exhaustive exercise
what type of recovery is best
active recovery specifically intensities from 30% - 50% VO2 max
better to recover better and faster, sometimes not worth it in a game bc of psychological thinking