Structure and Bonding
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is valence bond theory?
A chemical bond forms when two atomic orbitals overlap, and the electrons in those orbitals pair up.
Sometimes, atoms "mix" their orbitals (like an s orbital and a p orbital) to form new, equivalent orbitals better suited for bonding.
In VBT, orbital orientation tries to minimize electron-electron repulsion.
That’s why, when orbitals hybridize (like in sp³), the resulting orbitals arrange themselves as far apart as possible — leading to specific molecular shapes.
Example: In methane (CH₄), the sp³ orbitals point to the corners of a tetrahedron (109.5° angles) to minimize repulsion.
SEARCH UP HYBRIDISATION.
What are constituional isomers (structural isomers)?
Molecules with the same molecular formular and molar mass, but their atoms are linked differently, and they differe in physical properties.
What are conformational isomers?
Conformational isomers are different shapes that a molecule can adopt by rotation around single bonds, without breaking any bonds.
They are the same molecule, but they look different in 3D space because parts of the molecule have rotated around single (σ) bonds.
Two basic types of conformations:
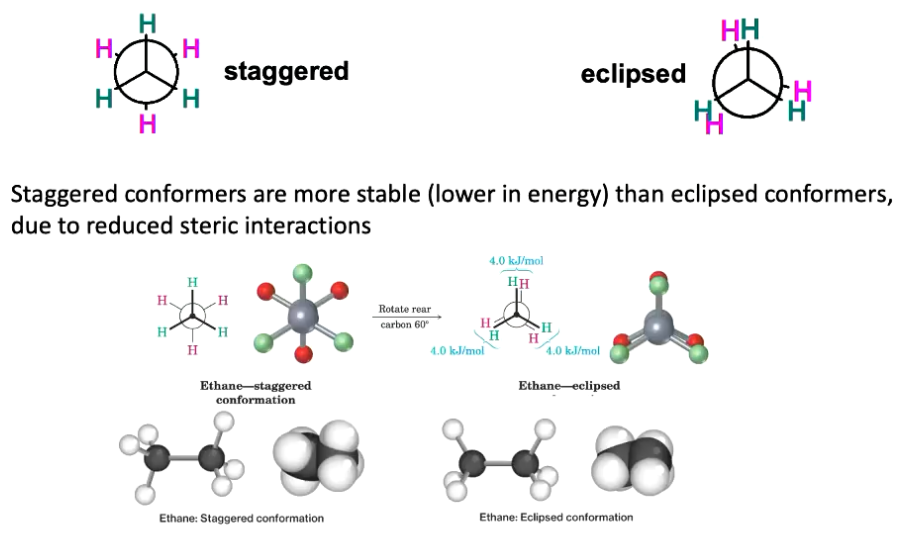
Staggered conformers is when hydrogen atoms are as far away from each other. The molecule is most stable here, due to minimal electron repulsion. Describes as having low energy.
Eclipsed conformers is when hydrogen atoms are positioned directly in front of each other. The molecule is less stable, but has higher energy.
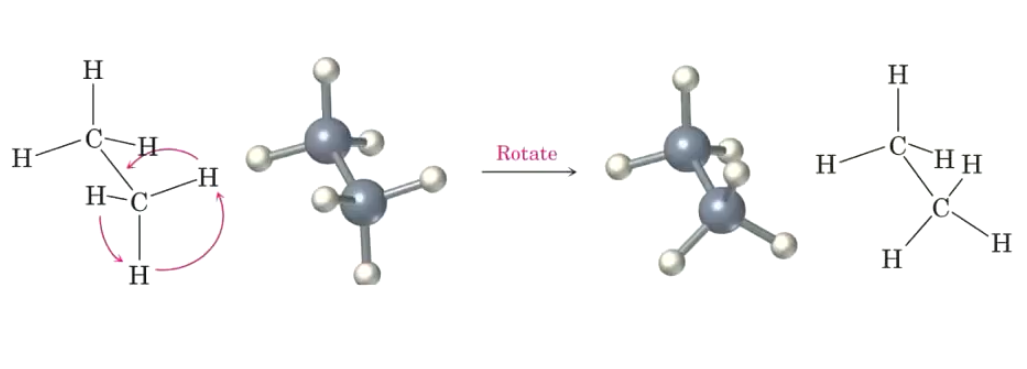
What are the Sawhorse representations and Newman projection?
Sawhorse: the carbon-carbon bonds are tilted.
Newman: looking directly into the carbon-carbon bond. The circle represents the carbon-carbon bond.
What does staggered and eclipsed conformation look like for ethane?
These bonds are constantly moving (assuming not frozen), thus any conformation is possible at a point in time, but ofc the molecule spends more time in the staggered conformation.
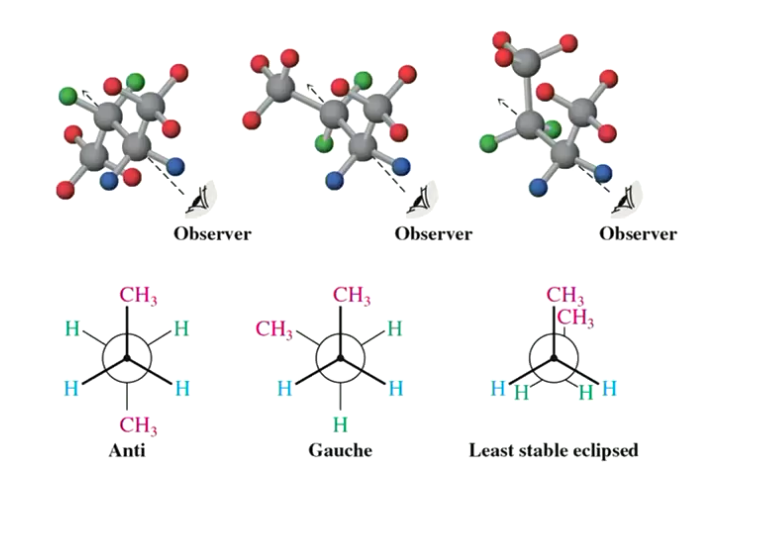
What are the possible conformers of butane?
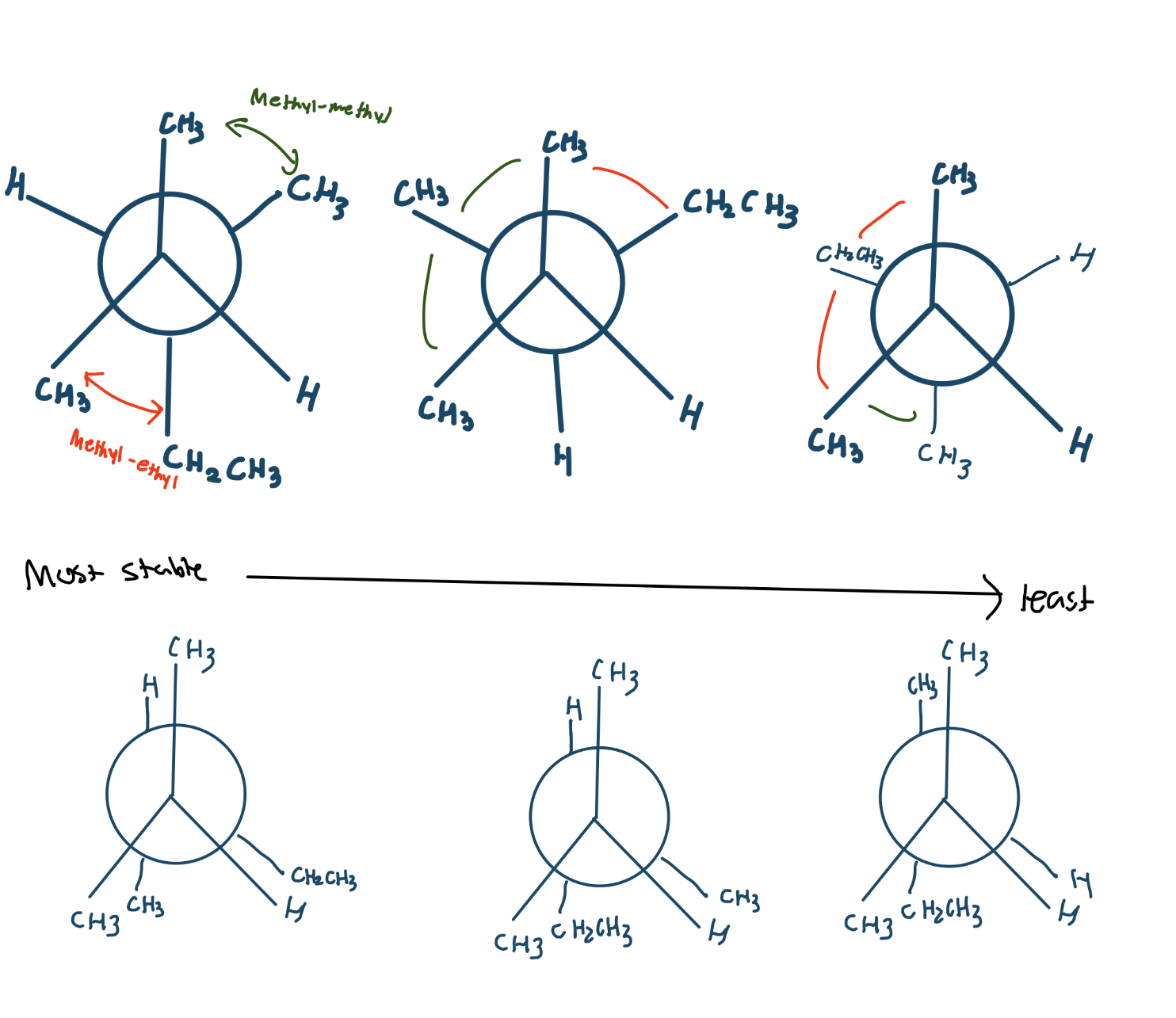
Draw all possible conformers for 2,3-dimethylpentane
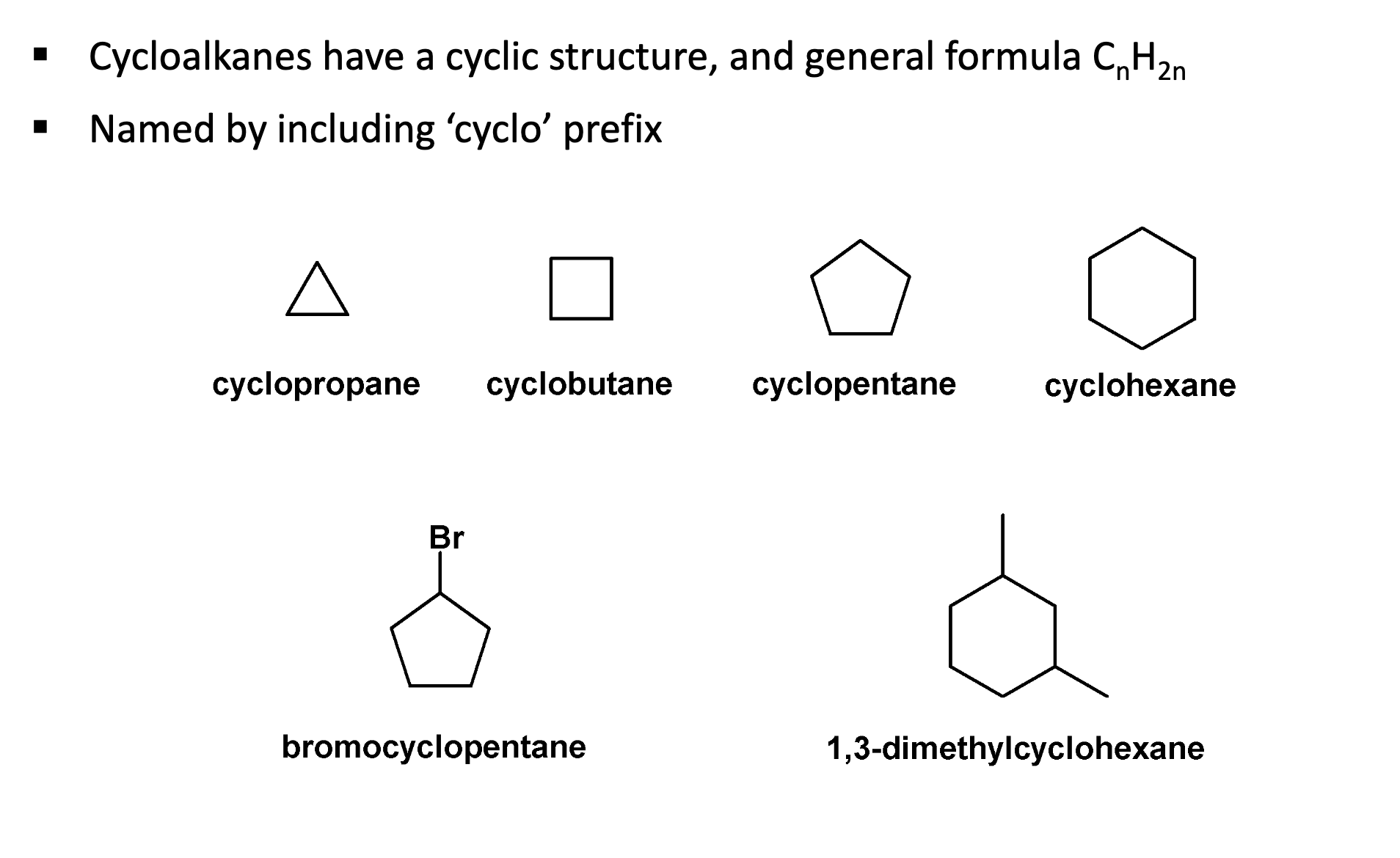
What are cycloalkanes?
Cyclopropane has the most stressed bonds.
What is ring strain in cycloalkanes?
The ideal bond angle for a sp3 hybridised C atom (4 single bonds) is 109.5º
This isn’t possible with the small rings, thus they will suffer ring strain.
Describe cyclopropane and butane.
Must be familiar with why it is flat.
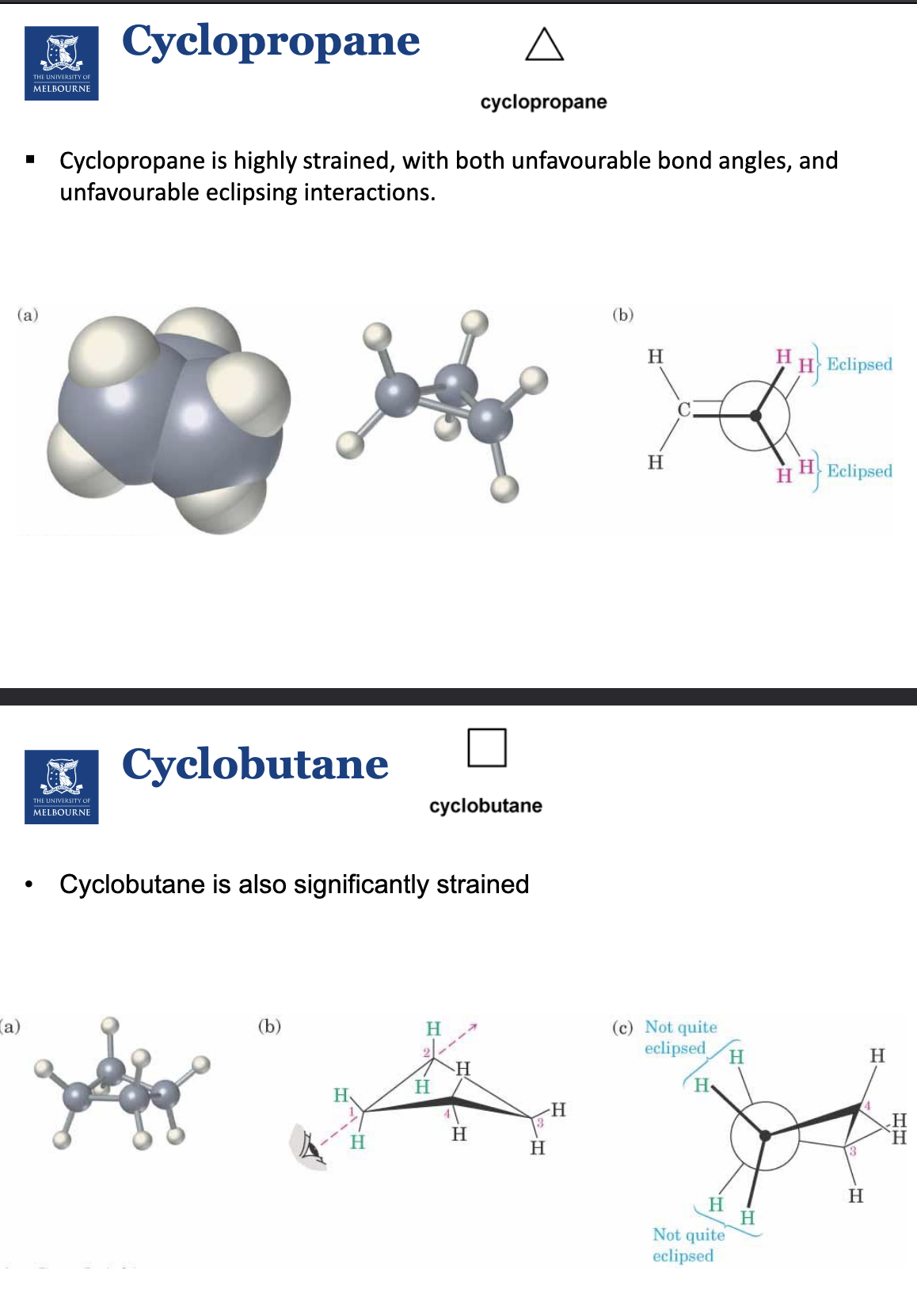
Describe cyclopentane and cyclohexane.
https://qrchem.net/viewer?cid=8078&name=cyclohexane&desc=false&ballStick=false
look at the cyclohexane morecule, and how it is folded like a chair.
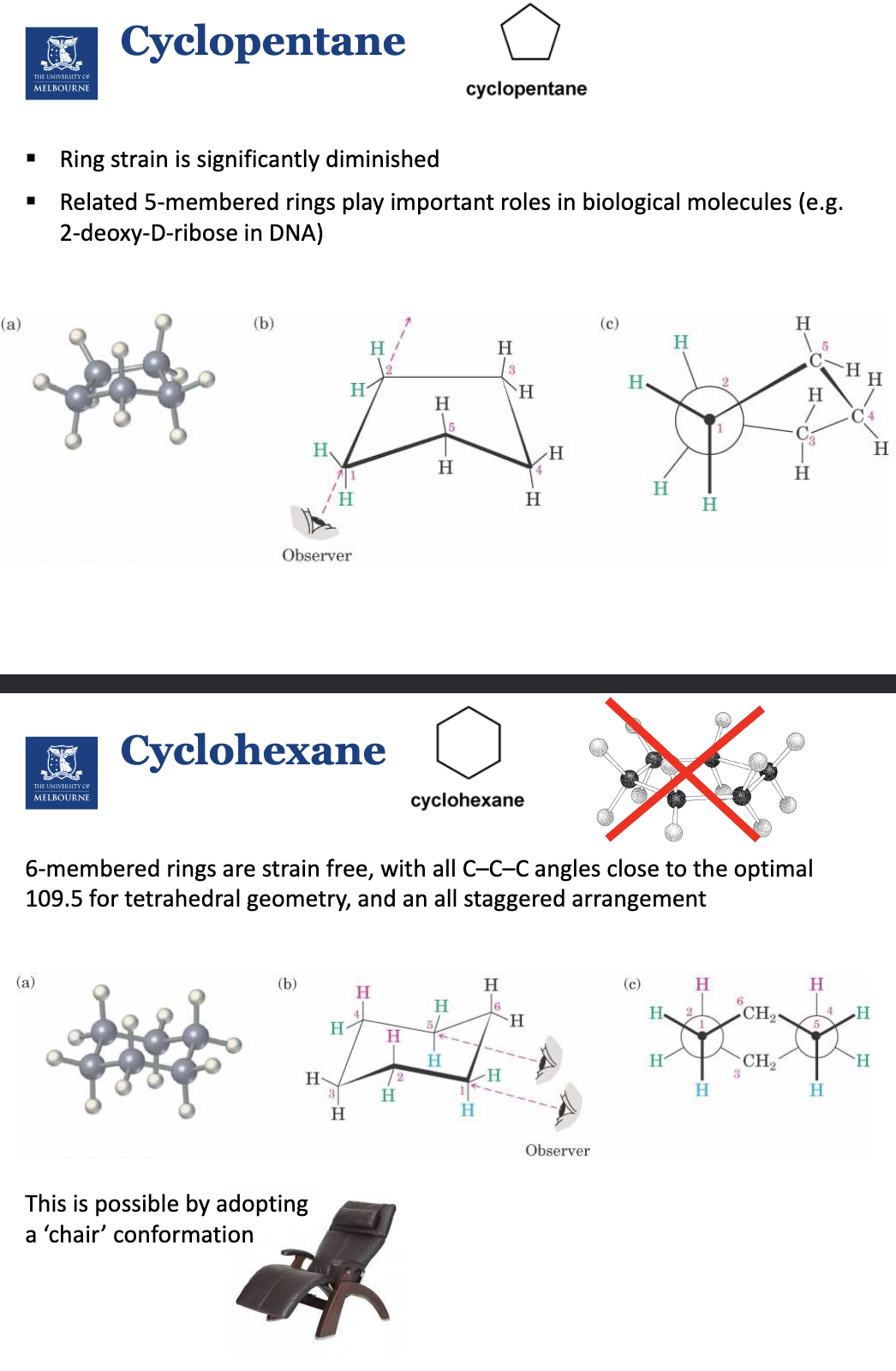
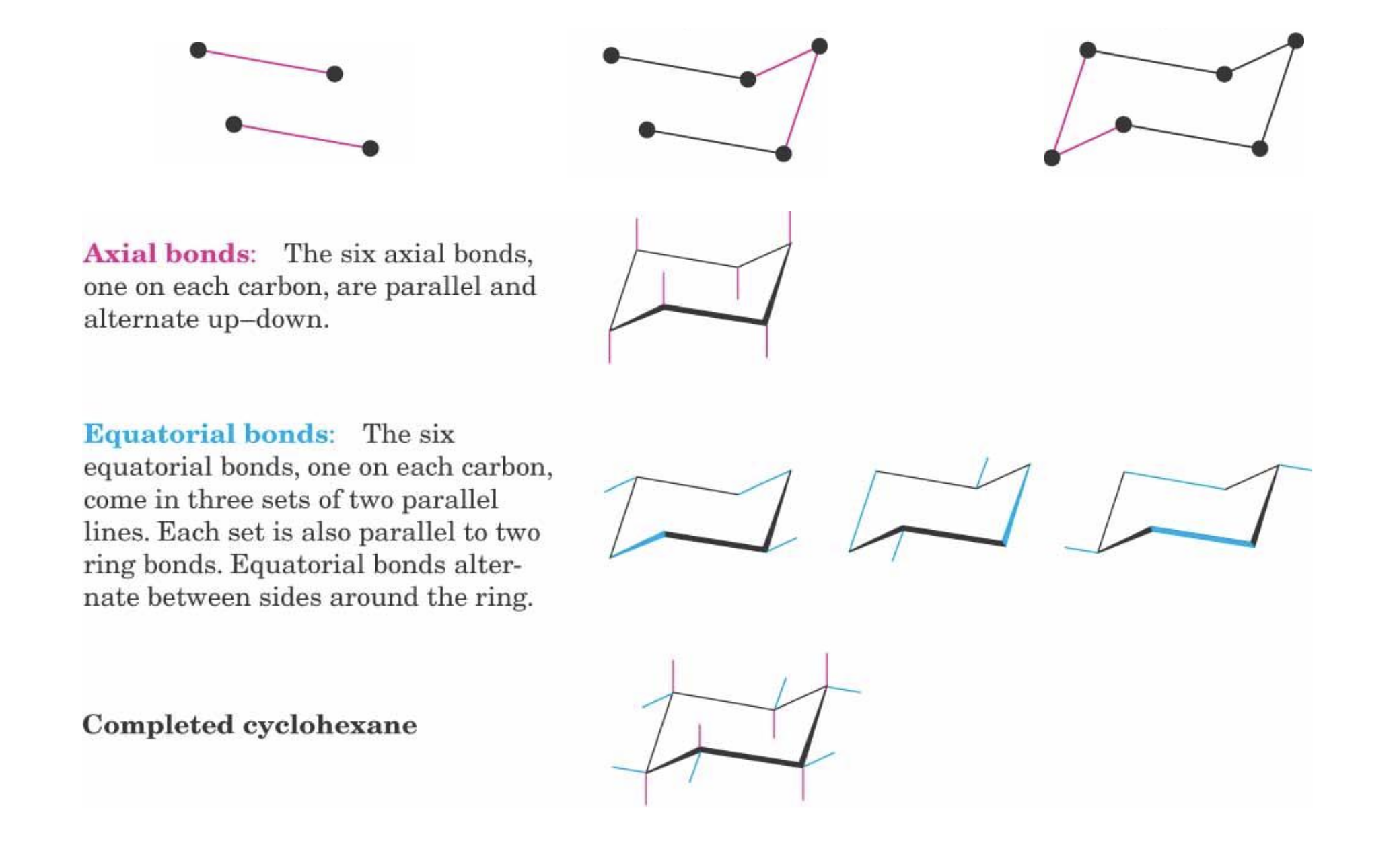
What are the hydrogen environments in the cyclohexane chair conformations?
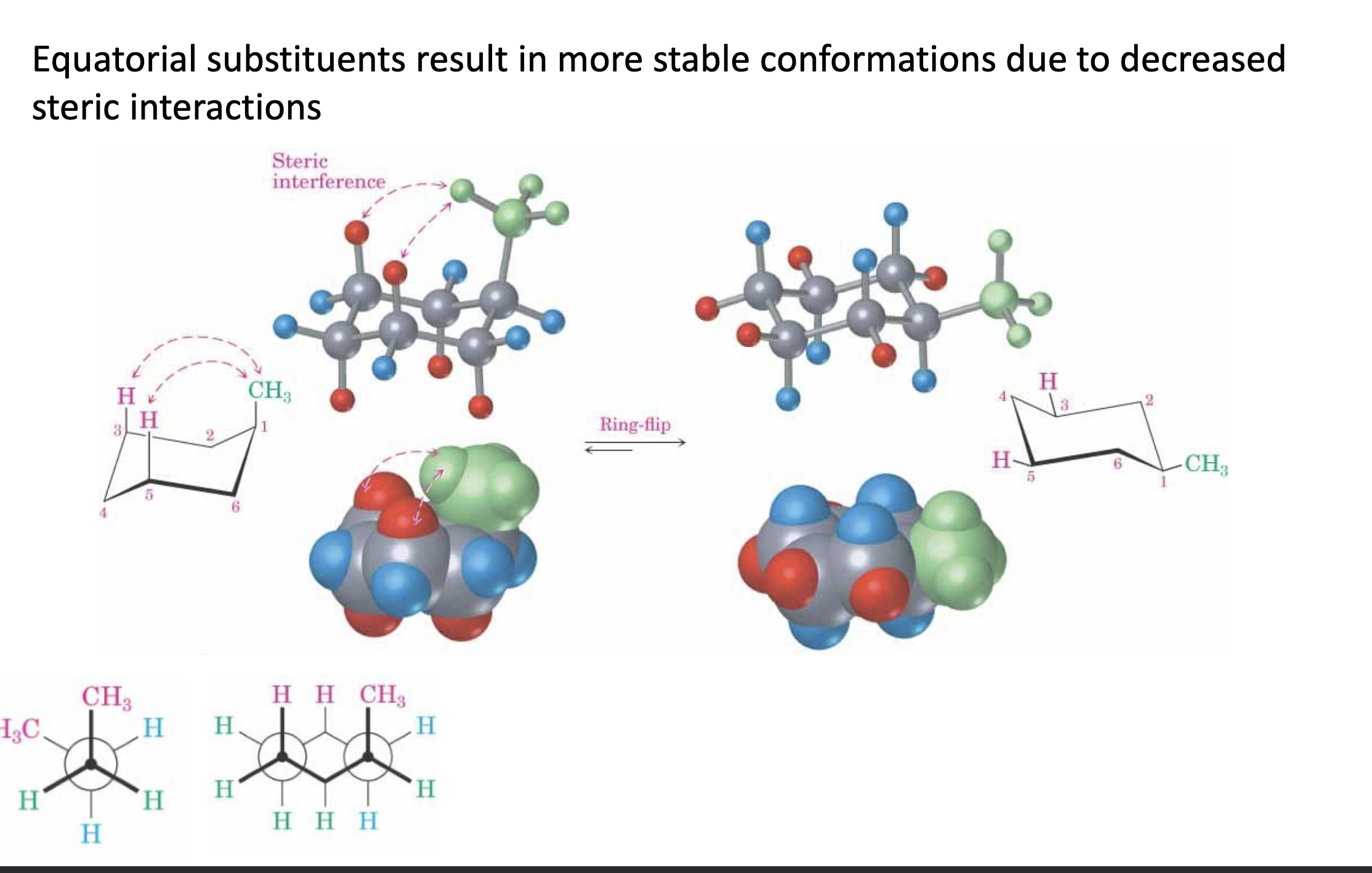
Axial and equatorial positions.
Bulky substituents prefer to be in the equatorial position, as if they were in the axial position, they would clash.
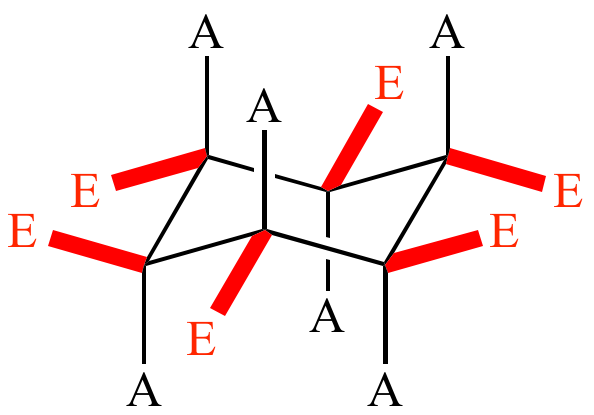
Draw cyclohexane chair conformation.
All are slightly tilted.
Rank all chair structures based on stability for 1-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane.
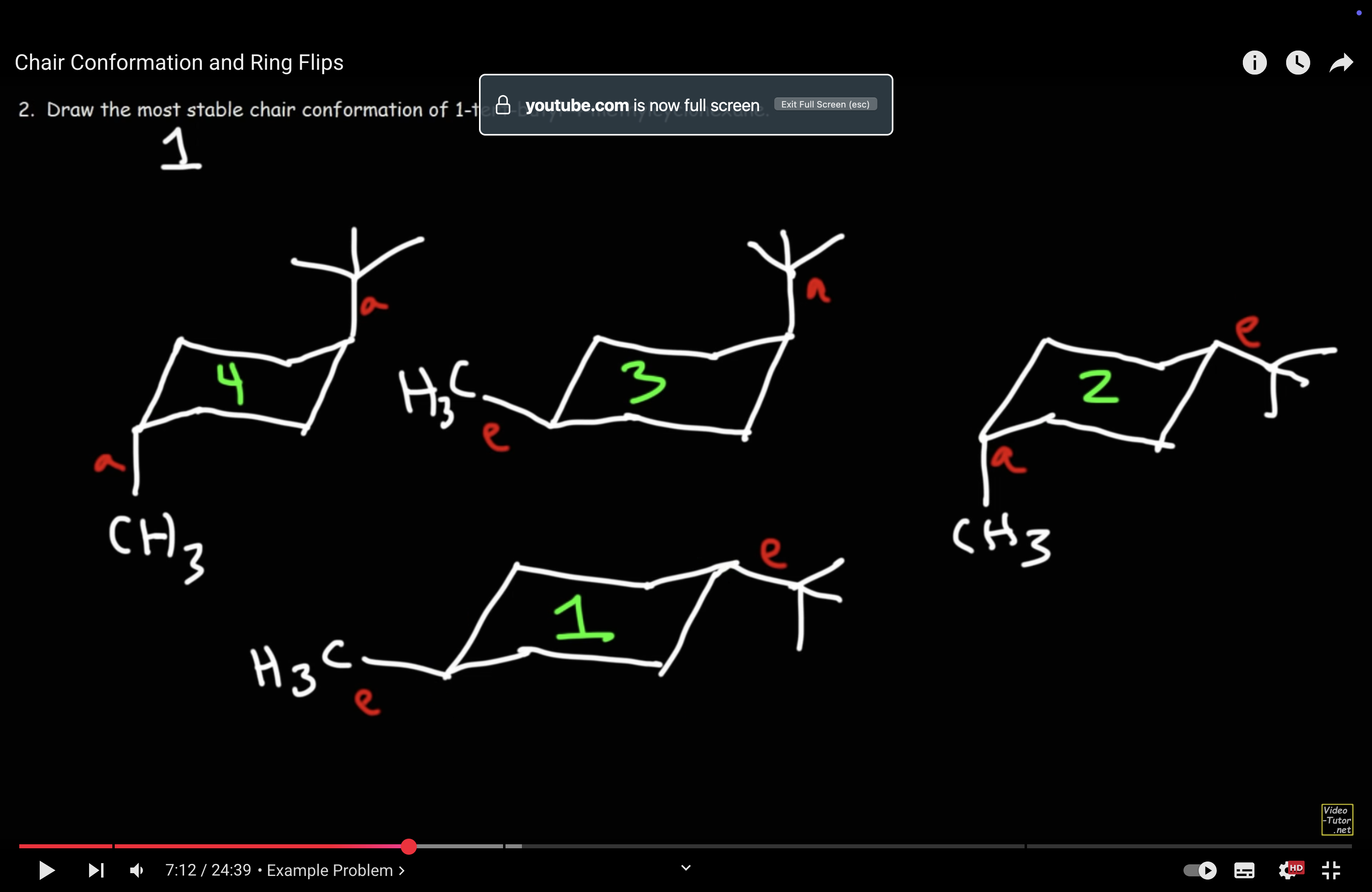
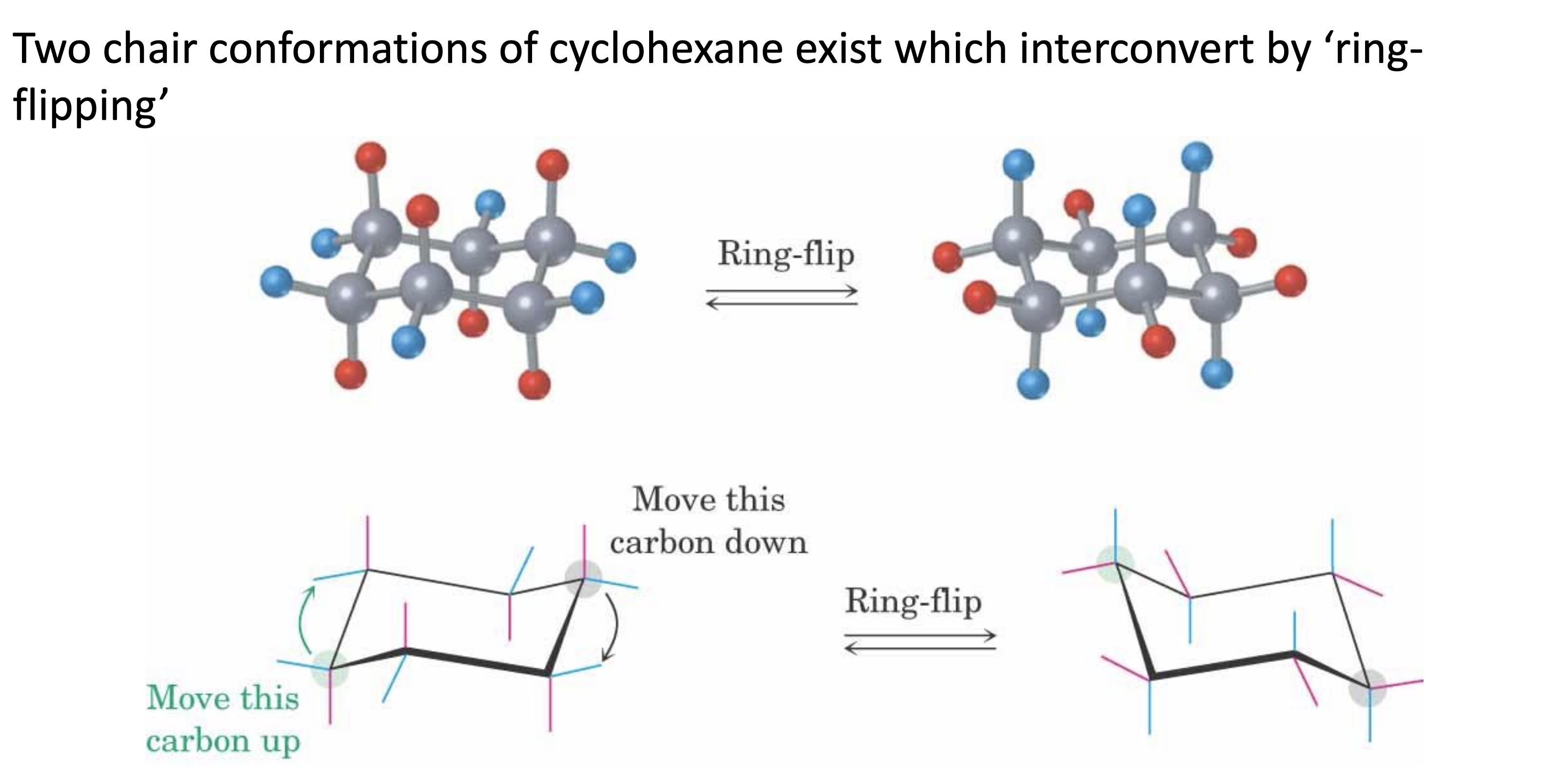
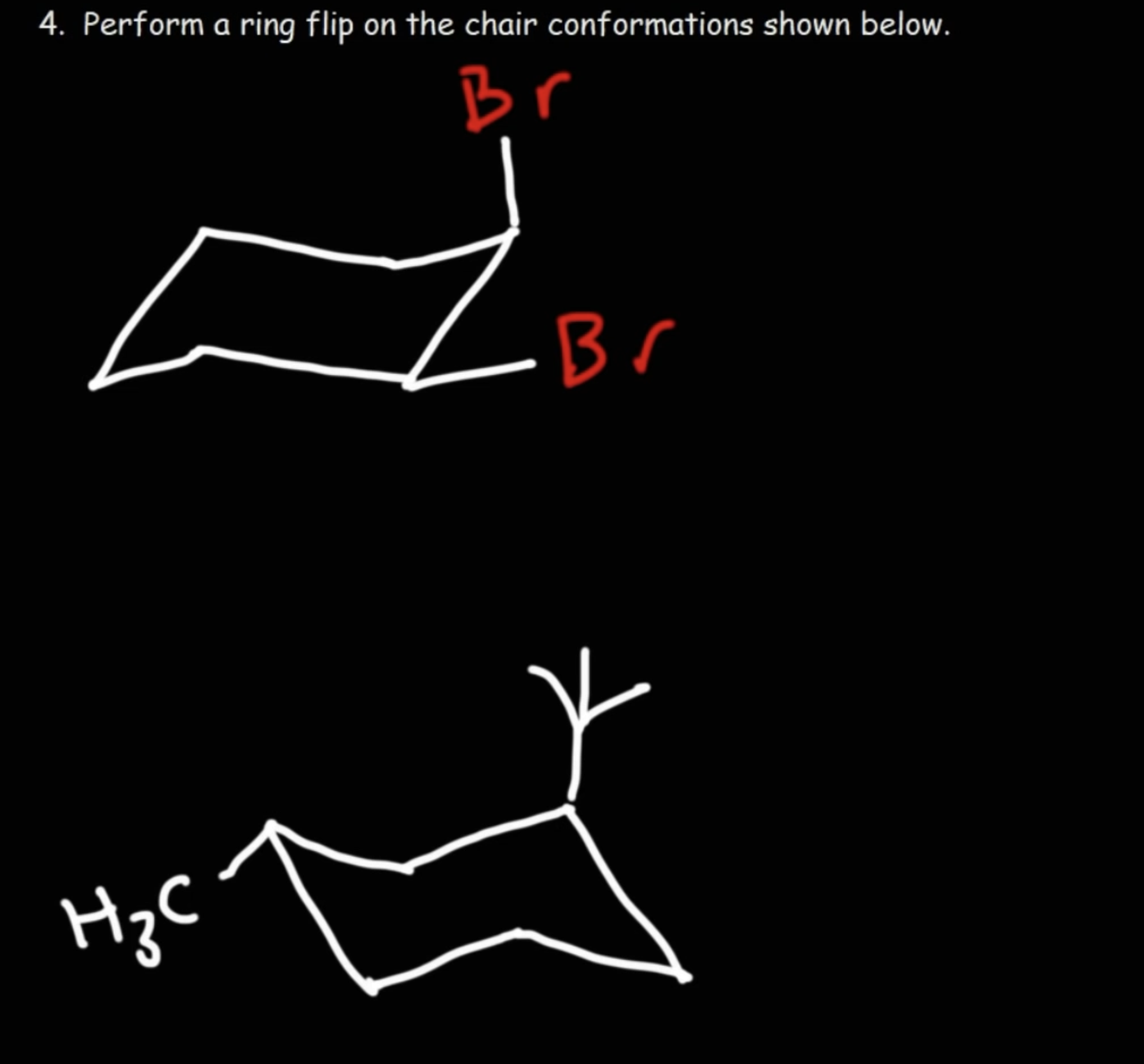
Describe ring flipping.
Axial positions can turn into equatorial positions, vice versa.
This is because the molecule is not static, and is rotating.
What are substituted cyclohexanes?
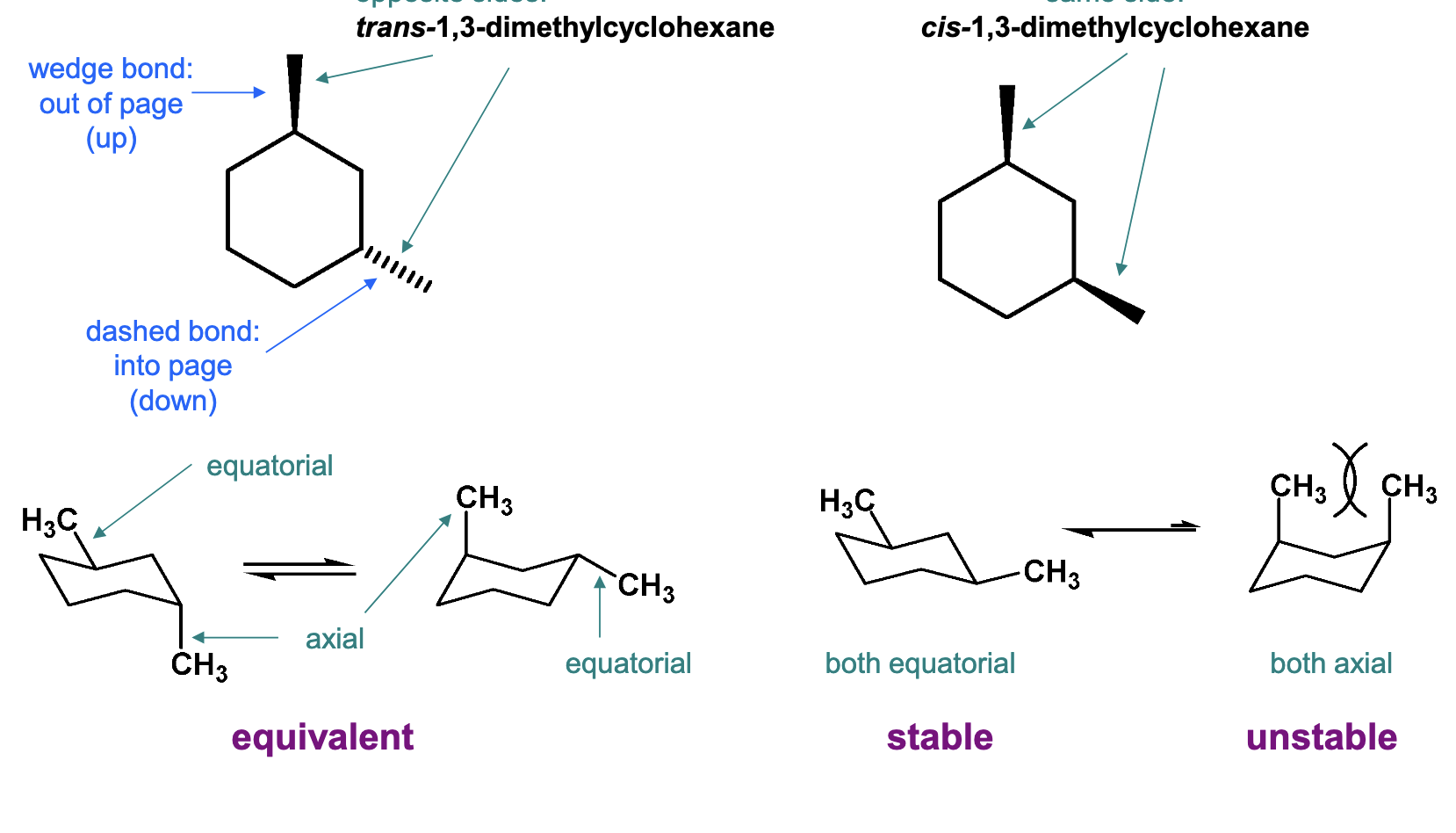
What are disubstituted cycloalkanes?
Rings prevent free rotation around single bonds.
Isomers can exist when two or
more substituents are attached.
▪ The isomers do not interconvert
(would require breaking of C–C
bonds).
▪ These isomers are stereoisomers
- they differ by the arrangement
of atoms in space
▪ Also called cis/trans isomers,
diastereomers
WHEN BOLD LINE, THE BOND IS POINTING UP, WHEN IT IS DASHED IT IS POINTING DOWN (can be axial or equatorial).
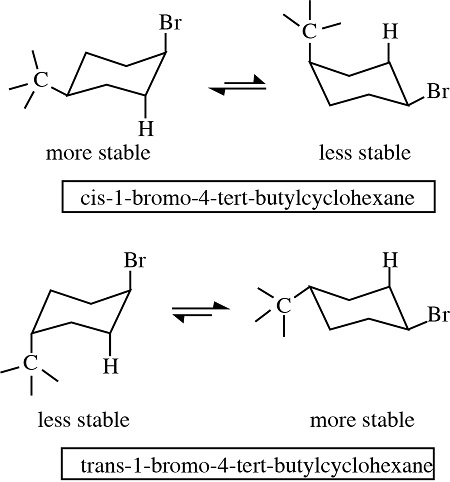
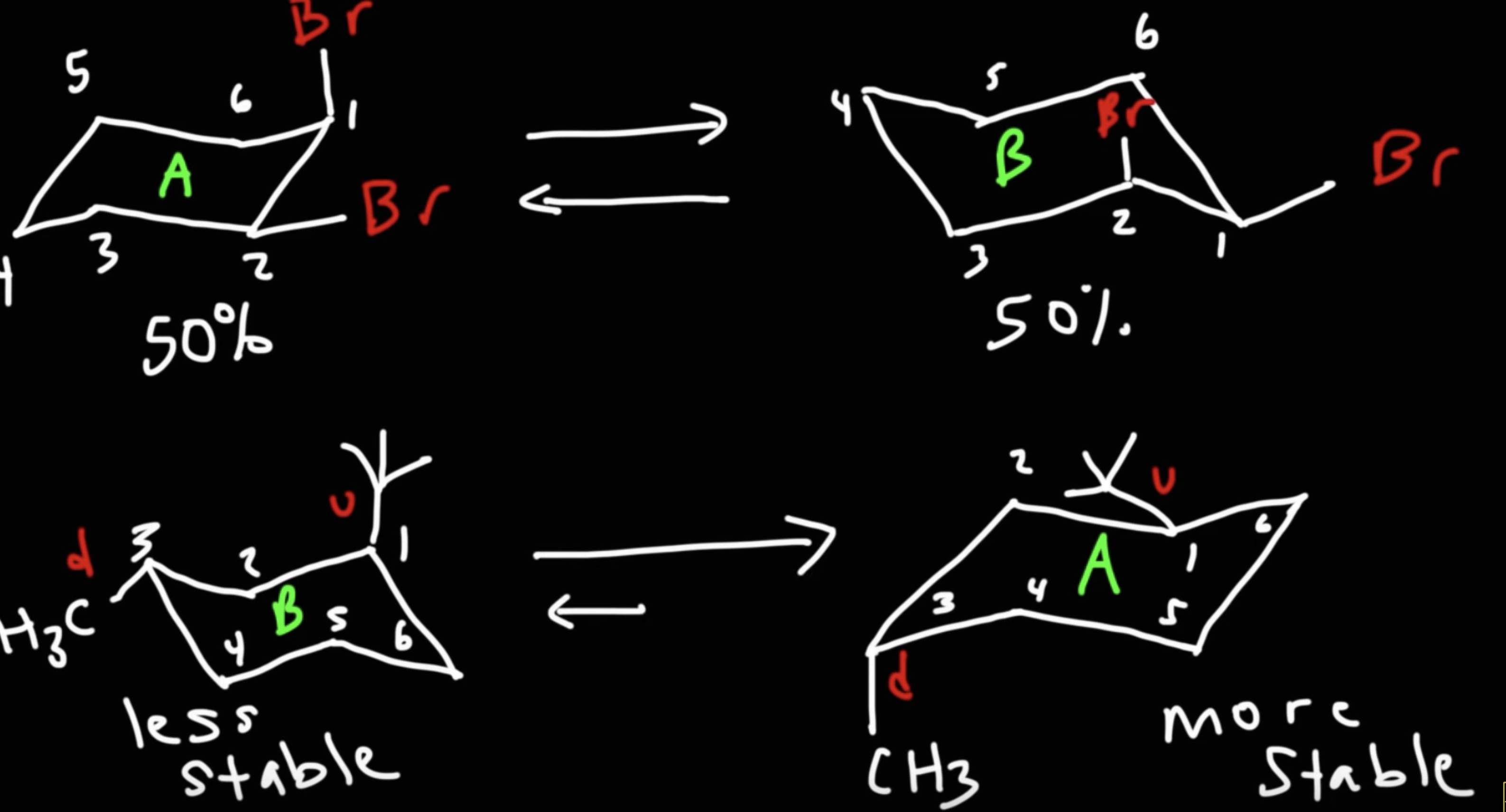
Draw the two chair conformations of
cis-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane.
Which is the most stable?
t-But is always equatorial because it is very big
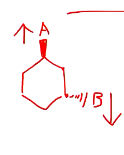
Given this molecule, draw the chair structure.
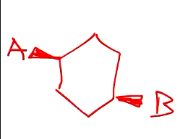
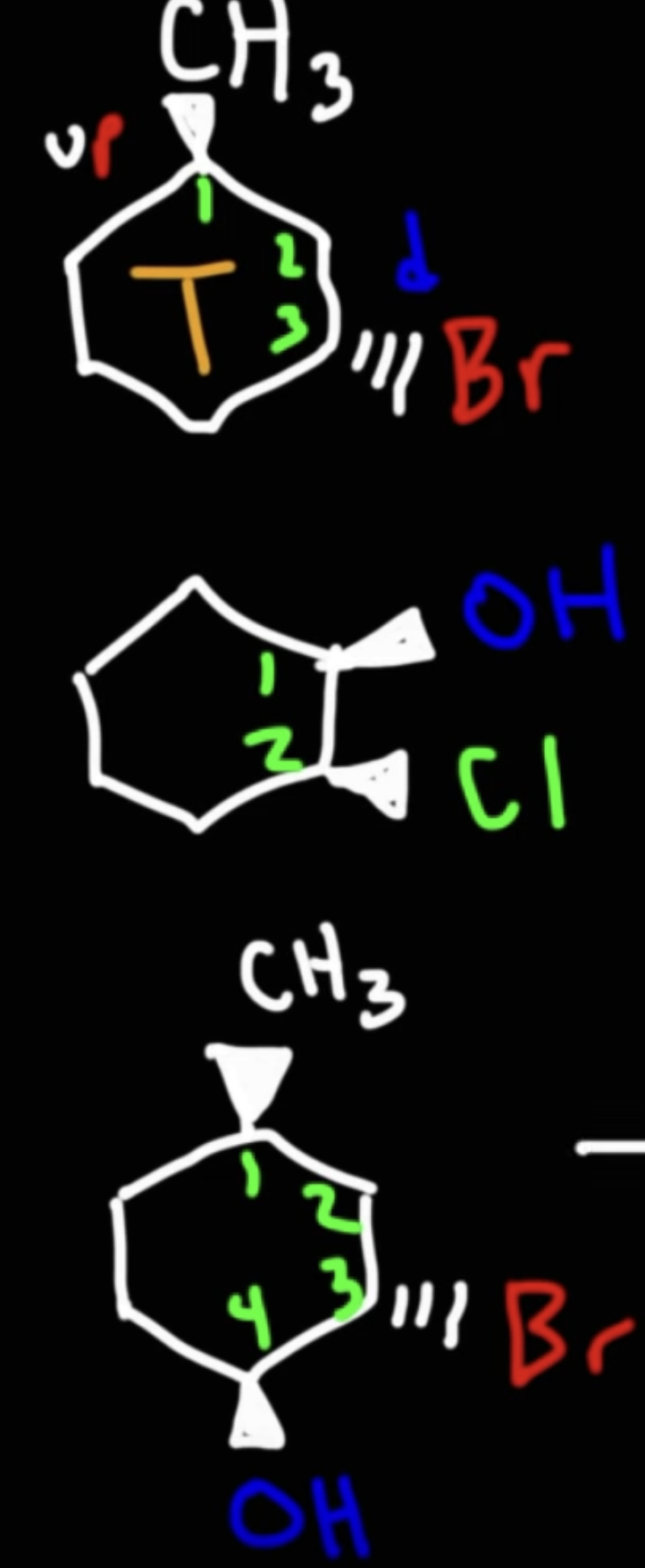
Dashed wedge implies it is going down, vice versa.
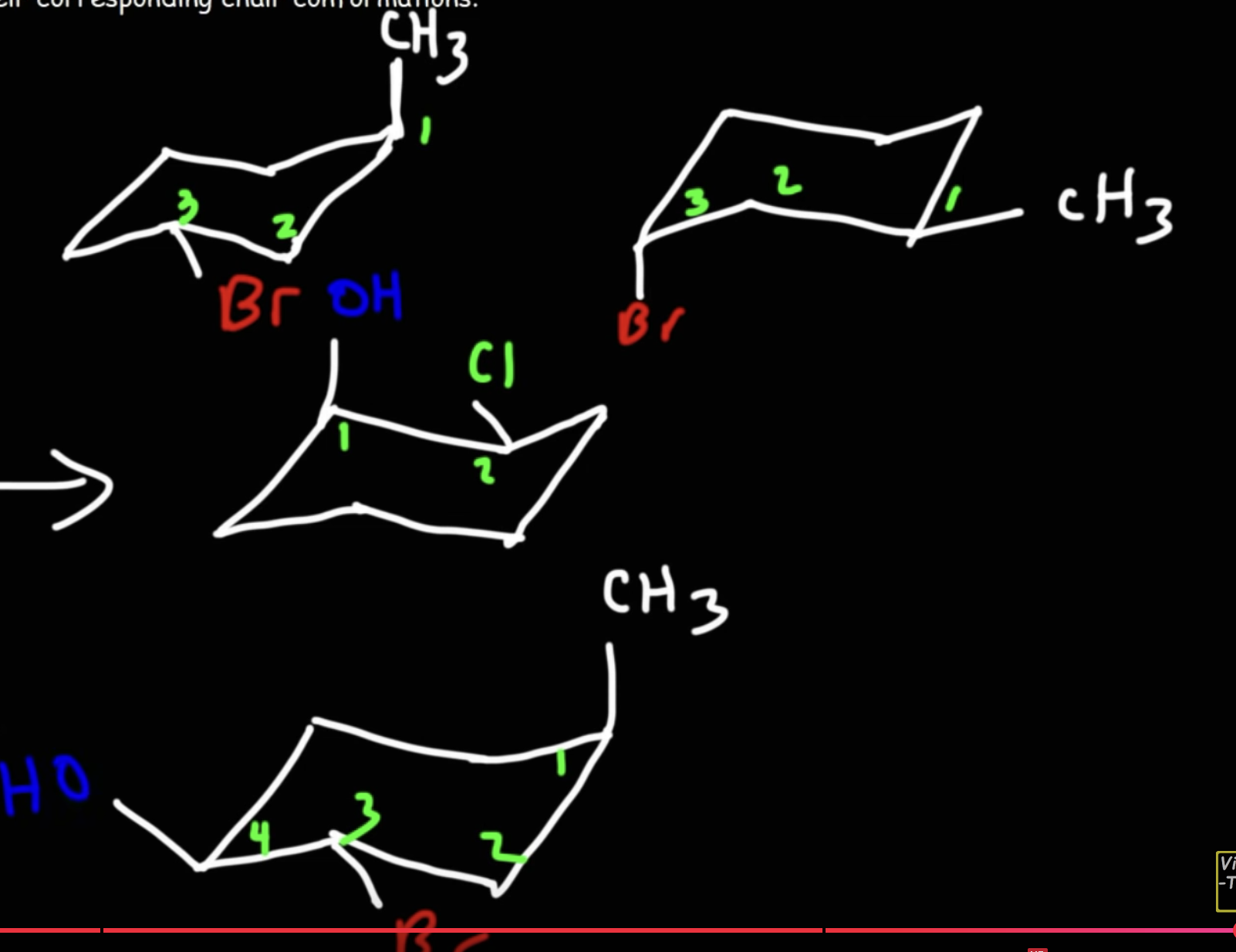
Given this molecule, draw the chair structure.

For a tetrahedral carbon to be not superimposable (enatiomers), how many unique groups must be present?
4 different groups. The rest would be the same if rotated.
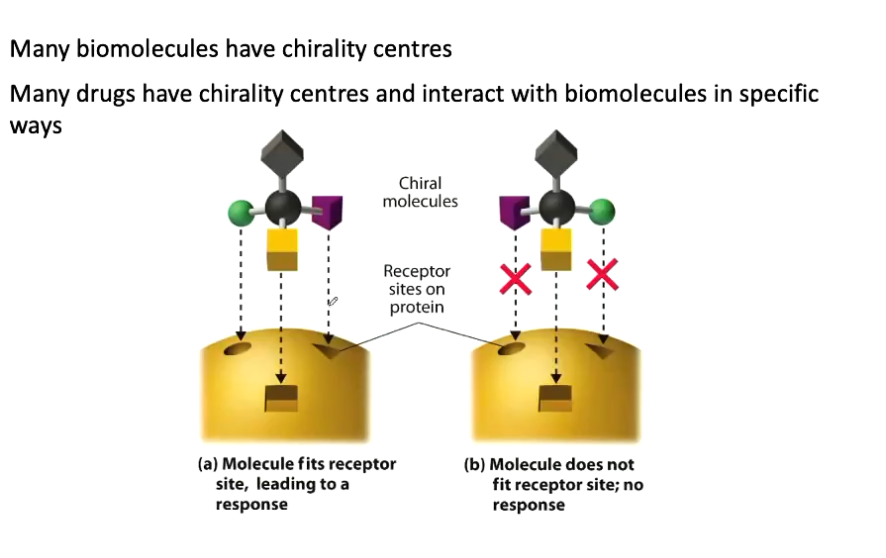
What is chiral?
Molecules that possess non-superimposable mirror images.
A molecule can have multiple chiral centres.
A molecule is not chiral if it contains no planes of symmetry.
A tetrahedral carbon with 4 different groups has no planes of symmetry; such carbon atom is called a chiral (stereogenic) centre.
How do enantiomers differ?
The way they interact under polarised light, making them optically active (not important for this subject). One enantiomer rotates clockwise (+) and anticlockwise (-).
The way in which they interact with other chiral molecules.
What are the CIP rules?
A stereogenic centre is described as being either R (clockwise) or S configuration M(anti).
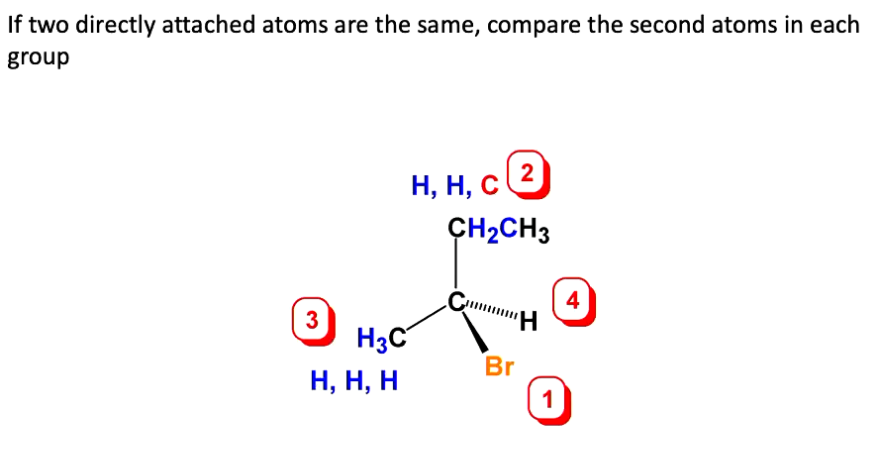
1) Rank the four substituents. Prioritise substituents in decreasing order of the atomic number of the atom directly attached to it.
2) If two directly attached atoms are the same, compare the second atoms in each group. HHC has higher priority, due to C.
3) Treat multiple bonds as the equivalent number of single bonds. i.e. if there is a double bond of C, you count C twice. https://imgur.com/a/OPyO8tJ
4) Make 4th priority go into the page. https://imgur.com/a/7RTHHYQ
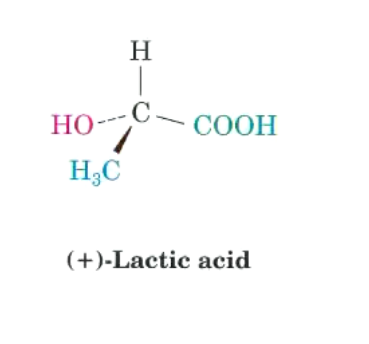
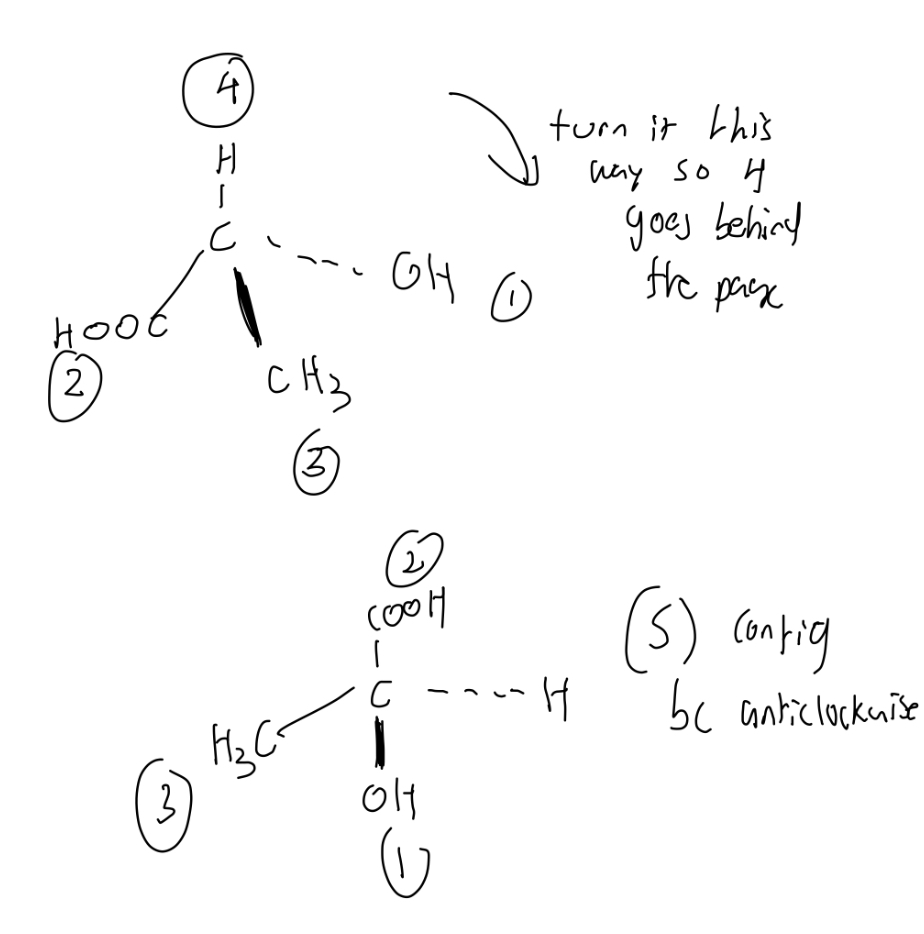
Apply CIP rules for lactic acid.
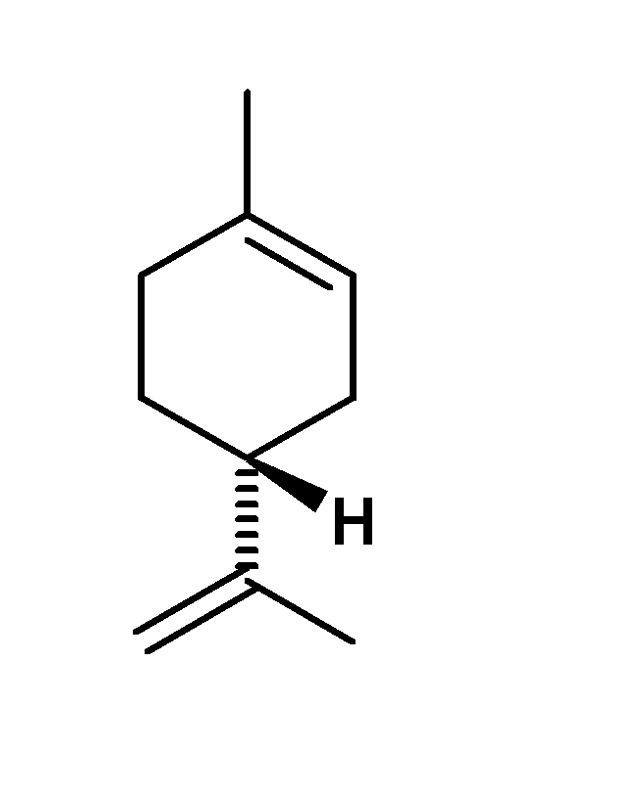
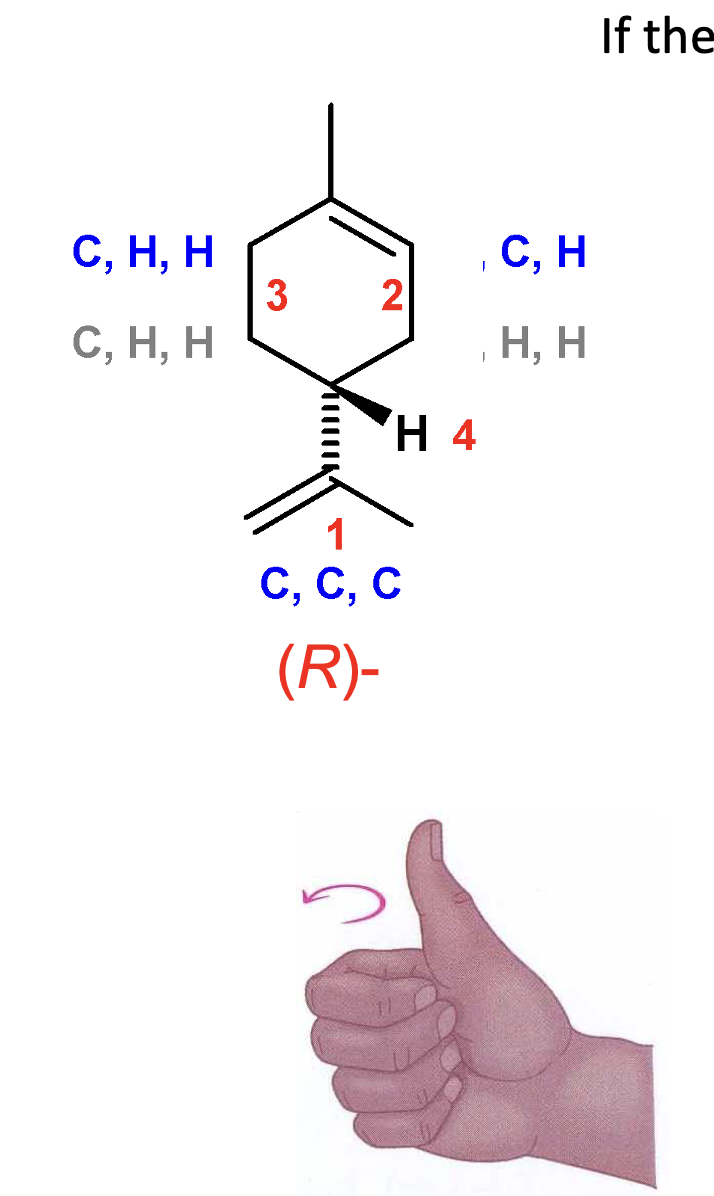
Determine whether if this molecule is R or S.
What is a racemic mixture?
Equal mixture of enatiomers.
It can be difficult to separate enatiomers from a racemic mixture, as they have the same physical and chemical properties.
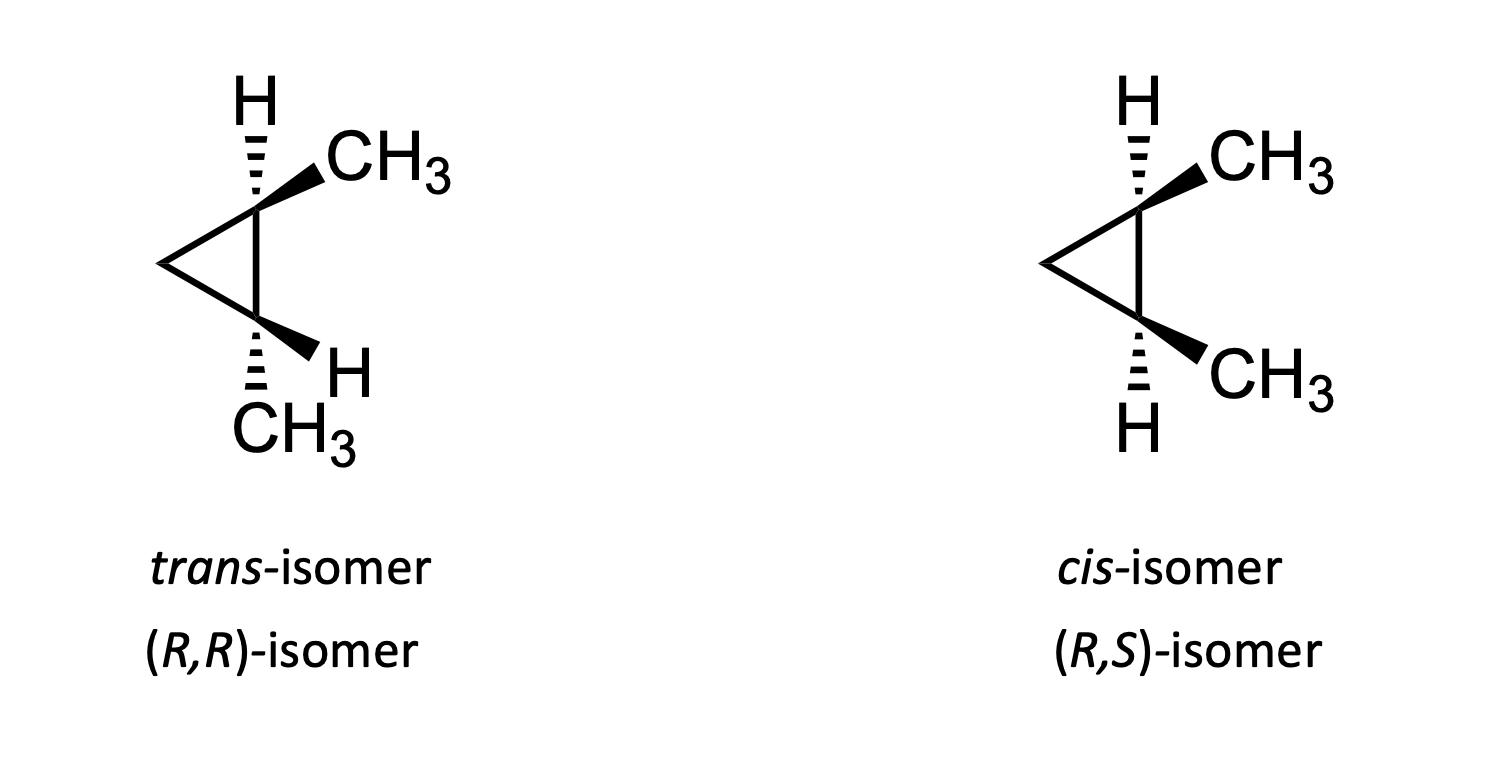
What are diasteromers?
Stereousomers which are non superimposable and not mirror images of themselves.
This can occur when there are more than 1 chiral centres.
A molecule with n chiral centres has a maximum of 2n steroisomers.
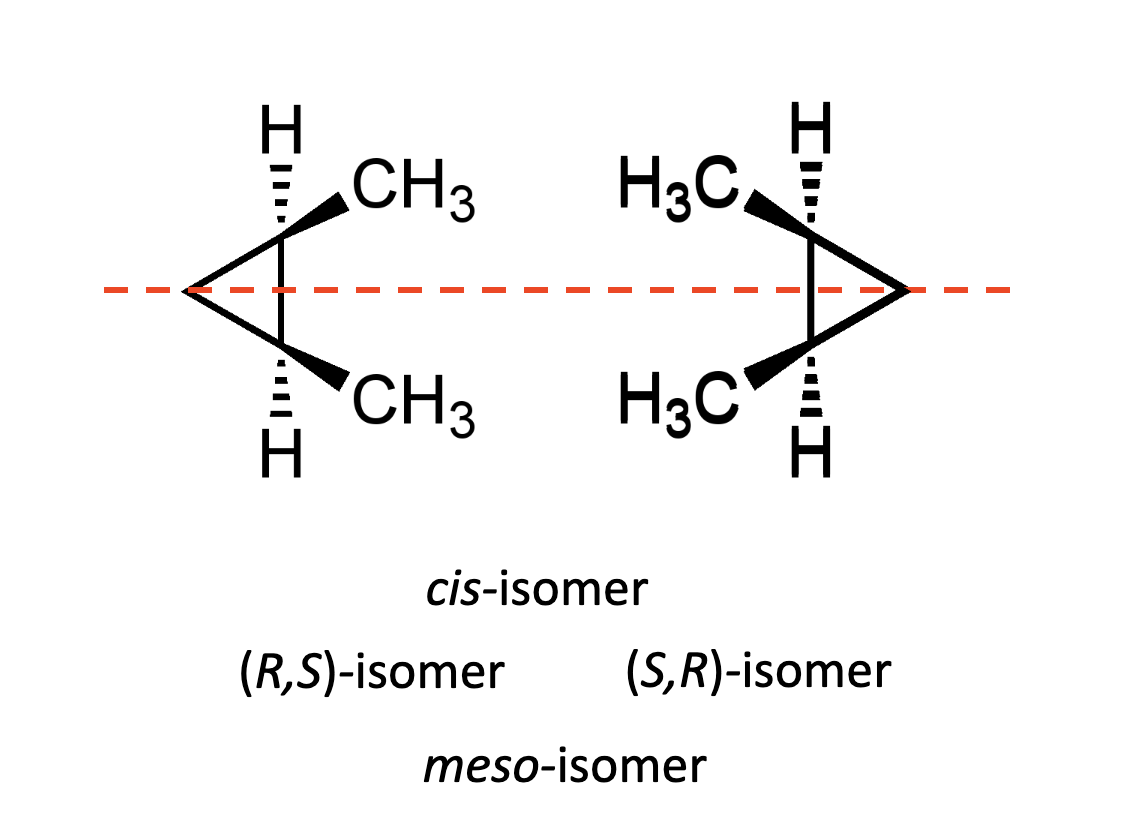
What are meso compounds?
Compounds that possess asymmetric centres but are achiral, as they also possess a plane of symmetry.
How to seperate enatiomers in a racemic mixture?
Turn them into diasteriomers, then seperate them due to their difference in boiling point.
Describe alkenes.
CnH2n
Planar arrangement of atoms (flat molecule).
Geometry of carbons is trigonal planar.
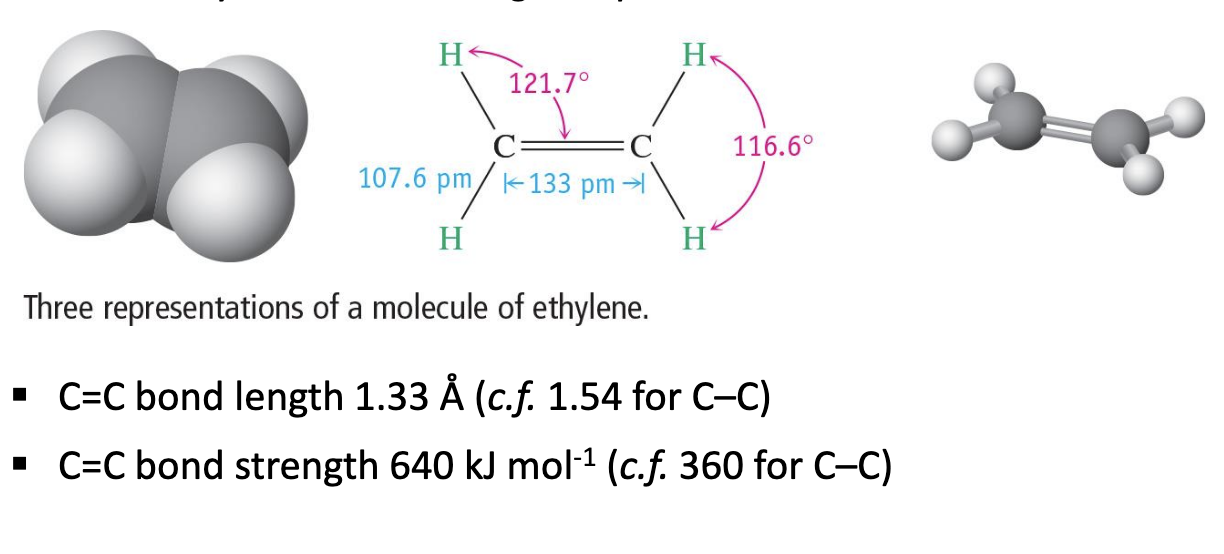
Why is a C=C is slightly less stable than C-C?
CHECK LECTURE RECORDING 7TH MAY SLIDE ALKENES-GEOMETRY.
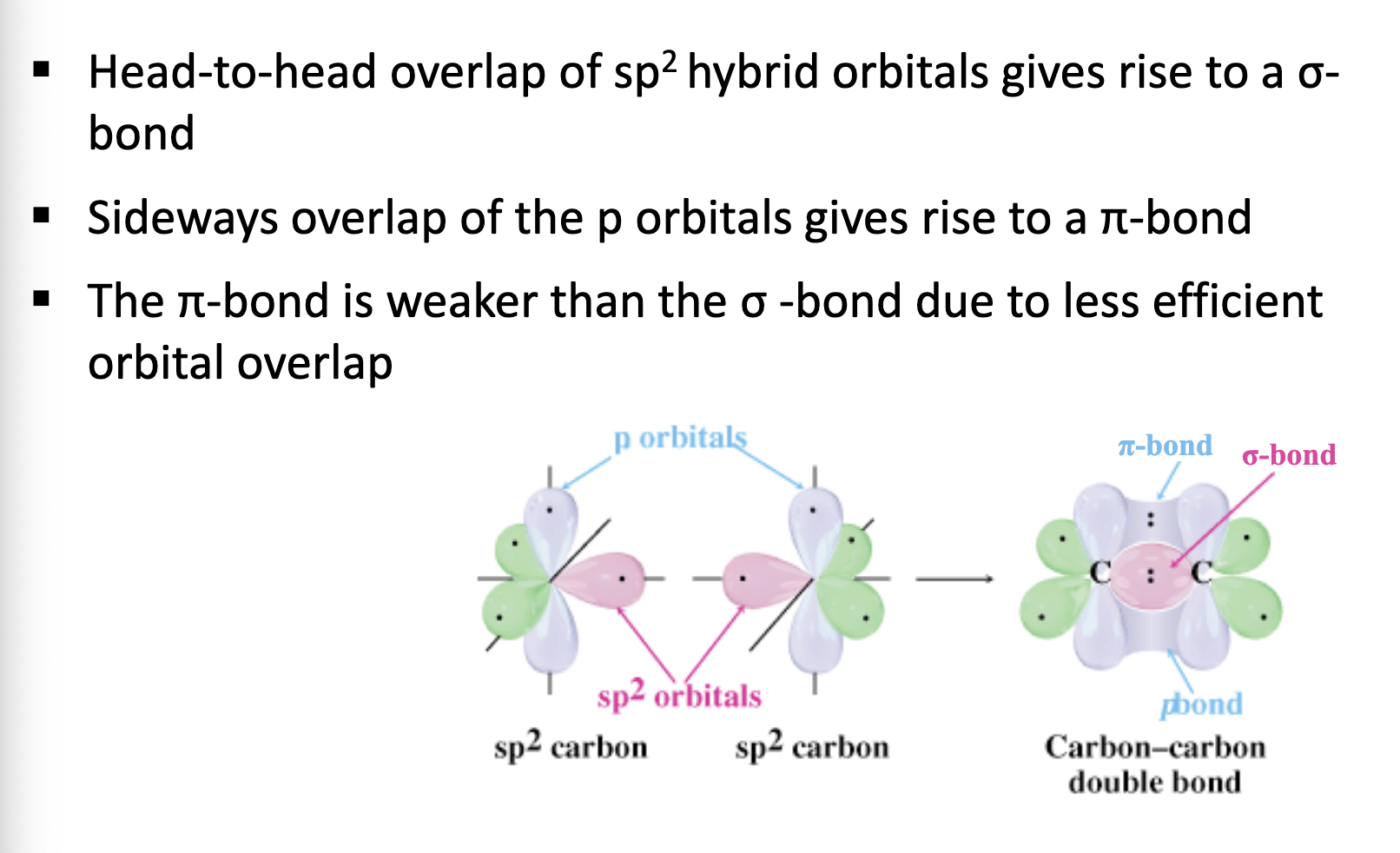
Describe sp2 hybridisation.
Each carbon atom forms three sigma bonds:
One sigma bond with the other carbon (part of the C=C).
Two sigma bonds with other atoms (like H, or another group).
To form these 3 sigma bonds, each carbon mixes one s orbital and two p orbitals → this gives three sp² hybrid orbitals.
The remaining unhybridized p orbital (on each carbon) overlaps sideways to form the π bond of the double bond.
What are the isomers for 2-butene?
Since the C=C cannot rotate (to rotate must break π bond), the arrangement of atoms in space can differ.
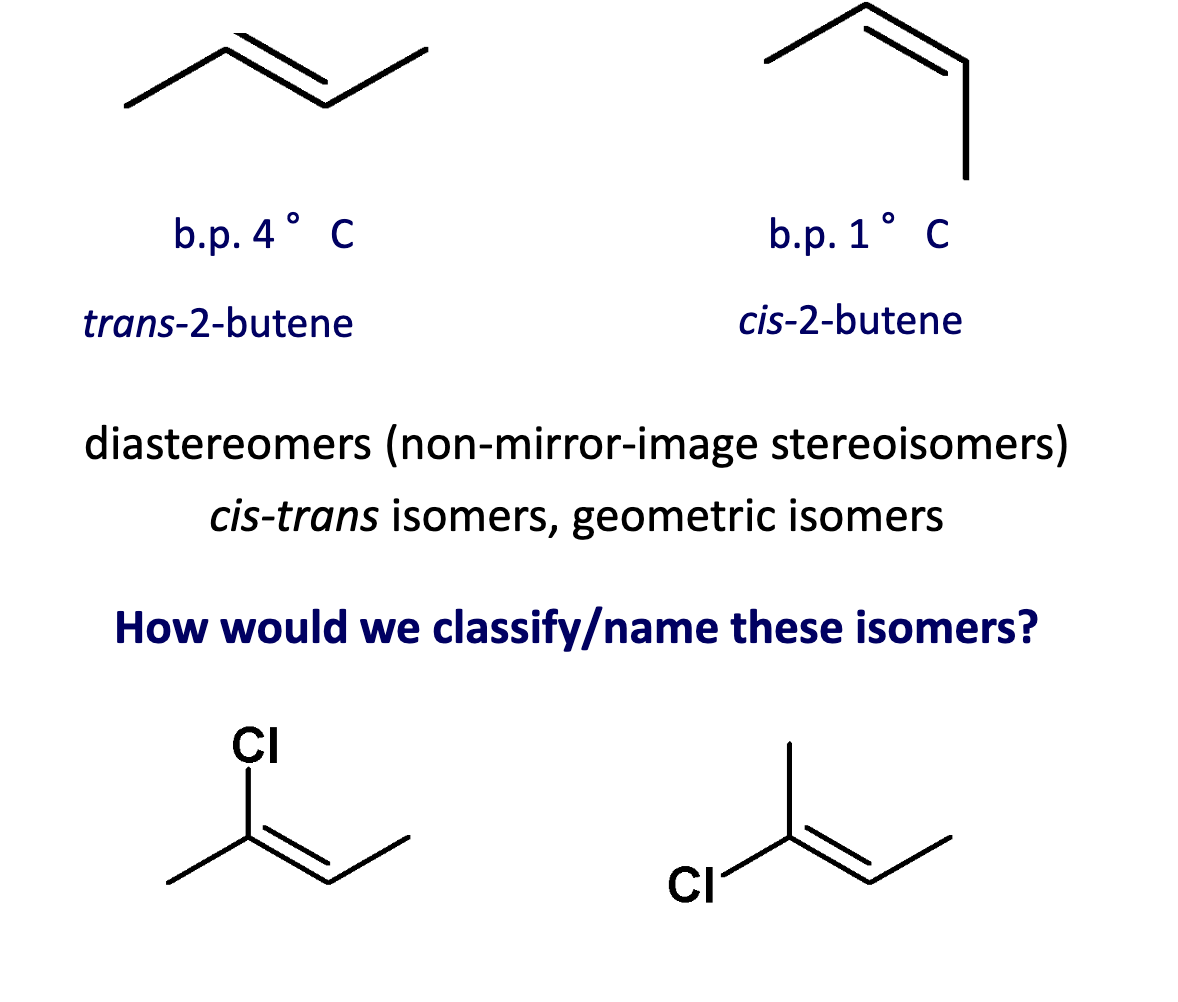
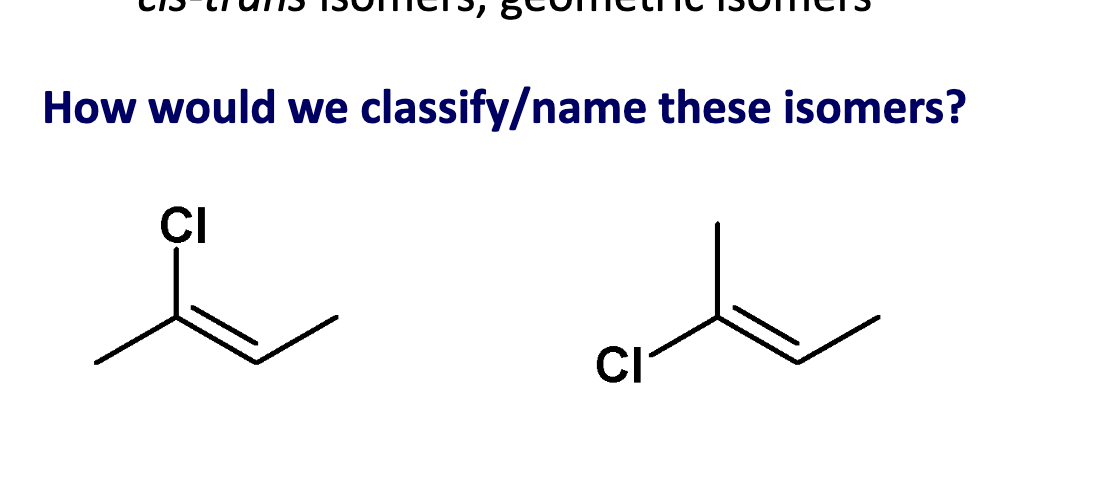
1st one is Z.
Apply CIP rule to C=C to nearby substituents.
zeezamezide
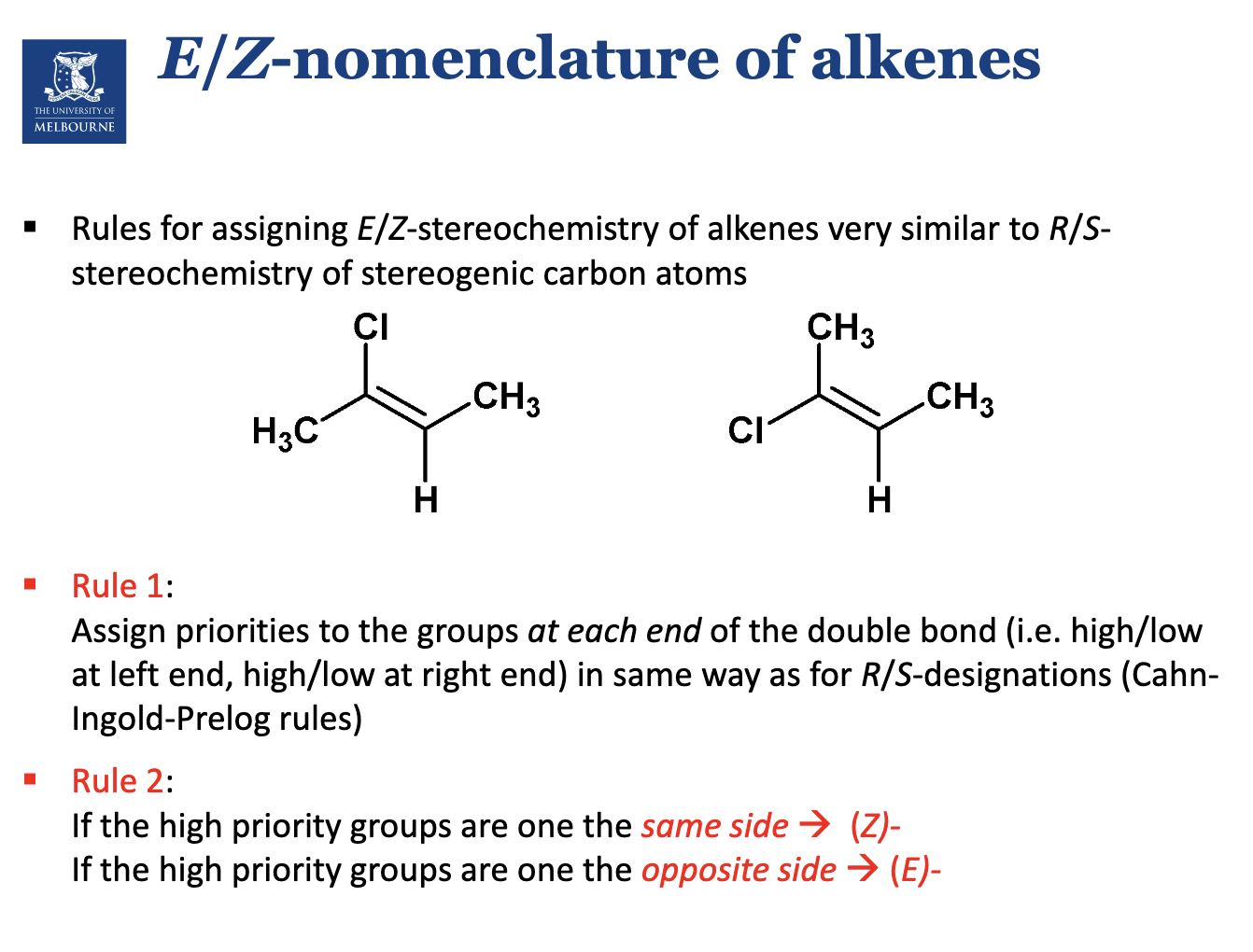
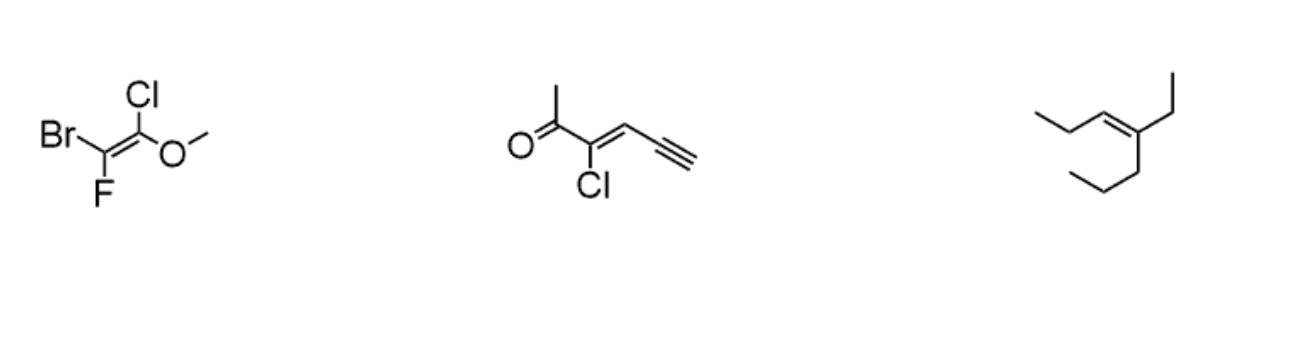
Assign E or Z
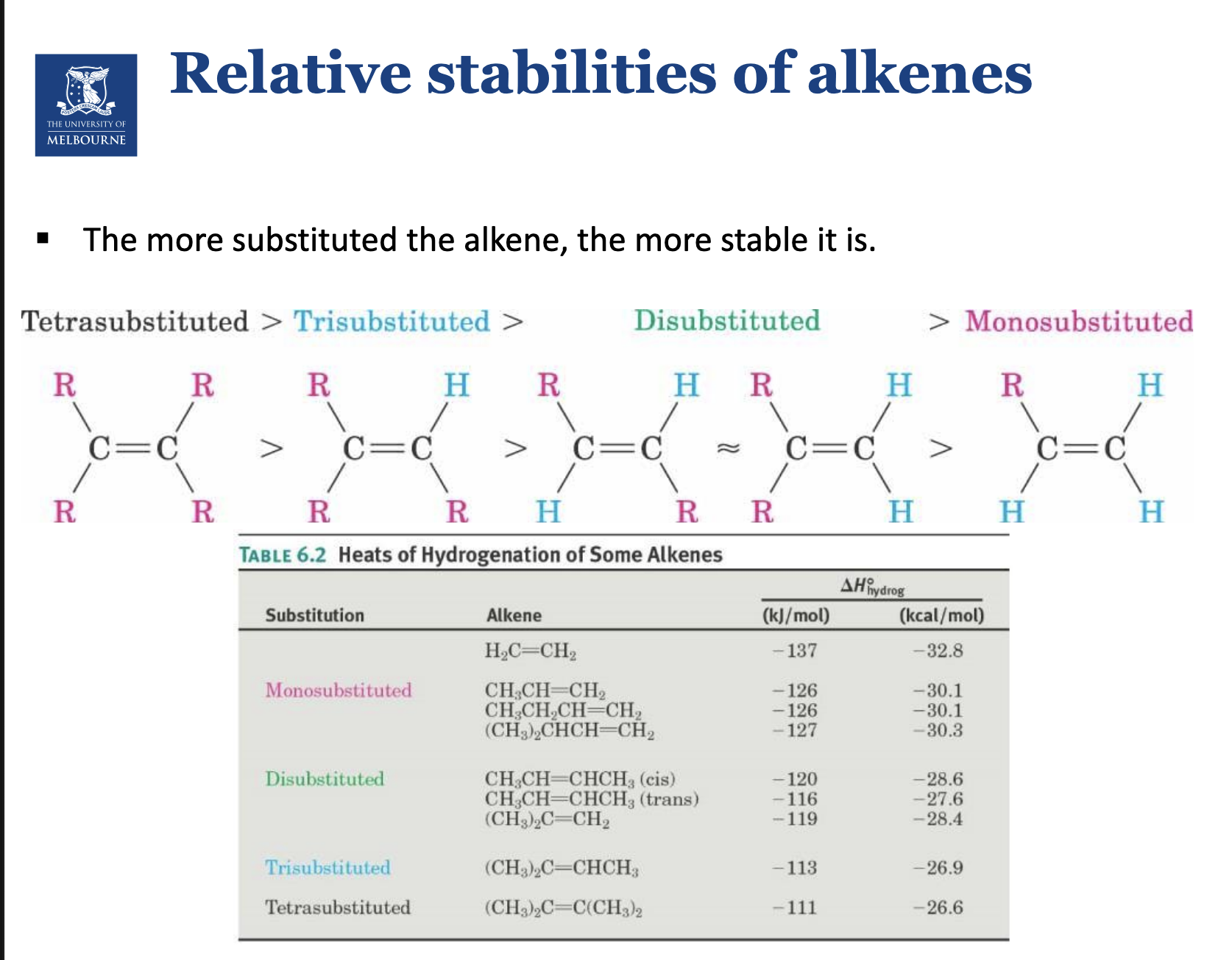
Describe the relative stability of alkenes.
Cis is generally less stable than the trans.
Steric seperation, wanting the bulky chemical groups to be as far away from each other.
Describe alkynes.
CnH2n-2
The structure is linear. Note the 2-penthyne has 5 carbons.
General drawing is R-C(triple)C-R, not C(triple)C.
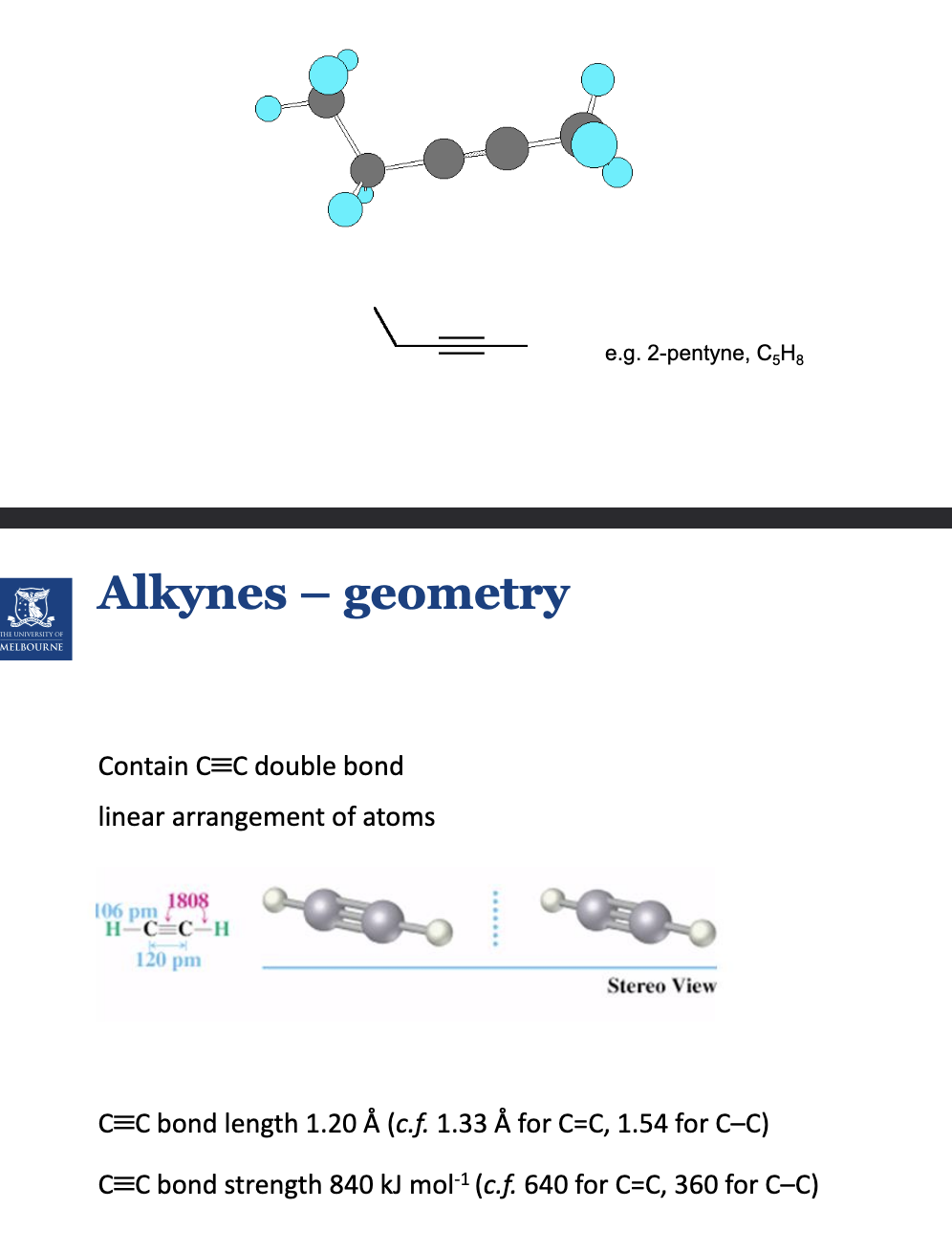
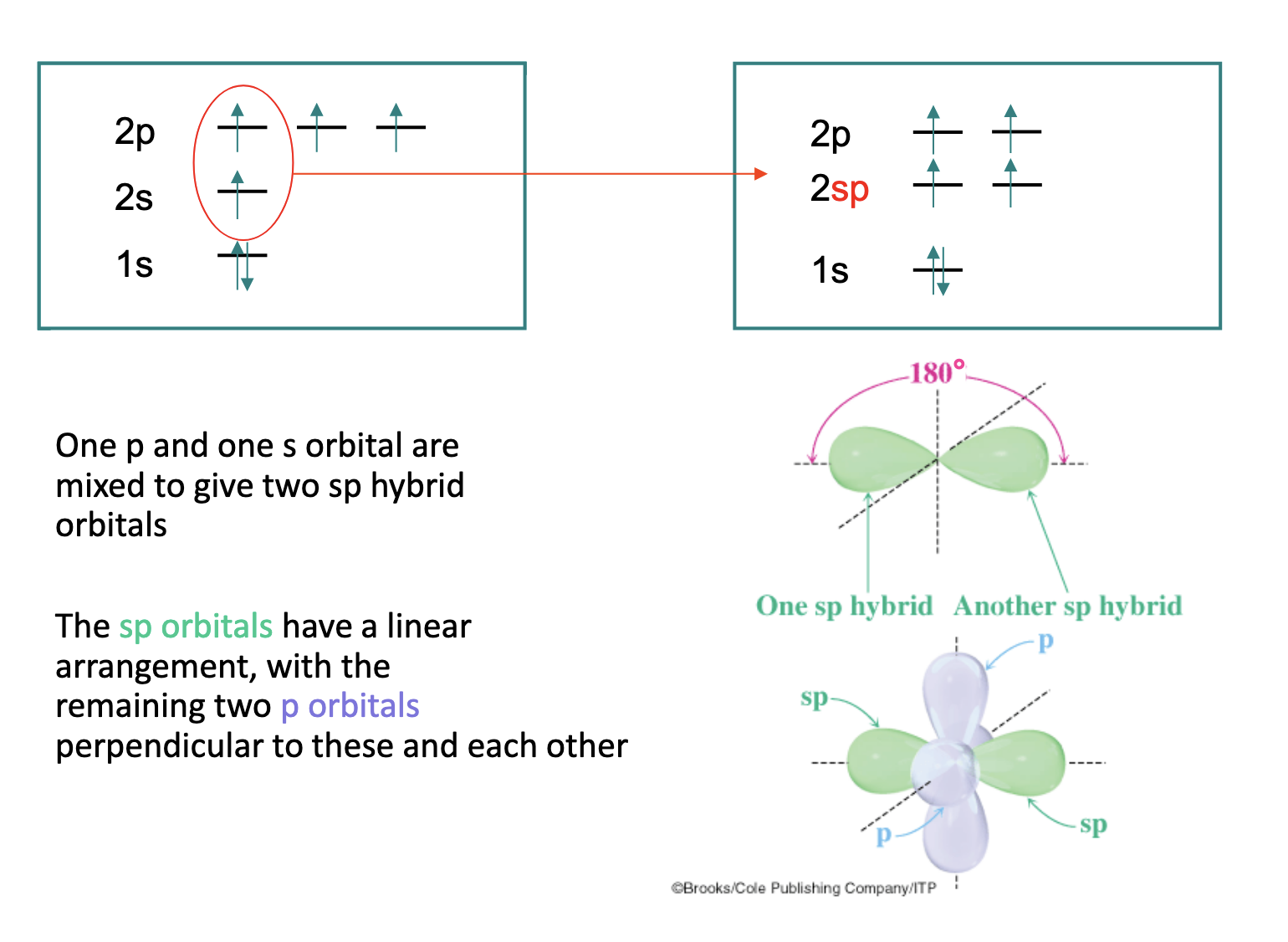
Describe sp hybridisation.
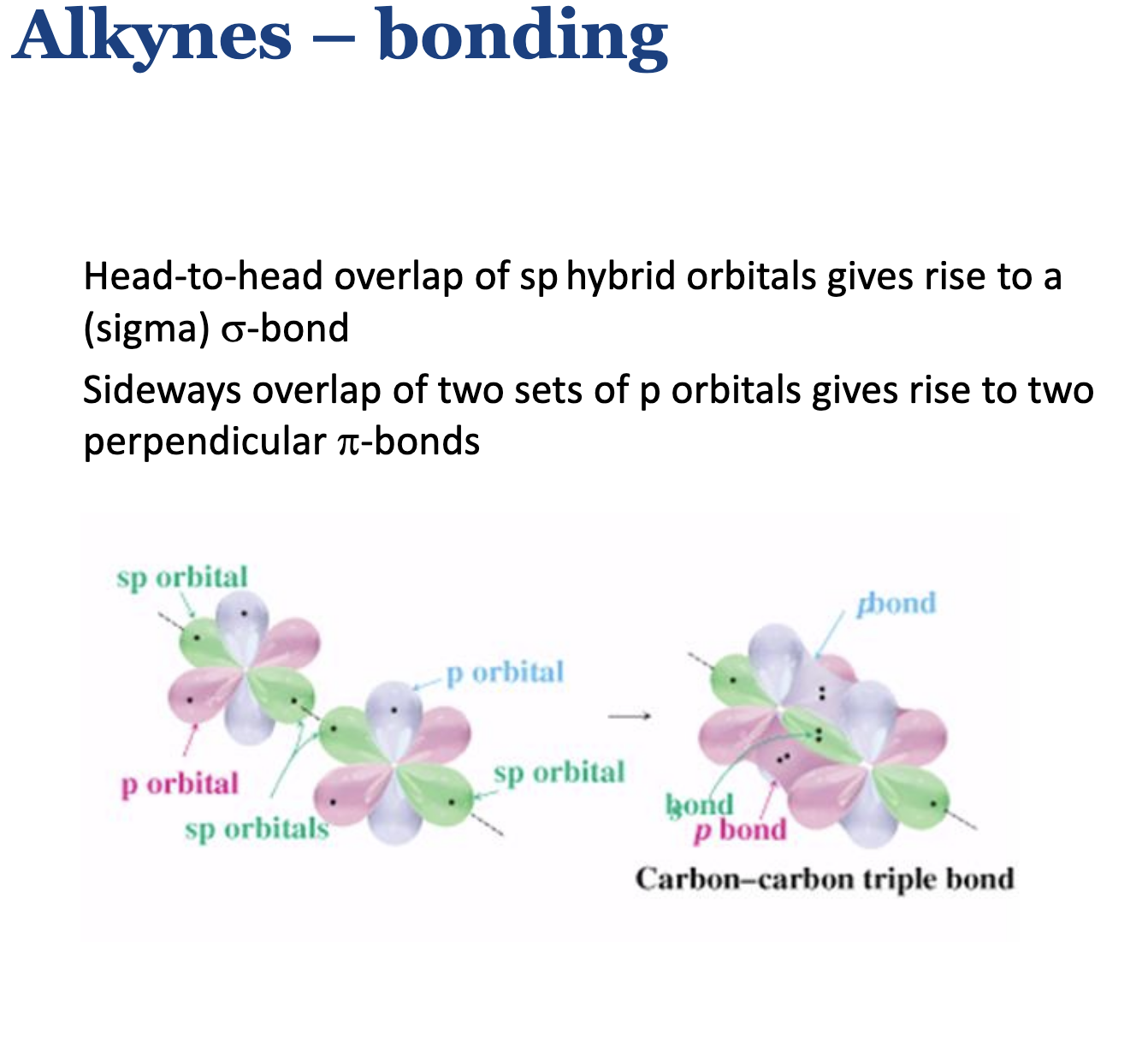
Describe bonding of alkynes.
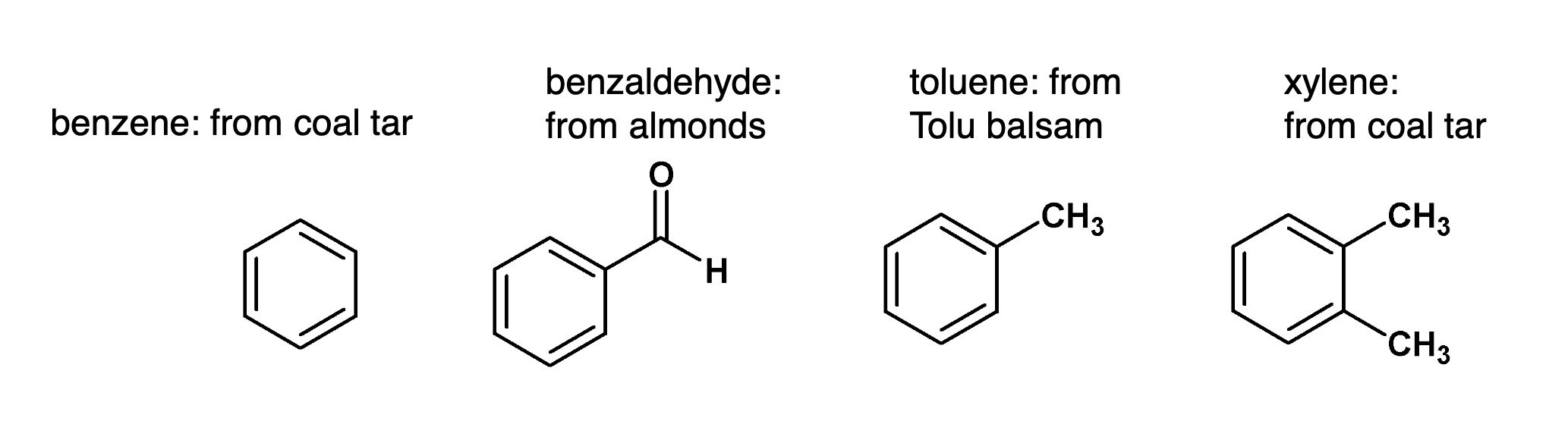
What are aromatic compounds?
They have distinct odors.
They tend to be conjugated, thus are usually coloured.
Aromatic compounds now refer to benzene and its structural relatives.
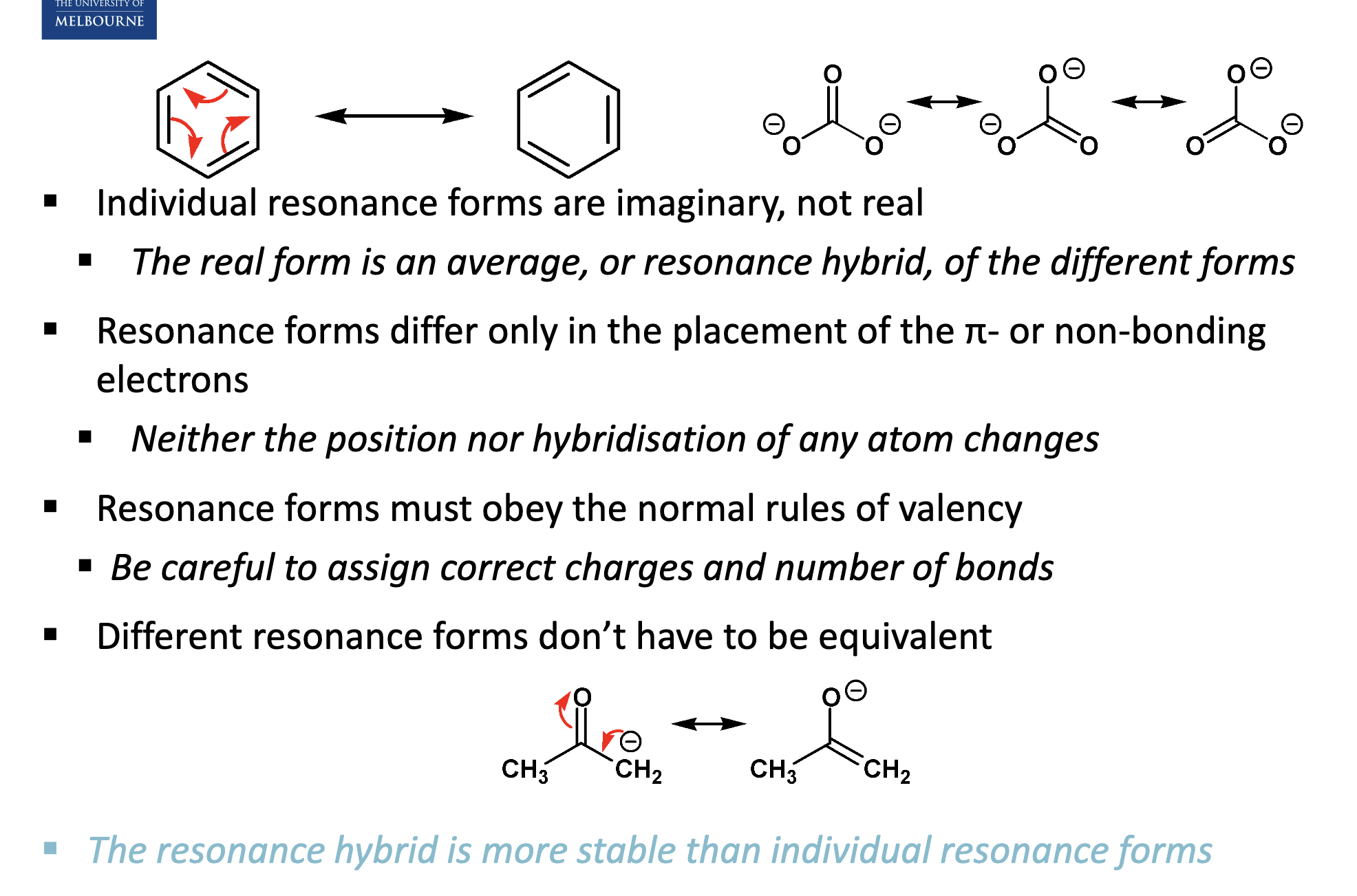
Describe the structure of benzene.
In benzene, despite having C=C, all bond lengths are the same.
Benzene is a planar molecule, thus all bond angles are 120º.
Why is benzene more stable than expected?
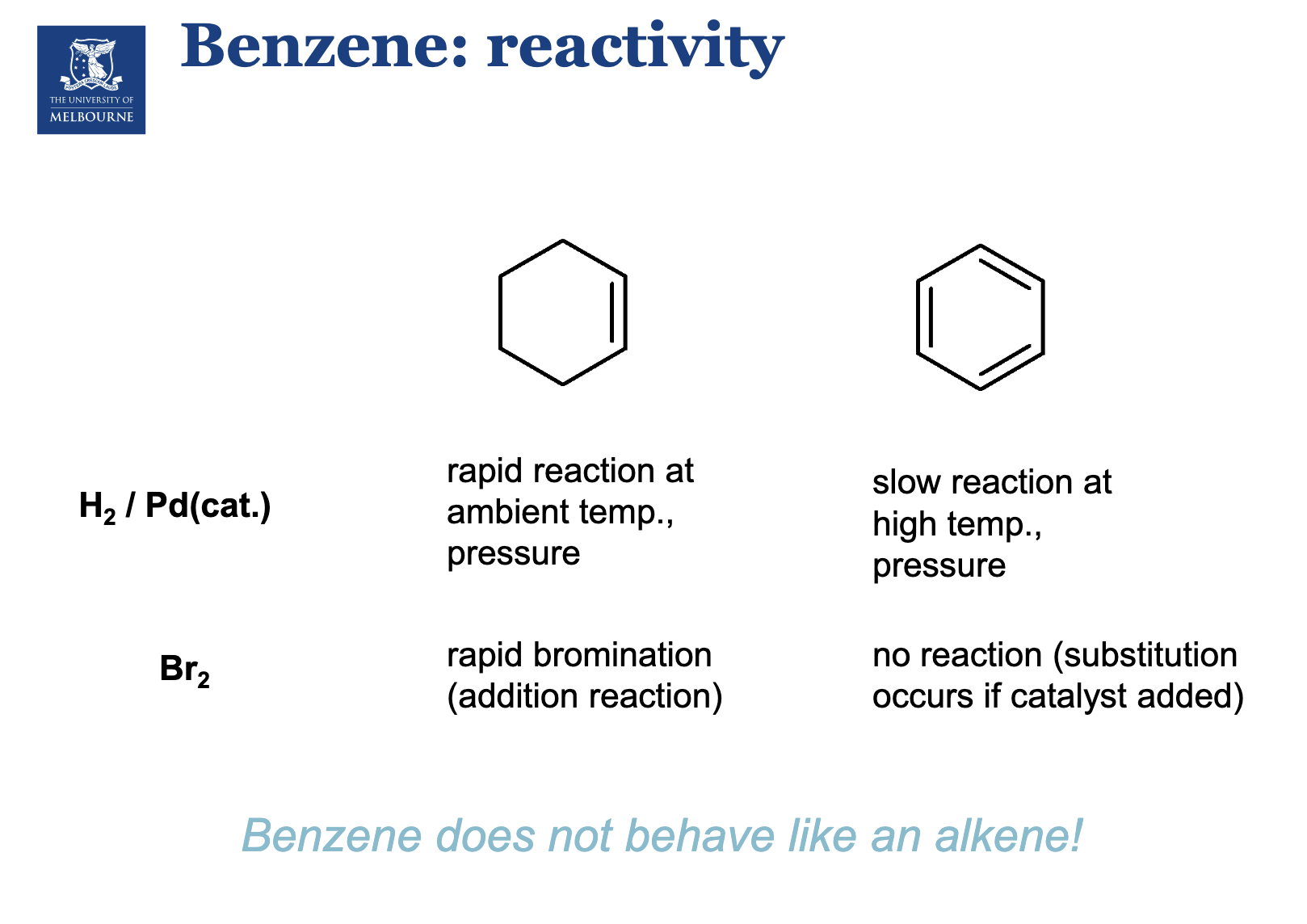
Describe benzene’s reactivity.
Describe the resonance stabilisation of benzene.
The π-electrons are not localised between specific carbon atoms - they are delocalised, suggesting that the double bonds are moving.
How do we draw the different resonance forms of benzene?
Top image.
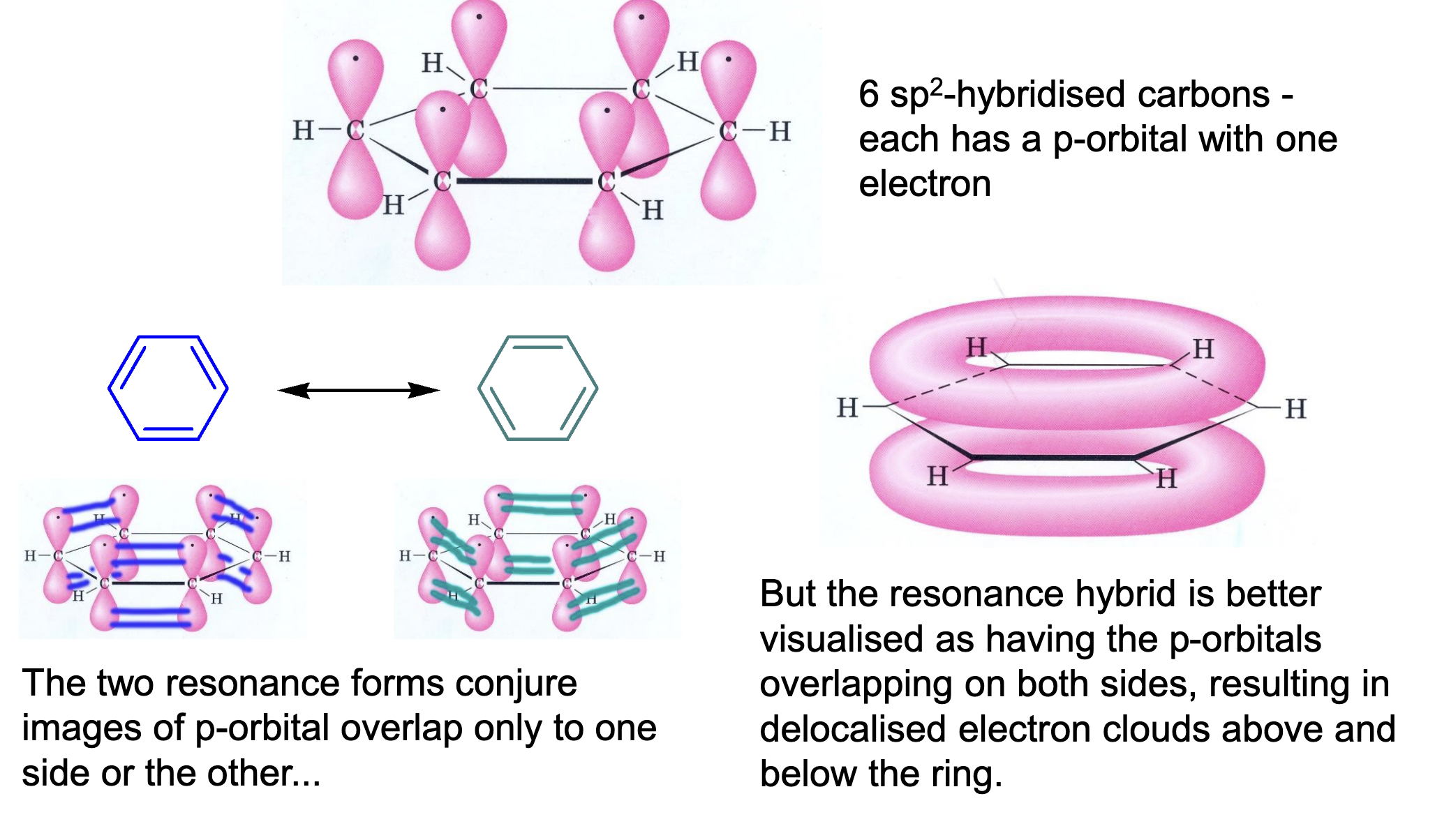
Describe the orbital description of benzene.
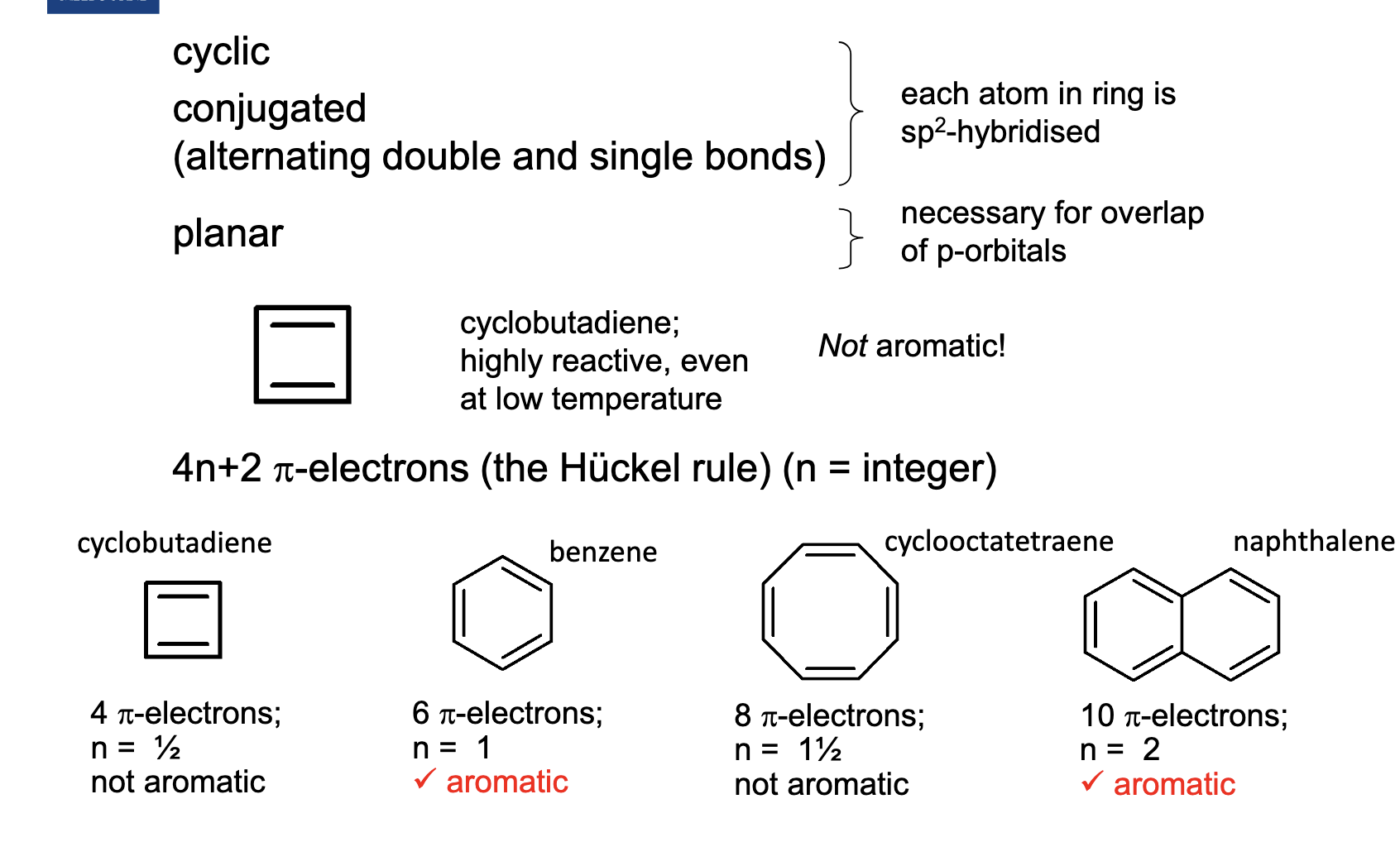
What are the requirements for aromatic?
For example, the first one is cyclic and conjugated, but we don’t know if its planar.
We use the Huckel rule, where the π electrons are present in the double electrons.
4n+2π=4π
n=1/2 (not aromatic).
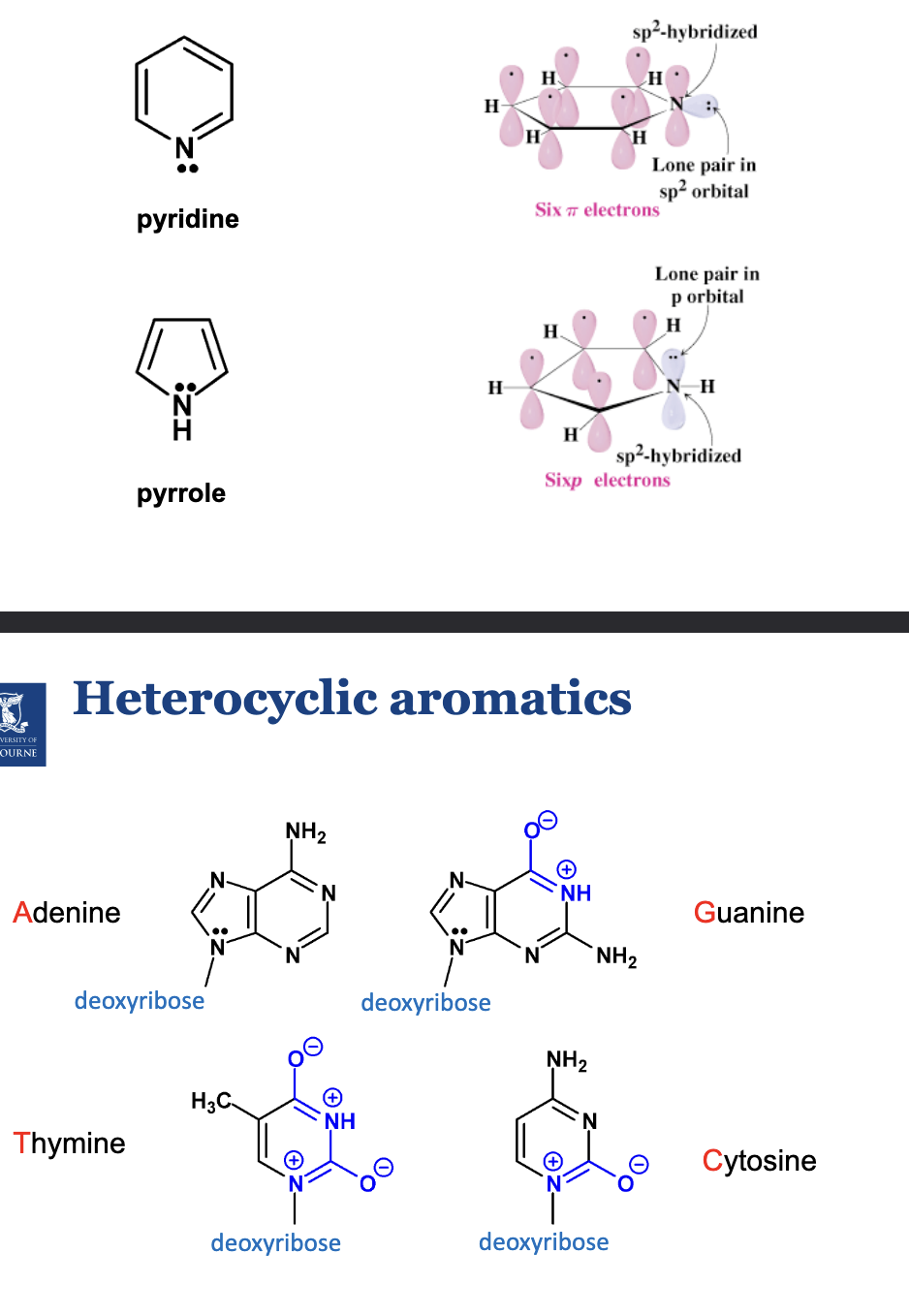
What are heterocyclic aromatics?
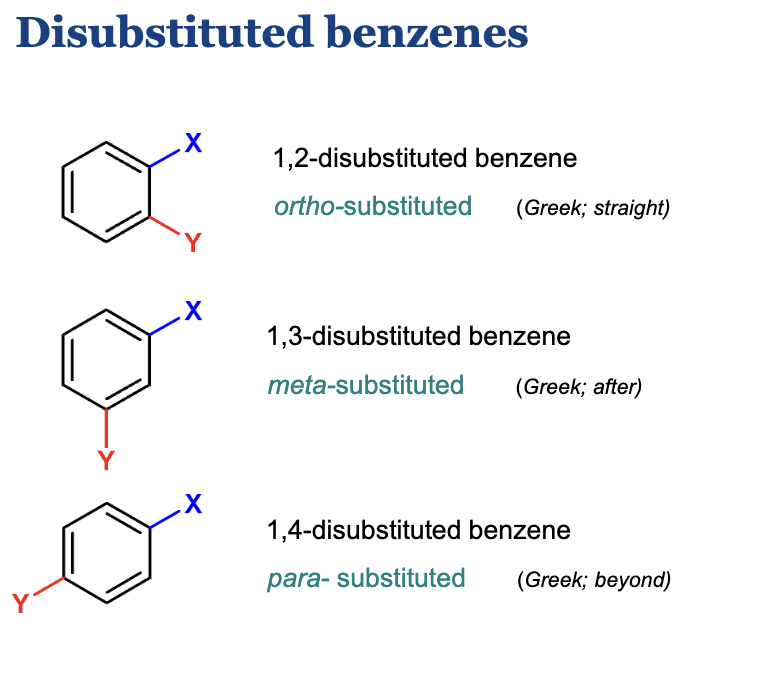
Describe how to name a disubstituted benzene.