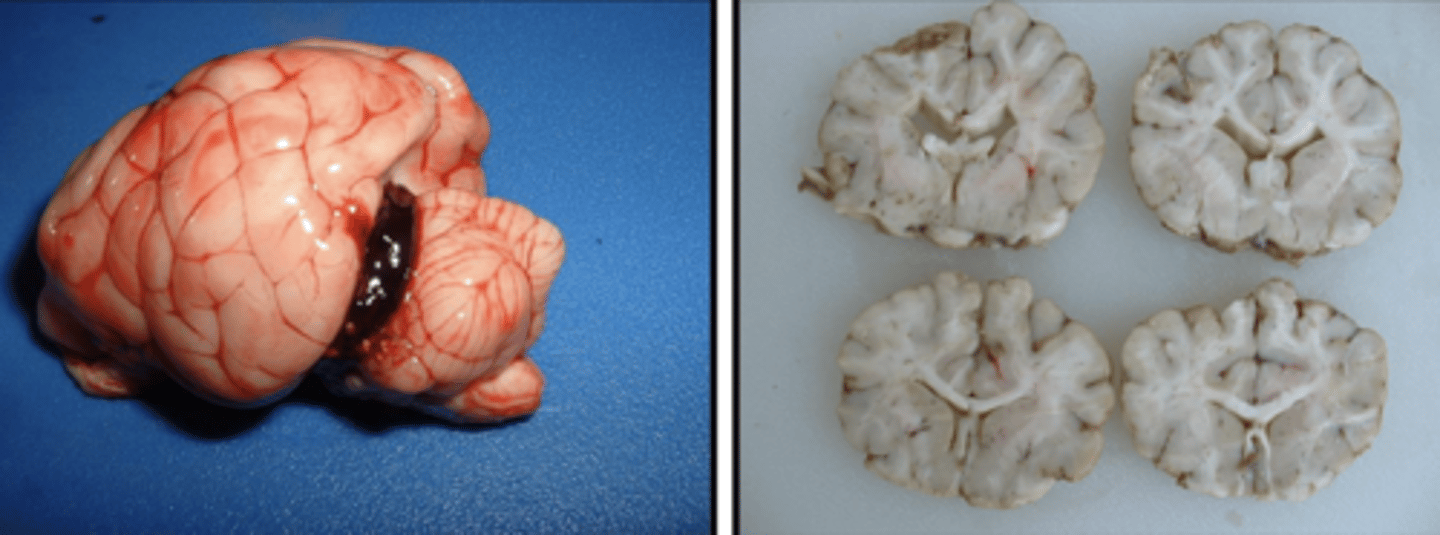
lecture 4 & 5 - cell injury: postmortem changes & necropsy tips
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
what is hypostatic congestion aka livor mortis?
gravitational pooling of blood
with liver mortis, why are some of the bone/joint areas white when the rest of the body on that side is red?
these are considered 'pressure points' where the blood gets dispersed elsewhere d/t the bone/join causing pressure
_____mortem lesions can mask _____ lesions
postmortem, antemortem
how will fibrin look when trying to identify it post-mortem?
strand-like material that adheres, usually yellowish in color, but not always. can be red/pink if absorbed any hgb
if there is a presence of fibrin, this means that it is a _____mortem lesion. why?
antemortem - this is because if you have fibrin, you also have inflammation (cant have one without the other) and inflammation can only happen when pt is alive
if there is a greenish hue to your tissue sample that is submitted, what does this mean?
likely means that autolysis has already begun
what animal/species is more likely to have unilateral prolapse? what can it be caused by?
- cattle
- can be caused by lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma
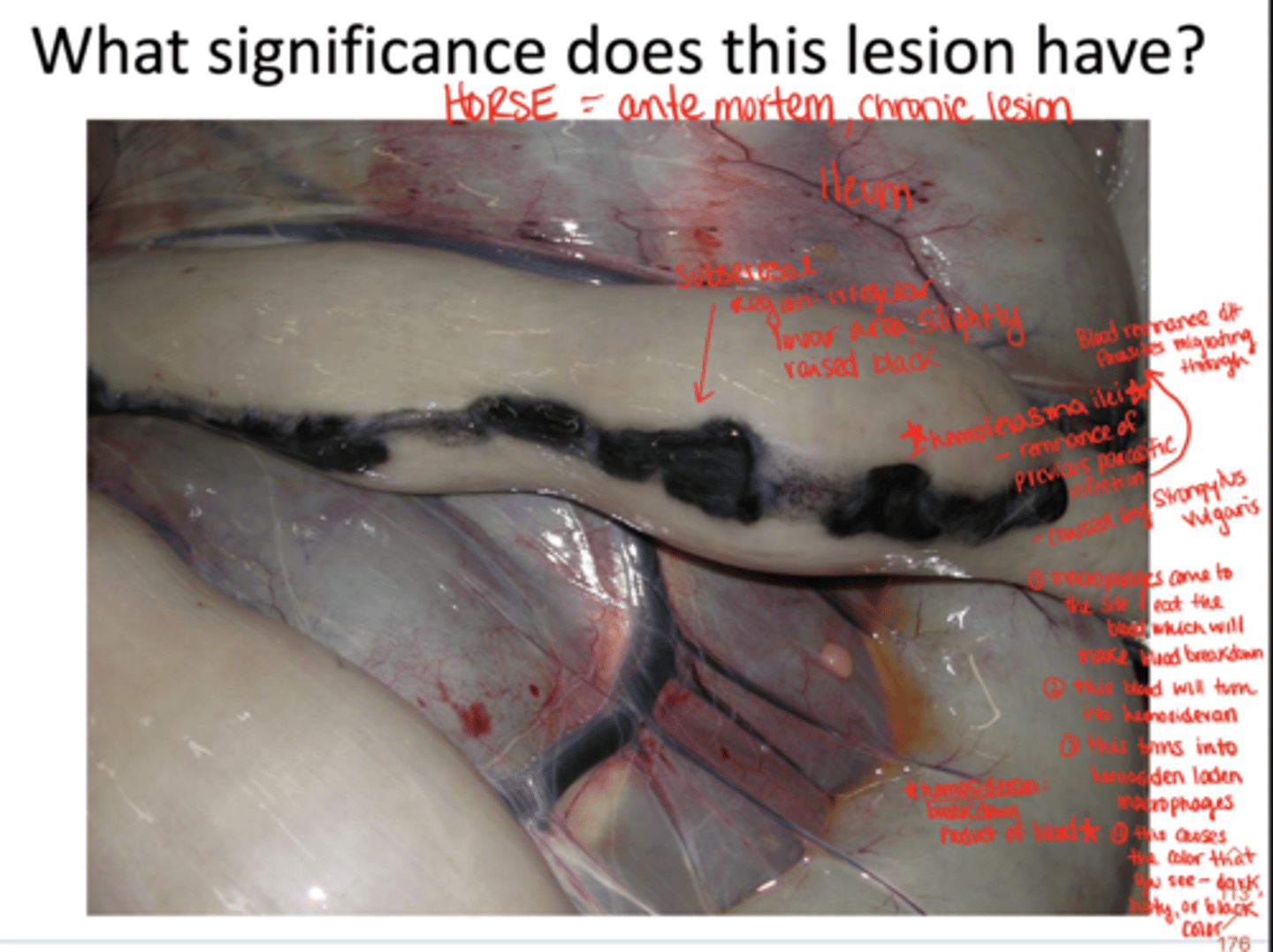
hemomelasma ilei is caused by what bacteria?
strongylus vulgaris
what are the steps to hemosideran stain in a horse with strongylus vulgars?
1. macrophages come to the site and eat the blood which will make blood breakdown
2. this blood will turn into hemosideran (breakdown product of blood)
3. this turns into hemosiden laden macrophages
4. this causes the color that you see (dark, rusty or black color)
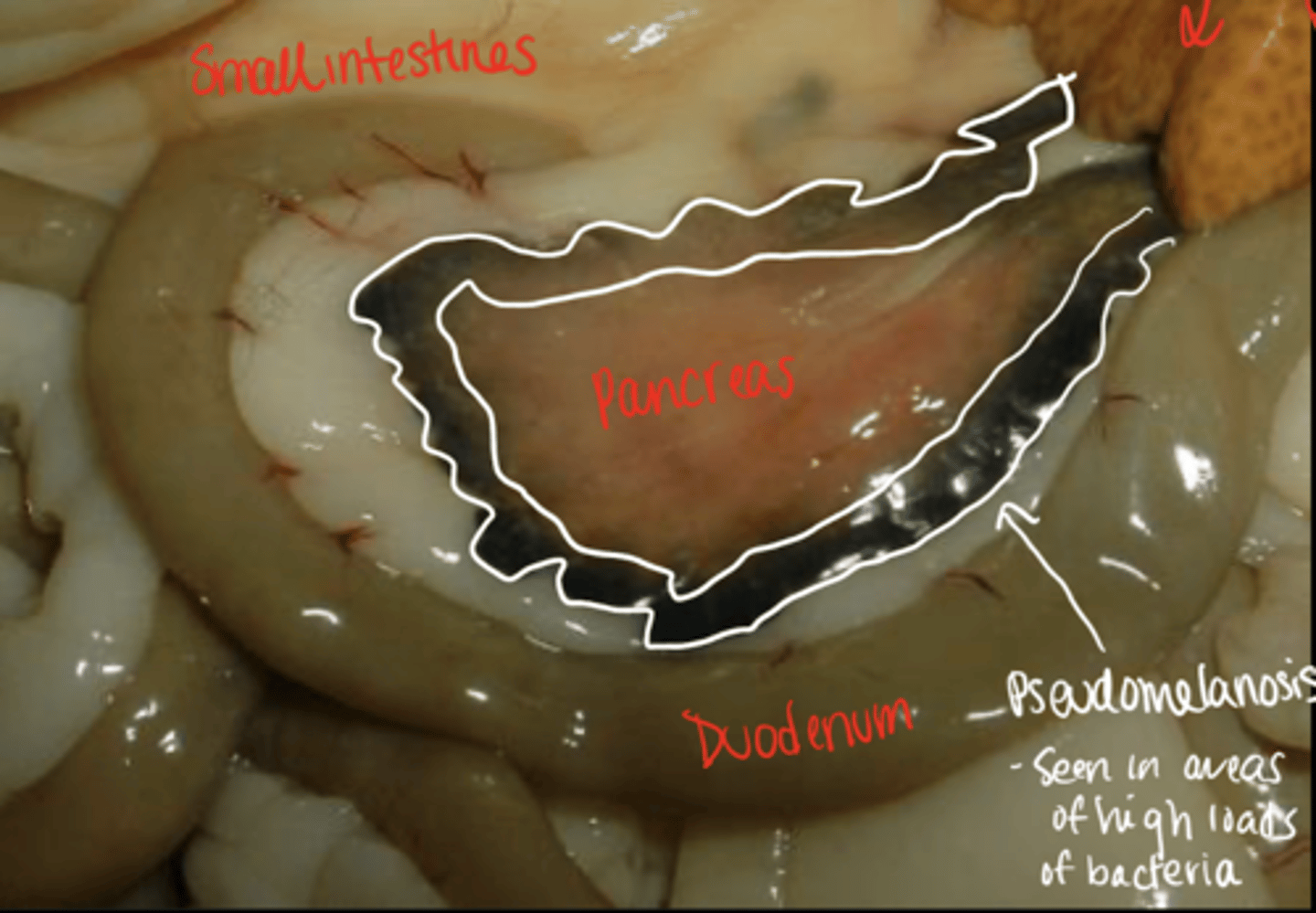
T or F: pseudomelanosis is always postmortem
true - this is a false black color
pseudomelanosis:
- bacteria uses iron _____ to break down blood
- ______ sulfide is the by product which causes tissues to be pigmented
- sulfide
- hydrogen sulfide
bile imbibition can be either antemortem or postmortem. what is this caused by?
breakdown of blood and bilirubin
T or F: when melanosis occurs, it is typically a patchy or mottled appearance
true
hemoglobinuric/myoglobinuric nephrosis can look the same but they are not. what is the difference?
- hemoglobinuric: peeing out hgb and staining the tissues around it
- myoglobinuric: muscle fibers being peed out by the kidney
abnormal sings of kidney postmortem?
- shiny
- any color other than burgundy
- not smooth
if the kidney capsule is thickened and you can see impressions on it from the kidney, what does this tell us about it being ante or postmortem?
if the capsule is thickened it means that something was being added to make this happen and lets us know it is antemortem
????
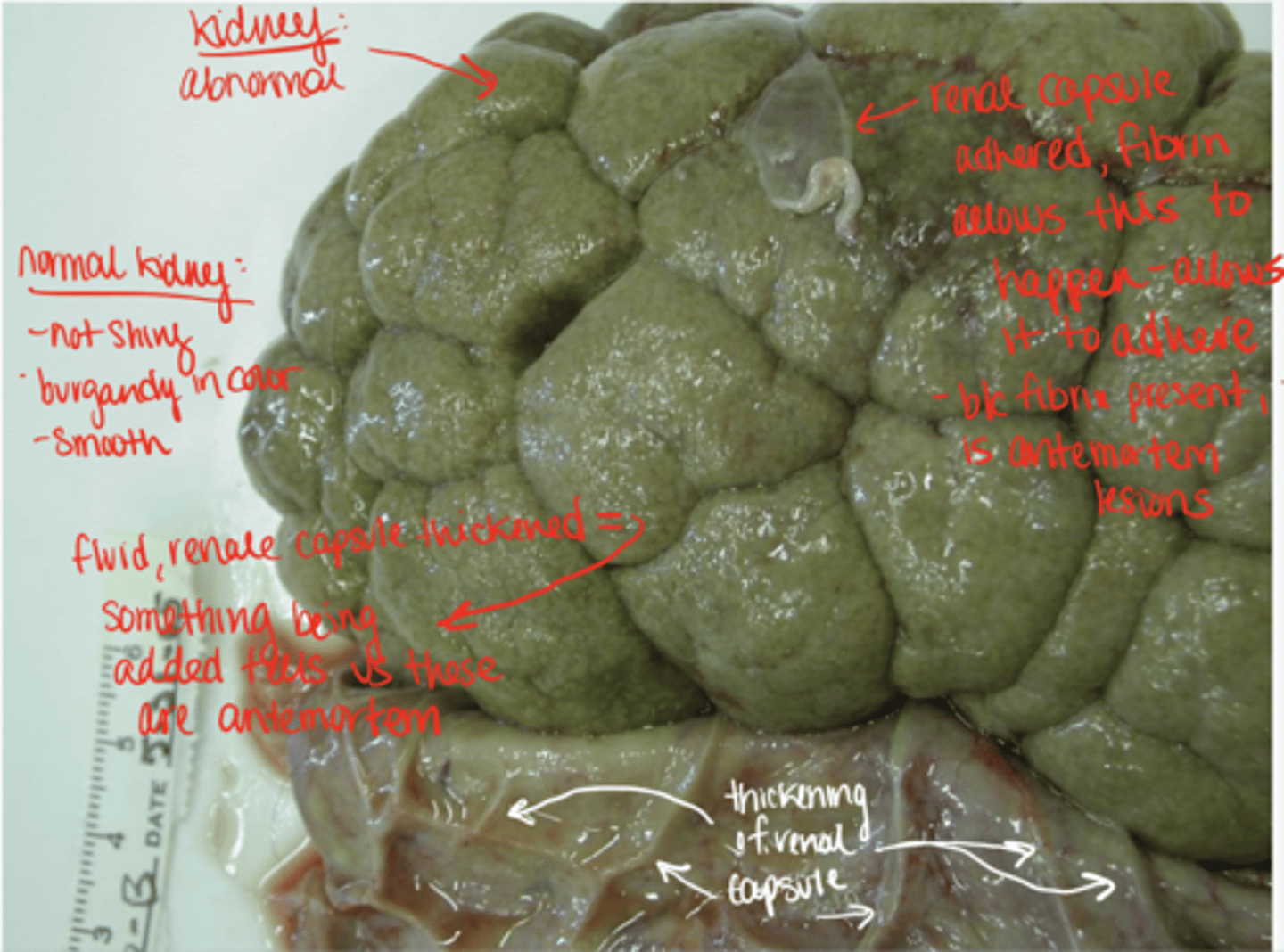

what is hgb imbibition and how does it happen?
it is the staining of tissue by Hgb caused by --> RBC carrying hgb that get lysed/damaged, this will then cause the release of hgb and it will seep out and stain adjacent tissues
what is a parasite that can cause hg imbibition?
babesia - can also cause "pink brain" in bovine
review: arteries take blood to or from tissues? veins?
- arteries: take blood to tissues
- veins: take blood away from tissues back to the heart
what are the 3 'stages' where intussusception can happen?
antemortem, perimortem, or postmortem
postmortem intussusception can be d/t irregular _____
peristalsis
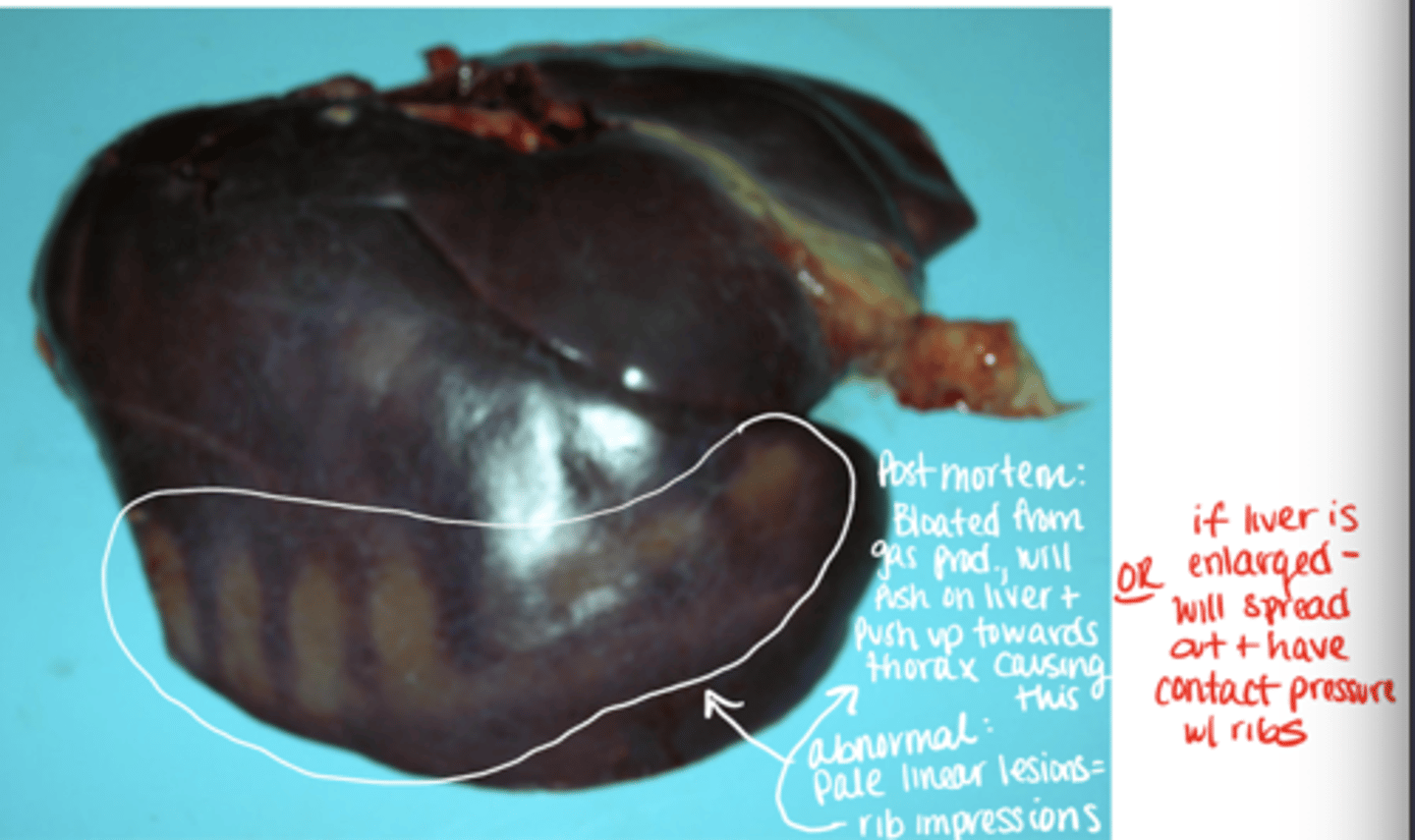
what are ways impression lesions can be caused on organs?
example - if impression lesions are on the liver, the liver could have been enlarged and pushing on the ribs, could be due to bloat/gas production, can also be d/t other organs being pushed up and causing ribs to rest on liver, etc
what is a chicken fat clot? ante or postmortem?
a yellow/orange clot with a dark red portion that is found in the body postmortem
T or F: postmortem leasions and interpretations) should always be included in a. necropsy report
false - postmortem changes are not true lesions and should not be included. only time they should be is if you are unsure of whether it is postmortem or antemortem
the person doing the necropsy is called what?
prosector
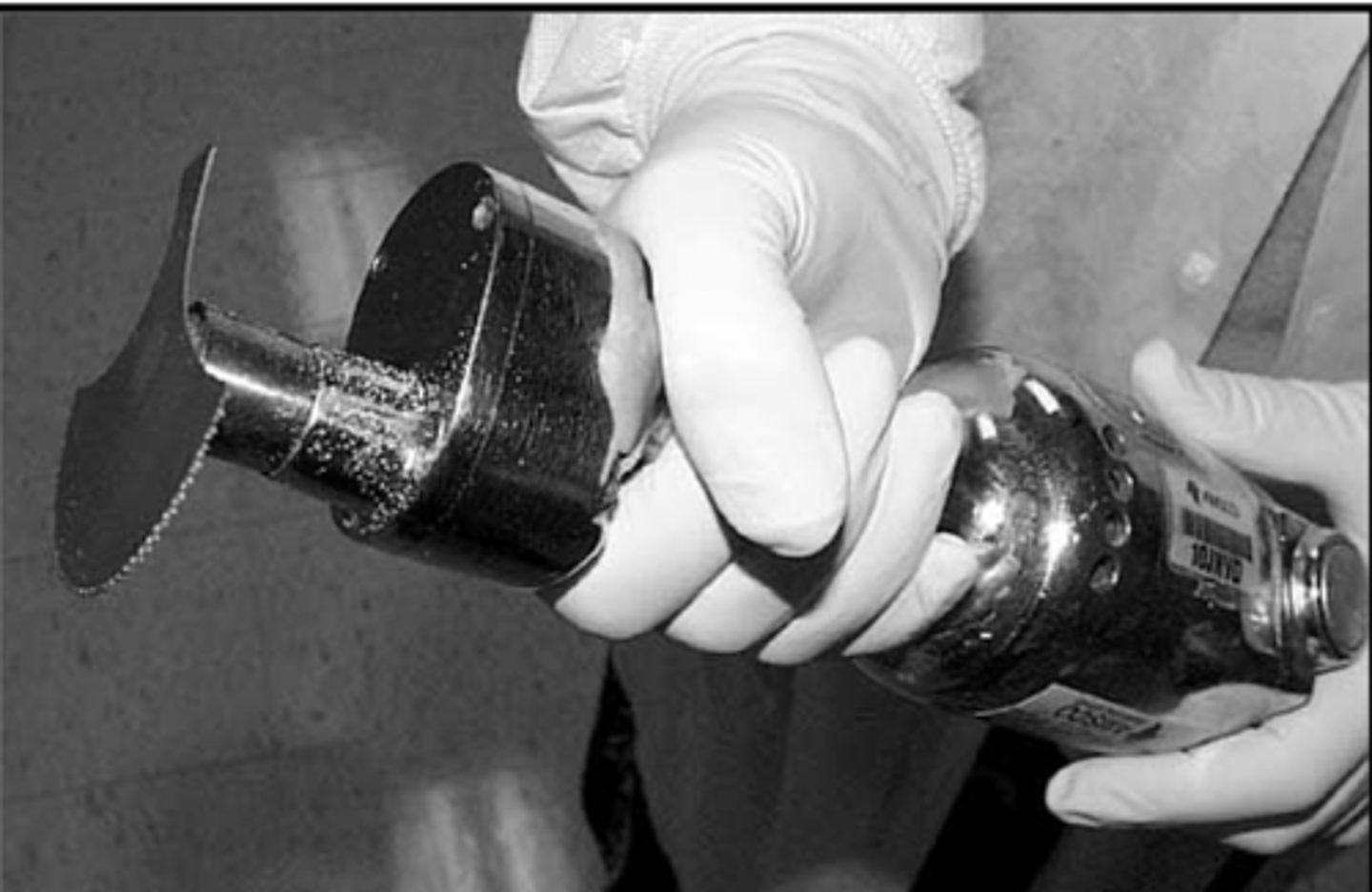
what is a stryker saw used for?
motorized saw that is used for cutting bone) flat bones of the skull to remove the brain)
- only cuts bone, not soft tissues

formalin to tissue ratio?
10:1
specimens should be routinely collected from all major ____ in all necropsies
organs
postmortem changes result from a combination of the release of _____ lysosome enzymes from the tissue cells as they die (_______)
proteolytic, autolysis
postmortem autolysis occurs how soon after death?
immediately/automatically after death
what is rigor mortis? when does it begin? when does it pass?
- contraction and stiffening of muscles after death
- begins: 1-6 hrs after death
- passes: 36-48 hours after death
what is liver mortis? it is aka what?
gravitational pooling of blood, aka hypostatic congestion
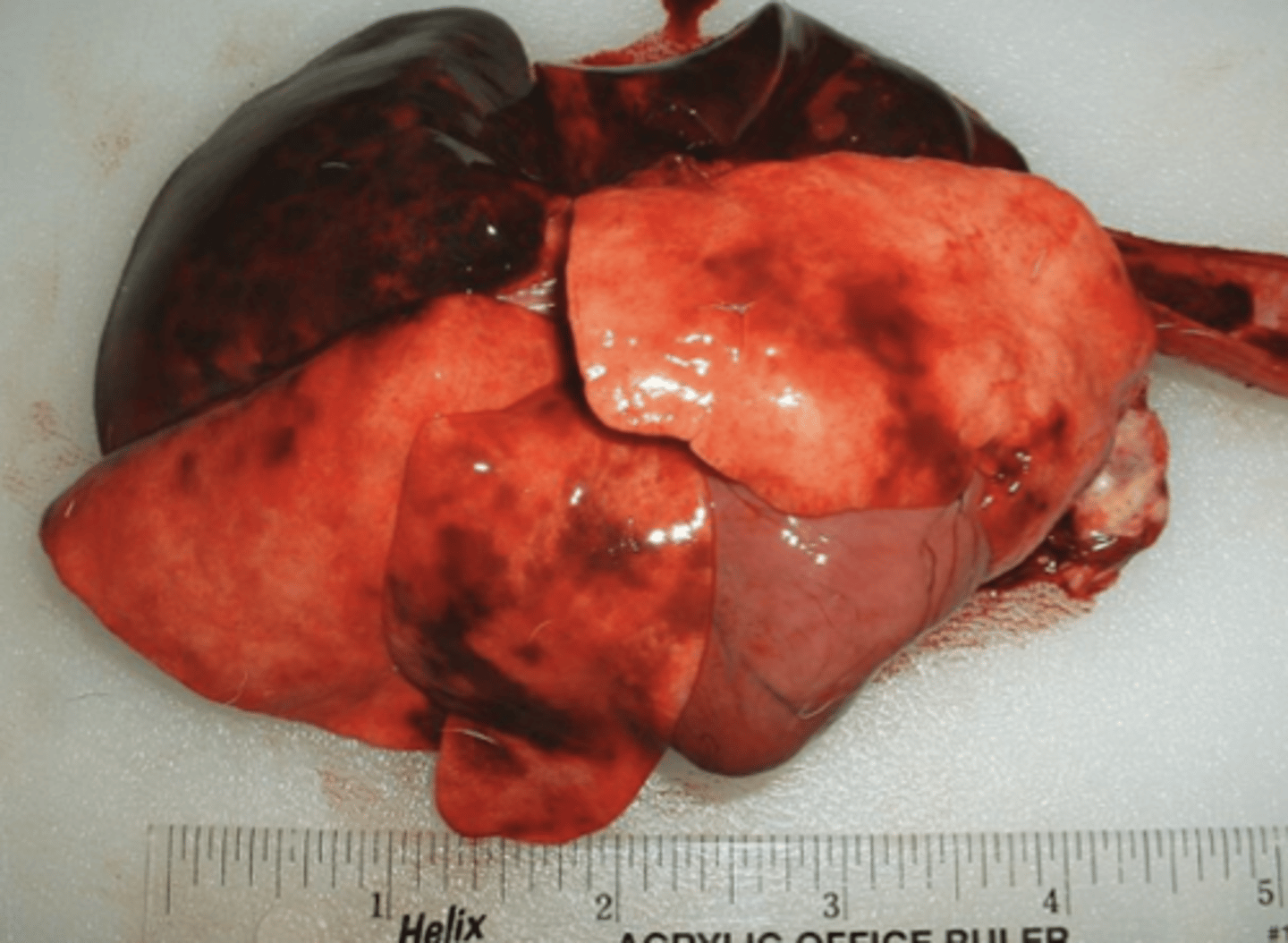
what is hgb imbibition?
pinkish to reddish coloration due to lysis of RBCs - hgb leaks out and stains adjacent tissues
hgb inhibition is most evident on _____ surfaces of large arteries and outer surfaces of light colored organs
intimal
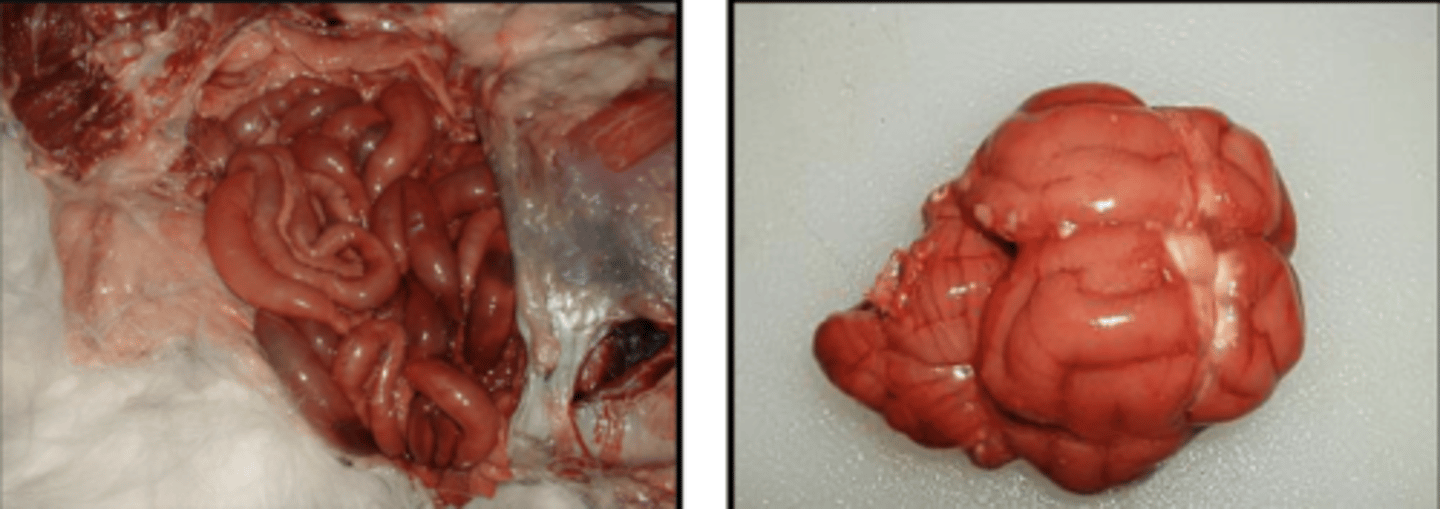
what is pseudomelanosis?
greenish gray to black coloration of tissues due to the action of bacteria on hgb forming hydrogen sulfide (byproduct) which allows tissues to be pigmented
most important thing to supply the pathologist with when sending in a necropsy report?
HISTORY

during a necropsy exam, all animals except horses should be placed how? how should horses be placed?
- horses: R lateral recumbency
- all other animals: L lateral recumbency
what must be removed top thoroughly examine the buccal cavity?
the tongue

what is blood in the peritoneal cavity called?
hemoparitoneum
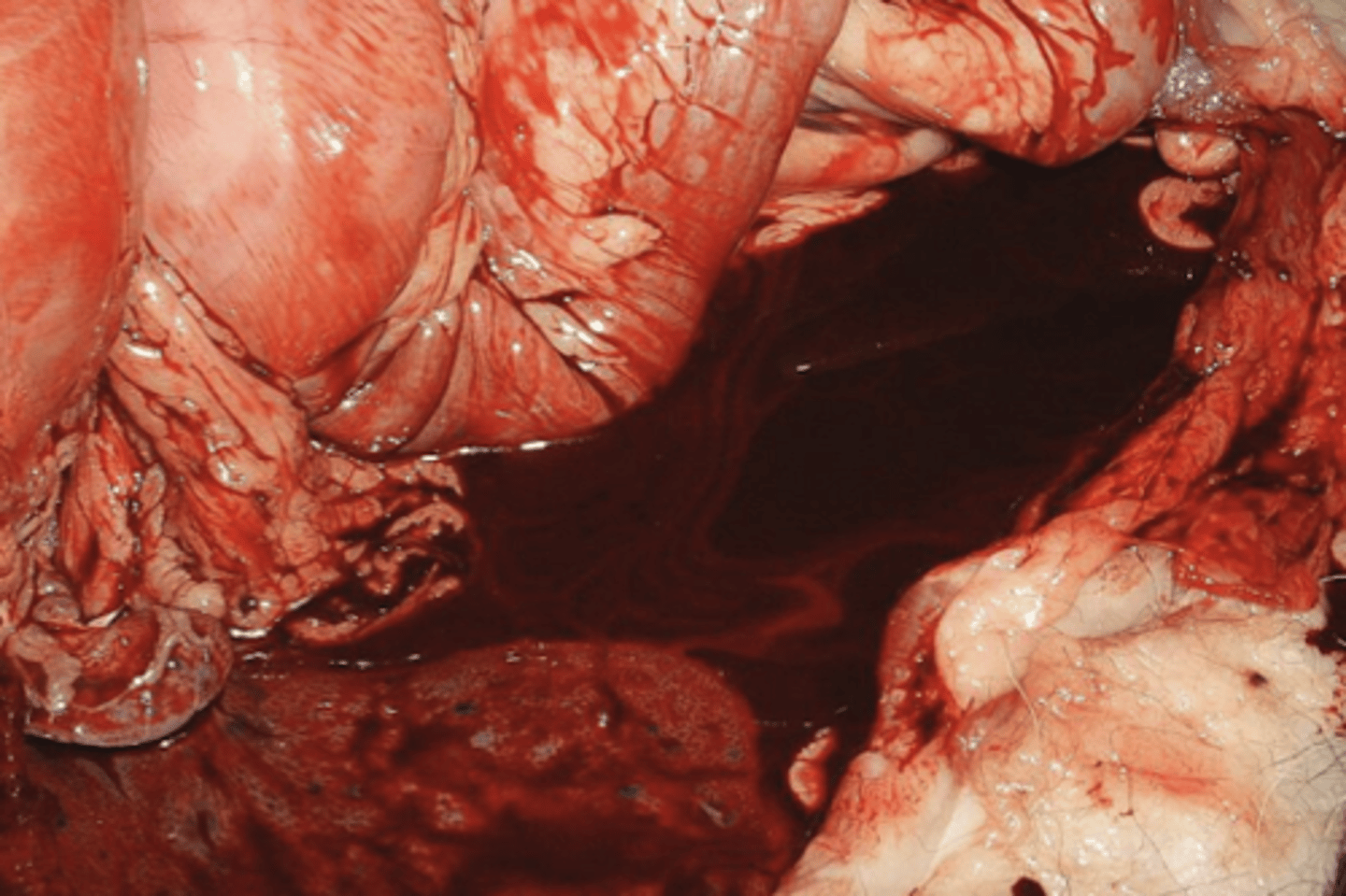
what is non-blood fluid in the peritoneal cavity called?
ascites
what is a malposition?
any organ that is not in its proper anatomical position, or that is twisted or distorted abnormally
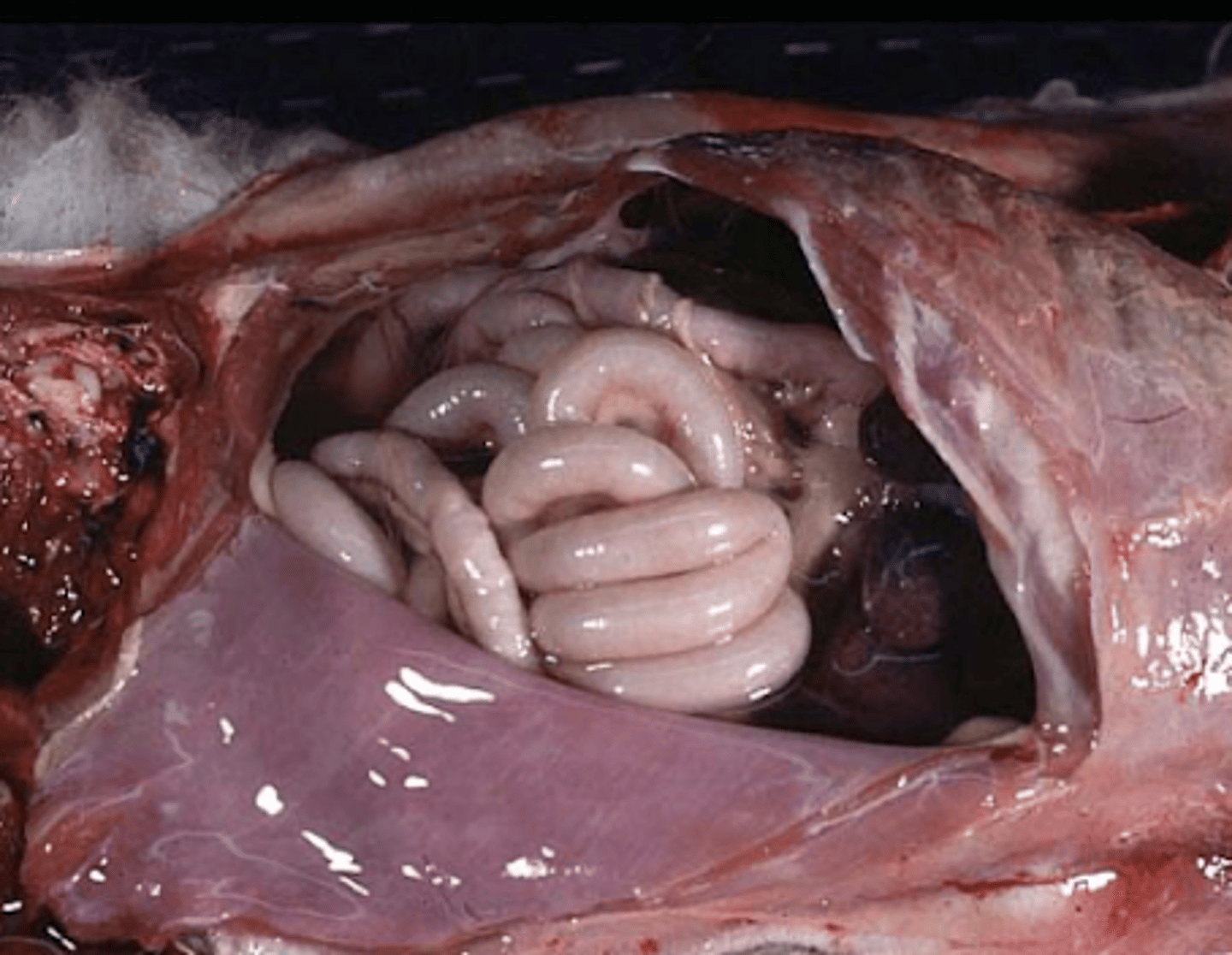
a normal liver should not extend much beyond what?
the edge of the last rib
what is volvus/torsion?
involves a twisting of the mesenteric attachments of the stomach and/or intestines
what is a common consequence of volvulus/torsion?
bloating (gaseous dilation) of the stomach
gastric volvulus pulls the ____ from the left side of the body to the right side and causes it to be engorged with blood
spleen
what is intussusception?
when the intestines telescope on itself - the telescoped portion dies from ischemic necrosis
what is a diaphragmatic hernia?
when the diaphragm ruptures allowing the intestines to move up into the chest cavity
what is a hemothorax? hydrothorax? serosanguinous fluid?
- hemothorax: blood in the thoracic cavity
- serosanguinous: if the fluid is not blood, but is red because it is "blood-tinged"
- hydrothorax: fluid in the chest cavity that is not blood
what is known as "the pluck" in a necropsy?
the heart and the lungs
after removal of the heart, lungs, and the diaphragm, the abdominal viscera can be removed systemically, starting with the ______
liver
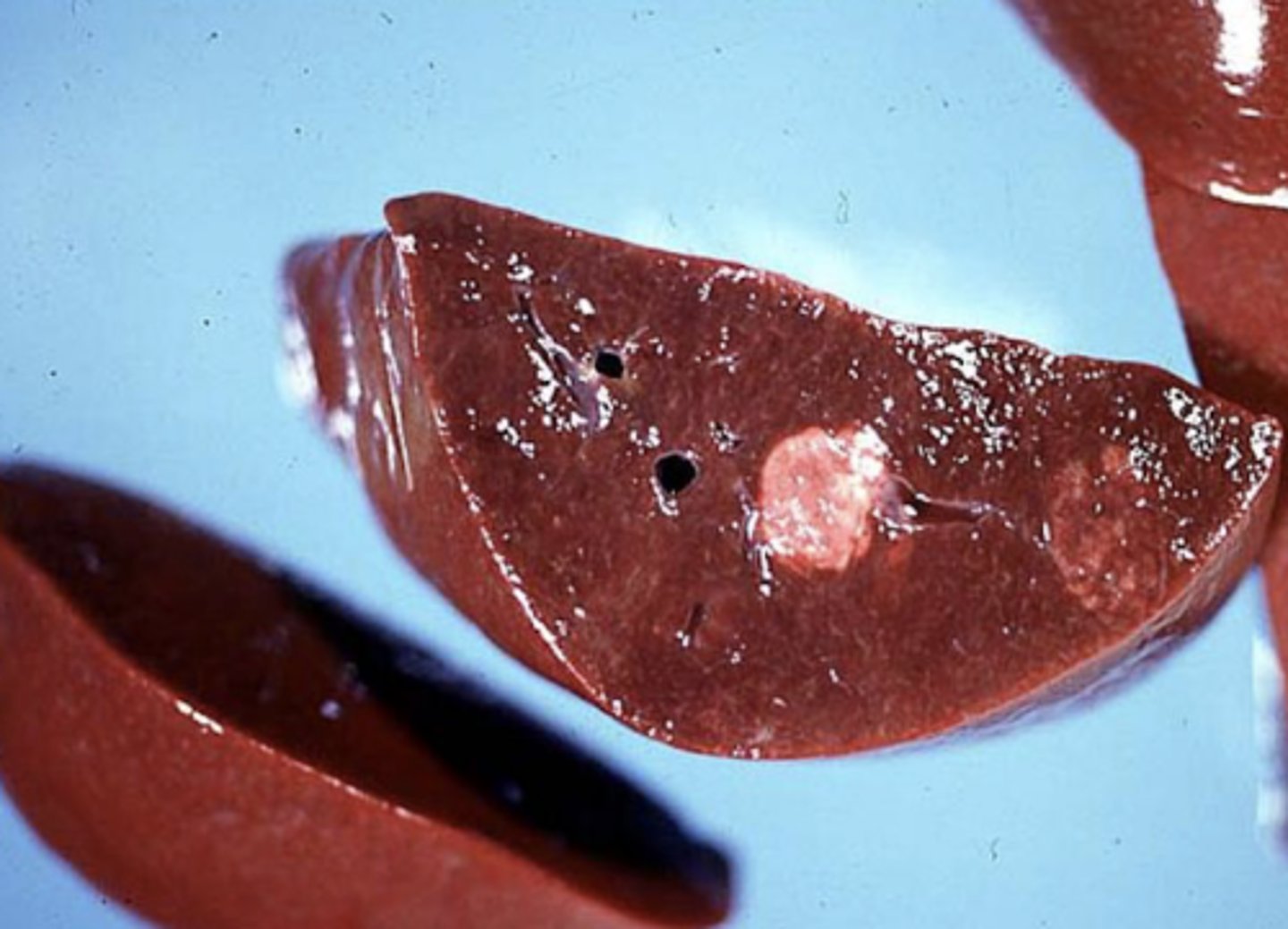
the liver should be "bread loafed" to expose any _____ that may be below the surface
lesions
when is the only time that samples of the stomach contents are collected?
only if ingestion of a toxin is suspected
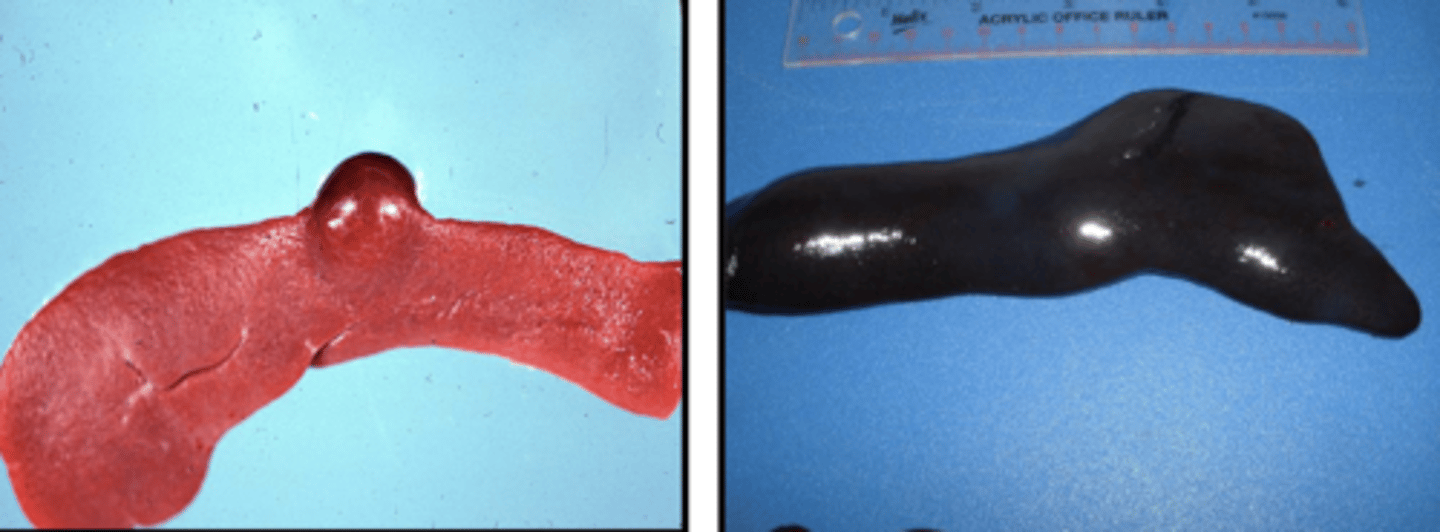
during a necropsy, the ____ should be examines for enlargement, nodular masses, or hemorrhage secondary to rupturing or fracture
spleen
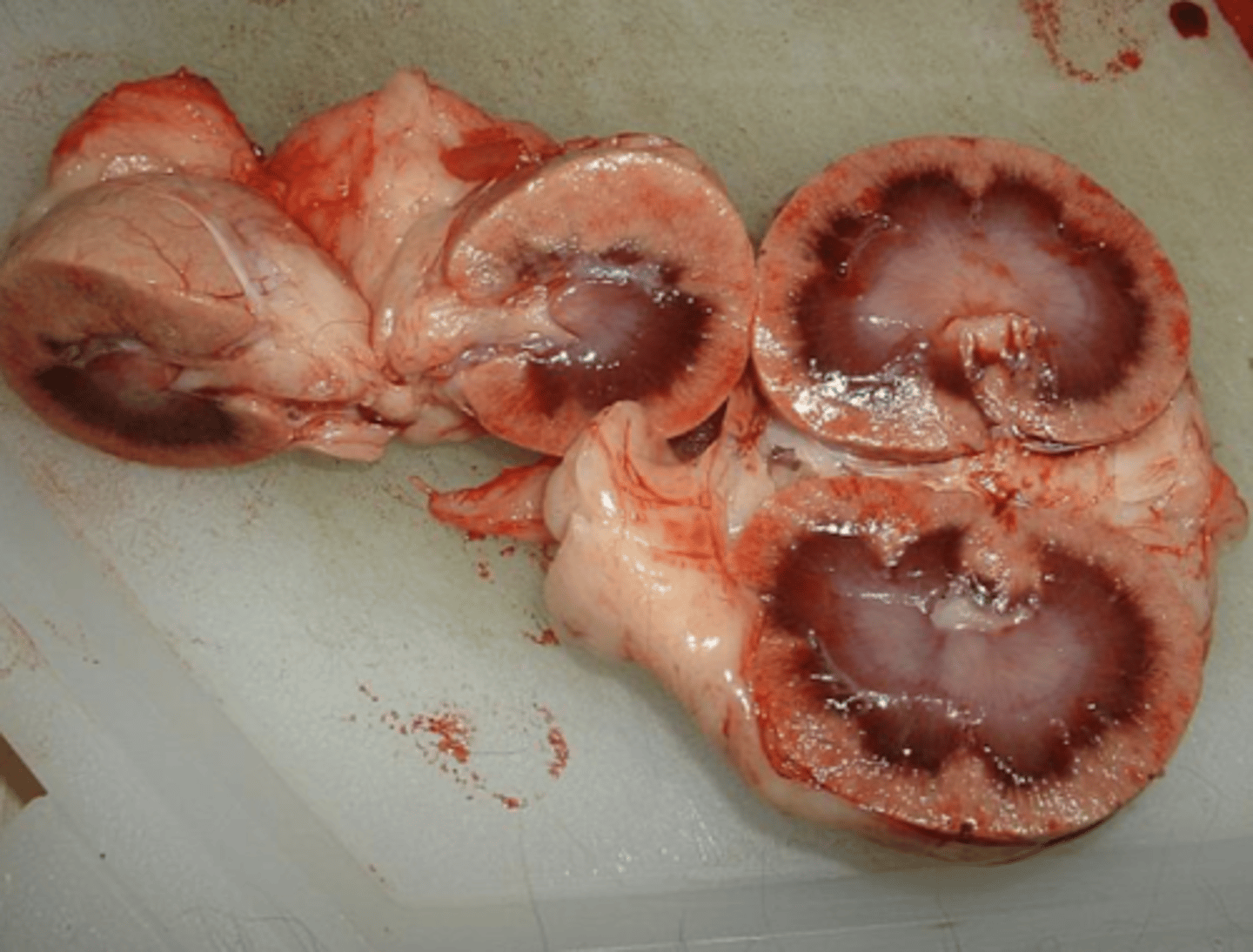
how do you maintain left and right orientation of the kidneys?
- right kidney: should be cut at a right angle
- left kidney: should be cut longitudinally
what does it mean/what is the term if urine is red? brown? cloudy?
- red: hemoglobinuria
- brown: myoglobinuria
- cloudy: cystitis
what is the calvarium?
the brain case
to remove the head in a necropsy, you will use your knife to sever all attachments at what joint?
atlanto-occipital joint
how should the brain be sectioned during a necropsy?
sagittally sectioned
often, the entire brain is placed in _____ to harden before cutting and taking of sample for histopath because of its soft consistency
formalin