FINAL HISTORY STUDY GUIDE
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
SPANISH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
acquire wealth
spread Catholicism
create a land empire
LOCATION
Columbus first lands in the Bahamas
Columbus continued to Hispaniola
Cortes conquers the Aztecs
METHOD
2 Vice-royalties: Peru and New Spain
Ruled by a Viceroy: King Appointed official
No elected officials
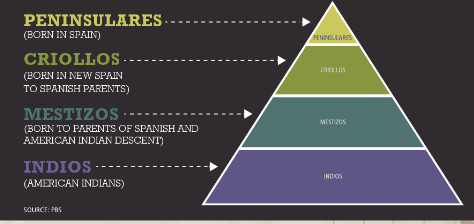
Racial Hierarchy:
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE PEOPLE
Columbus brutally captured and killed natives on Hispaniola after they attacked his men
conquistadors —> conquerors who brutally enslaved natives
enslaved native americans on encomiendas (large, Spanish owned plantations)
missionaries —> those sent to the Americans to forcibly convert natives to Catholicism
FRENCH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
trade intended with Asia —> ended up trading with the natives to acquire wealth
spread Catholicism
create a land empire
LOCATION
Caribbean
While searching for NW Passage, landed in Newfoundland (Canada) via the St. Lawrence River
Explorer Robert De Salle explored the Mississippi River
Landed in Louisiana → Founded New Orleans
METHODS
Jesuit Catholic missionaries converted some Huron Indians of the Great Lakes
Intendant: Military governor general appointed by the monarch
No representation in government
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE AMERICANS
Traded (beaver) furs for metal tools like arrowheads, axes, knives, etc.
Competition → Conflict between Native groups
Adopted some Native cultures and marriages between groups
Alliances with Algonquian language speaker nations in the Great Lakes region
Fewer immigrants → Claimed less territory → Lessened conflict
ENGLISH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
acquire wealth initially believed gold —> became cash crops
spread Christianity and religious freedom
create a land empire
LOCATION
Caribbean
attempt in Roanoke → failed
Jamestown
METHODS
Headright System: VA company granted 50 Acres of land to anyone that a settler paid to bring over
Indentured Servants: 7-10 years of service in exchange for transportation & eventual freedom
Representative Government seen in the House of Burgess and Mayflower Compact
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE PEOPLE
Some positive relationships - EX. New England & Thanksgiving
Disease killed many Indigenous
Conflict arose as more territory was claimed by settlers
DUTCH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
acquire wealth
spread Christianity
create a land empire
LOCATION
Caribbean
Hudson river and in modern day New York
Connecticut and New Jersey
METHODS
encouraged emigration with patroonship system
stockholders of dutch west India company would receive 50 emigrants to work on their land
reflected feudal system in medieval Europe
unsuccessful - most who had emigrated worked on their own land
second Anglo-dutch war (1664-1667)
the dutch ceded all their american colonies to great Britain
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE PEOPLE
purchased land from local Indians
leasing vs owning
refrained from learning culture and inter-tribal conflict
dutch setters disrupt traditional way of life and encroached on ancestral land
THE YEAR 1619
CREATION OF THE HOUSE OF BURGESS
first popularly elected legislature in the american colonies
todays virginia general assembly
had to obey the king and governor
SLAVES INTRODUCED TO THE VIRGINIA COLONY
mercantilism —> gaining wealth and power by developing countries
cash crops
english emigration began to decrease
NORTH
CLIMATE
cold winters with short growing seasons
small farms for own use
rocky soil
corns, beans, squash
ECONOMY
depended largely on the ocean
efficient in:
fishing
trapping
ship-building
logging
manufacturing
GOVERNMENT/RELIGION
predominately puritans
strict religious lives
the clergy devoted to the study of the scripture and the natural science
MIDDLE
CLIMATE
mild climate with warm summers
better for farming
deep rich soil
longer growing season
ECONOMY
fur trading
farming
fertile soil—> grain. corn, wheat exports (breadbasket of the colonies)
GOVERNMENT/RELIGION
religiously tolerant and diverse
welcomed people of all religious background
run by authoritarian governors
SOUTH
CLIMATE
fertile soil
warm climate, mild winters
good for agriculture
cash crops
tobacco, cotton, indigo, rice
ECONOMY
lots of plantations —> slavery
indentured servants
lots of cash crops
agriculture
GOVERNMENT/RELIGION
not religiously tolerant
Catholics
slaves
debtors/criminals
house of Burgess
Jamestown - 1st representative government
Sir Walter Raleigh
English explorer
tried to create permanent solutions 2x
tried to establish Roanoke
John Smith
leading role in establishing Jamestown
established the first permanent English settlement in north america
John Rolfe
credited with introducing marketable tobacco to Virginia
planted the first tobacco seeds
helped turn Jamestown into a profitable venture
Powhatan
powerful leader and principal contact for English colonists from 1607-1618
united dozens of tribes into a single powerful alliance
led his people through the early years of colonial invasion
Pocahontas
Powhatan’s daughter
encouraged interest in Virginia and the company
Cash crops/tobacco
crop that is grown for the purpose of selling
fueled the transatlantic slave trade
boosted the economy
the great awakening
a religious movement in the north American countries that emphasized individual salvation and high standards of personal mortality
challenged traditional beliefs and practices
new sense of American identity
Bacon’s rebellion
1676
protests against the governor
governor prevented war against Native Americans
high taxes benefiting the wealthy
governor is removed
taxes reduced
showed that population will not be ruled by wealth elites
individuals can find own salvation
challenged authority of the church
Indentured servitude vs. slavery
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
natural rights
all people are born with them
life
liberty
property
social contract
people give the power to the government but can take it away
it led to the revolutionaries to break free of Britain
consent of the governed
the government’s power is only legitimate when it it determined by those who are being governed
patriots
2/5 of colonists
wanted a new government based on merit, not inherited privilege
opposed taxes
emphasized Locke’s natural rights
fought the British
Loyalists
1/5 of colonists
believed that the British government was more legitimate and disliked violent protest
opposed taxes but wanted to follow the law
feared destruction/chaos
fought with the British
appealed to British natives and slaves
neutralists
the people who didn’t choose a side in the war
remained neutral
Native Americans
most native Americans thought colonists were more dangerous than the British
6 Iroquois tribes
4/6 fought with the British
2/6 fought with colonists
enslaved African Americans
England promises freedom to slaves that fought for the loyalist cause
most African Americans assigned to non-combat positions
were initially prohibited from the joining the continental army
later allowed due to labor shortages
advantage/disadvantages of both sides
|
|
disadvantages | disadvantages |
|
|
french and Indian war
caused by increasing hostilities between the french and the Indians at the american frontiers over territory
war is expensive → British gets the colonies to pay for the share
increases taxes, cracking down on smuggling, end of salutary neglect
anger and resentment towards the British
proclamation of 1763
prohibited colonists from moving west of the Appalachian mountains
increased anger and resentment to the British policy
Paine’s common sense
1776
pamphlet
colonies would be better off as an independent country
circulated throughout the colonies
widespread audience
George Washington
leader of the continental army
became the first president of the US
sugar act
lowered duty (tax) on foreign molasses (sugar) coming to the colonies
actually prosecuted smugglers
stamp act
march 1765
required colonists to pay a tax on almost all printed materials
first direct tax that wasn’t a duty (tax)
Boston massacre
march 1770
colonists insulted stationed British soldiers and threw rocks on them
soldier shot into the crowd
5 colonists killed
first and second continental congress
the first continental congress announces the boycott of all British goods
fall 1774
second continental congress agrees to send troops to support New England
may 1775
Boston tea party
1773
colonists are upset with the tea act → dumped tea into the Boston harbor out of protest
declaration of independence
written and published on July 4th, 1776
written primarily by Thomas Jefferson
explains to the world why the 13th colonies regarded themselves as independent
battle of Saratoga
Sept. 19, 1777 → Oct. 7, 1777
British general john Burgoyne → ambitious plan to capture New York
allow the British to cut off northern colonies from southern colonies
persuaded the french to recognize american independence and provide military support
battle of Yorktown
Sept. 28, 1781 → Oct. 19, 1781
Yorktown, VA
the american forces under the command of George Washington surrounded the British army
Cornwallis (leader of the British army) surrendered his army after a siege that lasted 20 days
last major battle
articles of capitulation signed
ordered liberty
a system of laws and order
separation of church and state
government/religious leaders are different
separation of powers
different branches of government with different functions
VA declaration of rights
George Mason
1776
documents that listed rights that were granted to all men
inspired the bill of rights
VA statute for religious freedom
Thomas Jefferson
1786
document that said the government should not force a certain religion on to its people
articles of confederation
constitutional convention in 1777
original constitution
established national government
loosely tied the states together
US constitution
James Madison
1788
document that outlines supreme law of the US
outlines role/function of government
bill of rights
James Madison
1791
first 10 amendments to the constitution
guarantee individual liberties to American citizens
George Washington
first president
creation of the national bank
whiskey rebellion
john adams
XYZ affair
alien and sedition acts
Kentucky and VA resolutions
James madison
federalists
wanted to have close relations
favored strong central government
seen as an elitist
Thomas Jefferson
democratic-republican
disliked taxes imported during adam’s presidency
denounced alien and sedition acts
accessible to the people
federalists vs anti-federalists
federalists | anti-federalists |
|---|---|
|
|
federalist paper
essays that urged the ratification of the new constitution
convinced votes to support the constitution
convinced votes that the articles of confederation needed revisions
democratic-republicans
strict interpretation of constitution
no national bank
loved the French revolution
the great compromise
proved for a bicameral federal legislature that used a dual system of representation
upper house → equal representation from each side
lower → proportional representation based on the states population
the 3/5 compromise
agreed to hold a national census every 10 years that would be used in determining the apportionment for the following 10 years
slaves would count as 3/5 of the population during the census
north and south would be both represented
Louisiana purchase
1803
Jefferson purchased the land from the France
expands US territory for $15 million
allowed for later addition of new states
seen as an overstep of the government power
led to Lewis and Clark expeditionIndian removal act
Indian removal act
may 1830
signed by Andrew Jackson
native Americans would be required to exchange their territory for land west of the Mississippi
the trail of tears
1838-1839
movement of Cherokee native Americans to reservations in present-day Oklahoma
forced to walk the distance between Florida and Oklahoma
Mexican-american war
conflict over the Texas-mexico border
US wins
border reaffirmed at the Rio grande
southwest boundaries expand
Monroe doctrine
part of the annual message to Congress that included a warning to European powers to not interfere in the affairs of the western hemisphere
manifest destiny
it is the cultural belief in the US that expansion was inevitable because of their god-given ability to spread liberty and democracy
federalists
merchants and businessmen opposed war
relied on trade with Britain
anti-federalists
anti-British feelings grew in the south and west
demanded war against the British
wanted more land = push the British from Canada
wanted to restore national honor after impressment
British
occupied Washington DC
burned the public buildings
didn’t want Americans to supply food to enemies
a partial blockade
Andrew Jackson
became a hero at the battle of new Orleans
led his troops through enemy territory to victory
Missouri compromise
1820
admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a non-slave state at the same time
outlawed slavery about 36*30* latitude line in the remainder of the Louisiana territory
known as the 36th parallel
Nat Turner’s rebellion
1831
Nat Turner → enslaved laborer and preacher
led to the largest slave revolt in South Hampton VA
the fugitive slave law was put into place
required slaves go be returned to their owners even if they were in a free state
Tariff of 1832
brought imported taxes back down to 35%
shrunk English demand for southern raw cotton and increased the final cost of finished goods to American buyers
nullification crisis
South Carolina nullified a federal tariff that favored northern manufacturing over southern agriculture
compromise of 1850
California enters union as a free state
strengthened fugitive slave laws
banned the slave trade in DC
proto-government for new mexico territory →but could be set up as free or slave once it was ready for statehood
proto-government for Utah territory → could be slave or free once it was ready for full statehood
Kansas Nebraska act
1854
repealed the Missouri compromise since both were north of the 36th parallel
established new territories of Kansas and Nebraska
said that these states would use popular sovereignty to determine if they would be slave or free
bleeding Kansas
1854 - 1859
series of violent conflicts in Kansas between pro-slavery and pro-abolition advocates
pro-slavery advocates rushed from Missouri to Kansas to pretend to be residents
wanted to use popular sovereignty to make Kansas a slave state
violence from both groups ensued for four years
advantages/disadvantages of both sides during the civil war
advantages of the Union | advantages of the confederates |
|---|---|
|
|
leaders of the Union | leaders of the confederates |
|
|
fort Sumter
April 12, 1861
marked the official beginning of the civil war
Charleston, South Carolina
forces from the confederates attacked the Union military Garrison
the fort surrendered 2 days later
Antietam
Sept. 17, 1862
one of the major turning points of the war
showed that the union could stand against the Confederate army
enabled Lincoln to issue the emancipation proclamation
emancipation proclamation
Jan. 1, 1863
issued by Lincoln
enslaved people in the southern states would be declared free
announced the acceptance of African Americans into the union and the navy
battle of Gettysburg
July 1-3, 1863
marked the turning point of the war
union victory
brought the war to an end
one of the bloodiest battles of the war
Gettysburg address
Nov. 19, 1863
Lincoln’s short but powerful speech
places civil war into the historical context of American fight for freedom
urges American to devote themselves to the task of preserving freedom for all Americans
Sherman’s March to the sea
Nov. 15, 1864 - Dec. 21, 1864
most destructive campaign against civilian population
purpose → frighten Georgia’s civilian population to abandon confederate cause
was a strike to the heart of the confederacy
Appomattox
Apr. 9, 1865
Robert E. lee surrendered his army to Ulysses S. Grant
brought an end to the civil war
wounded knee massacre
dec. 29, 1890
US soldiers killed hundreds of Lakota men, women, and children in an attempt to suppress a religious movement
reservations
an area of land that is reserved for a tribe or tribes under the us government
able to better subdue them
homestead act of 1862
government encourages farming with free 160 acres if you farm it for 5 years
Carlisle industrial school
mission was to remove indigenous children from their families and communities to assimilate them
stop the spread of native cultures
wanted to strip away native identity and culture
captains of industry
a business leader whose means of personal fortunes contribute positively to the country in someway
laissez-faire capitalism
an economic philosophy that advocates for minimal government interference in the economy
political machines
political parties organization that wins voter loyalty and grants power to a small group of leaders often for political gain
often created loyal bases of immigration by offering housing or jobs
tenement housing
housing buildings with multiple units
run down, low quality, typically many families in a room
result of urbanization and immigration
“new” vs. “old” immigration
|
|
Chinese exclusion act
congress passed it
suspended the immigration of all Chinese laborers for 10 years
required every Chinese person entering or leaving the country to carry paperwork
first law to broadly restrict immigration based on national origin
Jim crow laws
federal, state, and local laws that enforced racial segregation
buck v. bell
may 2, 1927
affirmed the constitutionality of Virgina’s law allowing state-enforced sterilization
social Darwinism
social economic and political philosophy emerged in late 19th and early 20th century
principles of natural selection and survival of the fittest should be applied to human societies
used to justify race and class distinctions
INDUSTRIES AND BUSINESS TYCOONS
John D. Rockefeller → standard oil
Andrew Carnegie → Carnegie steel company
J.P. Morgan → JP Morgan bank
Spanish-american war
April - Dec 1898
caused by the atrocities of the Spaniards against the Cuban population
USS Maine sent to protect the US interests but explodes
McKinley insisted that Spain give Cuba
treaty of Paris signed
represented decline of the Spanish empire and the emergence of the US as an International force
US-Philippine war
Feb. 4, 1899 - July 2. 1902
the US government didn’t want any other countries to take over the Philippine islands
the US gov. also wanted to build an overseas empire
Spanish colonialism collapsed
helped establish the US as a power in the Pacific
annexation of hawaii
hawaii
the monarchy was overthrown by the resident American businessmen
Grover Cleveland refused to take over islands until a majority of Hawaiians favored it
extended US territory into the Pacific
MAIN causes of WWI
M → militarism
A → alliances
I → imperialism
N → nationalism
Woodrow Wilson’s 14 points
no militarism/secret alliances
freedom of the seas
self determination
league of nations