Biology - B3 Movement into and out of cells
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
within cells interlinked. - osmosis - diffusion - active transport
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
diffusion
the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration (i.e. down a concentration gradient) until they are evenly distributed, as a result of their random movement
some substances move into and out of cells by diffusion through…
the cell membrane
Why is diffusion important for gases in living organisms?
Diffusion is essential for gas exchange in living organisms. For example, oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood in the lungs, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
How does surface area influence the rate of diffusion?
more particles can diffuse across the surface simultaneously
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
if temperature is increased, particles gain more kinetic energy and move faster
if temperature is decreased, particles move more slowly, and the rate of diffusion decreases.
Explain the impact of concentration gradient on diffusion
A steeper concentration gradient increases the rate of diffusion as particles move more rapidly from high to low concentration. The greater difference in concentration creates a stronger driving force for particles to move towards the area of lower concentration.
concentration gradient
the difference in concentration between two areas
How does distance influence the rate of diffusion?
Shorter distances increase the rate of diffusion because particles have less space to travel, resulting in quicker movement from one area to another.
Longer distances slow down the rate of diffusion because particles need more time to traverse the greater distance.
osmosis
the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane
water moves into and out of cells…
by osmosis through the cell membrane
water diffuses through…
partially permeable membranes by osmosis
turgid
plant cells that are swollen with water, causing them to be firm and maintain structural support.
flaccid
plant cells that have lost water, causing them to become limp and unable to maintain structural support.
turgor pressure
the pressure exerted by the cell membrane against the cell wall when a plant cell is full of water
What happens to plant tissues when immersed in a hypertonic solution?
When plant tissues are immersed in a hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration than the cell sap), water exits the cells by osmosis, causing them to become plasmolyzed and flaccid.
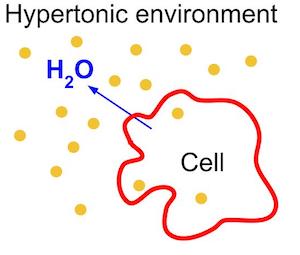
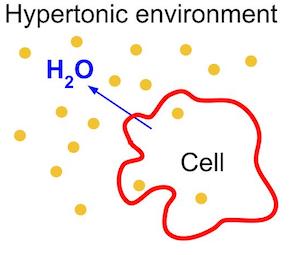
What happens to plant tissues when immersed in a hypotonic solution?
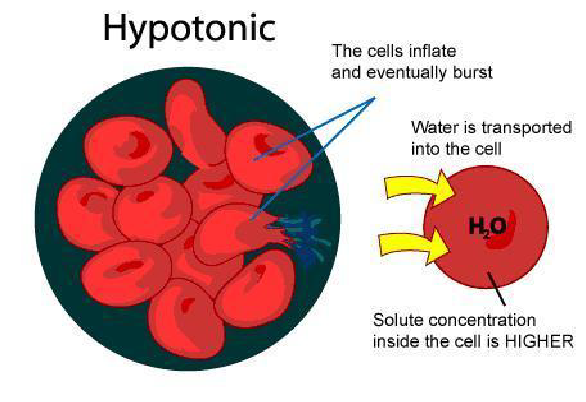
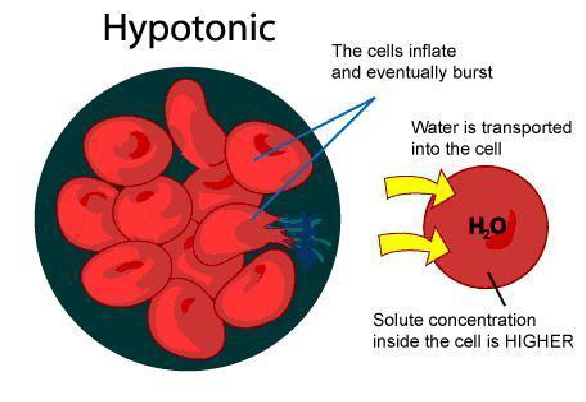
When plant tissues are immersed in a hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration than the cell sap), water enters the cells by osmosis, causing them to become turgid.
What is the effect of a hypertonic solution on plant cells?
In a hypertonic solution, plant cells lose water, the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall (plasmolysis), and the cells become flaccid.
What is the effect of a hypotonic solution on plant cells?
In a hypotonic solution, plant cells gain water, swell, and become turgid due to the influx of water, which increases turgor pressure against the cell wall.
plasmolysis
the process where plant cells lose water in a hypertonic solution, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell wall.
What happens to plant tissues when immersed in an isotonic solution?
When plant tissues are immersed in an isotonic solution (same solute concentration as the cell sap), there is no net movement of water, and the cells remain in their normal state.
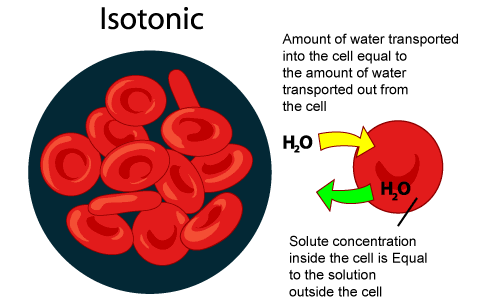
Explain the concept of water potential in relation to plant cells
Water potential is a measure of the potential energy of water in a system, influencing the direction of water movement. Water moves from areas of higher water potential to areas of lower water potential.
Why is osmosis important for the uptake of water by plants?
Osmosis is crucial for the uptake of water by plant roots from the soil, allowing essential water and nutrients to enter the plant cells.
active transport
the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration (i.e. against a concentration gradient), using energy from respiration
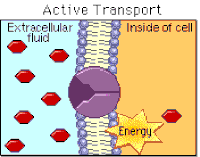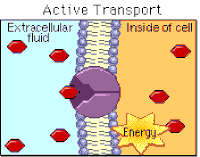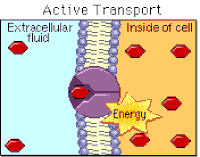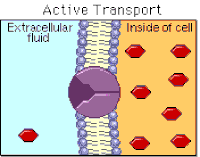
importance of active transport
a process for movement of molecules or ions across membranes, including ion uptake by root hairs