Forensic Biology: Lecture 7 – Biological Fluids Identification
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Typical ejaculation consists of:
2-5 ml of semen, 160 million sperm
3 pg DNA/sperm =
= 480,000 ng DNA/ejaculate
How many ng DNA needed for STR typing?
Only 1
Seminal fluid consists of:
Enzymes and other proteins; acid phosphatase (AP), prostate specific antigen (PSA), and semenogelin
Acrosome
A vesicle at the tip of a sperm cell that helps the sperm penetrate the egg
What part of the sperm contains the DNA?
head (nucleus)
Presumptive tests for semen:
- visual search
- UV light
- acid phosphatase test
Brentamine Fast Blue Test:
color changing reagent; fresh stains will produce a strong color change reaction; old stains and other materials (urine, vaginal secretions, perspiration) may produce weak reactions
AP assays (spot tests, overlays):
Acid phosphatase liberates naphthol from alpha-naphthol and the naphthol then reacts with brentamine to form a purple-colored dye
MUP test:
AP catalyzes the removal of the phosphate residue on the substrate 4-methylumbelliferone phosphate, which generates fluorescence under UV light.
PSA test:
Prostate-specific antigen; Hydrolyzes semenogelins; Can confirm seminal fluid in SAP+ samples that do not contain sperm cells; Detected with immuno-chromatographic test strip assay
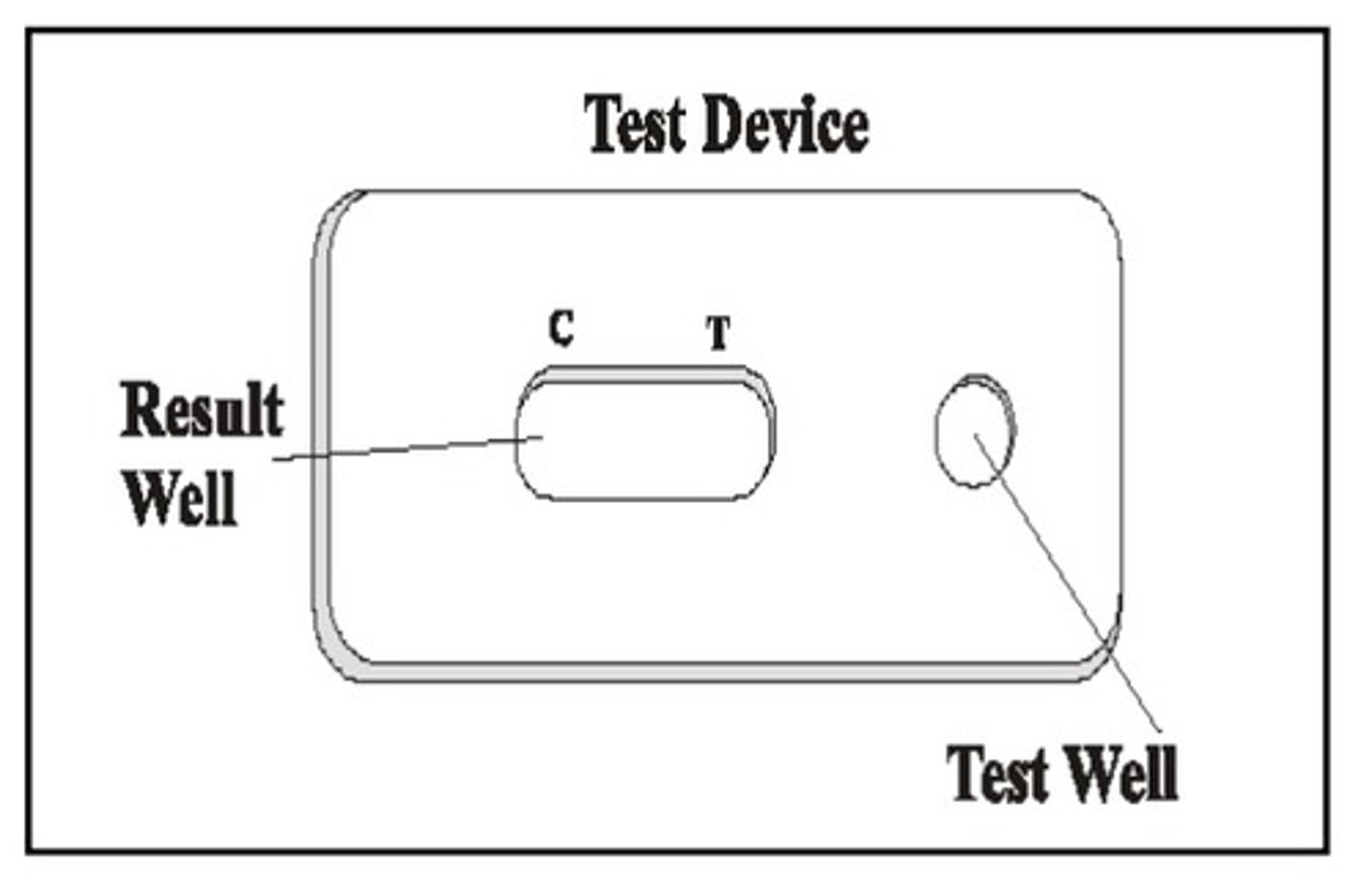
Half-life of PSA in a dried stain:
3 years
Confirmatory tests for semen:
- Rapid Stain Identification (RSID-Semen)
- Christmas Tree Stain (of sperm cells)
Semenogelins
proteins that spontaneously coagulate after ejaculation to form gel matrix (keeps sperm in vagina after withdrawal); higher concentration than PSA in seminal fluid; greater specificity for semen than PSA
Rapid Stain Identification
immuno-chromatographic test strip assay
"Christmas Tree" stain
Nuclear Fast Red stains nuclei red, Picroindigocarmine stains tails green
Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
The starch-iodine test:
Gel containing starch is stained blue with iodine. Sample is added to well in gel. If amylase (saliva) is present, the blue color begins to vanish.
Phadebas Reagent (PAT):
Starch is linked to a colored dye, and tresence of Amylase releases the dye.
PAT Press Test
Phadebas paper placed on area to be tested. Paper is sprayed with water and pressed against area. Paper is left on area and watched for blue color change.
PAT Tube Test
Piece containing stain is placed in tube. Water and Phadebas tablet added. Heated. Centrifuged to pellet tablet remnants and piece of cloth. Amount of color in top liquid is measured by a spectrophotometer.
Presumptive tests for saliva:
- Starch-iodine test
- Phadebas reagent
Presumptive tests for urine:
Look for urea or creatinine
What is the only way to get DNA from urine?
(some) epithelial cells from urinary tract lining
Control/substrate samples:
swabs or cuttings from an unstained portion of the surface material near the recovered stain; confirms that the results of the test performed were from the stain and not from the surface material
Double collection
Collect enough for both the original testing and for retesting by the defense
Phenolphthalein (Kastle-Meyer test)
Presumptive test for blood; indicator which is clear in acidic solution and pink in basic solution.
Hemastix
a strip coated with tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) will produce a green or blue-green color with the presence of hemoglobin.
Hematrace
- presumptive test for blood
- stain extract is applied to the bottom of the test strip
- resembles pregnancy test
Tests for latent blood stains:
- Luminol
- Leucocrystal Violet (LCV)
- Amido Black
Luminol
Catalytic test for blood; chemiluminescent; bluish glow is given when in contact with hemoglobin in blood
False positives for luminol:
Bleach and metals
Fluorescein (Hemascein)
alternative to luminol; has higher DNA recovery; does not require complete darkness; visualizes for as long as 10 minutes.