PHM 338 Quiz 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:12 AM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
partial agonist
* increasing concentrations of agonist will produce an increase in biologic effect up to an intrinsic activity < 1
\
* all receptors bound → activity level < 100%
\
* can be used therapeutically for withdrawal symptoms
\
* ex. methadone
\
* all receptors bound → activity level < 100%
\
* can be used therapeutically for withdrawal symptoms
\
* ex. methadone
2
New cards
antagonism
binding of a drug to a receptor that does NOT activate the receptor and prevents a response to an agonist
3
New cards
noncompetitive antagonism
* block can NOT be overcome by increasing dose of agonist
* aka “irreversible antagonist”
* no activity
* ex. naloxone
* aka “irreversible antagonist”
* no activity
* ex. naloxone
4
New cards
competitive antagonism
* block can be overcome by increasing the dose of the agonist
* agonist can be reversed (usually by flooding with agonists)
* agonist can be reversed (usually by flooding with agonists)
5
New cards
pharmacologic antagonism
* competitive & noncompetitive antagonism
* based on one effect on the same receptor
\
ex. drug A ↑ HR by binding to receptors in heart, but drug B ↓ HR by blocking drug A from reaching receptors
* based on one effect on the same receptor
\
ex. drug A ↑ HR by binding to receptors in heart, but drug B ↓ HR by blocking drug A from reaching receptors
6
New cards
effect antagonism
* 2 receptors are working, but the EFFECTS/ACTIONS oppose each other
* based on 2 effects on different receptors
\
ex. drug A ↑ BP in brain, drug B ↓ BP in arm
* based on 2 effects on different receptors
\
ex. drug A ↑ BP in brain, drug B ↓ BP in arm
7
New cards
ligand-gated ion channels
ligand binds to active site → conformational change → drugs can manipulate how long channels stay open
\
ex. acetylcholine agonist keeps channel open longer
\
ex. acetylcholine agonist keeps channel open longer
8
New cards
enzymes
proteins that speed up chemical reactions
\
can cause conformational change by binding 2 molecules together
\
ex. renin → ANG I → ANG II can be done faster with use of these
\
can cause conformational change by binding 2 molecules together
\
ex. renin → ANG I → ANG II can be done faster with use of these
9
New cards
oral drugs
most common dosage form
10
New cards
enteral administration
most common route of administration
11
New cards
mouth
* enteral administration
* thin lining, rich blood supply
* sublingual and buccal routes
* thin lining, rich blood supply
* sublingual and buccal routes
12
New cards
stomach
* enteral administration
* medium surface area, rich blood supply, acidic pH
* drugs don’t stay here long
* medium surface area, rich blood supply, acidic pH
* drugs don’t stay here long
13
New cards
small intenstine
* enteral administration
* huge surface area, rich blood supply, basic pH
* huge surface area, rich blood supply, basic pH
14
New cards
rectal
* enteral administration
* small surface area, rich blood supply, basic pH
* inconvenient but advantageous for local activity, if pt is unable to swallow
* small surface area, rich blood supply, basic pH
* inconvenient but advantageous for local activity, if pt is unable to swallow
15
New cards
parenteral administration
advantages:
* can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed
* provide an immediate onset of action
* provide a longer lasting effect
* can concentrate drug at a specific location
* provide a more predictable response
* provide titratable dosage
\
disadvantages:
* pain
* irreversible
* extravasation (toxic chemical leak into tissue)/phlebitis (vein inflammation)
* not useful for self-admin
* contamination/infection
* can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed
* provide an immediate onset of action
* provide a longer lasting effect
* can concentrate drug at a specific location
* provide a more predictable response
* provide titratable dosage
\
disadvantages:
* pain
* irreversible
* extravasation (toxic chemical leak into tissue)/phlebitis (vein inflammation)
* not useful for self-admin
* contamination/infection
16
New cards
intravenous, intra-arterial, intramuscular, epidural, intrathecal, subcutaneous, intra-articular
types of parenteral administration
17
New cards
skin
topical administration
* ointments, creams, patches
* local and systemic
* ointments, creams, patches
* local and systemic
18
New cards
eyes
topical administration
* drops, ointments
* local distribution
* drops, ointments
* local distribution
19
New cards
ears
topical administration
* local distribution
* local distribution
20
New cards
intranasal
topical administration
* spray and drops
* local and systemic
* spray and drops
* local and systemic
21
New cards
inhalation
topical administration
* local and systemic
* local: asthma, COPD
* systemic: anesthesia
* local and systemic
* local: asthma, COPD
* systemic: anesthesia
22
New cards
vaginal
topical administration
* local and systemic
* mainly local, can be systemic for hormones
* local and systemic
* mainly local, can be systemic for hormones
23
New cards
disintegration
1st pharmaceutical phase of tablets
* tablet hits fluid → breaks into little chunks to increase surface area
* tablet hits fluid → breaks into little chunks to increase surface area
24
New cards
dissolution
2nd pharmaceutical phase of tablets
* broken into molecules, can be absorbed
* broken into molecules, can be absorbed
25
New cards
dissolved liquid
oral dosage form
* ex. elixir, syrup
* not convenient compared to tablets
* ex. elixir, syrup
* not convenient compared to tablets
26
New cards
suspensions
oral dosage form
* chunks of drug floating in liquid (must shake)
* thick, gloopy
* chunks of drug floating in liquid (must shake)
* thick, gloopy
27
New cards
powders
oral dosage form
* ground up drug
* not common, inconvenient
* ground up drug
* not common, inconvenient
28
New cards
capsules
oral dosage form
* gelatin shell containing powder
* gelatin shell containing powder
29
New cards
tablets
oral dosage form
* compressed powder (made w/ pressure)
* compressed powder (made w/ pressure)
30
New cards
coated tablets
oral dosage form
* coating for extended release, easier swallowing, taste
* coating for extended release, easier swallowing, taste
31
New cards
enteric-coating
oral dosage form
* specific coating made to survive stomach acid, only dissolves in basic pH
* specific coating made to survive stomach acid, only dissolves in basic pH
32
New cards
sustained-release
oral dosage form
* a short-term drug turned into a longer-lasting drug
* a short-term drug turned into a longer-lasting drug
33
New cards
dissolved liquid
fastest absorbed oral dosage form
34
New cards
sustained-release
slowest absorbed oral dosage form
35
New cards
rate
_____ of absorption can determine
* onset of action
* duration of action
* intensity of response
* onset of action
* duration of action
* intensity of response
36
New cards
variables affecting absorption
* nature of absorbing surface
* surface area
* blood flow to site of administration
* pH at the site of absorption
* surface area
* blood flow to site of administration
* pH at the site of absorption
37
New cards
primary method of excretion
kidneys
38
New cards
drug elimination
2 types:
1. biotransformation
2. excretion
1. biotransformation
2. excretion
39
New cards
biotransformation
active drugs transformed into inactive for elimination
40
New cards
hepatic metabolism, tissue enzymes
types of biotransformation
41
New cards
secondary method of excretion
GI tract
42
New cards
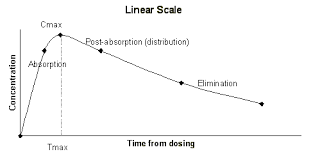
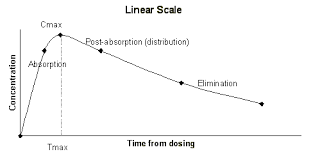
absorption phase
absorption rate more than elimination rate
43
New cards
elimination phase
no significant absorption occurs
44
New cards
toxic level
concentration of drug that will predictably cause problems
45
New cards
minimum effective concentration
how much drug in the body before there is an effective concentration
46
New cards
therapeutic range
safe and effective concentration of drugs in the body
47
New cards
onset of action
time for drug to become effective
48
New cards
body weight
variable affecting dose/response
* larger doses often given to patients with greater weight or BMI
* dependent on where drug is distributed to
* larger doses often given to patients with greater weight or BMI
* dependent on where drug is distributed to
49
New cards
age
variable affecting dose/response
* altered capacity to metabolize and/or excrete drugs (usually decreased)
* most common in very young and very old
* altered capacity to metabolize and/or excrete drugs (usually decreased)
* most common in very young and very old
50
New cards
gender
variable affecting dose/response
* differences in body composition and hormonal activity
* differences in body composition and hormonal activity
51
New cards
genetics
variable affecting dose/response
* enzymatic differences can lead to alterations in magnitude or effect
* decrease or increase
* enzymatic differences can lead to alterations in magnitude or effect
* decrease or increase
52
New cards
tolerance
variable affecting dose/response
* larger doses must be given to maintain the same effect
* commonly seen with opioids
* larger doses must be given to maintain the same effect
* commonly seen with opioids
53
New cards
psychological factors/beliefs
variable affecting dose/response
* placebo effect
* placebo effect
54
New cards
comorbid medical conditions
variable affecting dose/response
* can affect all phases of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic response
* can affect all phases of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic response
55
New cards
drug-drug interaction
pharmacological or clinical response to the administration of a drug combination difference from that anticipated from the known effects of the two agents when given alone
56
New cards
synergism
one drug enhances the effect of other drugs
57
New cards
pharmacokinetic
* drug interaction in which one drug alters the rate or extent of absorption, distribution, metabolism or excretion of another drug
* one drug causes a change in the plasma concentrations of another drug
* one drug causes a change in the plasma concentrations of another drug
58
New cards
pharmacodynamic
* drug interaction in which one drug induces a change in a pt’s response to a drug without altering the object drug’s kinetics
* pharmacological interactions
* pharmacological interactions
59
New cards
pharmaceutical
* drug interaction that includes physical and chemical incompatibilities
* IV admixtures
* IV admixtures
60
New cards
pts at greatest risk of interactions
pts on multiple medications, multiple prescribers/pharmacies, elderly, obese pts, critically ill pts
61
New cards
object drug
drug for which an effect is altered (increased or decreased)
62
New cards
precipitant drug
drug that provokes an interaction onto an object drug
63
New cards
narrow therapeutic range, steep dose response curve, metabolized by hepatic enzymes, typically used chronically
characteristics of important object drugs
64
New cards
small intestine
primary site of drug absorption
65
New cards
complexation
drugs that form chemical complexes with other agents may lower the rate and extent of drug absorption
* ex. divalent and trivalent metal ions; Mg, Ca, Zn, Fe, Al can bind to prescription drugs and prevent absorption
* ex. divalent and trivalent metal ions; Mg, Ca, Zn, Fe, Al can bind to prescription drugs and prevent absorption
66
New cards
complexation, changes in pH, changes in GI motility
mechanisms of altered absorption
67
New cards
H2 receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitors, antacids
drugs that can change gastric pH (acidic to basic)
68
New cards
ketoconazole, itraconazole, iron supplements
drugs that need an acid pH for dissolution