Bacteriology Lab Exam
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 2 Semester 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Explain the gram staining protocol:
o Crystal violet à iodine à alcohol à safranin
Purple > glue > strip > pink
- What is the Kirby-Bauer Method (Disk Diffusion)?
o A lab test to see which antibiotics can actually stop a specific bacterium from growing.
Why is it important to rub the bacterium all over the entire plate?
o If the plate isn’t fully covered by bacteria, the test wont work because antibiotics need uniform competition
What are the results of the Kirby-Bauer Method?
o After incubation
§ Clear circles around antibiotic disks = bacteria couldn’t grow (sensitive to that antibiotic – would pick that antibiotic)
According to CLSI, 0.75 McFarland standard is used for the disk diffusion antimicrobial sensitivity test. T/F
False. 0.5 McFarland standard (equivalent to ~1.5 × 10⁸ bacteria per mL)
Plate streaking method is the best method for disk diffusion antimicrobial sensitivity testing. T/F
False - create a bacterial lawn by swabbing the entire surface of the Mueller-Hinton agar in 3 directs, using a standardized 0.5 McFarland
What is the difference between Blood Agar (BA) and MacConkey Agar (MAC)?
Blood Agar: shows hemolysis
§ Beta = double hemolysis
§ Alpha = single zone hemolysis
§ Gamma = none
MacConkey Agar: selective and differential
§ Selective: only GRAM-NEGATIVE bacteria grow (positive bacteria inhibited)
§ Differential: tells you if they ferment lactose
· Pink = lactose fermenter
· Colourless = non-lactose fermenter
Do you plate MAC or BA plate first?
BA plate should be inoculated first, then MAC plate. Because BA is non-selective and supports all bacteria. MAC contains bile salts and crystal violet that can inhibit or kill gram positive bacteria
Whats the difference from Straphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius?
S. aureus = small golden/yellow BA plate; S. pseudointermedius = small grey BA blate
Examine the photomicrograph. What bacteria is it and what is it demonstrating?
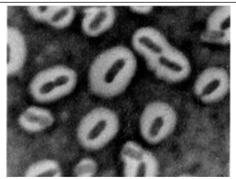
Klebsiella pneumoniae; rod shape bacteria with large white capsule indicated by the india ink stain
Explain what is happening during a positive CAMP reaction:
In positive reactions, a CAMP factor produced by a test organism will have a synergistic effect with the beta hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus and forms an enhanced beta hemolysis

Tube coagulase test for oranism A. A negative control for comparison. What is a positive test result?
The presence of a fibrin clot
What is a reverse/inhibitory CAMP reaction? What does it mean?
Instead of the bacteria helping staphylococcus aureus break down blood, the bacteria produce something that blocks/inhibits its hemolysis.
What is a bacteria that has reverse/inhibitory CAMP reaction?
corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
What is a bacteria that has a positive CAMP reaction but with a special characteristic?
Rhodococcus equi - Shovel shaped
What is the purpose of a citrate test?
- Can help to identify bacteria by seeing what they can or can’t use for energy.
o If it can use citrate: it grows on media, tube turns blue à citrate positive
o If it cannot use citrate: it doesn’t grow, tube stays green à citrate negative
what bacteria was the only citrate + bacteria?
Klebsiella pneumoniae
What is the purpose of a urease test?
- Checks whether a bacterium can break down urea into ammonia using an enzyme called urease.
o If it can break down urea (urease +): it releases ammonia, tube becomes hot pin à positive
o If it cannot break down urea (urease -): no ammonia, tube stays yellow or light orange à negative
What 3 bacteria are urease +?
Corynebacterium renale, Klebsiella pneumoniae, proteus mirabilis
What is the purpose of using TSI agar?
Helps figure out what sugar’s enteric bacteria ferment, whether it makes gas and whether it makes sulfur. NOTE: it is grown slanted so you can see aerobic vs anaerobic reactions in one tube
What is the TSI for E. coli? (Slant, Butt, Gas, H2S)
· Slant = yellow
· Butt = yellow
o Means that E. coli ferments glucose AND lactose and/or sucrose
§ Lots of fermentation so it stays yellow
· Gas +
o E. coli makes gas during fermentation à you’d see bubbles, cracks or lifting of agar
· H2S –
No hydrogen sulfide produced (no black line in tube)
What is the TSI for Salmonella? (Slant, Butt, Gas, H2S)
· Slant = red
· Butt = yellow
o Means that salmonella ferments ONLY glucose, not Lactose/sucrose
o Slant turns black because it uses proteins in the presence of O2
o Butt stays yellow because glucose fermentation continues in anaerobic conditions
· G +
o Salmonella also makes gas (cracks or bubbles may appear)
· H2S +
o Produces hydrogen sulfide (black precipitate appears in the butt)
True or false: when collecting fecal field samples, you directly plate it
False - You don’t plate salmonella directly from feces because other bacteria would take over and hide it
· Instead, you use selective enrichment (Rappaport and MSRV) to help salmonella grow and move so you can find it in a sample of full normal gut bacteria
o Put feces in Rappaport broth à kills off competitors, lets salmonella multiply
o Streak the enriched sample onto MSRV agar à salmonella swims and forms a spreading halo
o Anything that swims – suspect salmonella
What bacteria is partially acid-fast? and why is something acid fast?
Nocardia sp
Really thick, waxy cell wall made of mycolic acid - they trap red dye and prevent acid-alcohol from washing the dye out
What is the purpose of Edwards media?
- Selective for streptococci and enterococci, meaning it inhibits other bacteria, so streptococcus and enterococcus grow better. Also, a differential for esculin hydrolysis
o Esculin positive organisms (enterococci, some strep) produce grey-black colonies
o Esculin negative streps stay pale/white
oEdwards agar is commonly used to identify mastitis from:
§ Streptococcus agalactiae
· Clinically: decreased milk production, udders only, contagious, high SCC
§ Streptococcus dysgalactiae
· Edwards agar: growth + esculin – (no colour change)
· Clinically: mild to moderate mastitis with flakes following teat injuries
§ Streptococcus uberis
· Edwards agar: growth + esculin + (black/brown colonies)
· Clinically: cow kept in dirty bedding develops moderate to severe mastitis
§ Enterococcus spp.
· Clinically: milk mastitis, antimicrobial resistant
What is the purpose of the California Mastitis Test (CMT)?
- To quickly check how many somatic cells (inflammatory cells) are in the milk to see if a cow has mastitis.
o Mix milk and CMT reagent
§ Mixture becomes thick: lots of somatic cells (happens during mastitis)
§ Mixture stays watery: few somatic cells (normal milk)
o Why use it? Fast, cheap, detects subclinical mastitis
How could you tell the difference between Actinobacillus Pleuopneumonia (APP) and glaesserella parasuis?
Clinically present different:
§ APP: pigs dying fast from lung disease (severe pleuropneumonia); often older
§ GPS: young pigs with fever, swollen joints, meningitis; polyserositis (Glasser’s) arthritis, meningitis
What is the purpose of the oxidase test?
- To determine if a bacterium has cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme used in aerobic respiration.
o If bacteria have this enzyme, reagent turns purple (+)
o If bacteria do not have this enzyme, reagent stays clear (-)
What is the purpose of the indole test?
T o check if a bacterium can break down the animo acid tryotophan into indole
o If it can à indole is made à reagent turns bright pink à indole positive
o If it can’t à no colour change à indole negative
What bacteria are indole positive?
E. coli
Pasteurella multocida
Describe Quantitative Plating Technique (purpose, how you do it, how to determine infection):
Purpose: to figure out how many bacteria per mL are in a urine sample and decide if it’s a true UTI
> 1000 bacteria/ml = infection
Ture or false: C. jejuni’s main transmission route is venereal?
Flase - feco-oral
True or false: All mycoplasma species have a cell wall.
False - all mycoplasma species lack a cell wall, so they are naturally resistant to any drug that works by attacking the cell wall (i.e. B-lactams)
Why does mycobacterium avian subsp paratuberculosis appear clumped acid-fast?
Mycobacteria are intracellular bacteria with waxy/lipid cell wall which give the bacteria hydrophobic properties as a result they tend to clump together
What is PCR?
o PCR is a technique used for the rapid amplification of billions of copies of a specific region of DNA
What are the stages of PCR?
o Denaturation: heat separates the double-stranded DNA into single strands
o Annealing: primers stick (bind) to the target DNA sequence
o Extension: DNA polymerase copies the DNA starting from the primers
- What universal gene is used for bacterial identification?
o The 16S rRNA gene is conserved in bacteria and is widely used in identification of bacteria and taxonomic studies