Anthropology Exam 2 - Oliver Paine
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Omomyidae and Adapiade (similarities)
2 major taxonomic families of primates that appear in the Eocene era
vary diverse
both live in trees
Phylogeny - Omomyidae
give rise to haplorhini
evolve into modern haplorhines (our ancestors)
Ex:
tarsiers, new world monkeys (NWM), old world monkeys (OWM), humans, apessmaller
mostly Nocturnal
Phylogeny - Adapidae
give rise to strepsirrhini
evolve into lemurs, lorises, and galagos
larger
mostly Diurnal
Binomial nomenclature (human toxonomy, Taxonomic Families)
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata (have spinal cord)
Class: Mammalia
Order: Primates
Family: Hominidae
Genus: Homo
Species: Homo Sapiens
when writing a species name out
Italicize both parts of the name
Capitalize the first letter of the genus name (the first word).
Keep the specific epithet (the second word) in lowercase.
Taxonomic Families rule
always end in -iade
ex:
Family: Hominidae
Bonobo Behavior
close evolutionary cousins to chimpanzees (act very different)
Matriarchal society (less violent, more calm)
use sex / sexual contact as a form of social interaction
everything you think is unique to human sex, we see in bonobos
Ex:
male-male sex
female-female sex
C/P3 honing complex
C - stands for K9 (upper)
P3 - stands for lower per-molar
the upper K9 is perpetually sharpening itself against the lower pre-molar
designed to keep the K9’s razor sharp (honing the tooth)
particularly seen in the African and Asian monkeys (cercopithecoids)
Most pronounced in Baboons
Capuchin intelligence
very smart
use stone tools to crack nuts
throw rocks at predators
have a sense of fairness
(video of cucumber and a grape, 1 sees the other get a grape and it throws the cucumber back)
They are Platyrrhines from America
Rival what we see in chimpanzees
Carbohydrates
Structural - Fibers; cell walls of plants that we eat
Non-structural - what we usually think of
- sugars (sweet treats) that give instant hits of energy
- starches
Caribbean vervets
The monkeys that get drunk
Not native to caribbean
came from slave trade with West Africa
They set up colonies and in one area they learned they could steal alcoholic drinks from people on vacations at resorts
Some drink till passing out, others don’t drink at all
they follow the same pattern of alcohol abuse we see in humans
children of alcohol abusers tend to be alcohol abusers as well
Dunbar's Number
Hypothesis where they looked at the neocortex (front of brain that does executive functioning)
found a correlation between the size of the brain and the size of the group
correlation graph showing this
Main idea:
The larger the group is (as a monkey) the more intelligent you have to be because you have more social relationships you have to manage
What’s the maximum group size that this particular species of monkey can be, based on the size of their neocortex?
Encephalization quotient (EQ)
relationship or measure of brain size compared to body size
If it has an EQ of 1 that means that it is pretty much what you would expect for a mammal of that size
Lions have an EQ of 1
All primates have an EQ above 1
(larger brains than expected for their body size)
Humans have an EQ of 6 or 7
Evolutionary relationships of hominoids
apes, evolved from a common primate ancestor and diverged into several lineages over millions of years, including gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, and the human lineage
Fallback foods
less preferred food that they must eat because the regular (prefered) food is unobtainable or gone
have important adaptations that allow them to get through the lean periods when preferred food aren’t around
Gigantopithecus
the largest primate (that we know of) that has ever lived
Extinct relative of Orangutans
We only know of them through dental stuff like teeth and jaws
Their teeth are HUGE
Gorillas
Coco the gorilla learned sign language
Very intelligent creatures
Video Example:
- A person helped raised a Gorilla and reintroduced him to the wild
- the same gorilla came back 5 years later and recognized him and treated him like an old friend
(good memory)
The massive strength that particularly males have are only used when males are competing with one another for control of the group
they are usually playful and calm animals - mello compared to Chimpanzees
largest living primate
Harlow Experiments
Took baby Macaques and removed them from their mothers and raised them in isolation with varying degrees of comfort
in a metal box with nothing but food and water
Ones with no contact with mother or anything else literally went insane and got physically and mentally ill
Trying to show that even when physically taken care of, they would detoriatre
it was terrible and torchered these monkeys
If a social primate, contact with other individuals is crucial to your health
(humans included)
Human genitals
Humans don’t have:
Baculum (bone that’s in penis)
Belbelum (bone that’s in clitoris)
Most other primates have these
testicular size ratio is also very different
humans have very interesting and unique morphology
Human settlement of Madagascar
Humans don’t arrive or at least don’t make permanent settlements on Madagascar until about 2000 years ago
When they get their:
tons of lemurs; some are gorilla sized
Within about 1500 years all of the large lemurs go extinct as well as things like giant birds
very common when humans enter a new landscape → large animals go extinct
both because humans are competing with them for resources and also hunting them as well
Human taste perception
5 elements of taste that we can actually taste
when combined together thats what makes us experience the flavor of food
Sweet
Sour
Bitter
Salty
Umami
(Japanese word meaning savory or protein flavored)
Kanzi
Rockstar of language Bonobos
understood lots of spoken english
video of handler wearing a welding mask and told Kanzi a series of really weird commands and Kanzi understood it
Ex: Put the TV in the refrigerator
Understood a lexigram board that spoke for him
a touch screen with images, Kanzi would press one and a computer would speak when he touched the icon
taught other bonobos sign language (very unexpected)
learned to start a fire and roast marshmallows
Language extinction
We live in a time where languages are going extinct and language diversity is plummeting
we are losing world perspectives
At one point the United States had incredible language diversity
At one point in California, there were more languages spoken when Europeans came when there were in Europe
Mimetic musculature
Facial muscles
mammals have them, others don’t
Birds and fish can’t make facial expressions
Humans and primates use faces to communicate emotions
Humans take it to another level
communicate every emotion through facial expressions
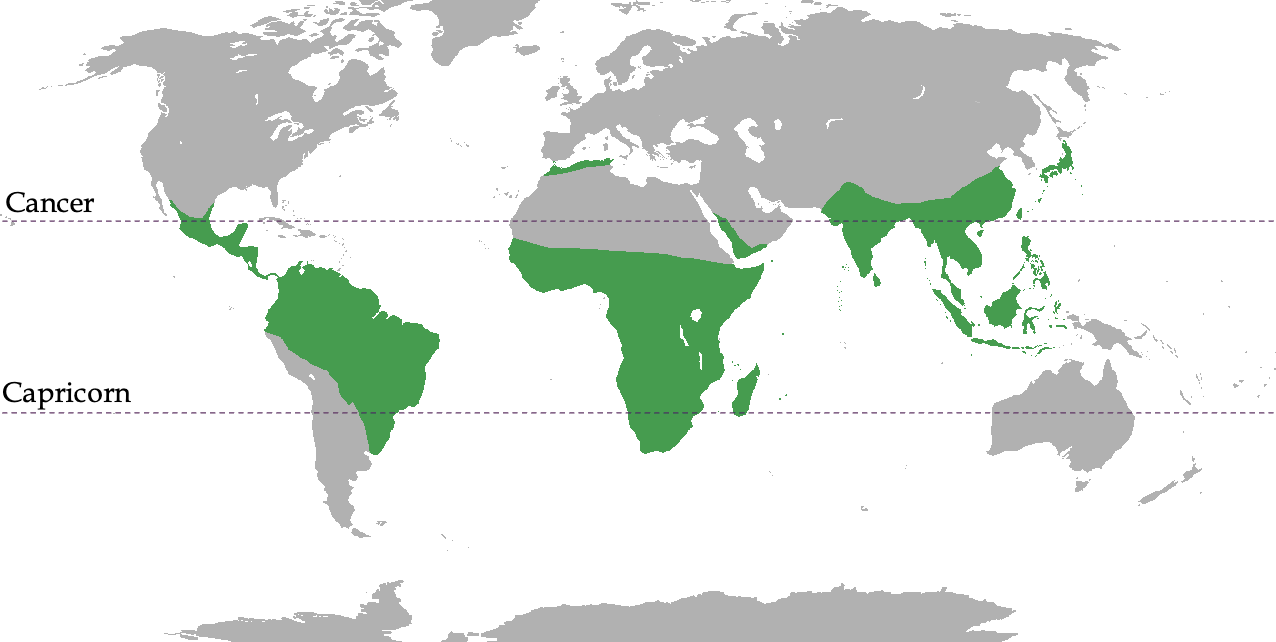
Non-human primate distribution
The green areas shown in the image
tropical / subtropical areas(usually)
couple exceptions
ex: Japanese Macaques
Madagascar
Most Strepsirrhines live (lemur diversity)
Americas Monkeys
Platyrrhines
Australia
None native
no primates until humans
catarrhines
Apes and monkeys of Africa and Asia
Non-human primate tool use
Jane Goodall made this a known thing
It was so revolutionary that people didn’t believe that Chimpanzees couldn’t use tools
Chimpanzees and Orangutans use sticks probe for insects
Chimpanzees and capuchins also use pieces of wood or rock to crack open nuts
the use of tools used to be a definition to define humans (made us different from other animals)
Now we know that many primates use tools
Orangutans
strange with social structure (all other apes live in groups)
Live in solitary
females live with children until they are old enough
Only come together when mating
Males have 2 forms of maturity (Bimaturism)
Unflanged
Flanged (some never reach)
Hypothesis: this is a mating strategy
Males unflanged aren’t perceived as threats by the flanged males
Unflanged males cruise along the slide lines until there strategy changes
Darkside: they then try to ambush females to force themselves on them
Platyrrhine origins
Rafting sweepstakes dispersal
Things called parapithecids (first true monkeys in Africa) clung to vegetation and somehow made it to the Americas
back then the continents were a lot closer and the currents checked out
genetics also suggest this is true
(Platyrrhine genetics link straight back to parapithecids)
Plesiadapiforms
lived right at the end of the reign of the dinosaurs (cretaceous era)
some argue that these are the the 1st primates (most don’t)
Very close characteristics to primates, but missing some as well
Many suggested that this was the last stage before evolving into primates
Primate dietary challenges
Primates are very good at solving these challenges
Mechanical challenges
thorns on food, or a hard shell over food
Chemical challenges
Plants can have toxins
Species have to develop immunity
Ecological
what season is it?
where certain things are going to fruiting
where certain foods might be found
Primate locomotor patterns
Quadrupedalism
Leaping
Suspensory
Bipedalism
Quadrupedalism
walking on all 4’s
Major kinds -
Arboreal - monkeys usually walk on branches, have a tail, smaller (larger break branches)
Terrestrial - no tail, larger
Ex: baboons
Specialized -
Knuckle - walking on knuckles
Ex: Gorillas, chimpanzees, bonobos
Leaping
Long legs compared to arms (they hop)
Ex: Tarsiers and Lemurs
Arboreal
Terrestrial
Suspensory
Hanging underneath trees
General - something humans would do
Ex: OrangutangsMobile shoulder joints
crawl thru trees, underneath branches, hanging
Brachiation - highly specialized
Ex: Gibbonsswinging through trees and letting go, flying through the air branch to branch
Knuckle walking
Bipedalism
walking on 2 legs (what us humans do)
Temporary - many primates can do temporary
Dedicated - humans
humans are dedicated and consistently doing this
Primate mating strategies
Main focus on males
Gorillas - physically fight each other for control over the group
They are polygamist (single male with multiple females)
Chimpanzees - all mate with each other
Sperm competition - males try to produce as much sperm as possible to out compete other males
Monogamy - mate for life, no fighting between males
males don’t have to worry about fighting each other
coupled, female / male basically the same size as one another
Ring-tailed lemurs
different than most lemurs
they live in large groups
diurnal
gregarious (not shy)
No problems being around humans (easy to study)
Female dominated
even female children out rank every male
No male alpha
Males have stink fights
Use smell to communicate
have glands that emit smells
Rub these smells on tails and waft it at other males to compete
Synapomorphies - Primates
have grasping digits (thumbs and big toes)
Forward facing eyes (stereo-vision)
nails instead of claws
Postorbital bar (ring bone around eye)
finger prints
only other thing that has fingerprints are Koalas (mammal)
Synapomorphies - Strepsirrhines
Wet noses (complex noses)
Faces are snoutier
tooth combs (lower teeth that jet out)
Use smell to communicate
no postorbital closure (gap behind eye)
Contain all Primate characteristics
Synapomorphies - Haplorhines
Dry noses (simple noses)
Postorbital closure (eye socket like a cup)
Larger brains (than strepsirrhines)
Contain all Primate characteristics
Synapomorphies - Platyrrhines
3 premolars (instead of 2 like humans)
Contain all Primate, Haplorhines characteristics
Synapomorphies - Colobines
Part of the cercopithecoidea (Asian / Africa monkeys)
leaf monkeys (diet mostly leaves)
specialized digestive system
allow them to extract more nutrients from leaves than humans can
Contain all Primate, Haplorhines characteristics
Synapomorphies - Cercopithecines
Part of the cercopithecoidea (Asian / Africa monkeys)
varied diet (no specialized digestive system)
Cheek pouches
pockets where they can stuff food
if not a safe area can take food else where and eat there
sometimes pockets are larger than their stomachs
Contain all Primate, Haplorhines characteristics
Synapomorphies - Hominoids (the apes)
lack of tail
shoulder blades (broad shoulders that are mobile)
Largest brain of all primates
Contain all Primate, Haplorhines characteristics
Tarsiers
Strange Primates
Nocturnal
Only solely carnivorous primate (eat insects and small vertebrates like birds)
Largest eyes compared to body size of any mammal
Can’t move them in eye sockets
Have to turn their whole head to look around
They are Haplorhines
They lack the reflective membrane in the back of their eyes (tapetum lucidum)
Theory of Mind
When something learns Empathy; understanding that others have emotions
Human children start to understand around ages 4-5
They figure out that not everyone is thinking the same thing
once thought to be unique to humans
However there is evidence of the great apes gaining this knowledge
Washo - a female Chimpanzee that was 1st to learn sign language
She understood that her Handler Katt had miscarried a baby
(washo also had complications with having children)washo signed that she was sad (the sign for a tear) and touched Katt’s stomach
At this point it was clear that Washo understood that Katt was sad. Washo had empathy for Katt
Vervet behaviors
They have social flexibility
figured out through the blue vs. pink corn conditioning experiments
2 groups 1 conditioned to eat pink the other blue corn; when the males swapped groups they quickly decided to eat the other corn previously not conditioned to eat because others were eating it
Clear alarm calls for certain predators
Avian (bird) - get down from trees, or get in the trunk
Snake - stand up to see snake in grass
Leopard - run up the tree
Viki the chimpanzee
Very first language Chimpanzee
- Failed experiment
Only was able to speak 4-5 words
They figured out that Chimpanzees are physically unable to produce human speech sounds
Even if mentally capable to speak, they are physically unable to
Washo came after her
They figured out that Chimpanzees do have a language capacity through sign language