BIOE2010 Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:37 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
Polyesters
synthetic fibers that consist of chains containing many esters
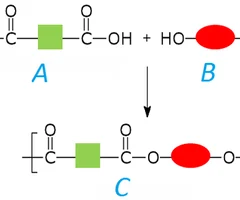
2
New cards
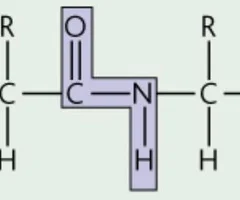
Polyamide
condensation polymer in which the monomers are joined through amide linkages
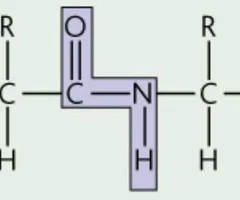
3
New cards
Polyanhydrides
What are the most reactive and hydrolytically unstable polymers used as biomaterials?
4
New cards
polyhydrocarbons
polymer linking simple linear, saturated hydrocarbon
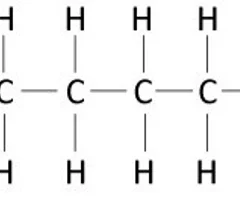
5
New cards
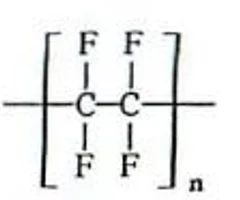
Substituted hydrocarbons
hydrocarbons that have one or more hydrogen atoms replaced with different atoms or groups of atoms
6
New cards
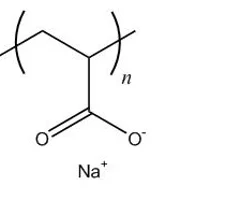
Polyacrylate
Becomes sodium polyacrylate
after neutralizing with NaOH
Water-soluble polymer
Used as thickening, suspending and emulsifying agents in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics and paints and disposable diapers
It does not biodegrade
after neutralizing with NaOH
Water-soluble polymer
Used as thickening, suspending and emulsifying agents in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics and paints and disposable diapers
It does not biodegrade
7
New cards
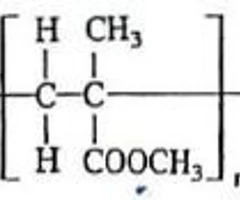
Polymethacrylates
Hydrogels, contact lenses, dental fillings
8
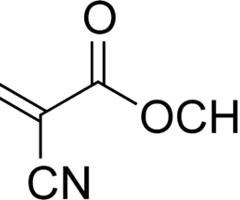
New cards
polycyanoacrylates
Specialized acrylic monomers that quickly polymerize with the addition of alcohol, water or any weak alkaline product to form an adhesive
9
New cards
Biomaterials
nonviable (not living) material intended to interact with biological systems
10
New cards
Isotropic materials
have the same mechanical properties in every direction
11
New cards
typical materials for biomaterials
Stainless steel, cobalt, chromium, titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
12
New cards
CNC machine
computer controlled milling machine (used to create precise detailed pieces, and multiples)
13
New cards
CAD/CAM
Computer Aided Drawing-Computer Aided Manufacturing. The instructions stored in a computer that will be translated to very precise operating instructions to a robot, for tasks such as assembling cars or laser-cutting signage.
14
New cards
Additive Manufacturing
the production of physical items by adding layer upon layer, much in the same way an inkjet printer lays down ink
15
New cards
Subtractive Manufacturing
Manufacturing processes based on controlled removal of undesired materials through cutting, drilling or milling to achieve the desired forms. Ex. CNC milling
16
New cards
Formation of Rust
water, oxygen, and metal essential
17
New cards
Problems with metals
Formation of rust, allergic reactions, deterioration of mechanical properties over time, except noble metals like gold and platinum.
18
New cards
Passivation
spontaneous formation of a stable oxide layer that minimizes corrosion (Ti and CoCr alloys)
19
New cards
Pitting Corrosion
defect in surface oxide layer creates a site for the initiation of corrosion
20
New cards
Magnetic nanoparticles
ferromagnetic fluids could possible be used to direct materials around the body
21
New cards
Magnetic nanoshells
absorb incident light energy and convert it to heat especially absorption in the near IR range.
22
New cards
Resorbable metals
Primarily based around Mg alloys
Surface coatings are commonly used to regulate (prolong) corrosion/ degradation
Surface coatings are commonly used to regulate (prolong) corrosion/ degradation
23
New cards
Alloy
A mixture of two or more metals
24
New cards
Raw metal ore
Oxide forms of metals
25
New cards
MAGNEZIX
Compression screw, Mg-Y-RE-Zr(similar to human bone) metal screw that is completely resorbed by the body and replaced with bone tissue
26
New cards
Ceramic properties
Corrosion resistance
Low conductivities (semi-conductors, insulators)
Stiff and Brittle
Mechanical properties consistent with teeth and bone
Bioinert / bioactive
Naturally occurring ceramics can be made in the laboratory (hydroxyapatite found in bone)
Examples: Alumina, Bioglass, Calcium phosphates, Hydroxyapatite
Low conductivities (semi-conductors, insulators)
Stiff and Brittle
Mechanical properties consistent with teeth and bone
Bioinert / bioactive
Naturally occurring ceramics can be made in the laboratory (hydroxyapatite found in bone)
Examples: Alumina, Bioglass, Calcium phosphates, Hydroxyapatite
27
New cards
Hydroxyapatite
Mineral compound that is the principal inorganic component of bone and teeth. Used as a stem coating for orthopedic implants.
28
New cards
Homopolymer
composed of a single monomer
29
New cards
Copolymer
a polymer made from two or more different monomers
30
New cards
Types of copolymers
random, alternating, block, graft
31
New cards
Polymer sturcture
Branched
Graft
Linear
Star
Network
Dendrimer
Graft
Linear
Star
Network
Dendrimer
32
New cards
Branched Polymer
A polymer having a molecular structure of secondary chains that extend from the primary main chains.
33
New cards
Graft polymer
a type of copolymer; another type of monomer is attached to the backbone polymer chain
34
New cards
Linear polymer
A polymer produced from bifunctional monomers in which each polymer molecule consists of repeat units joined end to end in a single chain.
35
New cards
Star Polymer
an important miscrostructural architecture that is related to polymer properties, this special type of patterned branching of the polymer chain is similar in form to ladders, dendrimers, and brush polymer branching
36
New cards
Network Polymer
A polymer produced from multifunctional monomers having three or more active covalent bonds, resulting in the formation of three-dimensional molecules.
37
New cards
Dendrimer
man-made molecules about the size of an average protein, and have a branching shape. This shape gives them vast amounts of surface area to which scientists can attach therapeutic agents or other biologically active molecules beginning with an initiator core.
38
New cards
Tm (melting temperature)
temperature at which polymer transforms from an ordered (crystalline or semi-crystalline) structure to an amorphous structure
39
New cards
Tg-glass transition temperature
temperature at which a polymer (semi-crystalline or amorphous) transforms from rigid to rubbery state
40
New cards
Plasticizer
a substance (typically a solvent) added to a synthetic resin to produce or promote plasticity and flexibility and to reduce brittleness by lowering its effective glass transition temperature. allow chains to move alongside each other more easily
41
New cards
Thermoplastics
Plastics that can be melted and remolded over and over again.
42
New cards
Thermosets
become permanently hardened when heat is applied and do not soften upon subsequent heating. Generally chemically cross-linked materials such as vulcanized rubber.
43
New cards
Biodegredation
chemical degradation of a material resulting from the activity of a biological agent (enzyme, cell, micro-organism)
44
New cards
Bioerosion
a water insoluble material that under physiological conditions is converted to a water-soluble material
45
New cards
hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
46
New cards
Ester degredation
hydrolysis and esterase enzymes
47
New cards
Addition Polymerization
a type of polymerization in which the monomers simply add together to form the polymer, with no other products
48
New cards
step growth polymerization
growing chains react with each other to form even longer chains.
49
New cards
Addition polymerization initiators
free radical, cation, anions, catalyst
50
New cards
condensation polymerization
type of polymerization in which the formation of a small molecule, such as water, carbon dioxide, HCl, and methanol, accompanies the extension of the polymer chain( EX Polyanhydride synthesis)
51
New cards
Free Radical Polymerization Steps
initiation (with a peroxide and hv), propagation, termination (when 2 radical ends meet)
52
New cards
Molecular weight distribution
The relative amount of each molecular weight of a material that comprises the entire sample
53
New cards
SEC/GPC
Size exclusion chromatography/gel permeation chromatography, used to separate polymers based on hydrodynamic volume in a porous material, which correlates with molecular weight. The larger the molecule the fatter it moves.
54
New cards
Stress (sigma)
the load divided by the original cross-sectional area normal to the applied load
55
New cards
Strain (epsilon)
change in length per initial length
56
New cards
Modulus of Elasticity (Young's Modulus)
Measure of stiffness of an object, defined as the amount of
strain resulting from applying a given stress.
strain resulting from applying a given stress.
57
New cards
elastic deformation
region where the material will return to its original shape when the stress is removed
58
New cards
plastic deformation
permanent change in shape by bending and folding
59
New cards
Yield stress (offset yield point)
The stress at which a material begins to deform plastically.
60
New cards
tensile strength
the resistance of a material to breaking under tension
61
New cards
Proportional limit
Point at which the deformation is no longer directly proportional to the applied force. Hooke's Law no longer applies.
62
New cards
Elastic limit
Maximum stress that a material will withstand without permanent deformation.
63
New cards
Fatigue properties
how materials respond to cyclic loading.
64
New cards
stress concentration
a condition in which the maximum normal stress is much greater than the average normal stress due to geometric discontinuity in the structure or concentration of load
65
New cards
Fatigue limit
stress below which there is no fatigue failure whatever the number of cycles
66
New cards
Compression molding
heat and pressure are applied directly to the polymer powder in the mold cavity
67
New cards
Injection molding
A process during which plastic is heated in a machine and forced into a cavity by a screw or ram. The material solidifies and is then ejected.
68
New cards
Blow molding
A solid bottom hollow tube is placed between two mold halves and heated. The heated tube is then expanded into the sides of the mold with compressed air.
69
New cards
Extrusion
A manufacturing process that forces material through a shaped opening.
70
New cards
Melt Spinning
The process of producing fibers by melting polymer chips and extruding the melt (the molten polymer) in fiber form. Coagulation occurs by cooling.
71
New cards
Dry Spinning
a fiber-forming process in which a solution of polymer dissolved in a solvent is extruded; the fiber coagulates as the solvent evaporates. TRY to avoid, often uses very harsh, environmentally unfriendly solvents.
72
New cards
Fiber Drawing
Control rolls that compress, and spin at different rates stretching fiber through a heater sometimes.
73
New cards
Electrospinning
Forming polymer melt into fibers by electrostatic forces
Fibers are irregular, thin, only slightly drawn-must be combined with supporting textile material
Fibers the size of nanometers
Fibers are irregular, thin, only slightly drawn-must be combined with supporting textile material
Fibers the size of nanometers
74
New cards
Fused Deposition Modeling
Rapid prototyping process in which a filament of wax or polymer is extruded onto the existing part surface from a workhead to complete each new layer.
75
New cards
Stereolithography (SLA)
common rapid prototyping: solid spots are formed in a pool of liquid polymer by focusing laser beams at a single spot in the pool, curing and hardening that spot.
76
New cards
Regenerative tissues
Bone, liver, and peripheral nerve
77
New cards
Extra Cellular Matrix
The substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded, consisting of protein and polysaccharides.
78
New cards
anchorage dependence
The requirement that to divide, a cell must be attached to a solid surface.
79
New cards
integrins
A transmembrane protein that interconnects the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton.
80
New cards
Parenchyma
functional tissues of any organ that perform specialized activites, such as the tissues of the bronchioles, alveoli, ducts, and sacs, that perform respiration
81
New cards
stromal component
required for structual integrity and biomechanics
strong tissue
fibroblasts-produce extracellular matrix
strong tissue
fibroblasts-produce extracellular matrix
82
New cards
Differentiation
process in which cells become specialized in structure and function
83
New cards
Phases of wound healing
inflammatory, proliferative, remodeling
84
New cards
Inflammatory phase
the initial phase of wound healing in which bleeding is reduced as blood vessels in the affected area constrict(~48 hrs)
85
New cards
Remolding phase
Restoration of function and development of mechanical strength (~2/4 wks to year)
86
New cards
Proliferative phase
Second phase of wound healing consisting of three concurrent process:
Granulation tissue formation-replacing of the extracellular matrix
Angiogenesis- formation of new blood vessels to supply new cells with oxygen
Re-epithelization- proliferation of new epithelial cells
(~2wks)
Granulation tissue formation-replacing of the extracellular matrix
Angiogenesis- formation of new blood vessels to supply new cells with oxygen
Re-epithelization- proliferation of new epithelial cells
(~2wks)
87
New cards
Growth Factors
Regulatory proteins that ensure that the events of cell occur (division, migration, matrix synthesis)
88
New cards
Hemostasis
Step 1- vasospasm, constriction of blood vessels
Step 2- platelet plug formation, platelets bind to sub endothelial collagen, von Willebrand Factor, then platelets activated by release of activator gP IIb/IIIa, Then platelets can bind to fibrogen leading to aggregation platelet plug.
Step 3- Coagulation and the formation of the fibrin clot
intrinsic vs extrinsic
Step 2- platelet plug formation, platelets bind to sub endothelial collagen, von Willebrand Factor, then platelets activated by release of activator gP IIb/IIIa, Then platelets can bind to fibrogen leading to aggregation platelet plug.
Step 3- Coagulation and the formation of the fibrin clot
intrinsic vs extrinsic
89
New cards
von Willebrand factor
plasma protein secreted by endothelial cells; facilitates adherence of platelets to damaged vessel wall
90
New cards
GP IIb/IIIa
This receptor aggregates platelets and binds to fibrinogen to stabilize the platelet plug:
91
New cards
Fibrinogen
inactive plasma protein that is converted to fibrin in the clotting process
92
New cards
Aggregation (Platelet Plug Formation)
clot formation to prevent leakage of blood vessel.
93
New cards
Intrinsic initiation of coagulation
activated by normally inactive blood proteins after injury initiating a enzymatic chain reaction. LARGEST issue for medical devices chronic response ALWAYS IN CONTACT WITH BLOOD
94
New cards
Extrinsic initiation of coagulation
mediated by tissue factors not present within endothelial cells but in sub-endothelial cells, injury causes exposure to this tissue factor.
95
New cards
Fibrinogen Polymerization
fibrin, provisional matrix, scaffold for repair (clot)
96
New cards
Control of Coagulation
-damaged cells at the site of injury (mast cells) release heparin (glycosaminoglycan)
-heparin binds to anti-thrombin III (thrombin inhibitor) and increases its potency 1000-fold
- thrombin also activates protein C-which deactivates earlier factors in the cascade (negative feedback)
-heparin binds to anti-thrombin III (thrombin inhibitor) and increases its potency 1000-fold
- thrombin also activates protein C-which deactivates earlier factors in the cascade (negative feedback)
97
New cards
Chemotaxis
movement by a cell or organism in reaction to a chemical stimulus
98
New cards
Phagocytosis
Non-specific defence where phagocytes engulf foreign antigens and digest them using digestive enzymes present in lysosomes
99
New cards
TNF-alpha
Secreted by macrophages
activate cell types and stimulate processes of proliferative phase
activate cell types and stimulate processes of proliferative phase
100
New cards
TGF-beta1
important fibroblast growth factor in angiogenesis, but also inhibits inflammation and cancer