inhibitors, prosthetic groups
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
what are reversible inhibitors?
enzyme’s activity is reduced/stopped temporarily
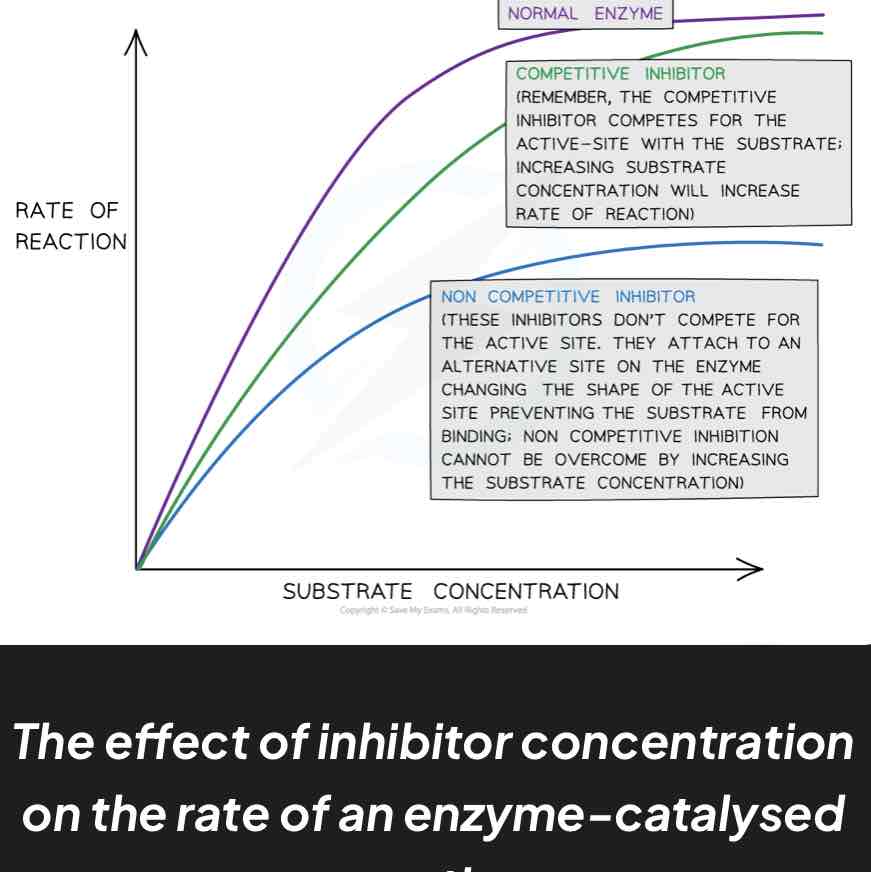
competitive inhibitors: similar shape to substrate molecules and compete with substrate for active site; reduces rate of reaction for given substrate concentration
non competitive inhibitors: bind to enzyme at allosteric site which alters active site’s shape and prevents substrate binding; increasing substrate/enzyme concentration has no effect but increasing inhibitor concentration decreases rate of reaction
what is end product inhibition?
enzyme inhibition that occurs when reaction’s product acts as inhibitor to enzyme that produces it
metabolic reactions are controlled using end product as non competitive, reversible inhibitor
as enzyme converts substrate into product, process slows down as end product binds to alternative site and prevents formation of enzyme substrate complexes
end product detaches from enzyme, allowing active site to reform and enzyme returns to active state; enzyme catalyzes reaction in continuous feedback loop
what’s an example of end product inhibition?
respiration is metabolic pathway resulting in ATP production
first, addition of two phosphate groups to glucose molecule and then addition of second phosphate group which results in breakdown of glucose catalyzed by PFK - competitively inhibited by ATP
when ATP levels are high, more ATP binds to allosteric site on PFK, preventing addition of second phosphate group to glucose; not broken down and ATP isn’t produced at same rate
as ATP is used up, less binds to PFK and enzyme catalyzes addition of second phosphate group to glucose; respiration resumes, leading to more ATP production
what are non reversible inhibitors?
inhibitors which form covalent bonds with enzymes, inhibiting them permanently; results in complete inactivation of enzyme
dangerous as biological reactions in organisms can be completely stopped; to avoid, organism should produce more enzyme that’s being inhibited (occurs by transcribing/translating genes)
some non reversible inhibitors are considered as metabolic poisons e.g. cyanide as it stops metabolic reactions
what are cofactors?
components which contain non protein substance which changes tertiary structure
require inorganic ions to function - inorganic cofactors; stabilizes enzyme’s structure or take part in reaction at active site
what are coenzymes?
larger organic cofactors where they’re permanently/temporarily bound to enzyme; carry electrons or chemical groups between enzymes
link different enzyme catalyzed reactions into sequence during metabolic processes e.g. vitamins
what are prosthetic groups?
cofactors which contain permanent part of enzyme’s structure they assist; essential to enzyme proper function as helps form final 3D shape e.g. zinc ion in carbonic anhydrase
inactive precursor enzymes where these enzymes cause damage within cells; often undergo change in shape by adding cofactor
before cofactor is added, precursor protein is called apoenzyme and when added and activated, it’s called holoenzyme
changes in conditions e.g. pH results in tertiary structure change called proenzymes