L10 - Motor control concepts and motor cortex
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
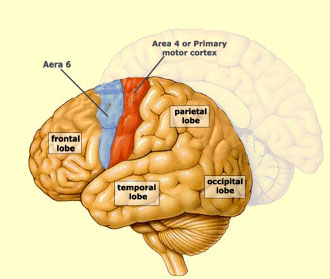
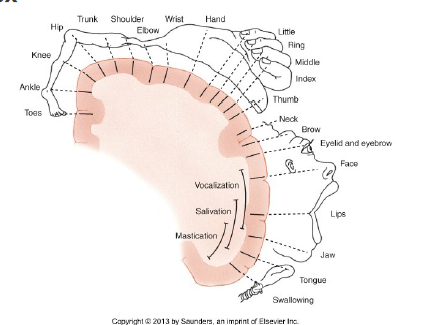
Primary motor
Location, Role in voluntary mvm, somatotopic organisation
location
frontal lobe —> pre central gyrus
role
execute commands to motor neurons,
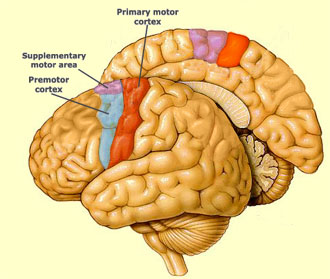
secondary motor area - premotor cortex
Location, Role in voluntary mvm, somatotopic organisation
location
frontal lobe —> anterior to the primary motor cortex
role
planning mvm (p=planning)
sensory input
spatial guidance
Explain the differences between ‘reflex’ and ‘voluntary’ movements.
a) Describe the sensory contribution to learning and movement control.
b) Describe a stepping pattern generator.
Central Pattern Generator (CPG)
neuronal circuit
produce rhythmic motor patterns in absense of sensory/descending inputs that carry timing info
initiated by higher centres (brainstem) modified by sensory input from PNS
Stepping pattern generators (SPG)
active lower motor neurons to innervate pattern of alternating flexion and extension rd for walking
output - adapted to …
task
environment
stage of walking cycle
Describe what is meant by the concept of ‘motor control’.
regulate and direct mechanisms pivotal to mvm
sensory info
proprioceptive
receptions in periopheral NS
info on weight bearing, limb position prior to mv
visual system
visual cues for mvm and guidance during mvm
vision to fixate on object, corrective adjustmend to achieve contact
vestibular system
input form inner ear about head position relative to gravity and mvm
Define coordination and degrees of freedom
degrees of freedom
humans have degrees of freedom that need ot be controlled
inherent variability that is critical to optimal funciotn
Contrast different models of motor control including hierarchical model, ecological and dynamical systems approach
dynamic interplay btwn perception, cognition, action systems
hierarchial model
organisation control that is top down
limitation; cannot explain dominance of reflex behaviour eg stepping on smth fast
dynamic systems theory (DST)
whole body as mechanical system
variability as necessary for optimal fx rather than result of error'
limitation; presume NS has less important role and mathematical formuals are dominant in motor control
ecological
motor control evolved to cope w. environment
suggests action rq perceptual info speciial to desired goal-direction action in speicifc environment
limitation; less acknowledgement to structure and fx of NS
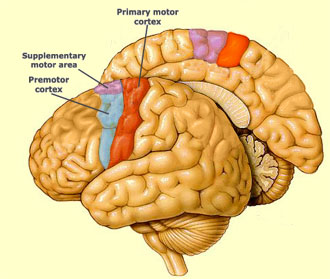
secondary motor area - supplementary motor cortex
Location, Role in voluntary mvm, somatotopic organisation
location
frontal lobe —> midline surface of the hemisphere anterior the primary motor cortex
role
feeds motor instruction in correct sequence esp in coordinated mvm
3 classes of mvm
reflexes
involuntary
rapid
sterotyped
eg; eye blink, coughing, knee jerk reflex
inittiated by an eliciting sitmulus
rhythmic motor patterns
combines voluntary and reflexive acts
voluntary initiation and termination
once initiated mvm repetitive and reflexive
eg; chewing, walking, running
voluntary
purposeful, goal oreinted
learnt and can be improved
process of planning, programming, execution
complex actions; writing, speaking, playing piano