3019PSY Mod 4 Word Recognition
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
parallel distributed processing (PDP) / triangle model to reading
the three processes of reading are semantics, phonology, and orthography
visual orthographic analysis module
identifies what letters are and codes them into their correct positions
orthographic input lexicon
a store of what visually familiar words look like
grapheme-phoneme conversion module
a store of our letter-to-sound rules
regularisation errors
pronouncing a word in an incorrect but logically sound way
semantic system (word recognition)
a store of the meaning and associates of known words
orthographic output lexicon
a store of all the words that we know how to write down
orthographic output buffer
a temporary store of the words/ letters we intend to write down
phonological output lexicon
a store of all of the words and letter strings we know how to pronounce
phonological output buffer
a temporary store of the sounds that we intend to utter
phoneme-grapheme conversion module
a store of all our sound-to-letter rules
dyslexia
a reading deficit or problem that may be acquired or developmental
developmental dyslexia
failing to meet age appropriate reading standards with normal intellectual functioning and educational opportunities
peripheral dyslexias
dyslexias caused by deficits at early stages of the word recognition model (aka the VOAM)
central dyslexias
dyslexias caused by more deeply rooted deficits in the word recognition model
neglect dyslexia
where a patient neglects to read one half of a word
pure alexia
inability to read whole words but an ability to read words letter-by-letter; caused by damage to the left inferior occipital lobe and corpus callosum
alexia
any acquired dyslexia
letter position dyslexia
issues with correctly arranging letter position while reading; called transposition errors
transposition errors
incorrectly arranging letters while reading
attentional dyslexia
difficulty isolating attention to letters/ words while reading, often resulting in migration errors
migration errors
re-arranging letter positions across words while reading
surface dyslexia
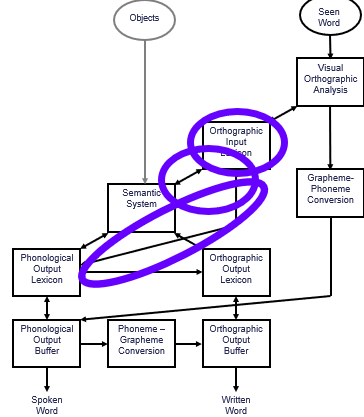
difficulty reading irregular words caused by deficits in the lexical route to reading
source of surface dyslexia
the orthographic input lexicon, the conncetion between the orthographic input lexicon and the semantic system, and the connection between the orthographic input lexicon and the phonological output lexicon
phonological dyslexia
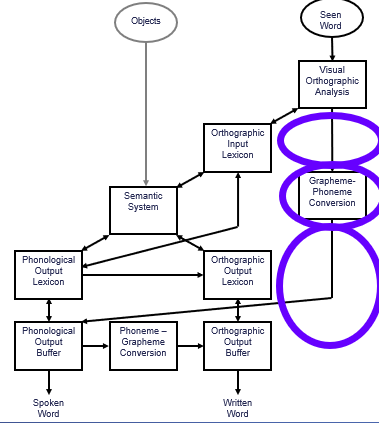
difficulty reading nonwords / unfamiliar words; caused by deficits in the nonlexical route to reading
sources of phonological dyslexia
access to the grapheme-phoneme conversion module, the graphene-phoneme conversion module, and output of the grapheme-phoneme conversion module
direct route dyslexia
difficulty accessing the meaning of words caused by a deficit of the semantic system
deep dyslexia
an acquired dyslexia characterised by 8 symptoms, primarily semantic errors
treatment of neglect dyslexia
finger tracking, vertical presentation of words, tapping next to words, placing a number next to words
treatment of pure alexia
multiple oral reading strategy
treatments of letter position dyslexia
finger tracking
treatment of attentional dyslexia
word-sized cutout, finger tracking
treatment of surface dyslexia
flashcards, repeat exposure to irregular words (written and spoken), sentence completion task
treatment of phonological and deep dyslexia
training of letter-sound correspondences
semantic errors
incorrectly reading a target word as a semantically related word (eg cost → money)
visual errors
incorrectly reading a target word as a visually similar word (eg signal → single)
visual-then-semantic error
incorrectly reading a target word as a visually similar, then semantically related word (eg sympathy → symphony → orchestra)
morphological / derivation error
incorrectly reading the end of a word (eg edition → editor)
imageability effect
a patient is better at reading highly imageable than abstract words (eg tree/ truth)
function word substitution
replacing function words with other function words (eg with → where)
LH cause of the inability to read nonwords
grapheme-phoneme conversion (left hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
LH cause of semantic errors, the imageability effect, and morphological errors
semantic system (left hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
LH cause of visual errors
orthographic input lexicon (left hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
LH cause of poor word reading and function word errors
connection between the orthographic input lexicon and phonological output lexicon (left hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
LH cause of correctly understanding printed words yet still making semantic errors
connection between the semantic system and phonological output lexicon (left hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
RH cause of inability to read nonwords
nonexistent grapheme-phoneme conversion module (right hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
RH cause of the imageability effect
better performance for concrete compared to abstract words in the right hemisphere (right hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
RH cause of semantic errors
semantic errors are more common in people with a damaged left hemsiphere (right hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
RH cause of poor function word performance
function words are poorly represented in the right hemisphere (right hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
RH cause of morphological errors
syntactic processing is worse in the right hemsipere (right hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
RH cause of visual errors
poor word representation in the right hemisphere (right hemisphere account to deep dyslexia)
left hemisphere
more often damaged in people with deep dyslexia
left occipital and occipitotemporal regions
associated with orthographic processing
superior and middle temporal gyrus + BA21 and BA22 areas
involved in semantic processing
frontal operculum in the left hemisphere
associated with phonological output