Medical Interventions & PT Complications
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
Thoracic Cage Incisions: The median sternotomy is commonly used for what type of surgery?
cardiac surgery, including heart & heart-lung transplantation
Median sternotomy
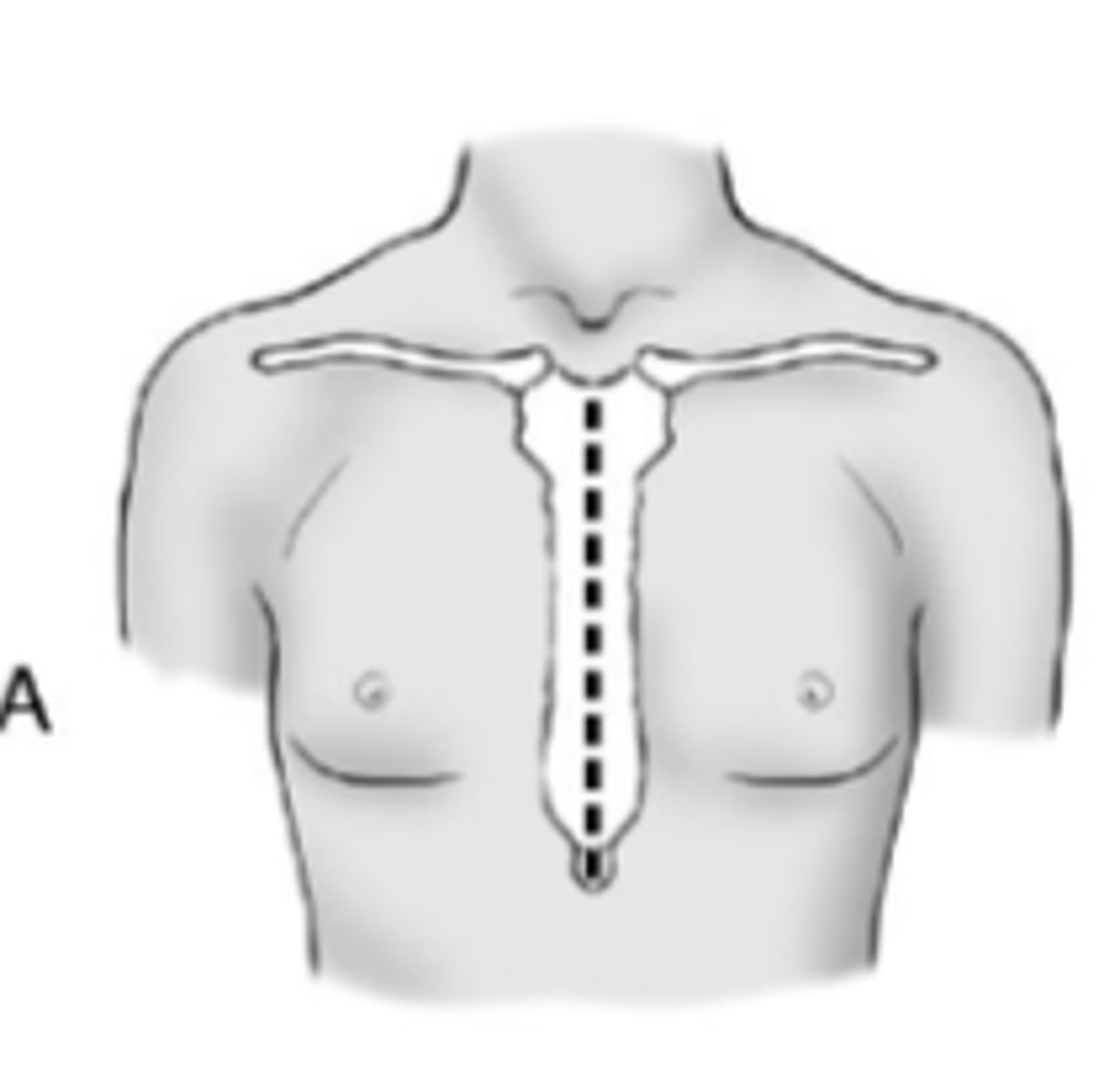
Thoracic Cage Incisions Some mitral valve surgery is performed via a ________________ thoracotomy
Posterolateral
Posterolateral thoracotomy for mitral valve surgery
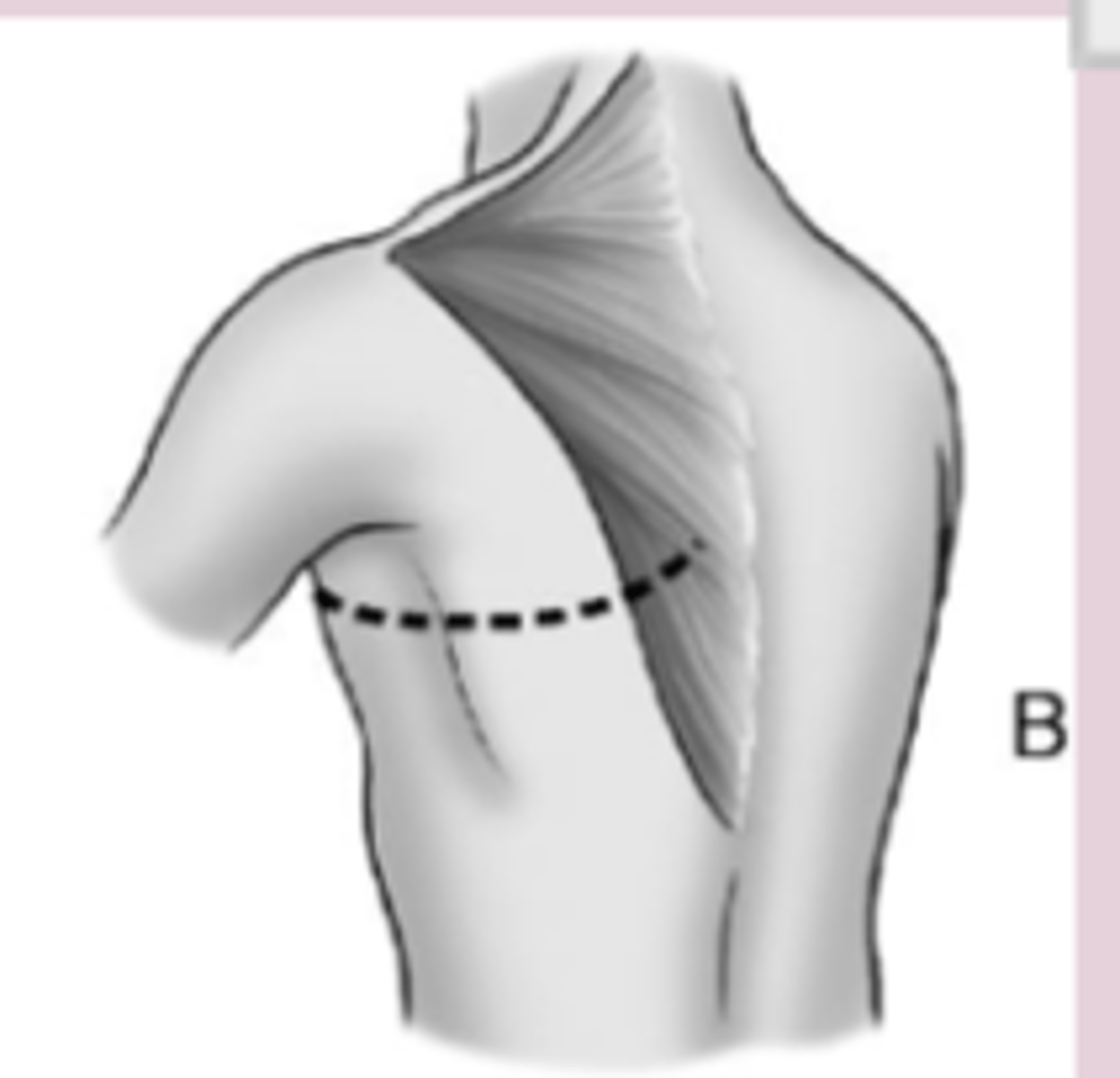
Thoracic Cage Incisions Lung surgeries are usually performed via the ___________ or ______________ thoracotomy incision
- Anterolateral
- Posterolateral
Anterolateral thoracotomy incision
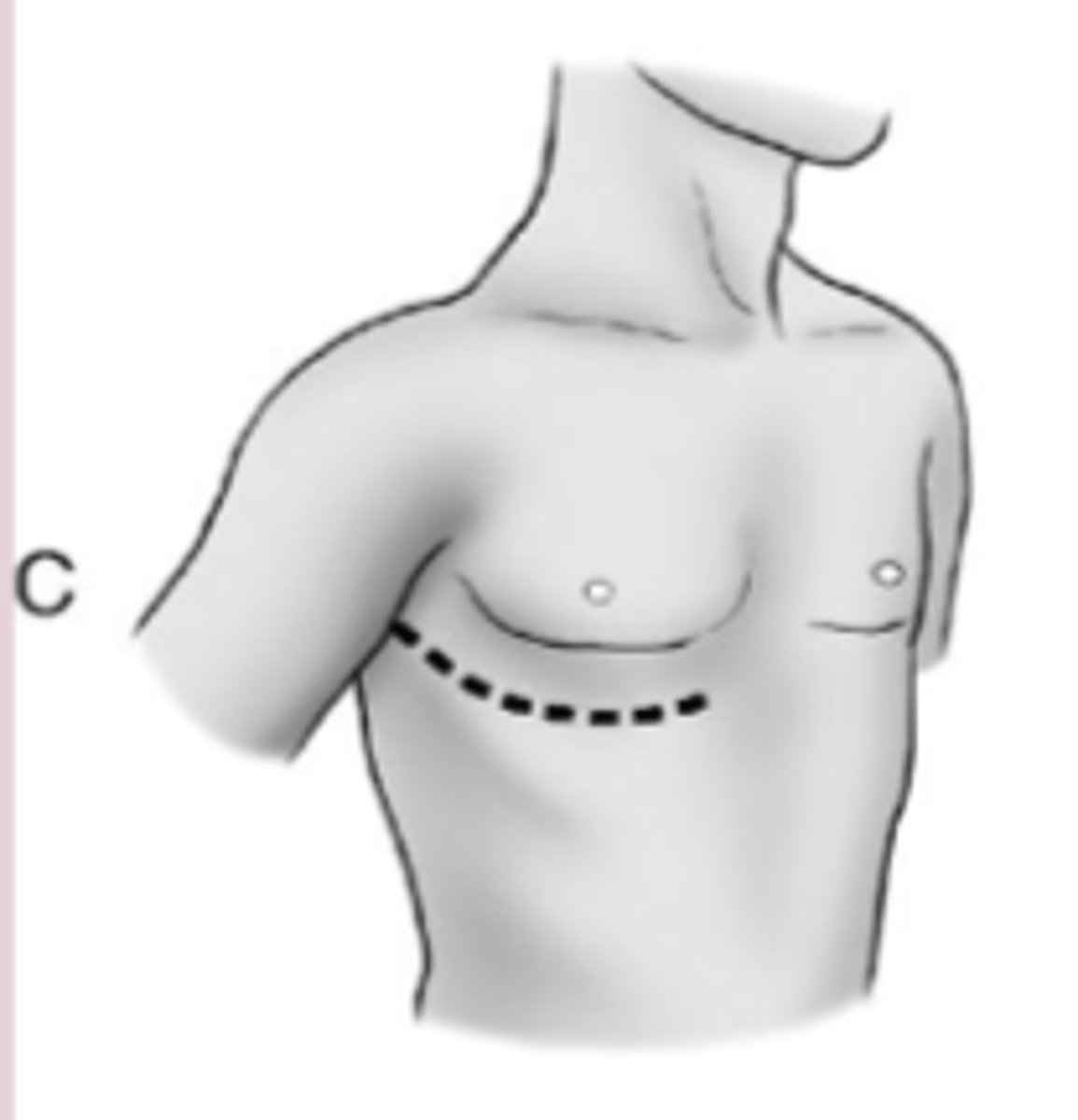
Posterolateral thoracotomy incision for lung surgeries
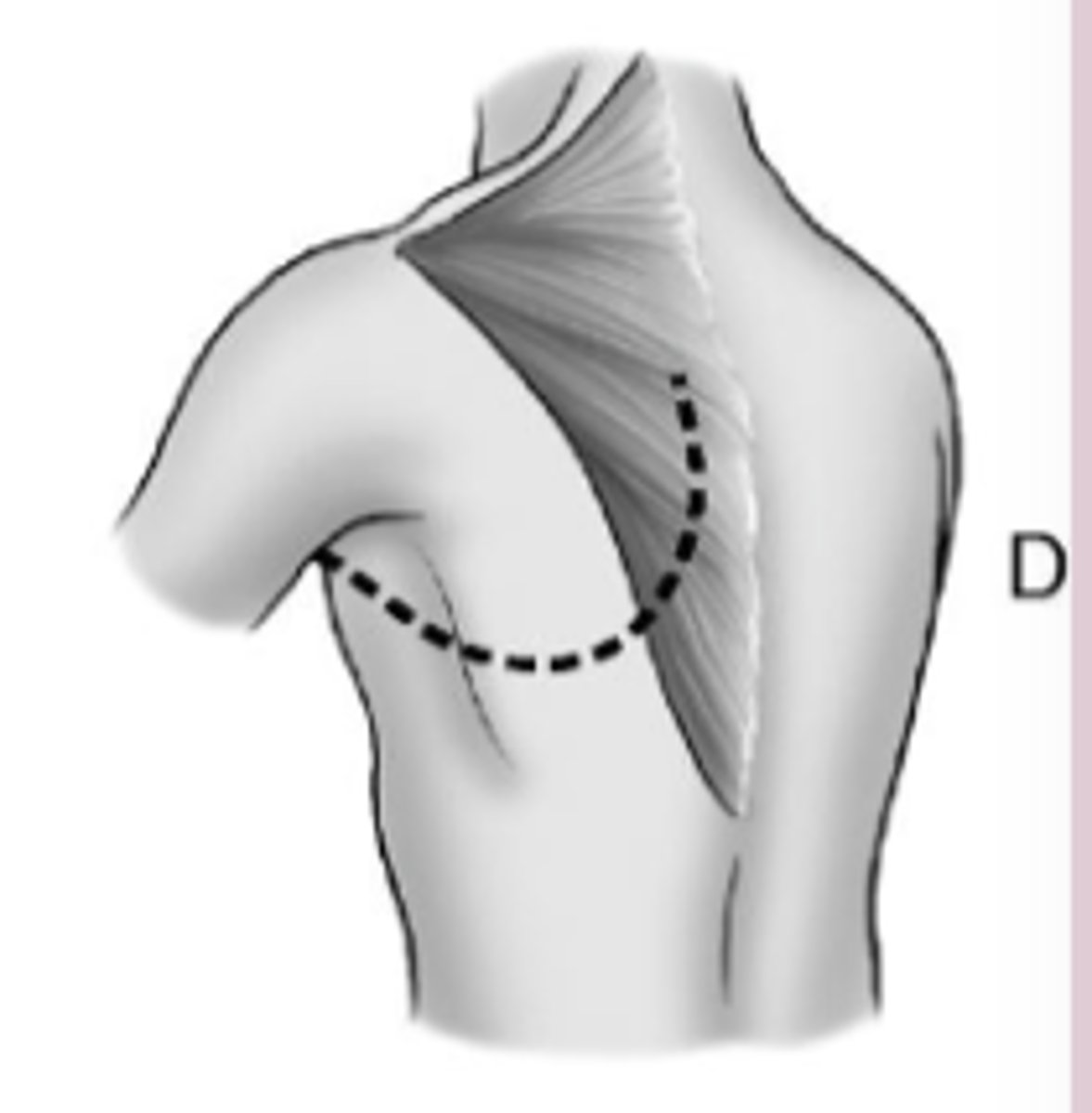
Thoracic Cage Incisions Bilateral lung and live donor lobar transplantations typically use the _____________ incision
Clamshell
Clamshell incision thoracotomy
What is a thoracotomy?
An incision into the pleural space of the chest
What are the most common types of thoracotomies? (3)
- Posterolateral
- Anterolateral
- Lateral
Thoracotomies: Usually requires an ____________ for a couple of days to control for high pain after this procedure
epidural
Thoracotomies: Post-thoracotomy pain syndrome is a result of a ___________ emanating from the __________ nerves around the surgical approach
Neuralgia, intercostal
Thoracotomies: What is sometimes done in this procedure that is likely to irritate the intercostal nerves?
A rib can sometimes be removed during this approach
Thoracotomies: 5-20% of those who undergo a thoracotomy end up w/ ___________ __________ d/t the incision & surgical approach
chronic pain
Doing heart surgery through thoracotomy: This procedure would be for someone in....?
Cardiac arrest
Thoracotomy to access the heart/pericardium: What do you need to be sensitive of? (2)
- What has been cut through
- The pts pain level
Bronchoscopy: Can be done as an ____________ OR an ______________ tool
Intervention, assessment
What is a Bronchoscopy
Using a flexible or rigid fiberoptic endoscope, the larger airways down to the third or fourth divisions of the segmental bronchi can be visualized directly.
Bronchoscopy: If abnormality, what can be done?
- Bronchial brushing
- Bronchoalveolar lavage
- Transbronchial needle aspiration/ lung biopsy
Bronchoscopy Can be used as a therapeudic intervention removing retained _________ or aspirated _________ ____________
- Secretions
- Foreign bodies
Bronchoscopy: Can be used as as intervention to assist in difficult __________ & _________, & managing ___________ obstruction
- Intubation
- Hronchodilation
- Malignant
What is a lung lavage?
Bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into the lungs & fluid is squirted into part of the lung & then collected for examination.
Lung Lavage: Also used to loosen and remove ___________
secretions
Lung Lavage: What is this the gold standard for?
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Lung Lavage: This is the procedure where you ________ one lung and _________ the other to “clean” the lungs
Inflate, deflate
Pulmonary Resection: Whare are the Indications? (5)
- Bronchogenic carcinoma
- Bronchiectasis
- Fungal infections
- Tuberculosis
- Benign tumors
Pulmonary Resection: ________________ or _______________ thoracotomy incision
Anterolateral, posterolateral
Pulmonary Resection: Incision through the ____________ _____ corresponding to the lesion
Intercostal space
Pulmonary Resection: Division of the ___________ ___________ & _______________ muscles
Serratus anterior, intercostal
Pulmonary Resection: Sometimes they cut through what other muscles? (2)
Latissimus dorsi & rhomboid muscles
Pulmonary Resection: How are the surgical procedures named?
For the portion of the lung removed?
What type of Pulmonary Resection?: Removal of a small localized lesion
Wedge resection
3 multiple choice options
What type of Pulmonary Resection?: Excision of a bronchopulmonary segment
Segmentectomy
3 multiple choice options
What type of Pulmonary Resection?: Resection of an entire lung lobe
Lobectomy
3 multiple choice options
What type of Pulmonary Resection?: Removal of the middle lobe along with an upper or lower lobe
Bilobectomy
3 multiple choice options
What type of Pulmonary Resection?: Excision of a lobe & part of the main stem bronchus followed by anastomosis of the lower lobe(s) to the proximal bronchus
Bronchoplastic/sleeve resection
3 multiple choice options
What type of Pulmonary Resection?: Resection of an entire lung
Pneumonectomy
3 multiple choice options
Pulmonary Resection: How many chest tubes are required?
2
Pulmonary Resection: Where are the chest tubes placed w/ this procedure? (2)
- One at the apex of the lung aka pleural space
- One at the base or mediastinum
Pulmonary Resection: The chest tube at the apex aka pleural space is used to remove _________
Air
Pulmonary Resection The chest tube at the base/mediastinum is used to drain what? (2)
- Blood
- Serous fluid
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery is what type of procedure?
Palliative
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: Resection of 20-35% of the lung tissue is most damaged by what?
Emphysema
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: Done Via __________ or ________ ___________, although video-assisted thoracoscopy (VATs) in some centers
Thoracotomy, median sternotomy
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: To improve the ___________ and recruitment of more functional lung tissue and to reduce _____________ volumes
Expansion, intrathoracic
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: Restores shape of the ____________
Diaphragm
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: For significant __________ & severe fixed _________ obstruction
Dyspnea, expiratory
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: What must the FEV1 % be to be considered for this procedure?
Less than 40-45%
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: Often done for obstructive or restrictive disease?
Obstructive
1 multiple choice option
Lung Transplant: What are the Indications? (7)
- End-stage COPD
- Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
- Cystic fibrosis
- Primary pulmonary HTN
- Bronchiectasis
- Bronchiolitis obliterans
Lung Transplant: The patient cannot have any other serious comorbidities such as... (5)
- Morbid obesity
- Severe hypertension
- HF
- Cancer
- Cachexia
Lung Transplant: Usually less than _____ years of age, nonsmokers, ambulatory, & able to participate in ___________ ___________
65, pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung Transplant: Is typically done via a ___________ or ___________ incision
Thoracotomy, sternotomy
Lung Transplant:BLTx usually involve's what type of incision
Clamshell
Lung Transplant: What is always required w/ this procedure?
Immunosuppression
Myocardial Revascularization Procedures: To improve myocardial blood flow through stenotic __________ arteries
coronary
Myocardial Revascularization Procedures: What procedures does this include? (3)
- Catheter-based percutaneous techniques (such as PTCA)
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- Transmyocardial revascularization
Myocardial Revascularization Procedures: The word percutaneous means the procedure is performed through the ________, rather than through an open surgical procedure
skin
What is a Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA)?
A balloon-tipped catheter is passed through the femoral artery → aorta → diseased coronary artery, using fluoroscopic guidance.
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): A balloon-tipped catheter is passed through the __________ artery, up the _________, and then into a diseased coronary artery, using _____________ guidance
Femoral, aorta, fluoroscopic
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): The balloon is positioned across a ___________ __________ & inflated
Stenotic lesion
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): What is the goal of this procedure?
To ↑ the intraluminal diameter by fracturing the plaque & disrupting the vessel intima
Intracoronary Stent for PTCA: An intracoronary stent before inflation and in its expanded configuration, used to maintain the?
Patency of a vessel after PTCA
Intracoronary Stent for PTCA: ___________ occurs in 10-50% of patients undergoing PTCA, usually within the first _____ months; therefore, about 70-90% of PTCAs also involve placement of a ________
Restenosis, 6, stent
Intracoronary Stent for PTCA: T/F Plaque cannot build up around the stent
False
1 multiple choice option
Intracoronary Stent for PTCA: Return to activity in a ½ day, you need to monitor very carefully monitor very carefully because...?
Could clot or re-stenose
Intracoronary Stent for PTCA: When is discharge?
Usually the next day
Intracoronary Stent for PTCA: Stents can be put where?
In different organs
PTCA- Implications: What is the number one complication?
vasospasms (can cause angina)
PTCA- Implications: If you stop antiplatelet therapy what may happen?
Increased risk for a thrumbus
PTCA- Implications: Other risks? (5)
- MI
-Re-stenosis
- Damage to coronary vessel
- Thrombosis
PTCA: For pts treated within 60-180 min from the first medical contact, a nearly linear relationship btwn contact-to-balloon times & mortality was found in all four STEMI groups. Every 10-min treatment delay resulted in more pt deaths, b/c of this what is VERY important?
Early intervention
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): also called what?
Aorto-coronary bypass (ACB) surgery,
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Uses autogenous ____________ vein or arterial grafts to bypass stenotic lesions of the coronary arteries
Saphenous
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Usually done through what artery?
The internal thoracic/mammary artery
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Do arteries or veins have longer longevity with this procedure?
Arteries
1 multiple choice option
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Performed via a?
Median sternotomy
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) At closing, the ___________ is wired back together again
sternum
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): After surgery how many chest tubes does the patient have in place?
2
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): What are the chest tubes used for? (2)
- One to drain the mediastinum
- One intrapleural tube to reinflate the left lung, which was collapsed during surgery
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): High ___________ demands are present post op
Oxygen
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Cooling of heart during CABG can affect ________ _______ and create arrhythmias (A FIB) after surgery
SA node
What are the Variations of a CABG? (4)
- Single, double, triple, quadruple
- On pump (ONCAB)
- Off pump (OPCAB)
- Minimally invasive (MIDCAB)
Variations of CABG: What does on pump mean?
On the cardiac bypass machine (machine that pulls blood out of body→ re-oxygenates it→ returns it to the body)
Variations of CABG: Which variation has higher risks such as CVA?
On pump (ONCAB)
2 multiple choice options
CABG: What should you check for post op?
EF
Complications of CABG? (7)
- A-fib
- CVA
- Pulmonary dysfunctions
- MSK & functional deficits
- Cognitive impairments
- Sternal instability and/or wound dehiscence
- Renal failure
After CABG A-fib usually occurs by day _____ & increased risk for _________
2, CVA
Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (MIDCAB): Is performed how?
Endoscopically & off-pump
Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (MIDCAB): How is it done?
Combination of small holes in the chest & a small incision made directly over the coronary artery to be bypassed
What are the Complications Associated with Cardiac Surgery via Median Sternotomy? (9)
- Myocardial injury
- Blood loss
- Atrial fibrillation
- Pneumonia
- Memory/cognitive impairment
- Subxiphoid incisional hernias
- Brachial plexus injury
- Superficial incisional infections
- Sternal instability/mediastinitis
What are the Primary RF's for Sternal Wound Complications? (3)
- Obesity/high body mass index
- Rethoracotomy
- Smoking
What is a Transmyocardial Revascularization?
Medical laser drills tiny channels into the myocardium, which improves blood flow by the physical contractility of the ventricles & triggers growth of new capillaries (angiogenesis)
Transmyocardial Revascularization: Transmyocardial laser revascularization ultimately stimulates the myocardium to form small ________ ___________, and this response appears to contribute to relief of ________ ___________ in 60% to 80% of patients within 6 months
Collateral vessels, chest pain
Transmyocardial Revascularization: During a typical procedure, approximately how many channels are made in each targeted region of the heart muscle?
10-50
Transmyocardial Revascularization: The channels in the heart muscle seal over almost immediately with little blood loss while the new channels allow....?
Fresh blood to perfuse the heart wall immediately
Surgical Treatment of Arrhythmias: What are the options? (4)
- Cardiac ablation
- Pacemaker insertion
- Automatic Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (AICD)
- MAZE
Cardiac Ablation: Involves the use of ________ to destroy areas of ___________ that are related to the onset or maintenance of arrhythmias.
Energy, endocardium
Cardiac Ablation: Used for what heart rhythms.... (4)
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular tachycardia