APHY 164 - Capillaries and Exchange
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
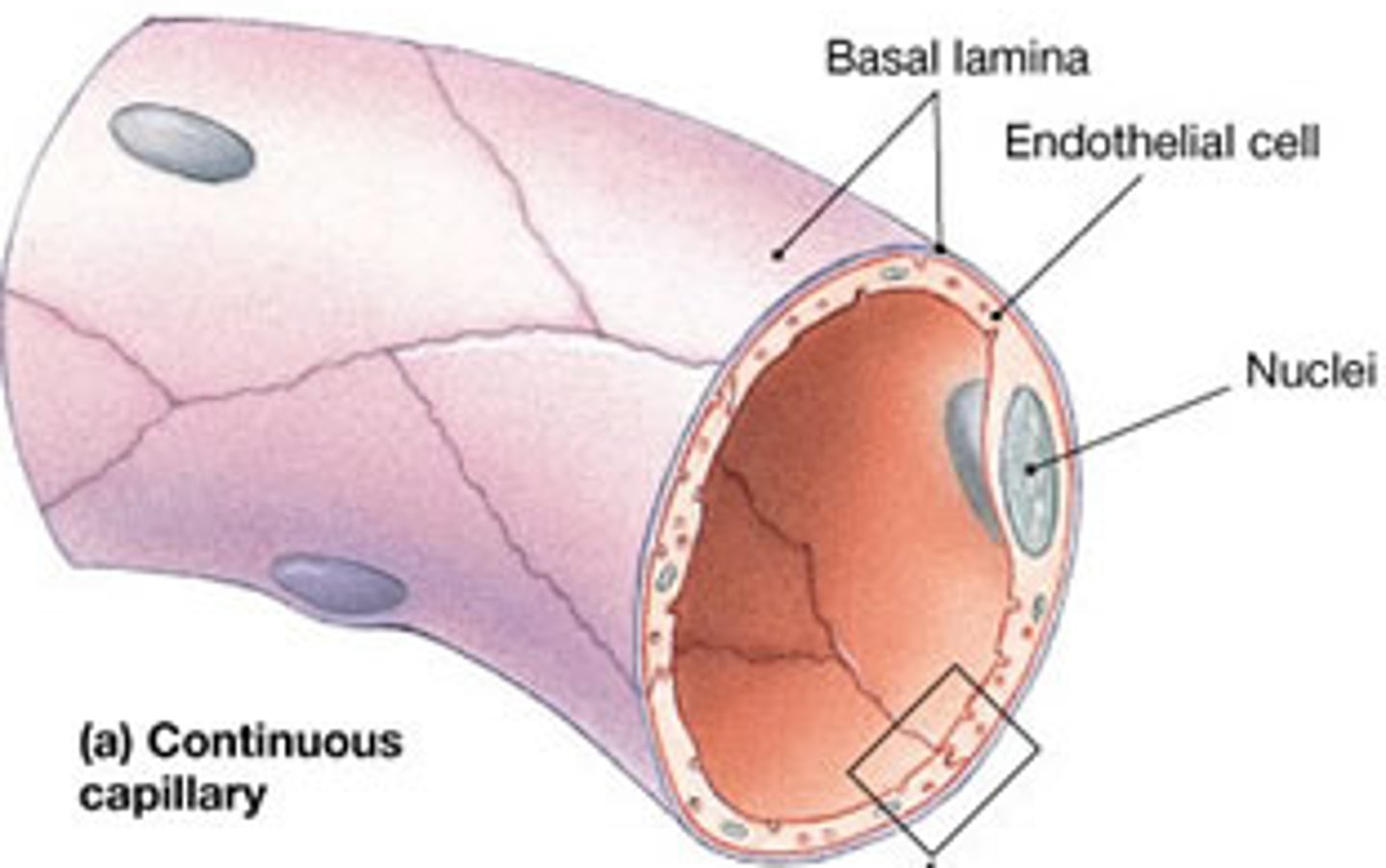
Continuous capillaries
least permeable and most common capillaries
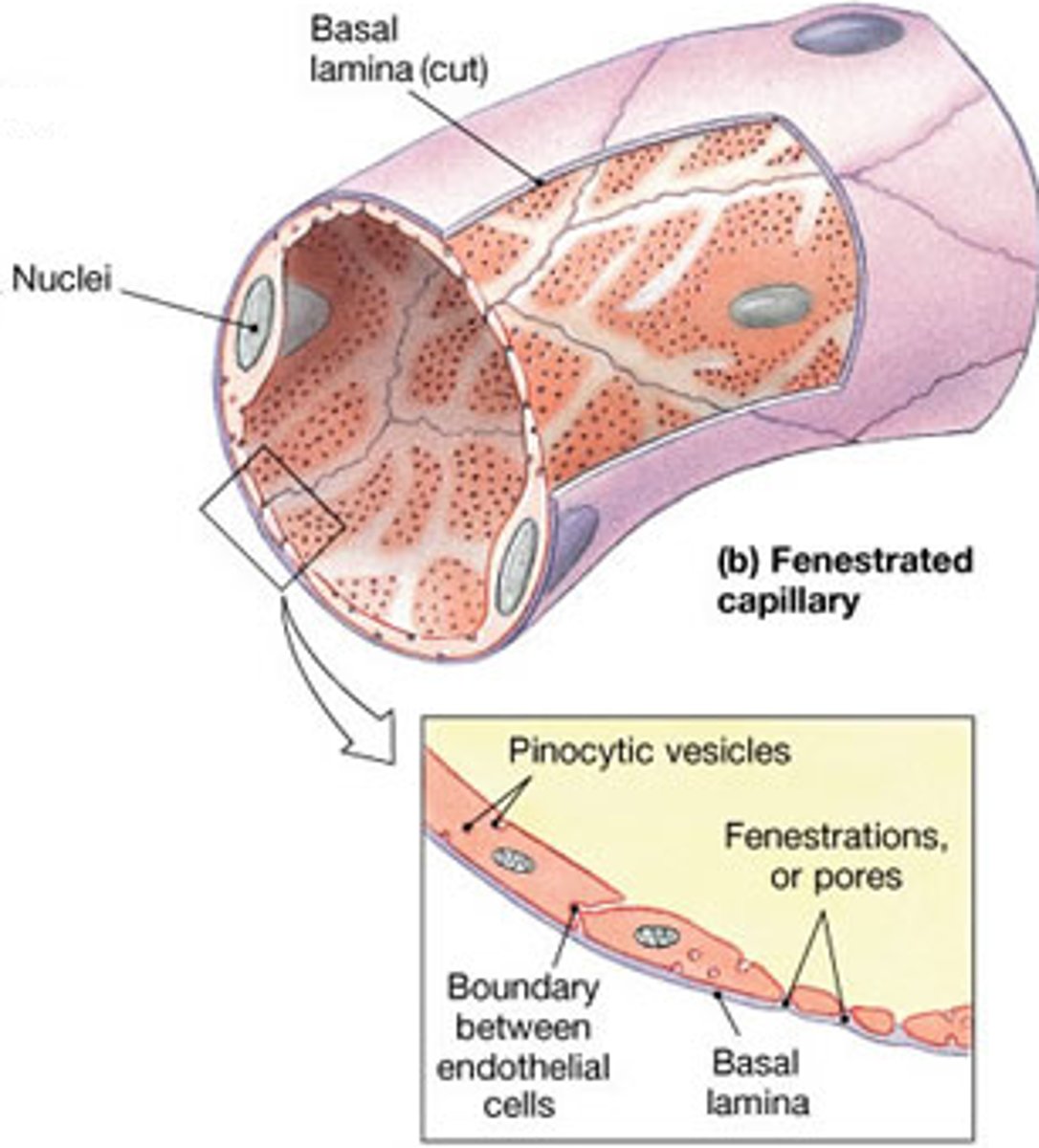
Fenestrated capillaries
have pores in vessel wall; found in kidneys, intestines, and endocrine glands
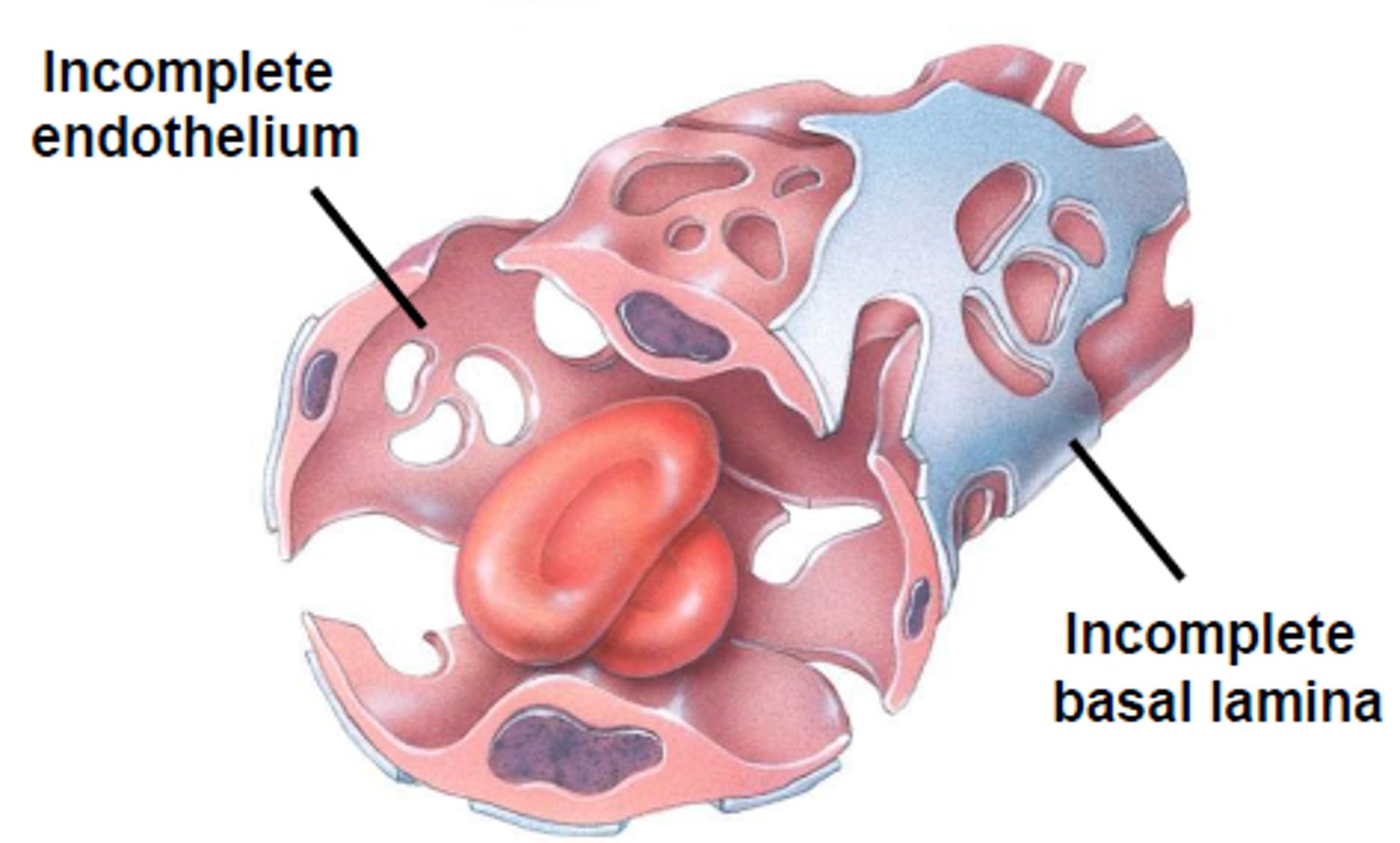
Sinusoidal capillaries
most leaky capillaries with large intercellular clefts, liver is a good example, allow large molecules to pass between blood and surrounding tissues
Capillary bed
interwoven network of capillaries between arterioles and venules
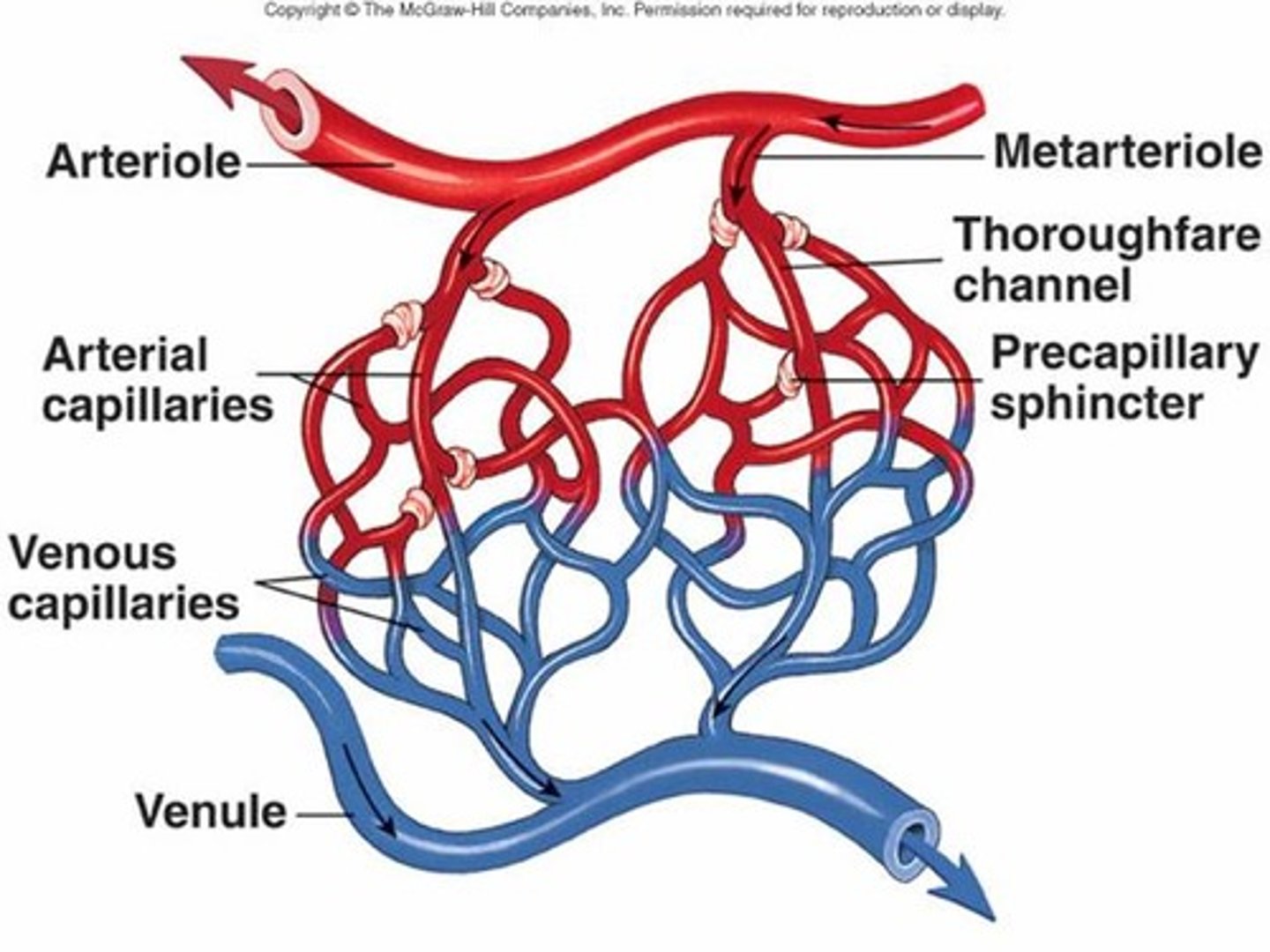
Metarterioles
Intermediate vessel between arteriole and capillary, contain pre-capillary sphincters to control flow into capillaries
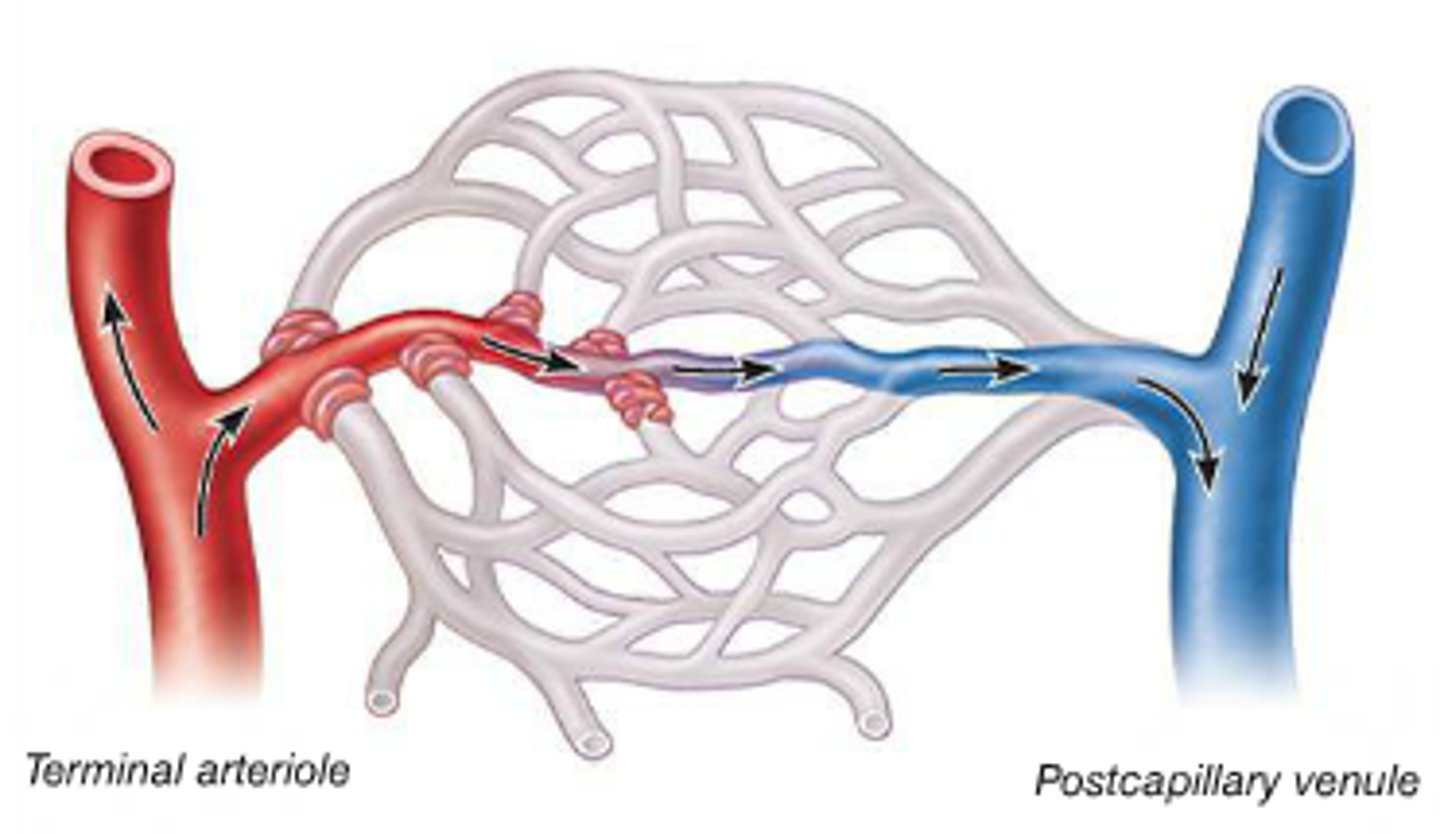
Post capillary venules
drain the capillary beds
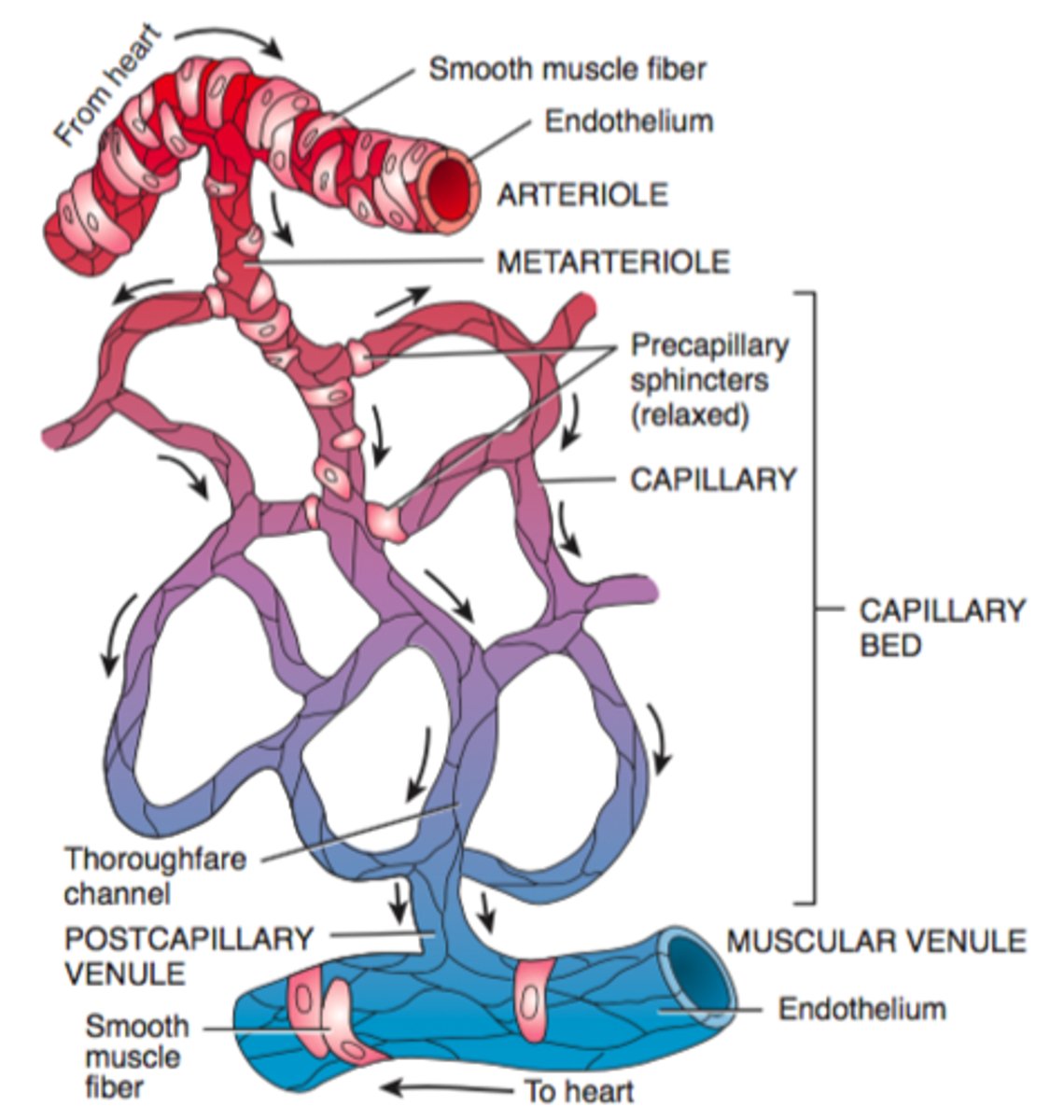
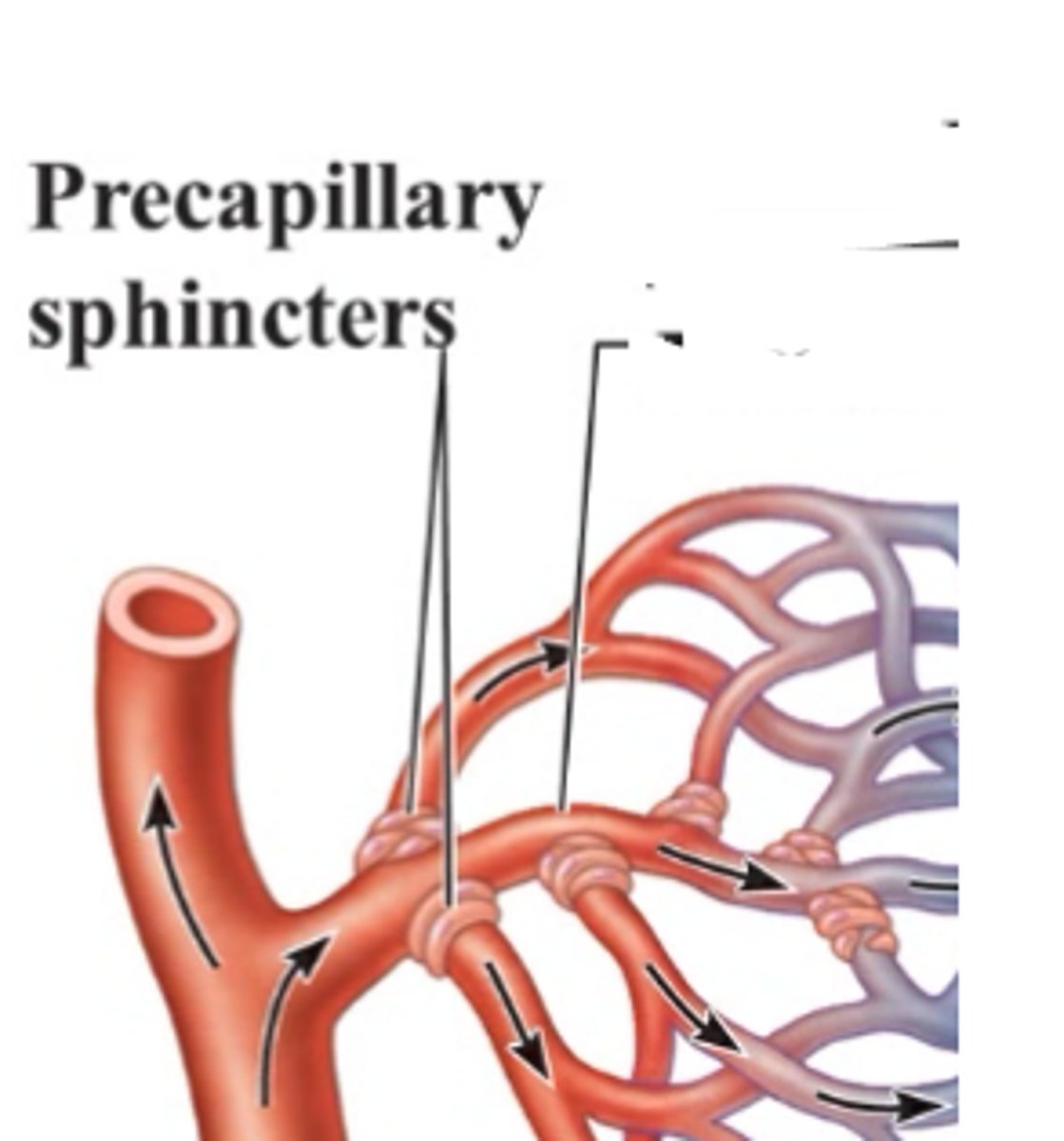
Precapillary sphincters
can contract or relax to prevent blood from flowing or allow blood to flow from the metarteriole into the capillary
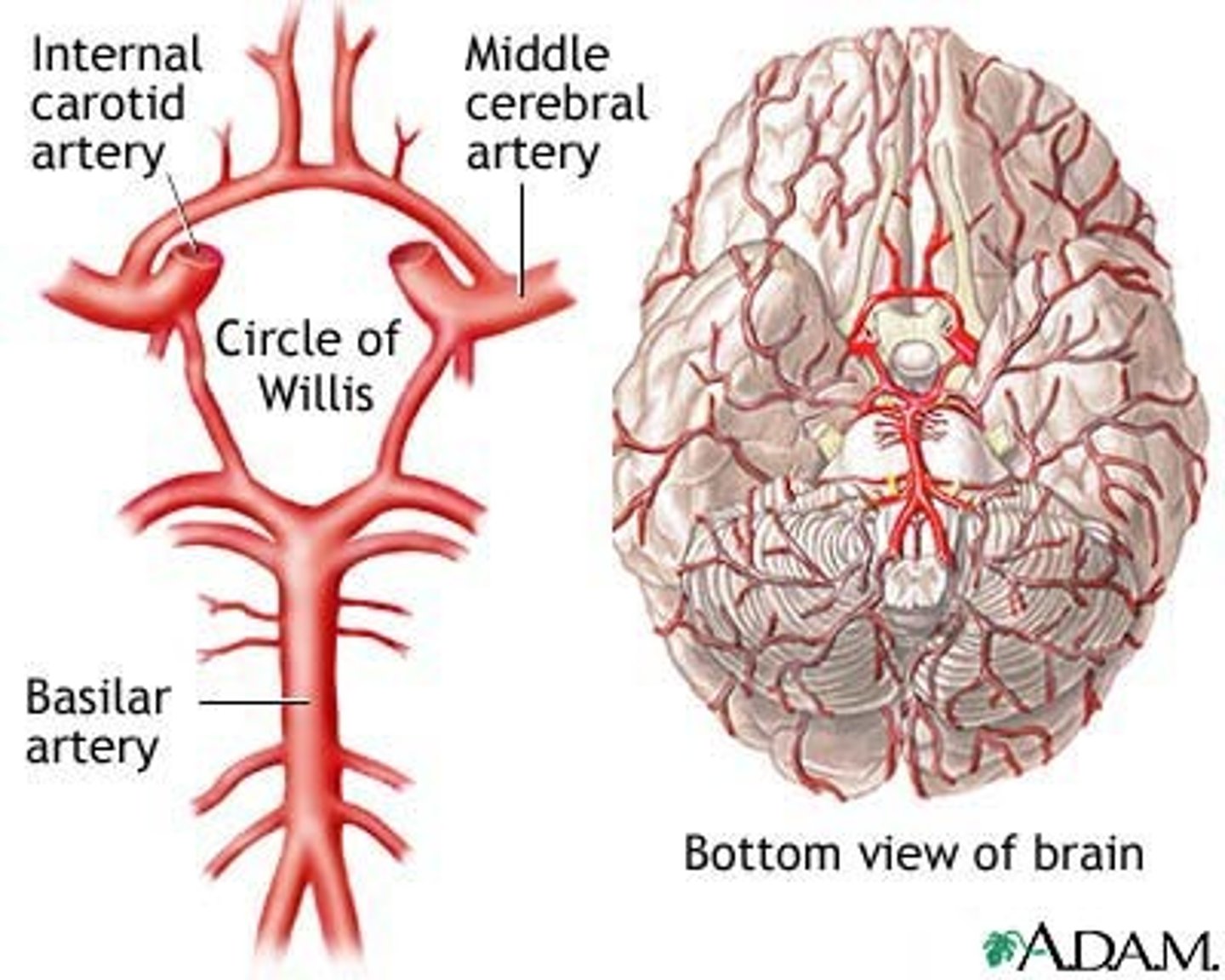
Arterial anastomosis
where two or more arteries supply blood to the same region. Eg. - cerebroarterial circle (circle of Willis), coronary circulation
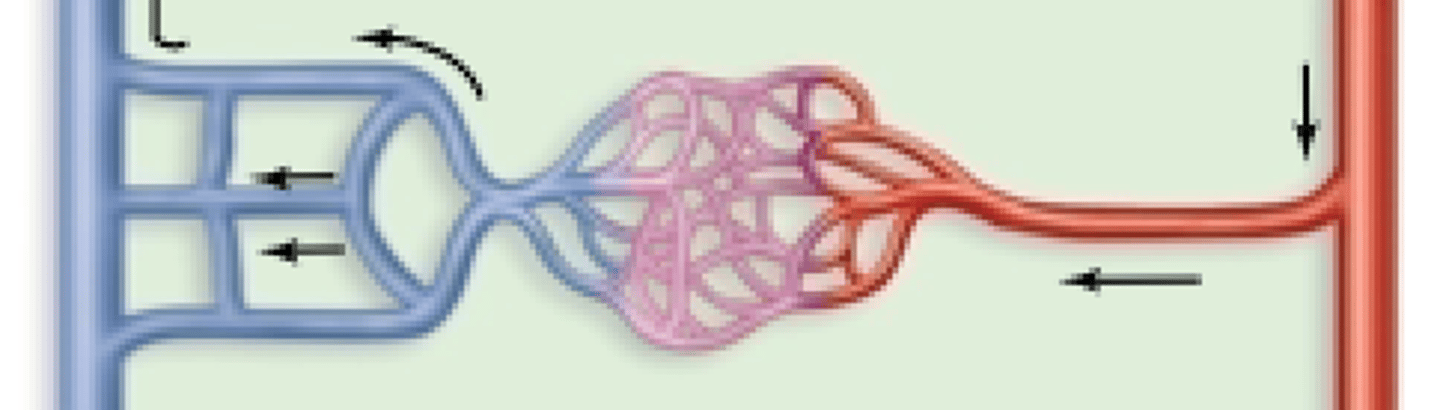
Venous anastomosis
most common type of anastomoses, where two or more veins drain blood from the same region. E.g. superficial veins draining into deep veins
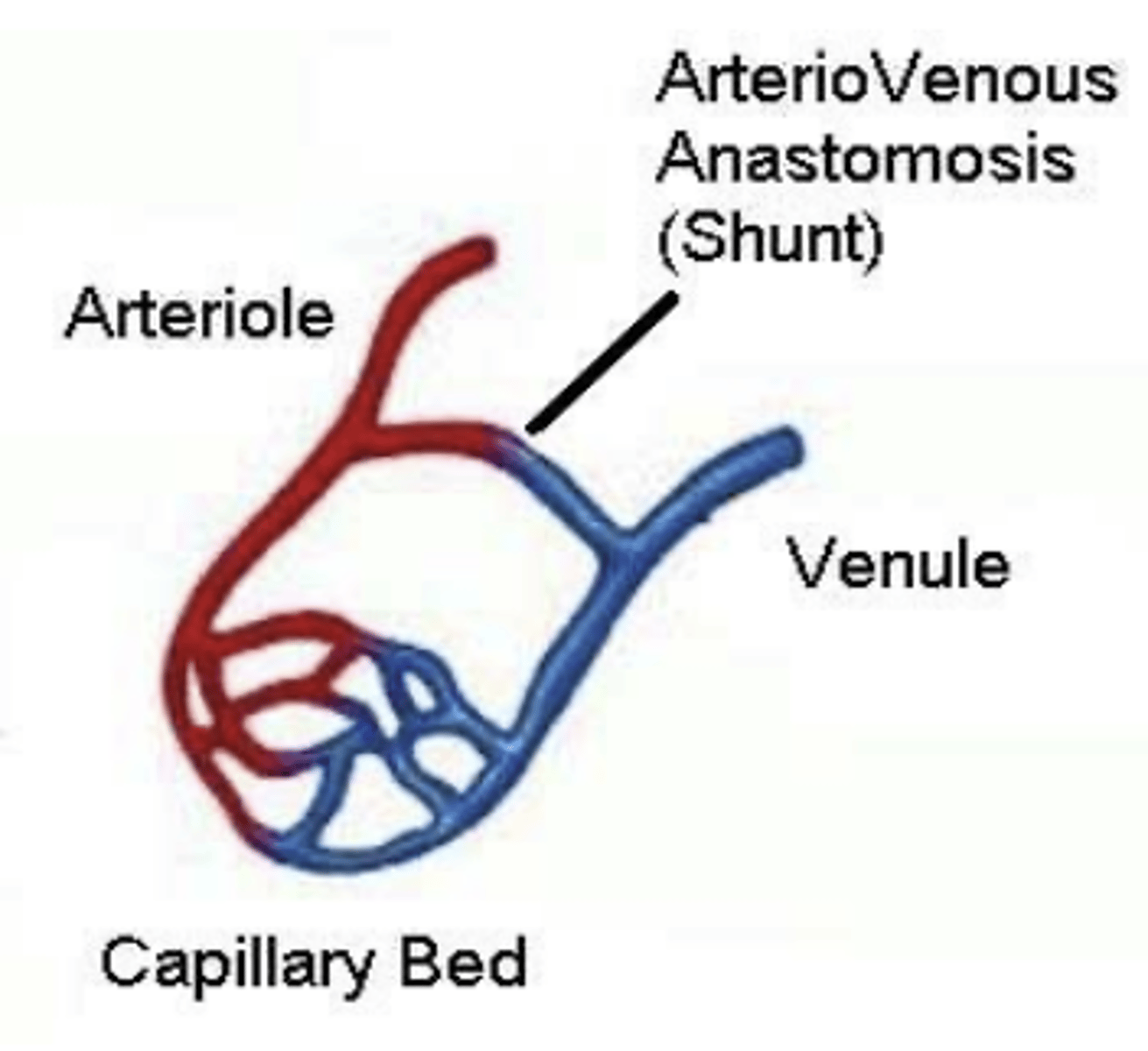
Arteriovenous anastomosis (shunt)
artery connected to a vein, bypassing a capillary bed. Found in areas subject to frostbite, used when there is a risk of hypothermia
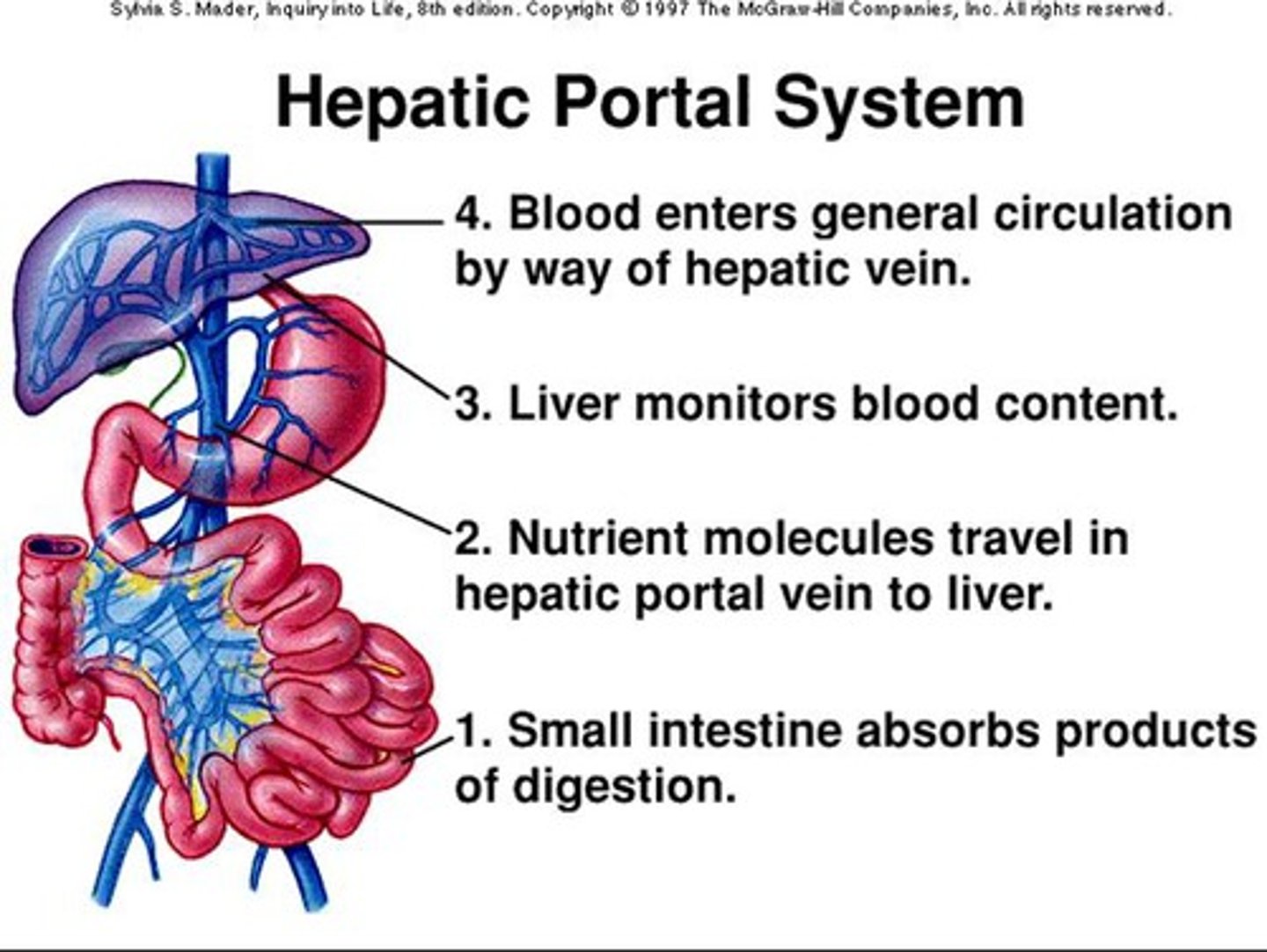
Portal system
blood flows through two consecutive capillary networks before returning to the heart. E.g. hepatic portal system
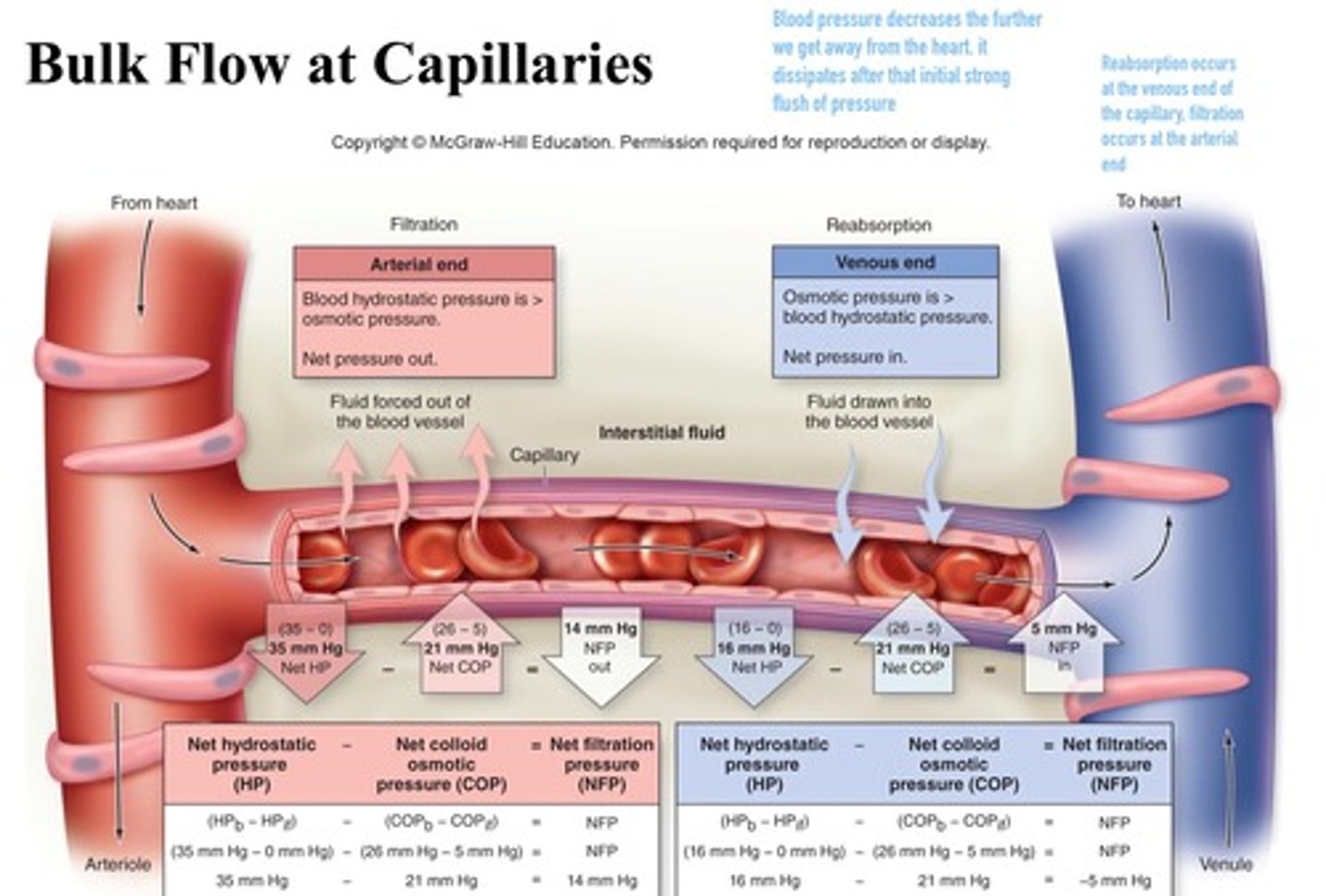
Capillary exchange
constant exchange of substances between blood (plasma) and interstitial fluid
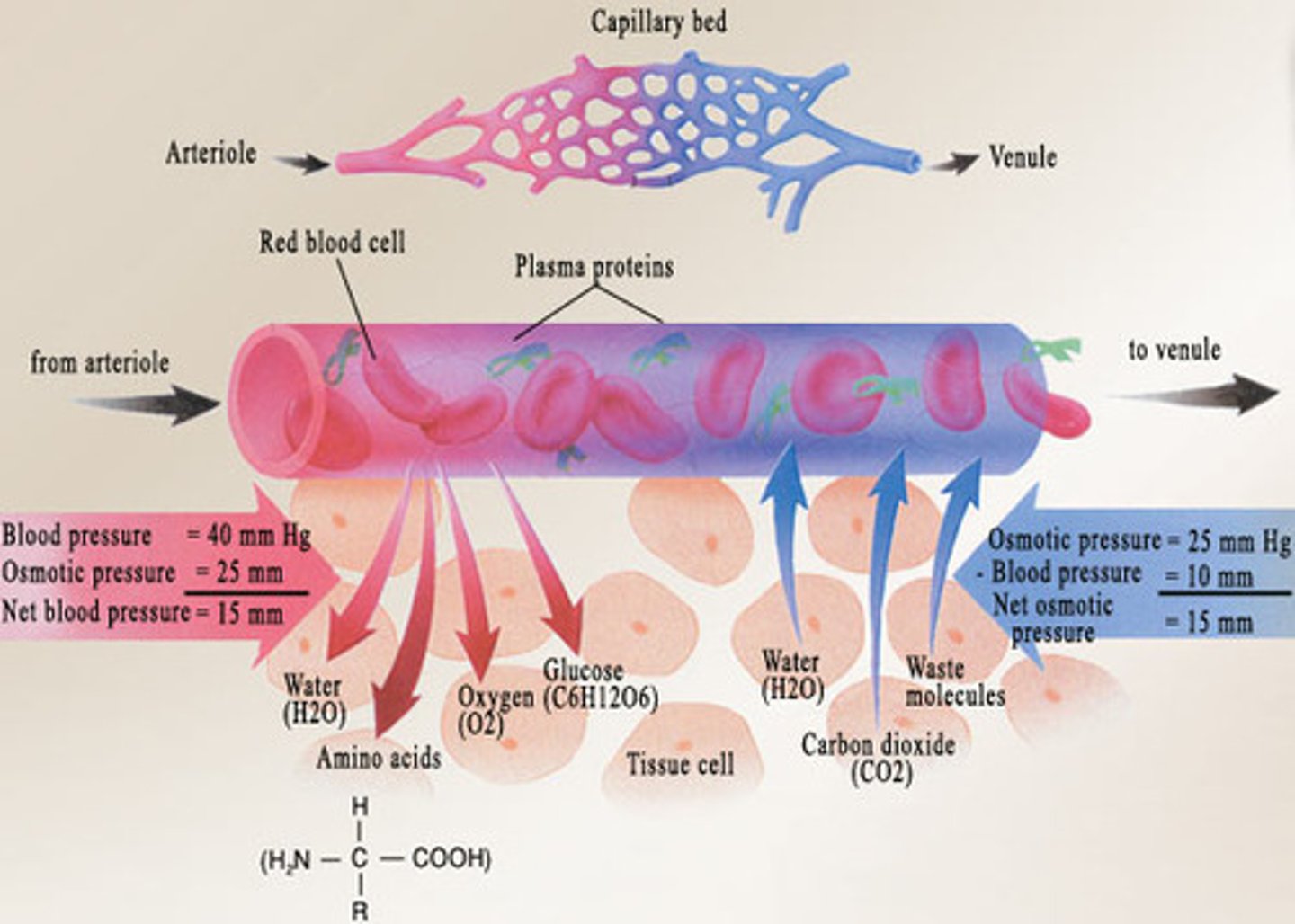
Bulk flow in capillaries
movement of a fluid due to a difference in pressure between capillaries and the interstitial fluid
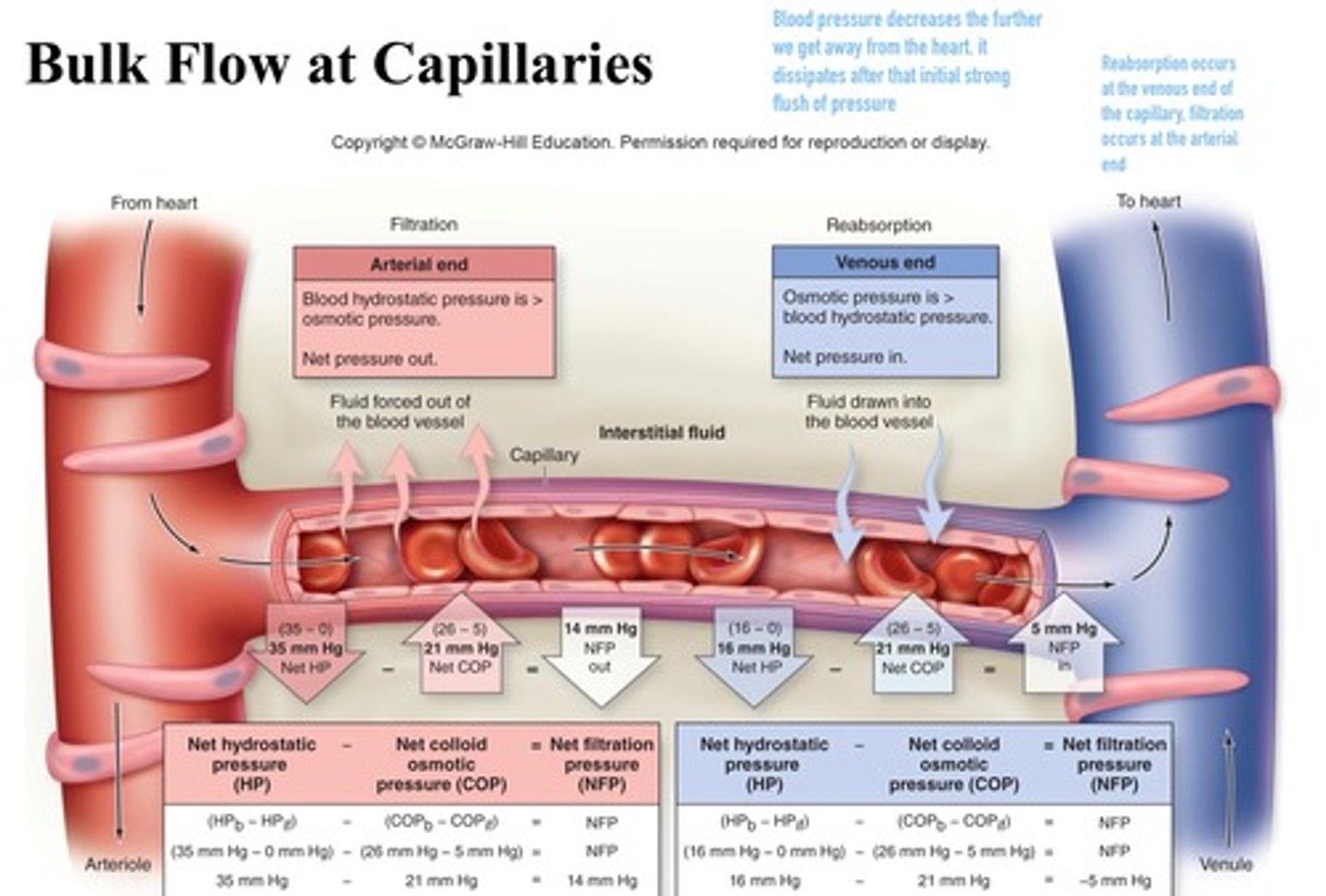
Filtration
type of transport that takes place at the arterial end of a capillary bed. Water and dissolved solutes move from the capillary into the tissues (driven by pressure gradient)
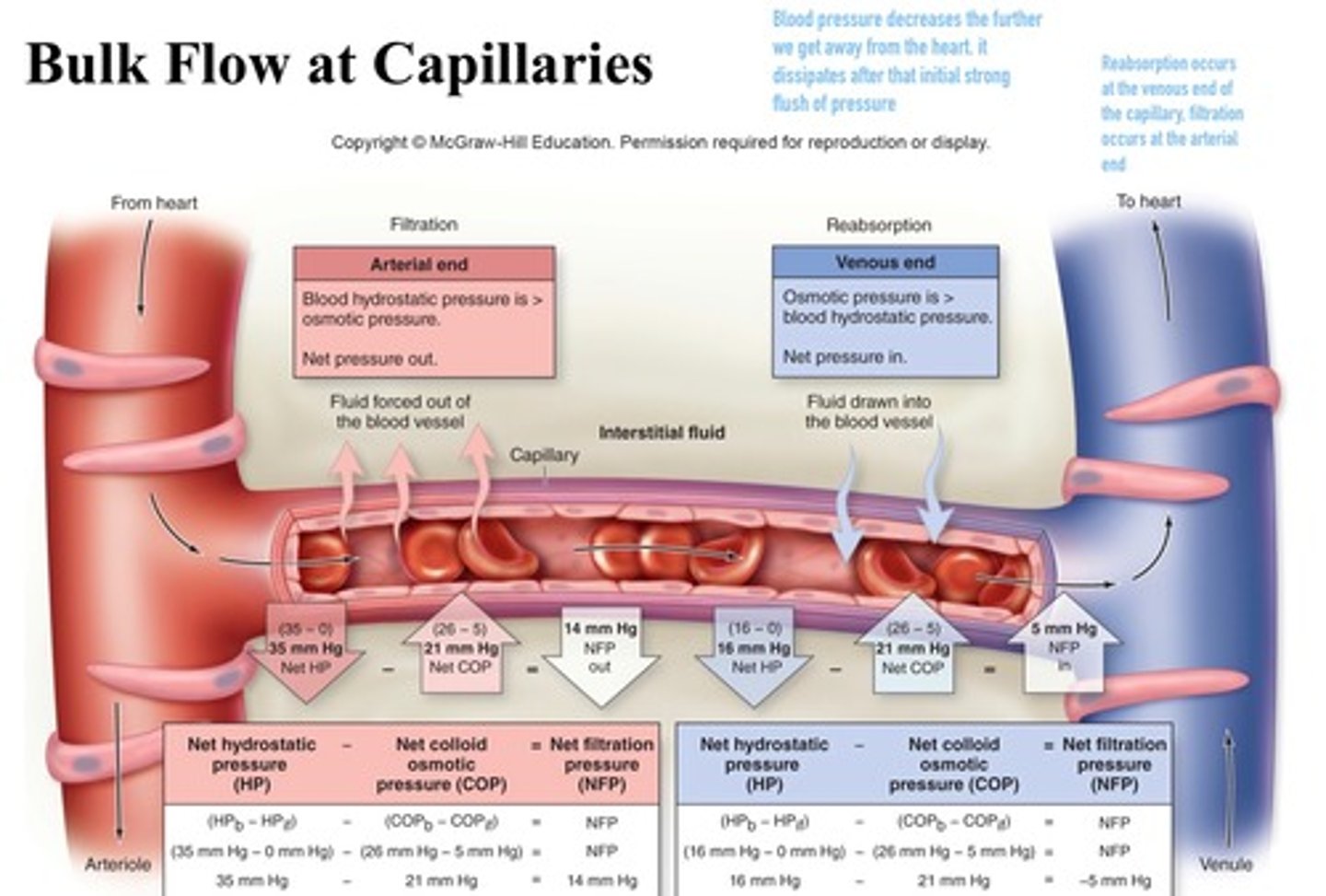
Reabsorption (Osmosis)
type of transport that occurs at the venous end of a capillary bed. Water and dissolved wastes move from the tissue into the capillary
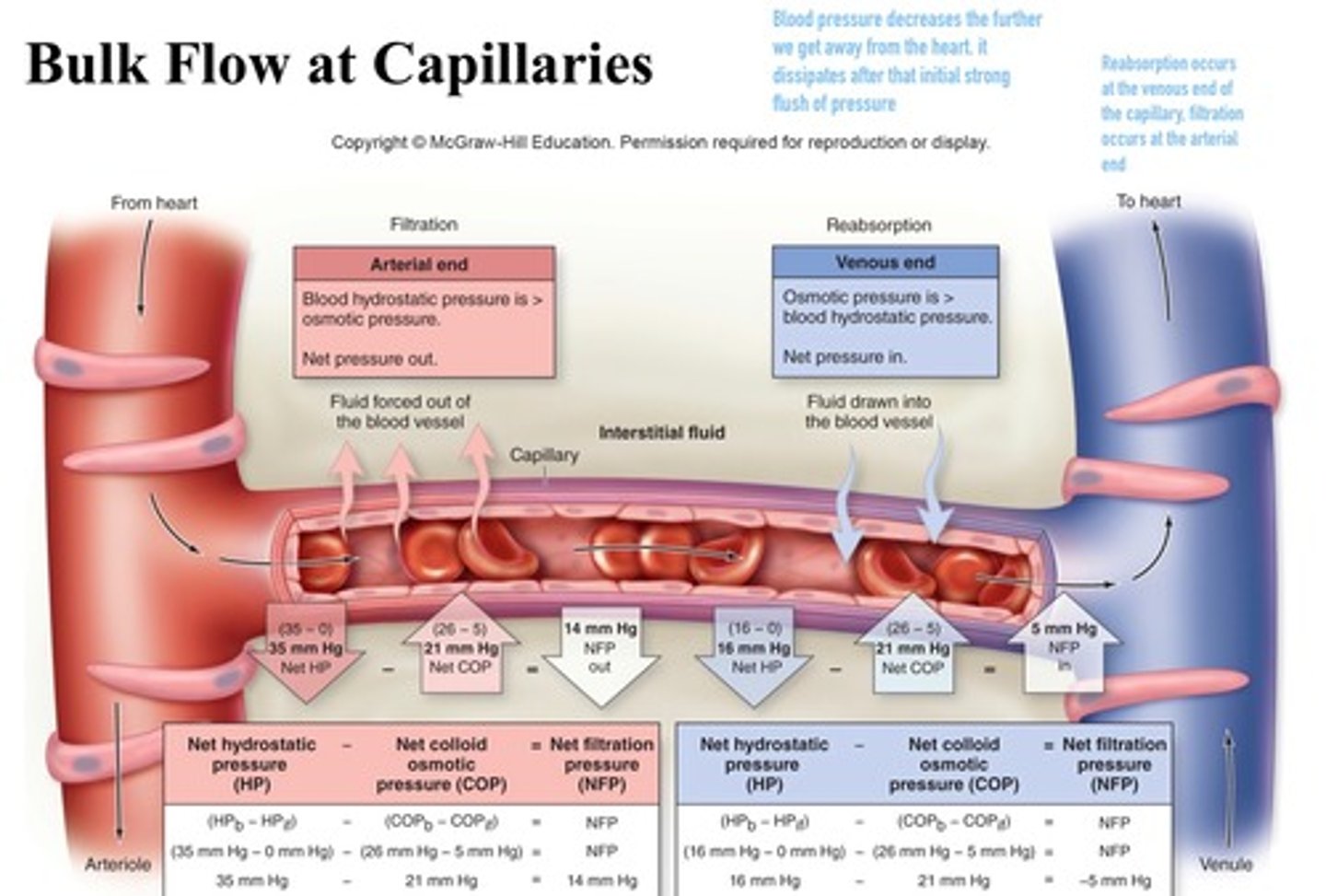
Net hydrostatic pressure
is the difference between the hydrostatic pressure of the blood and hydrostatic pressure of the interstitial fluid
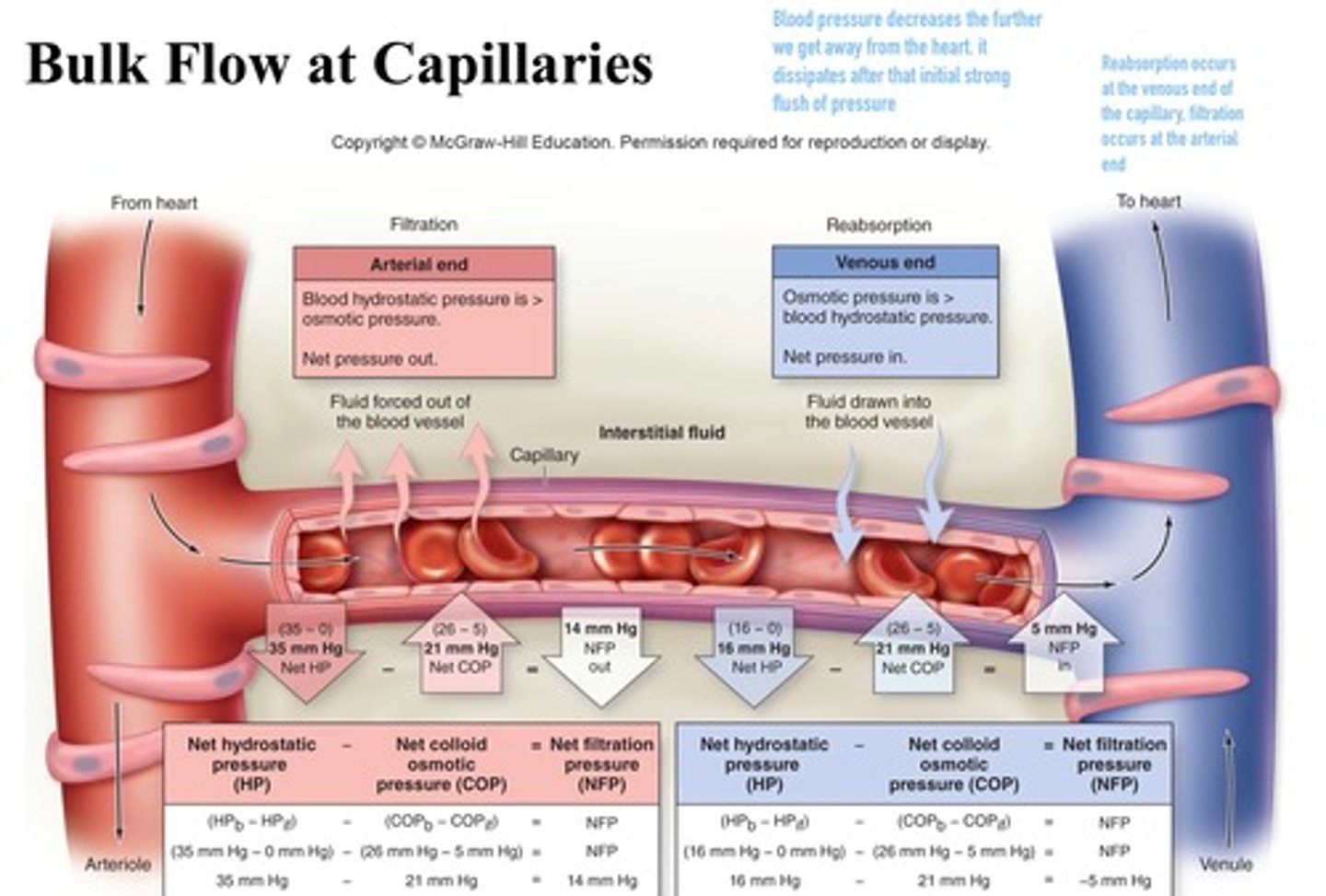
Net colloid osmotic pressure
is the difference between the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood and the colloid osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid