Orgo 1 Reactions
1/221
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
aldehyde (rxn with formaldehyde isn’t useful), ketone, acid chloride
What carbonyls does NaBH4 react with?
Carboxylic acids and amides
What carbonyls do grignard reagents and organolithium NOT react with?
Aldehydes (and formaldehyde), ketones, acid chlorides, esters, CO2
What carbonyls DO grignard reagants and organolithium react with?
All of them except CO2 and rxn with formaldehyde isn’t useful
What carbonyls des LiAlH4 react with?
An aldehyde
What can a grignard react with to form a 2° alcohol?
Aldehydes and acid chlorides
What can both hydrides react with to form a 1° alcohol?
Esters and carboxylic acids
What can ONLY LiAlH4 react with to form a 1° alcohol?
deprotonation to form a carboxylate anion
What happens when only ONE EQUIVALENT of LiAlH4 is reacted with a carboxylic acid
Acid chloride, esters
What carbonyls have normal leaving groups?
Need to add 2 equivalents
What does having a leaving group mean?
Amides and carboxylic acids
In which carbonyls does O-AlH3 function as the leaving group?
3, LiAlH4
How many equivalents do I need to add to carboxylic acid to turn it into a 1° alcohol? What do these equivalents have to be?
aldehyde
What does a grignard reagent/organal lithum react with to form a 2° alcohol?
A ketone
What can BOTH LiAlH4 and NaBH4 react with to form a 2° alcohol?
A ketone
Which is more unstable a ketone or ester?
Ketones, acid chlorides, esters
What carbonyls can a grignard reagent/organolithium react with to form a 3° alcohol?
hydrides
What type of reagent in carbonyl rxns CAN NOT form a 3° alcohol
React CO2 with a griganrd reagent or organolithium
How to form a carboxylic acid with carbonyls
React an amide with LiAlH4
How to form an amine with carbonyls
formaldehyde
What type of carbonyl when reacted with NaBH4 and LiAlH4 makes not useful products?
No because they’re resonance stabilized and the O is negative (repels the nucleophile)
Do carboxylate anions react with grignard or organolithium?
Deprotonation
What happens when the first equivilent of LiAlH4 is added to a carboxylic acid?
3
How many equivilants on LiAlH4 do you need to add to carboxylic acids to create a primary alcohol
Deprotonation
What happens when grignard, organolithium, and NaBH4 react with carboxylic acids?
2 attached atoms with opposite charges
Defintion of ylides
Ketones and aldehydes
What carbonyls do sulfur ylides react with?
Ketones and aldehydes
What carbonyls do phosphonium ylides react with?
Epoxides
When reacted with ketones and aldehydes what functional group do sulfur ylides form?
Alkenes
When reacted with ketones and aldehydes what functional group do phosphonium ylides form?
Oxygen’s LP
What makes up the 3rd bond in an epoxide formed by a sulfur ylide?
Sulfur dimethyl+(Methyl w/ LG), 1 set of Sulfur LP grabs the C in the methyl group= (positively charged)Sulfur trimethyl+n-butyl lithium (acting as a base)= One of S’s methyl groups loses a H
How to form a sulfur ylide
acid/base
What type of reaction forms ylides
(Pph3+Lp)+ alkyl group with a leaving group+ Lp grab the C (C MUST HAVE AT LEAST 1 H)=alkyl group attached to (positively charged) Pph3 (with the attached C having at least 1 H)+n-butyl lithium which takes a proton
How to form wittig reagents/phosphonium ylides
You can add lots of different alkyl or non-alkyl groups to them to get the product you want
What’s unqiue about phosphonium ylides?
P’s LP
What makes up the new C-P bond in the creation of a P ylide?
No
When attaching a Pph3 group to a carbon group do you gain a C?
The one directly bonded to the positive atom
Which C does n-butyl lithium take the H from (in the formation of ylides)?
The C- (directly bonded to the +atom)
What acts as the nucleophile in ylides?
2
If you create an OH with an epoxide how many Cs away is the nucleophilic C/the new C bond?nucleophilic
1
If you create an OH with a carbonyl how many Cs away is the nucleophilic C/the new C bond?
Gain of bonds to O
Oxidation
Gain of bonds to H
Reduction
reductions
What type of rxn is it when we react hydrides to carbonyls?
primary amines
What do nitriles reacted with LiAlH4 form?
Jones reagent
Chromic acid
Chromic acid
Jones Reagent
Jones/Chromic acid has water, PCC does not
Difference between PCC and Jones/Chromic acid?
oxidations
What type of rxns do Jones and PCC do when reacted with OHs
No rxn
Jones AND PCC with tertiary OH
Ketone
Jones and PCC with secondary OH
Primary
What type of alcohol differs with Jones and PCC
Carboxylic acid
Primary OH with Jones
aldehyde
Primary OH with PCC
Use Jones or PCC to get to a carbonyl
1st step in turning an OH into an alkene or epoxide
Change your OH into a carbonyl to avoid an acid base rxn
What should you do before creating a grignard if an OH is present?
mCPBA
reagent that forms an epoxide THAT IS NOT sulfur ylide
syn addition
type of epoxide addition with mCPBA
Grignards/organolithium and LiAlH4
What can epoxides react with?
React it with 2 eqvs of LiAlH4
How to form amines with a nitrile
An alkene
What does mCPBA react with to form an epoxide?
hydrate
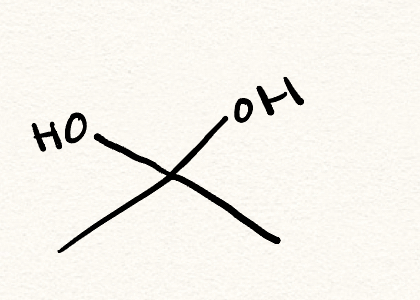
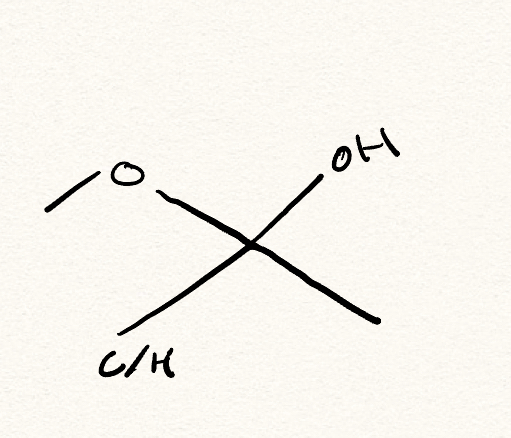
hemiacetal/hemiketal
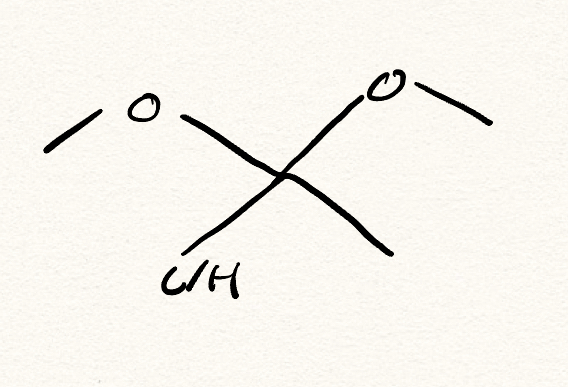
acetal/ketal
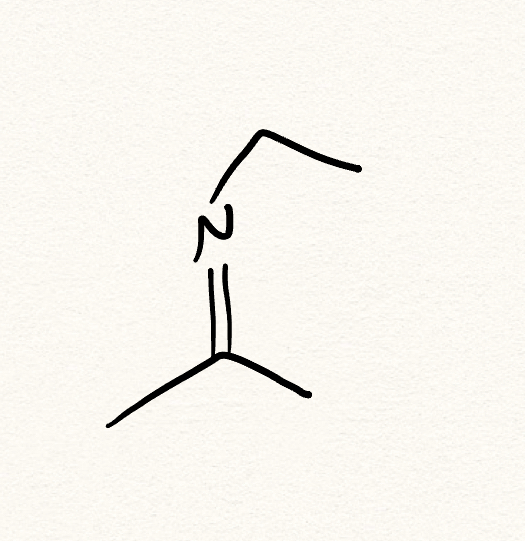
imine
enamine
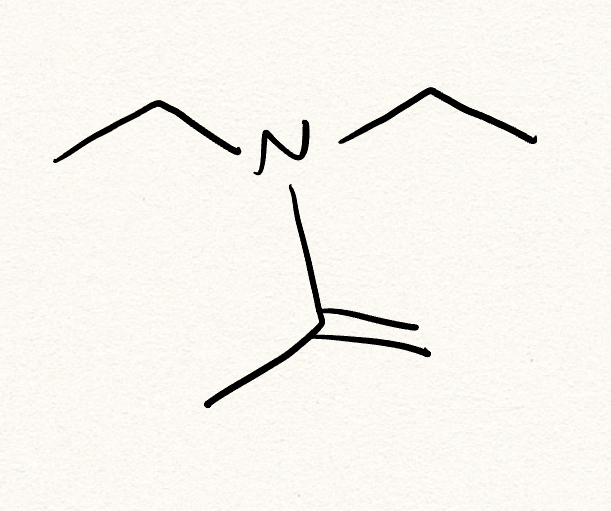
H2O (water)
What is the nuc for hydrate synthesis?
Alcohol
What is the nuc for hemiacetal/hemiketal synthesis?
Alcohol
What is the nuc for acetl/ketal synthesis?
1 amine
What is the nuc for imine synthesis?
2 amine
What is the nuc for enamine synthesis?
Add water
How to favor the hydrate (product)?
Remove water
How to favor the reactants (ketone/aldehyde) in hydrate synthesis?
remove water
How to favor the acetal/ketal (product)?
add water
How to favor the reactants (aldehyde or ketone) in acetal/ketal synthesis?
An acetal or ketal but with one addition instead of 2 and a deprotonation of that addition
What is a hemiacetal/hemiketal
The catalytic H+
What gives you the proton for protonation in hydrate, acetal, metal, imine, and enamine synthesis?
Water
What acts as your base when you add water?
the OH
What acts as your base when you’re removing water?
to favor acetal, ketal, enamine, and imine synthesis
When do you need to remove water?
To favor the formation of aldehydes and ketones from hydrates and to favor the formation of acetals, ketals, imines, and enamines from ketones and aldehydes
When do you need to remove water?
imine
What does a 1° amine +Ketone or aldehyde form?
enamine
What does a 2° amine + ketone or aldehyde form?
remove water
How to favor the imine side?
remove water
How to favor the enamine side?
add water
How to favor aldehyde or ketone synthesis from imines?
add water
How to favor aldehyde or ketone synthesis from enamines?
The N
What atom do we deprotonate from in the final step of imine synethsis?
The C closest to the iminium ion
What atom do we deprotonate in the final step of enamine synthesis?
1° amine
What is the nucleophile in imine synthsis from ketones or aldehydes?
2° amine
What is the nucleophile in enamine synthsis from ketones or aldehydes?
H2N-NH2, KOH, Delta (heat)
Wolff-Kishner reagents
Synthesize amines from iminium ions
What does reductive amination do?
NaBH3-CN+ 1eqv H+
Reductive amination reagent
The C= to the N
Where does the H- from the reductive amination reagent (Na-BH3-CN) attack?
Aldehyde/ketone, cat. H+, (-H2O), 1° amine
Reagents for imine synthesis
Aldehyde/ketone, cat. H+, (-H2O), 2° amine
Reagents for enamine synthesis
aldehyde/ketone, cat. H+, (-H2O), (an OH)
Reagents for Ketal/Acetal synthesis
aldehyde/ketone, cat. H+ (+H2O)
Reagents for hydrate synthesis