Biology Lab Final
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What are the four phases of Mitosis?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
What comes after Telophase?
Cytokinesis
What is a cuvette?
Small, rectangular container which holds water samples for wavelength observation
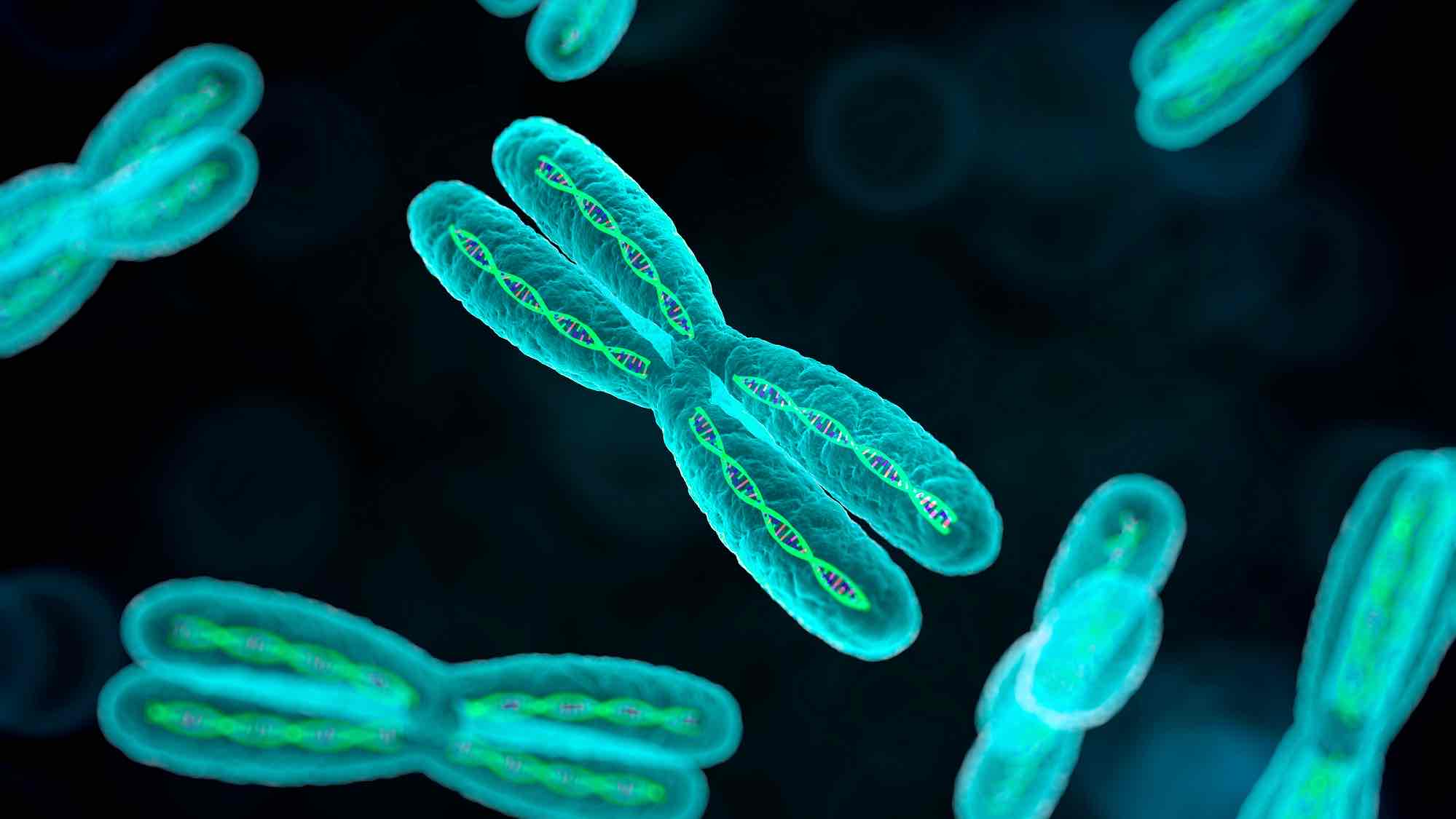
Is this a Chromosome or Chromatid?
Chromosome

Chromosome or Chromatid?
Chromatid
What is a Homologous chromosome?
The same chromosome, one from mom, one from dad
Does crossing over happen in Mitosis or Meiosis?
Meiosis
What does Polygenic mean?
One gene codes for multiple traits
What is a phenotype?
The physical expression of a gene
What is Co-Dominance?
When both traits are expressed equally
What is a example of a Co-Dominant trait?
Blood type
Why did we wrap foil around the tube in the photosynthesis lab?
To prevent sunlight from hitting the plant
What does O2 mean?
Oxygen
What does Co2 mean?
Carbon Dioxide
Where does Glycolysis take place?
The cytoplasm
What is the end goal of cellular respiration?
To create ATP
What does Anaerobic mean?
No oxygen required
What does Aerobic mean?
Oxygen is present/required
Where is ATP stored?
Phosphate bonds
Which type of bonds hold DNA together?
Hydrogen bonds
What is the backbone of DNA?
Phosphates/sugar
Is DNA single or double stranded?
Double
Is RNA single or double stranded?
Single
What are the end products of photosynthesis?
Oxygen and Glucose
What was the paper chromatography used for?
To observe the different pigments and how hydrophobic they are
Were the colors on the tip of the chromatography the largest or smallest molecules?
The smallest molecules
Name the stages of the cell cycle
G0, G1, S phase, G2
What replaces thymine in RNA?
Uracil
What does the “m” in mRNA stand for?
Messenger
What does the “t” in tRNA stand for?
Transfer
What is the role of tRNA?
To carry amino acids the ribosomes
What does the “r” in rRNA stand for?
Ribosomal
What holds amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
What does Locus mean?
The location of a gene on the chromosome
What happens in the G0 phase of the cell cycle?
Not much, cells are at rest, not dividing.
What happens in the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
Cells grow, cellular contents are duplicated, additional proteins and centrosomes and centromeres are produced
What happens in the S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA is synthesized and replicated
What happens in the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
Cells grow ridiculously quickly, preparing for mitosis, protein is synthesized, and DNA proofreading
What is Mitosis?
The process by which cells duplicate themselves
Why is Mitosis important?
It’s required for growth, repair, and development. It replaces worn out cells
What is the role of DNA Helicase?
To cut DNA for replication
What is the role of DNA polymerase?
Puts nucleotides back together
What do DNA helicase and DNA polymerase do?
Create complimentary strands for DNA
What is the role of Phenol Red?
To detect the presence of carbon dioxide
Does DNA have a positive or negative charge?
Negative?
What is KOH?
Potassium Hydroxide
What is the role of KOH?
To absorb Carbon Dioxide
What is the Photosynthesis equation?
Co2 + H2O > Photosynthesis > C6 H12 O6 + O2
True or False: Male flies have darker abdomen than female flies
True
Why was it important to place the flies on the side of the tube?
So they wouldn’t suffocate in the fly medium
Is XBXb colorblind or not?
No
Is XbYb colorblind?
Yes 💔
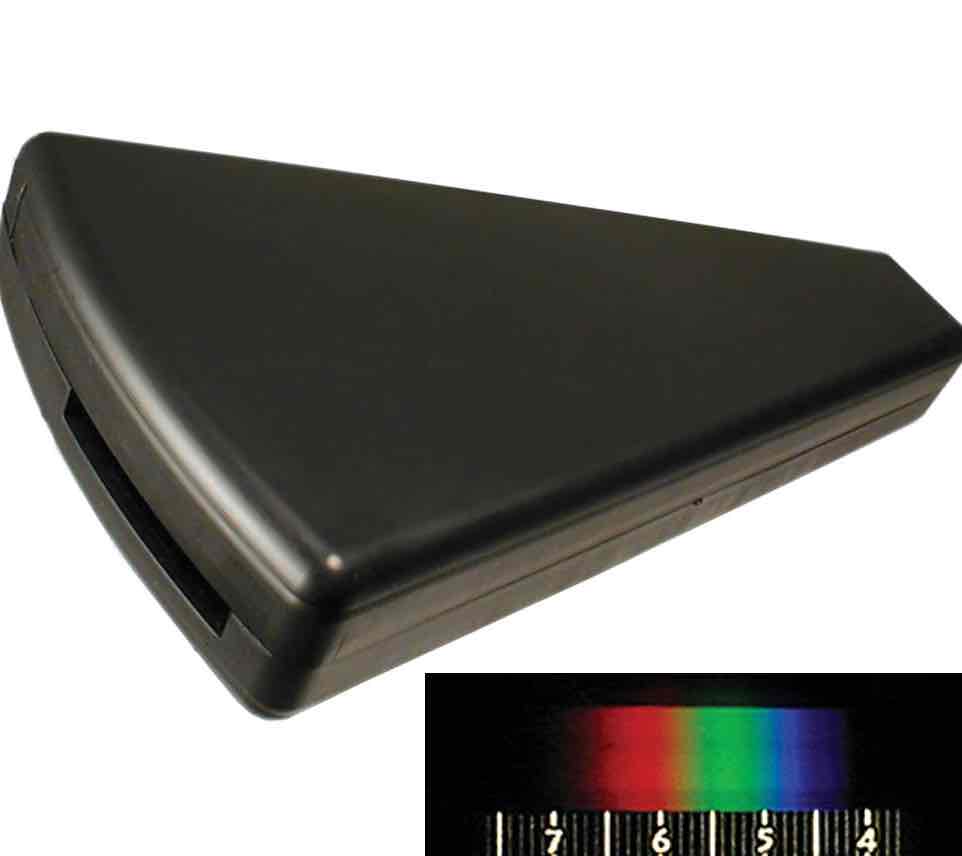

What does the light spectrometer do?
Helps us observe different color wavelengths
What is the law of segregation?
Chromosomes are separated in gametes, one from egg, one from sperm.
What is the Law of independent assortment?
One trait does not influence another. (Eye Color does not determine skin color)
During Gel Electrophoresis, does DNA move to the positive or negative side?
Positive
What is the Cellular Respiration equation?
C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 > Cellular Respiration > 6Co2 + 6H2O
Does DNA contain sulfur?
No
Name the Nucleotides of DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Name the Nucleotides of RNA
Uracil, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine
What is the name of the contraction created in the Cellular Respiration experiment?
Respirometer

In Gel Electrophoresis, DNA moves based on..
Size and shape. The smaller it is, the faster it’ll move
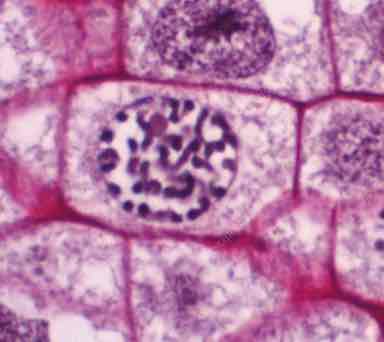
What phase is this cell in?
Prophase
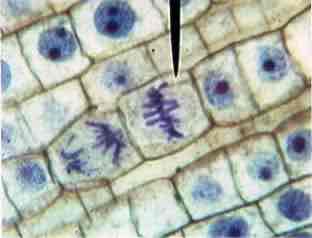
What phase is this cell in?
Metaphase
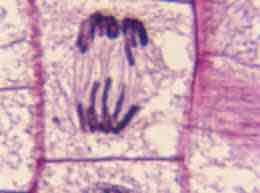
What phase is this cell in?
Anaphase
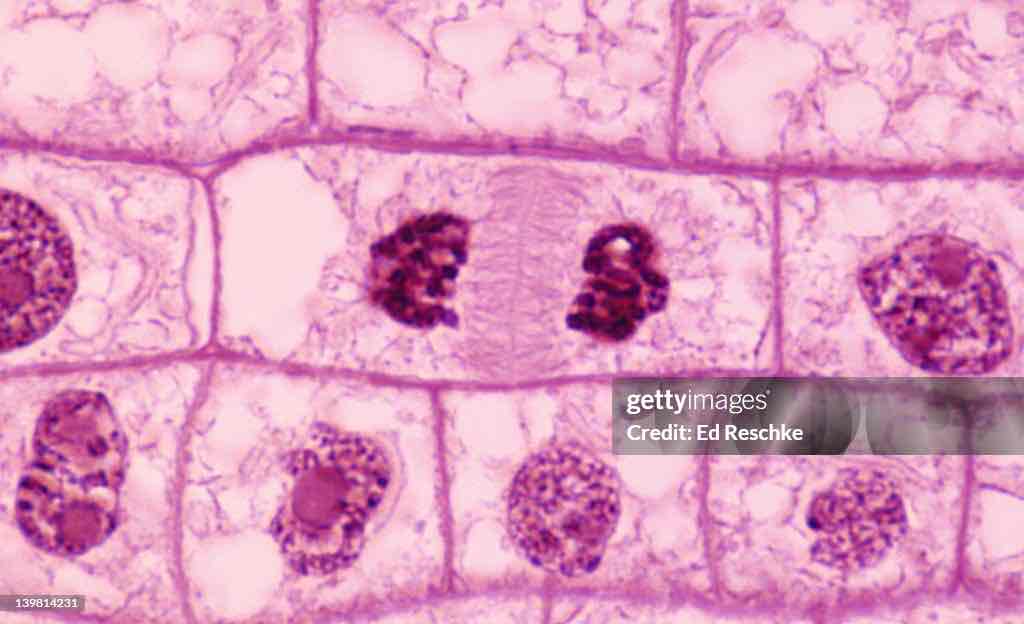
What phase is this cell in?
Telophase
In plant cells, the ____ is present in telophase.
Cell plate
True or False: Animal cells have a cell plate in telophase
False
What happens in prophase?
The nucleus begins to dissolve and chromosomes begin to disperse
What happens in metaphase?
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
What happens in Anaphase?
Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart, toward opposite ends of the cell
What happens in Telophase?
Sister chromatids are pulled completely apart, cleavage furrow forms and nucleus begins to form around the new cell.
What happens in cytokinesis?
Cells divide completely, we have two cells now!
How many chromosomes are in each cell at the end of mitosis?
46
How many daughter cells are created at the end of meiosis 1?
2
How many daughter cells are created at the end of meiosis 2?
4
How many chromosomes are in each cell at the end of Meiosis 1?
23
How many chromosomes are in each cell at the end of meiosis 2?
23
What is a Karyotype?
A chart of an organism’s chromosomes
What is a Genotype?
The genetic makeup of a trait
What is an allele?
An alternate form of the same gene
True or False: Celluar Respiration makes energy
False, it stores energy
Where is energy stored?
Molecular bonds
When is energy released?
When the molecular bonds are broken
Where is DNA stored in prokaryotes?
The cytoplasm
Where is DNA stored in eukaryotic cells?
The Nucleus
What is the first step of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
If the Phenol Red tube is red, what does that mean?
There is no Co2 present
If the Phenol Red tube is yellow/orange, what does it mean?
There is Co2 present
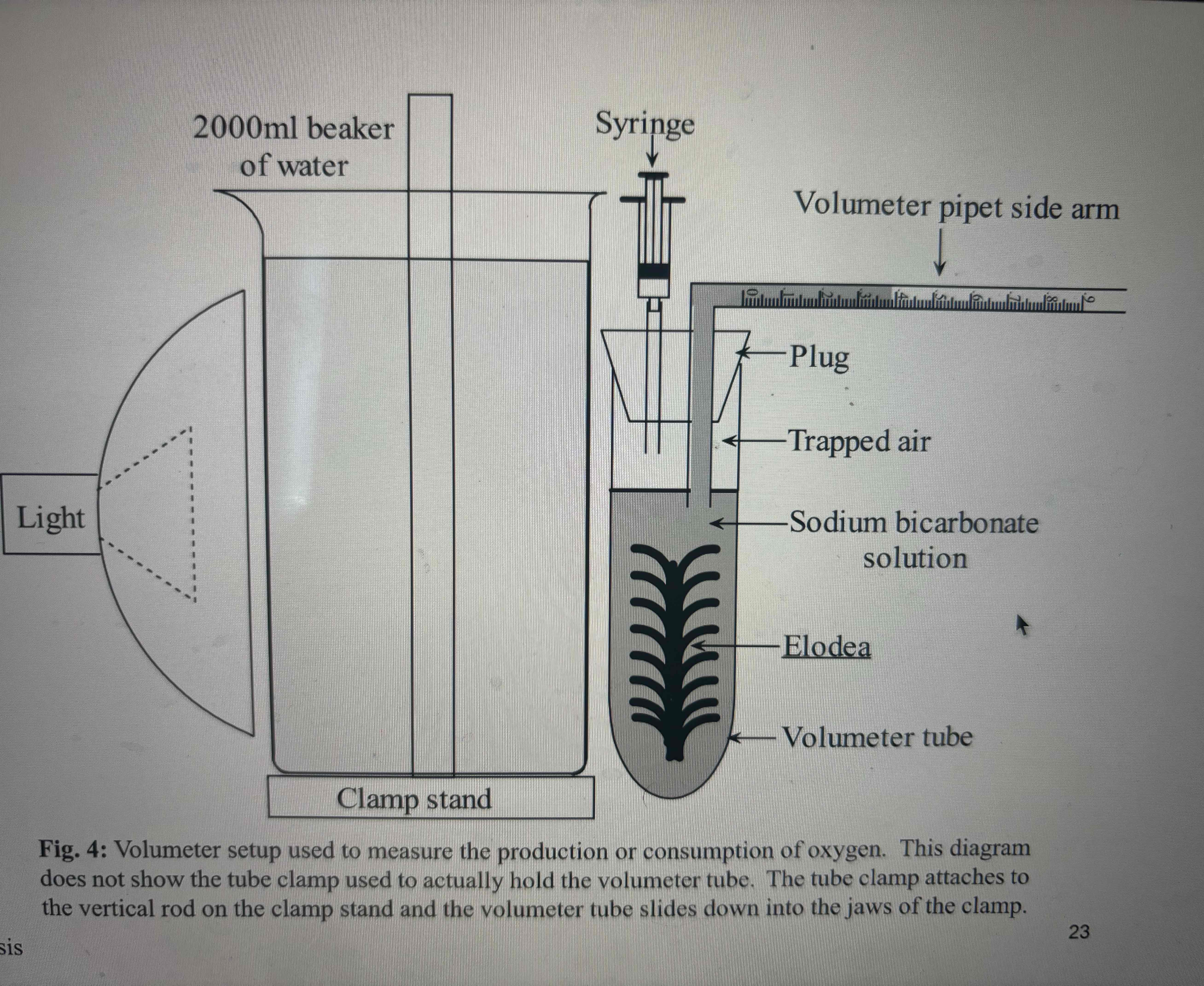
What is the name of the contraption created for the photosynthesis experiment?
Volumeter ( horrible photo💔)