inorganic chemistry - acids, bases, salt prep
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
describe a neutralisation reaction in terms of proton transfer
neutralisation reaction - proton is transferred from acid to base
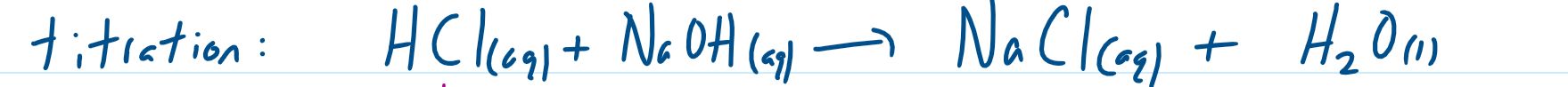
which are the spectator ions (for neutralisation reaction)
what is the ionic formula
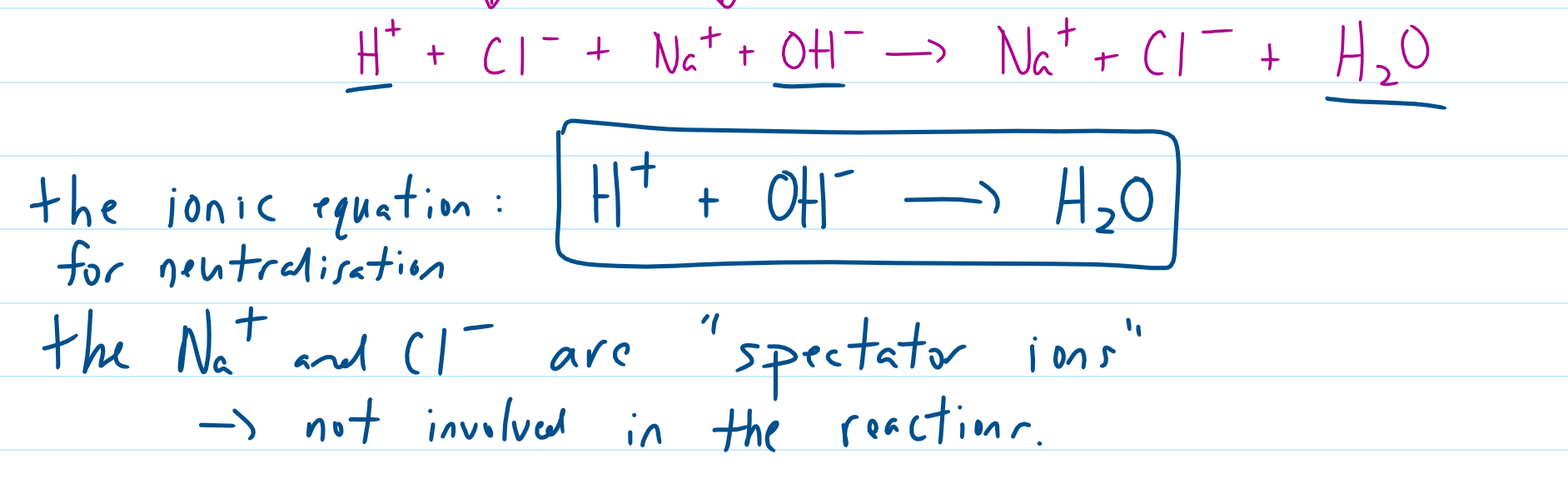
_____, ______ and _____ compounds are soluble
sodium, potassium, ammonium
all _______ compounds are soluble
nitrates
chloride compounds are ____ except with _______ and _____
chloride compounds are SOLUBLE, except with
silver and lead (II)
sulfate compounds are _______ except with ______ ________ _______
soluble, except with
barium, calcium, lead
carbonate compounds are _____ except with ____ _____ _____
carbonate compounds are INSOLUBLE
except with sodium, potassium, ammonium
hydroxide compounds are _______ except with ___x3
hydroxide compounds are INSOLUBLE except with
sodium, potassium, ammonium
what is calcium hydroxide, is it soluble
slightly soluble in water
limewater
acids are proton ______
what makes the solution acidic
donors
H+ ions make the aqueous solution acidic
bases are proton _______
what makes the solution alkaline
acceptors
OH- ions make the aqueous solution alkaline
what are bases vs alkali
alkali are soluble in water
bases may not be soluble
all alkali are bases but not all bases are alkali
general equation
metal + acid →
metal + acid ⟶ salt + hydrogen
Zn + H2s04 →
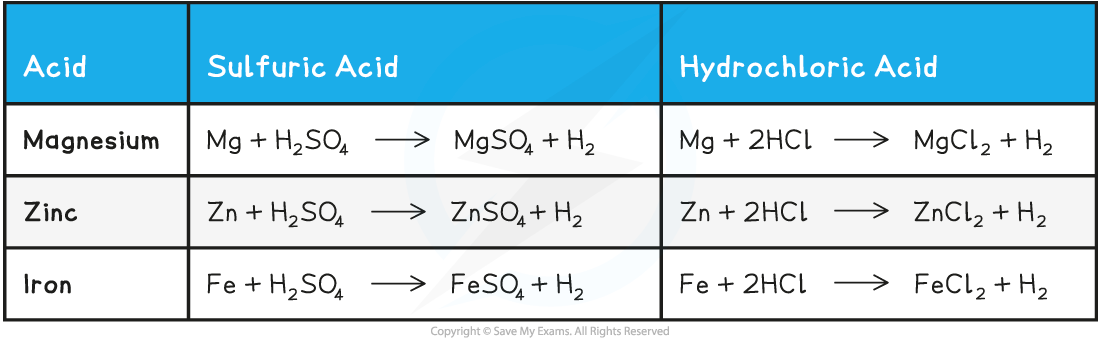
general equation
acid + base →
acid + base ⟶ salt + water
Metal oxides and metal hydroxides act as _____
Metal oxides and metal hydroxides act as bases
If in an acid-base reaction there is effervescence produced then the base must be a metal _______ which produces ____ ______ gas.
If in an acid-base reaction there is effervescence produced then the base must be a metal carbonate which produces carbon dioxide gas.
general equation
metal oxide + acid
metal oxide + acid → salt + water
(metal oxide is a base)
general equation
metal hydroxide + acid
metal hydroxide + acid → salt + water
(metal hydroxide is a base)
acid + ammonia →
acid + ammonia → ammonium salt
metal carbonate + acid →
metal carbonate + acid → salt + carbon dioxide + water
In basic (alkaline) conditions litmus paper turns ____ to _____
red to blue
metal oxides, hydroxides and carbonates are bases, but also this weird one:
ammonia solution
when ammonia gas dissolves in water it forms ammonium hydroxide. Be careful to use the correct terminology: ammonia is the gas, NH3, ammonium is the ion present in ammonium compounds, NH4+
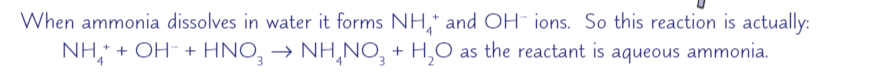
simple def, how to make an soluble salt
with solution + solid
from reaction of an acid with an insoluble base (in excess)
how is excess insoluble base removed
filtration
why add insoluble base in excess
the insoluble reactant is added in excess to ensure that all of the acid has reacted
any unreacted acid would become dangerously concentrated during evaporation and crystallisation
what is left after reaction, once acid reacted and solid base removed
Since all of the acid has reacted and the excess solid base has been removed then the solution left can only be salt and water
copper oxide + sulfuric acid equation, symbols
CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ⟶ CuSO4 (aq) + H2O (l)
how to sample of a dry soluble salt starting from an acid and an alkali - (8)
two parts
add alkali + phenolphthalein indicator to conical flask (25cm3 using pipette)
add acid to burette, record starting volume
add acid to alkali , swirling flask, until indicator changes colour. calculate volume of acid used.
repeat 1-3 and add acid dropwise near the point of neutralisation (colour change).
repeat 1-3 without indicator
transfer solution to evaporating dish/basin. heat until half water is evaporated, leave in warm place to cool and crystallise.
filter + rinse crystals with distilled water
leave to dry
why leave water behind in evaporating dish when crystalising
to allow for water of crystallisation in some salts and also to prevent the salt from overheating and decomposing.
reaction name for making insoluble salts
what is it
precipitation reaction
two solutions mixed together create insoluble salt
what is the pattern of a precipitation reaction
soluble salt 1 + soluble salt 2 ⟶ insoluble salt + soluble salt 3
AB + CD ⟶ AD + CB
how is precipitate recovered form result solution
precipitate is recovered by filtration and then it must be washed with distilled water remove contaminants, then left to dry
logic for a pure, dry sample of hydrated copper(II) sulfate crystals
CuSO4 is soluble, so either (acid/alkali titration - soluble salt) or (acid/excess insoluble base - soluble salt)
to make CuSO4 - H2SO4 + CuO
CuO, or any other copper metal compound will be INSOLUBLE
so need excess insoluble base (CuO) + acid (H2SO4)
steps for cuso4
heat acid until warm, then add CuO (insoluble) base until no more dissolves, mix with glass stirring rod.
filter mixture to remove excess base, transfer to evaporating dish
evaporate half the water from solution, leave to dry in warm place
filter/rinse the crystals with distilled water, leave to dry
why use excess CuO
so that all acid has reacted, otherwise it would become too concentrated and dangerous
also so that the acid doesn’t contaminate the crystals
why use a glass stirring rod instead of metal spatula
because metal could react with acid, glass won’t
why do crystals appear as the solution cools
if solution is saturated when hot
as it cools, it can dissolve/hold less crystals
so crystals form
how to prepare a dry sample of lead(II) sulfate from two soluble salts (solid first)
name of reaction
precipitation reaction
dissolve salts in water
mix together, stir with glass rod
filter to remove precipitate
rinse precipitate with distilled water
leave to dry
what are two salts that can be used to make lead sulfate
word equation
symbol equation
lead(II) nitrate + potassium sulfate → lead(II) sulfate + potassium nitrate
Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + K2SO4 (aq) → PbSO4 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)