Important Terms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply model
a model that explains short-run fluctuations in real GDP and the price level
Aggregate Demand (AD) curve
A curve that shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP demanded by households, firms, and the government (both inside and outside of the country)
Short-run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) curve
A curve that shows the relationship in the short run between the price level and the quantity of real GDP supplied by firms.
4 components of GDP
Consumption (C)
Investment (I)
Government purchases (G)
Net Exports (NX)
Nominal Assets
items that have value and are owned by an individual or organization
Movement along the AD curve will occur when _____ _____ changes and is NOT caused by a componentof real GDP changing
price level
A shift of the AD curve will occur when a _________ changes
component of real GDP
Monetary Policy
The actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue macroeconomic policy objectives.
Fiscal Policy
Changes in federal taxes and purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives
Aggregate Supply
the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply
Long-run Aggregate Supply (LRAS) curve
A curve that shows the relationship in the long run between the price level and the quantity of real GDP supplied.
Sticky
does not respond quickly to changes in demand or supply
3 reasons SRAS Curve is Upward Sloping
Contracts make some wages and prices sticky
Firms are often slow to adjust wages
Menu costs make some prices sticky
Supply Shock
an unexpected event that causes the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift
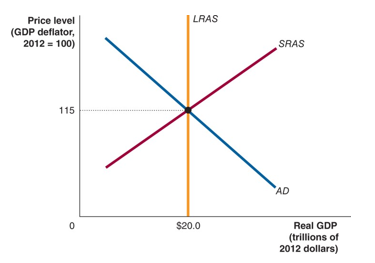
Long-run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
when the AD and SRAS curves intersect at the LRAS level; when the economy is in short-run equilibrium, and GDP is at its full-employment level
Stagflation
combination of inflation and recession, usually resulting from a supply shock
Main Factors that caused the Great Recession
The end of the housing bubble
The financial crisis
The rapid increase in oil prices during 2008
Keynesian Economics
a school of thought that focuses on the idea that government intervention can help stabilize the economy
Monetarism
the macroeconomic theories of Milton Friedman the idea that the quantity of money should be increased at a constant rate
Monetary Growth Rule
a plan for increasing the quantity of money at a fixed rate that does not respond to changes in economic conditions
New Classical Macroeconomics
emphasizes rational expectations, suggesting that individuals form forward-looking, unbiased predictions based on all available information.
Real Business Cycle Model
focuses on real, rather than monetary, causes of the business cycle
Austrian School of Economics
argues for the superiority of the market system over economic planning
Labor Theory of Value
attributed all of the value of a good or service to the labor embodied in it.