Special Senses - LCC
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
ciliary body (vascular tunic)
1; medial view
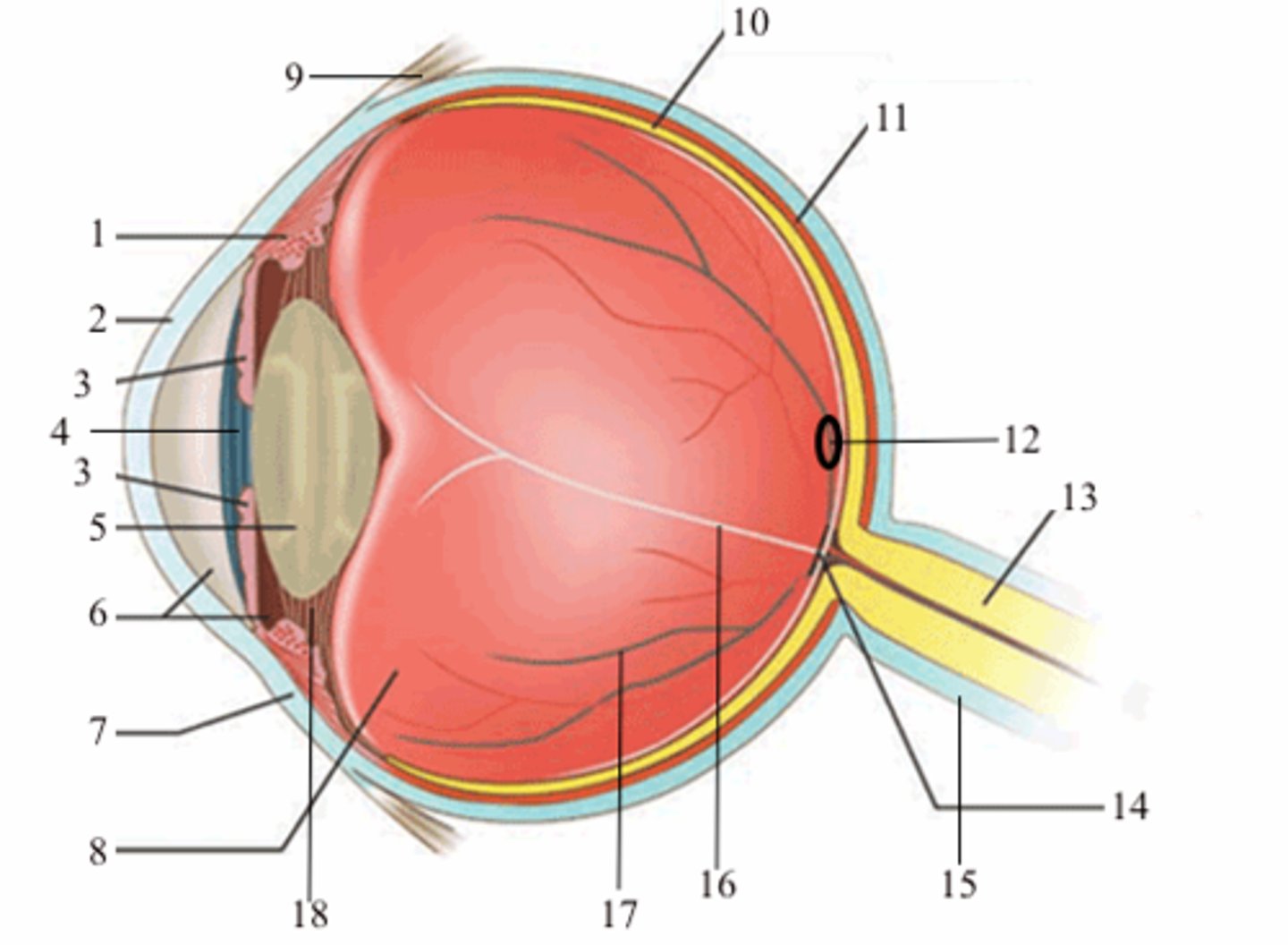
iris (vascular tunic)
3; medial view
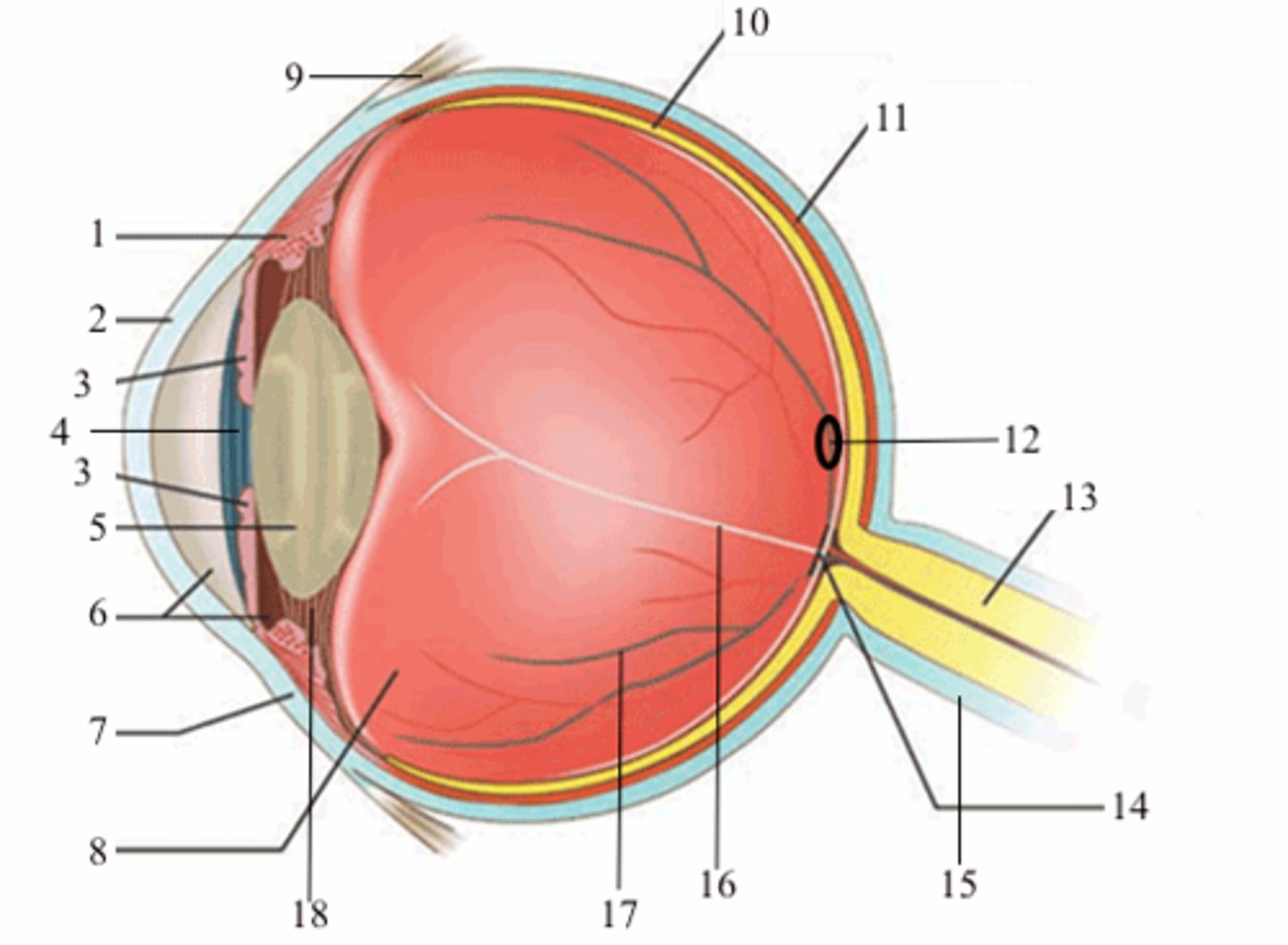
choroid (vascular tunic)
11; medial view
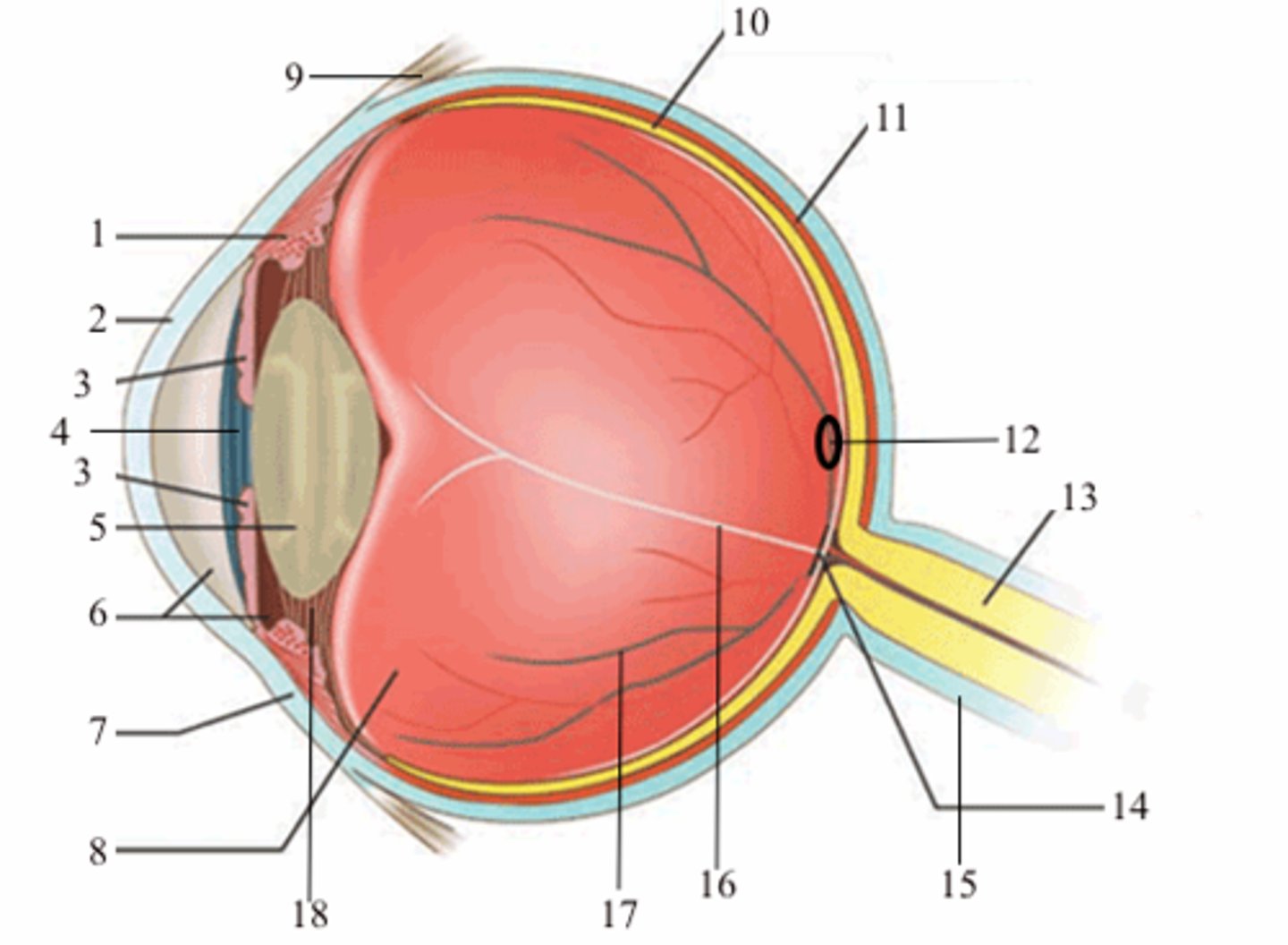
cornea (fibrous tunic)
2; medial view
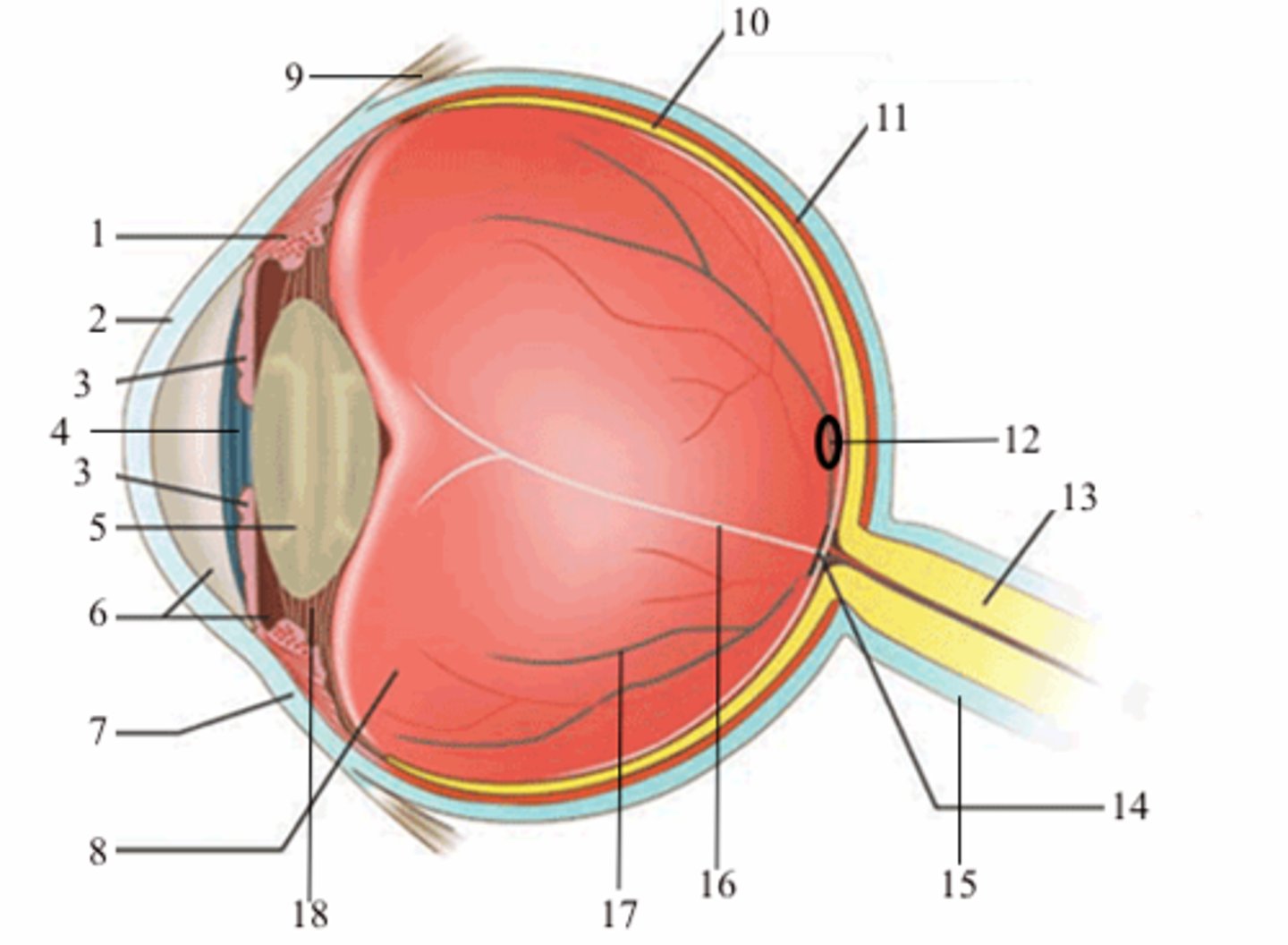
sclera (fibrous tunic)
7; medial view
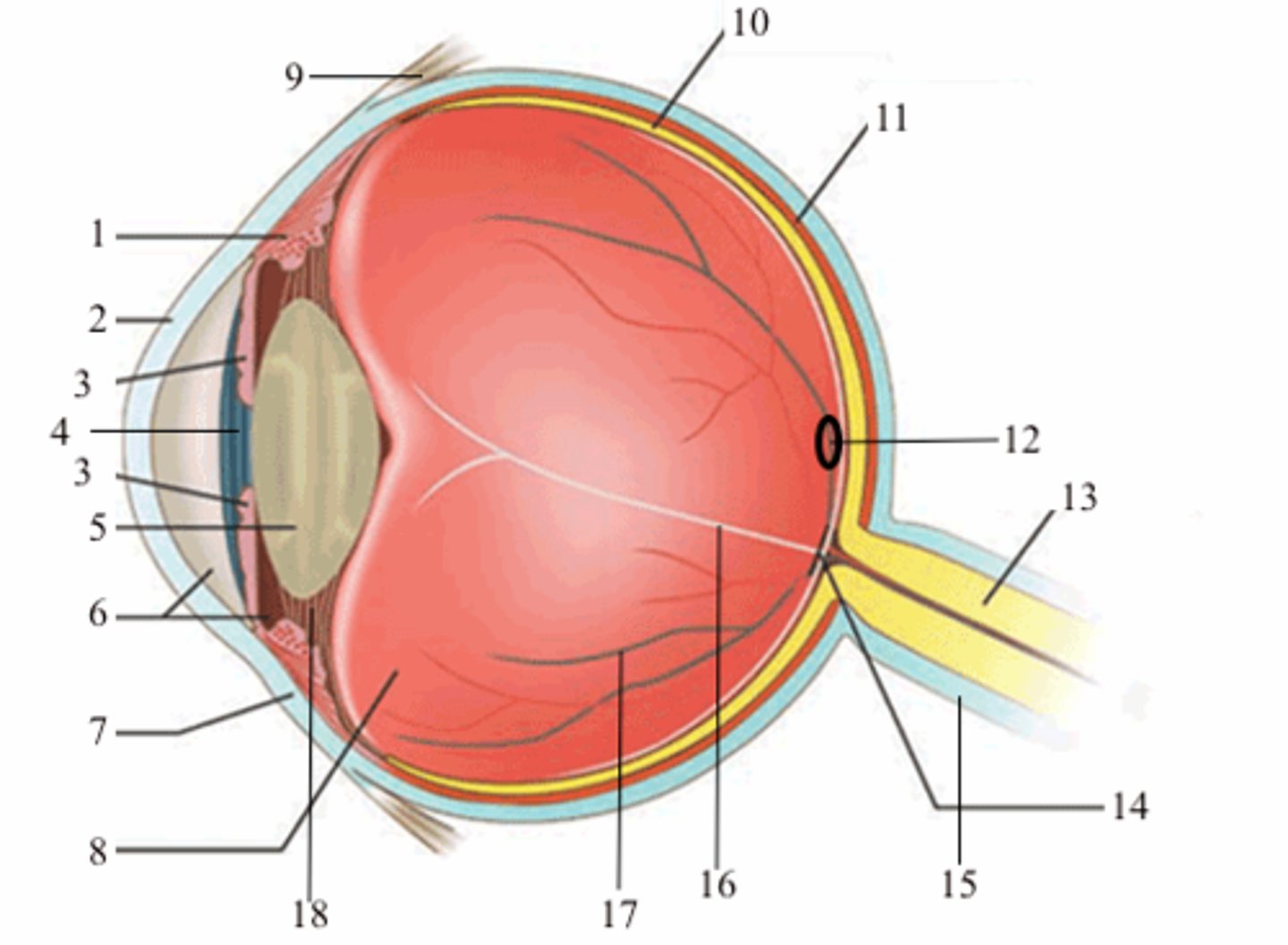
retina (neural tunic)
10; medial view
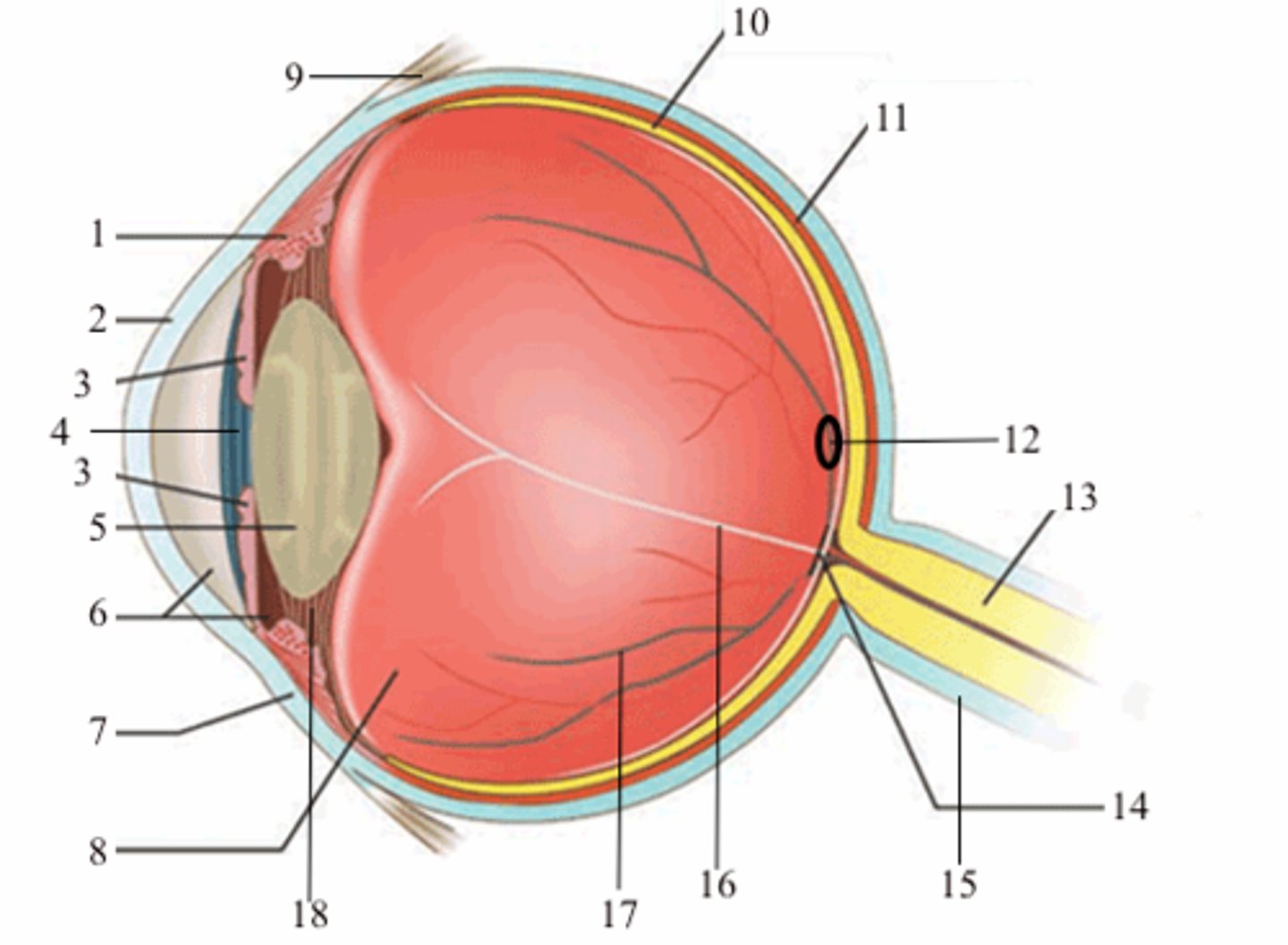
pupil
4; medial view
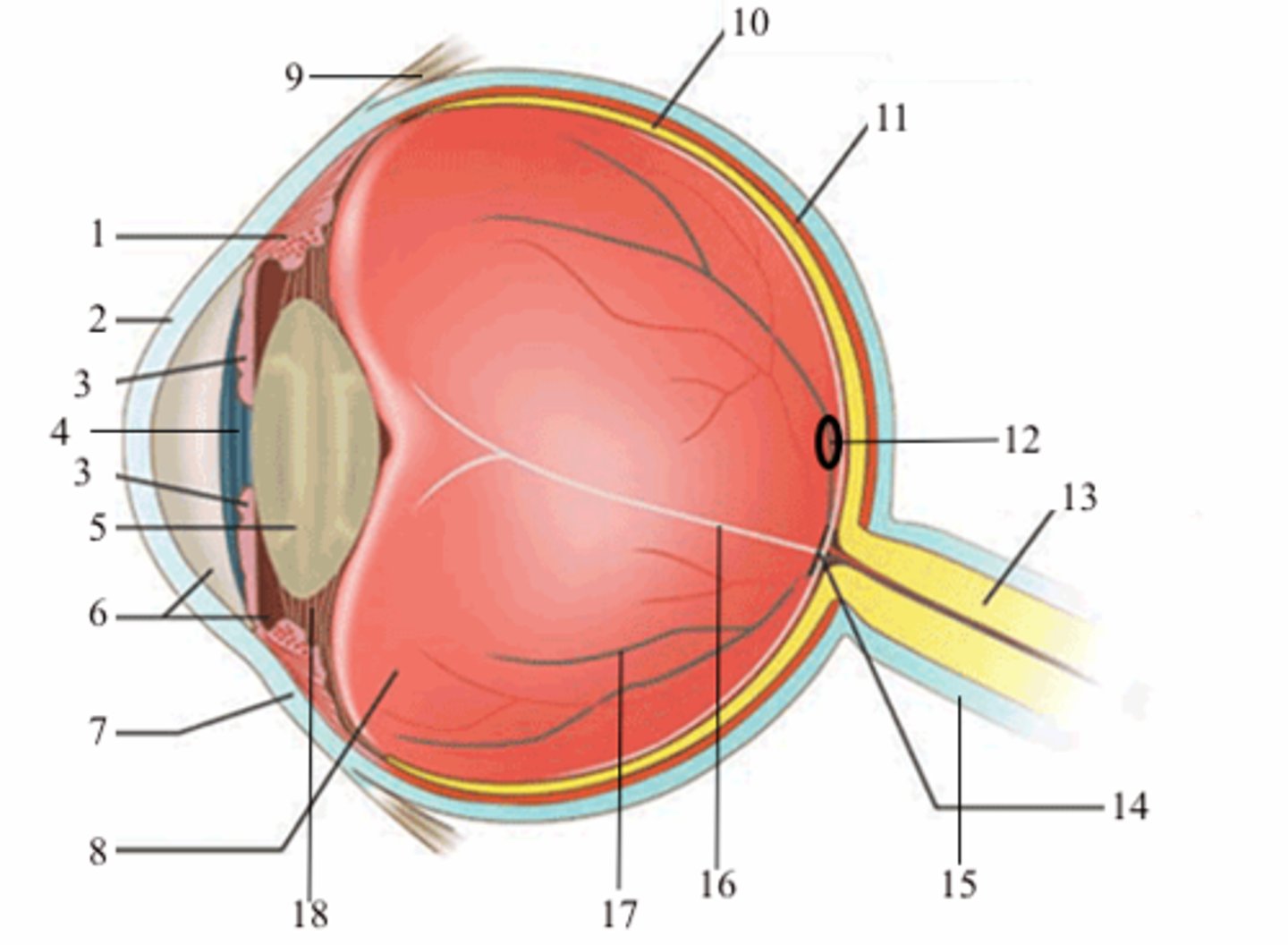
lens
5; medial view
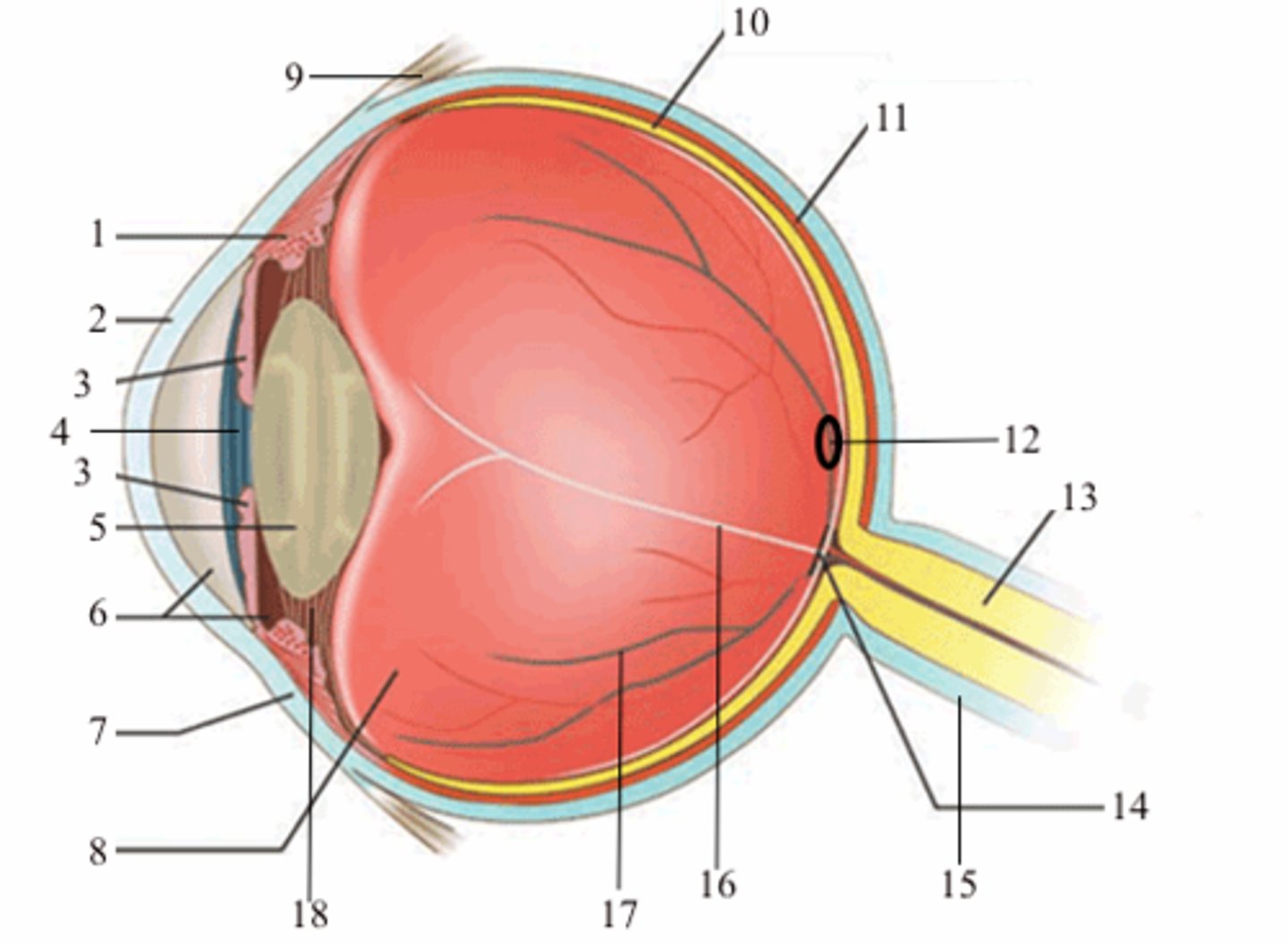
aqueous humor/anterior cavity
6; medial view
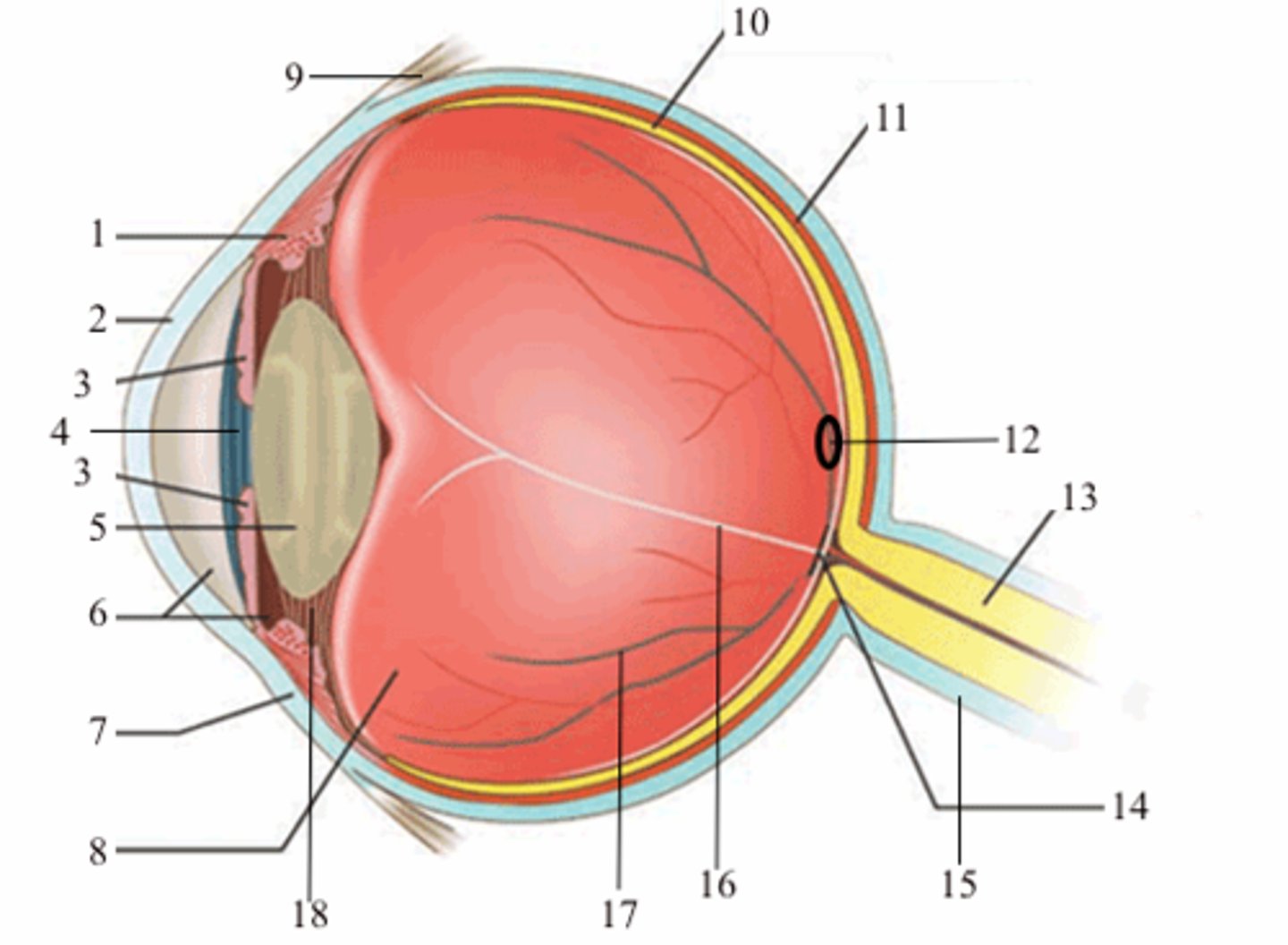
vitreous humor/posterior cavity
8; medial view
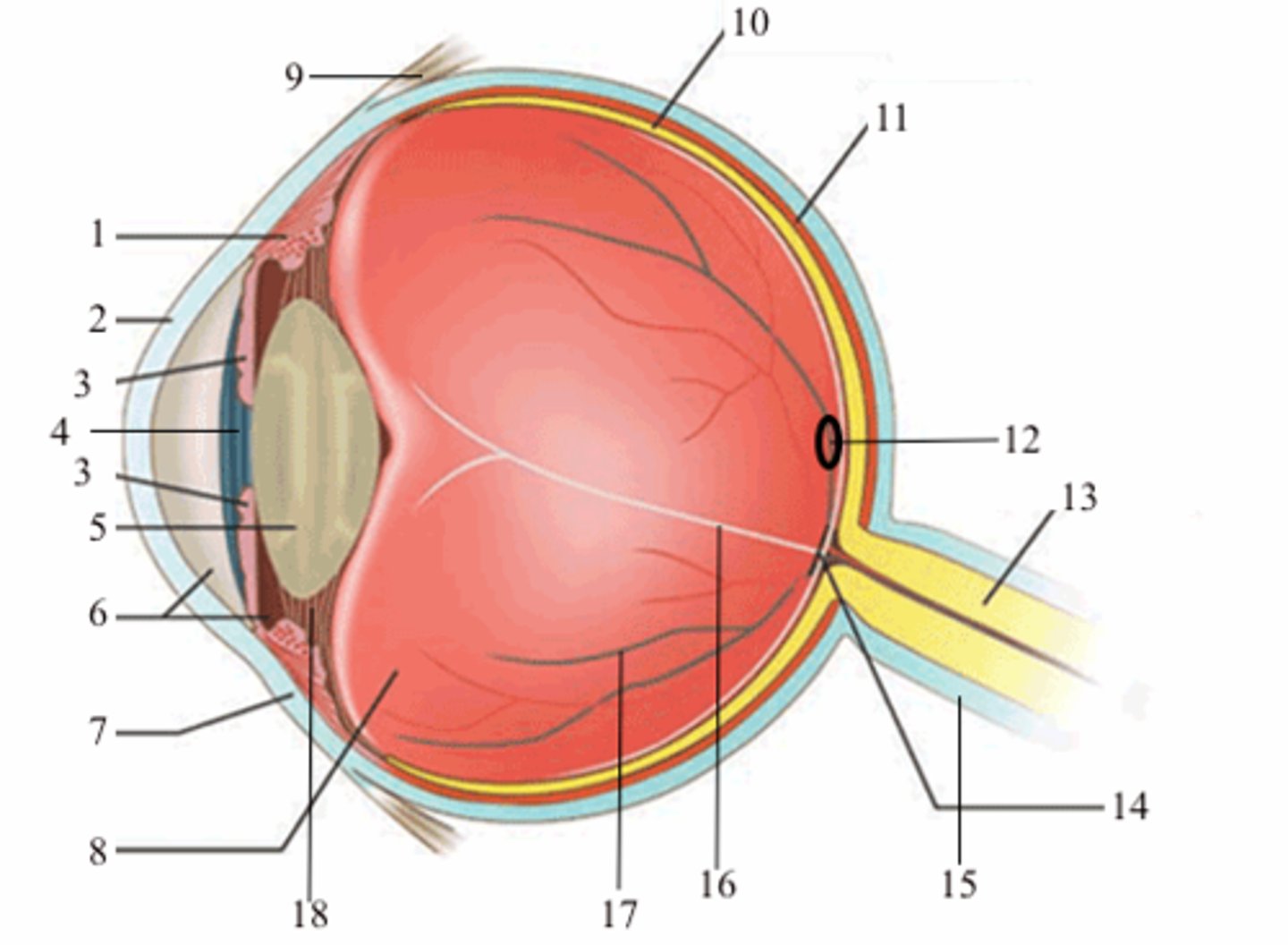
conjunctiva
9; medial view
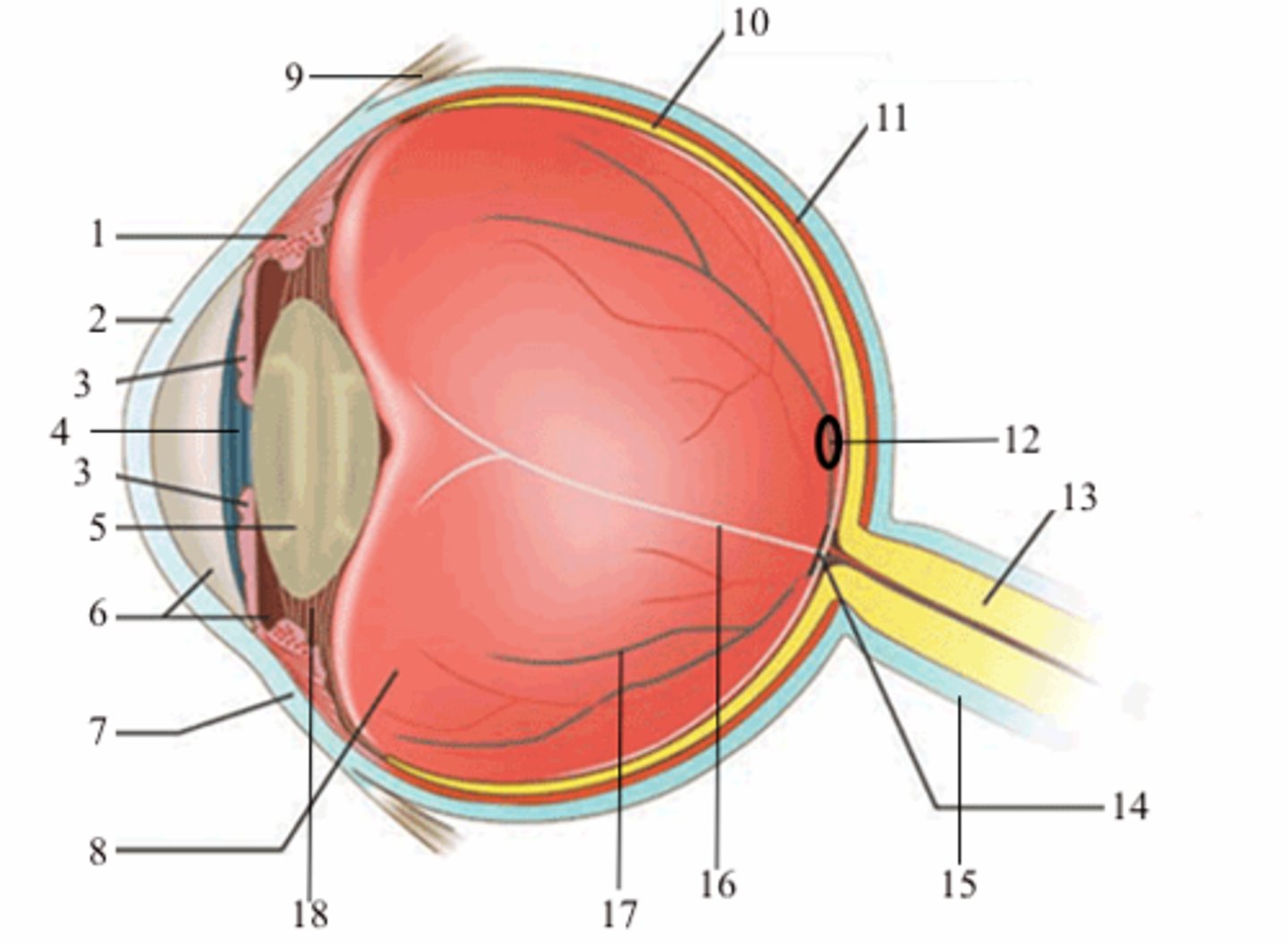
fovea centralis
12; medial view
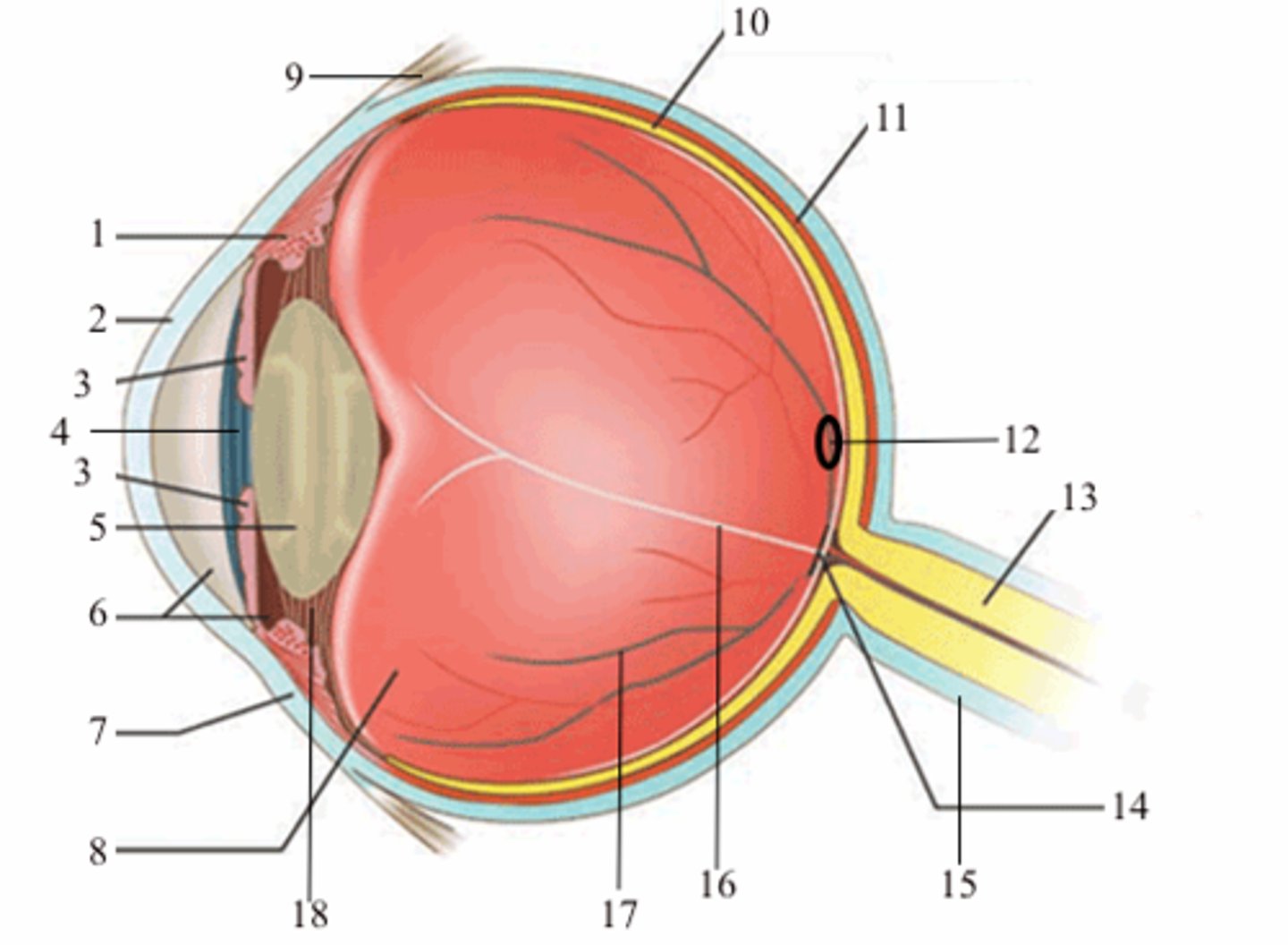
optic disc
14; medial view
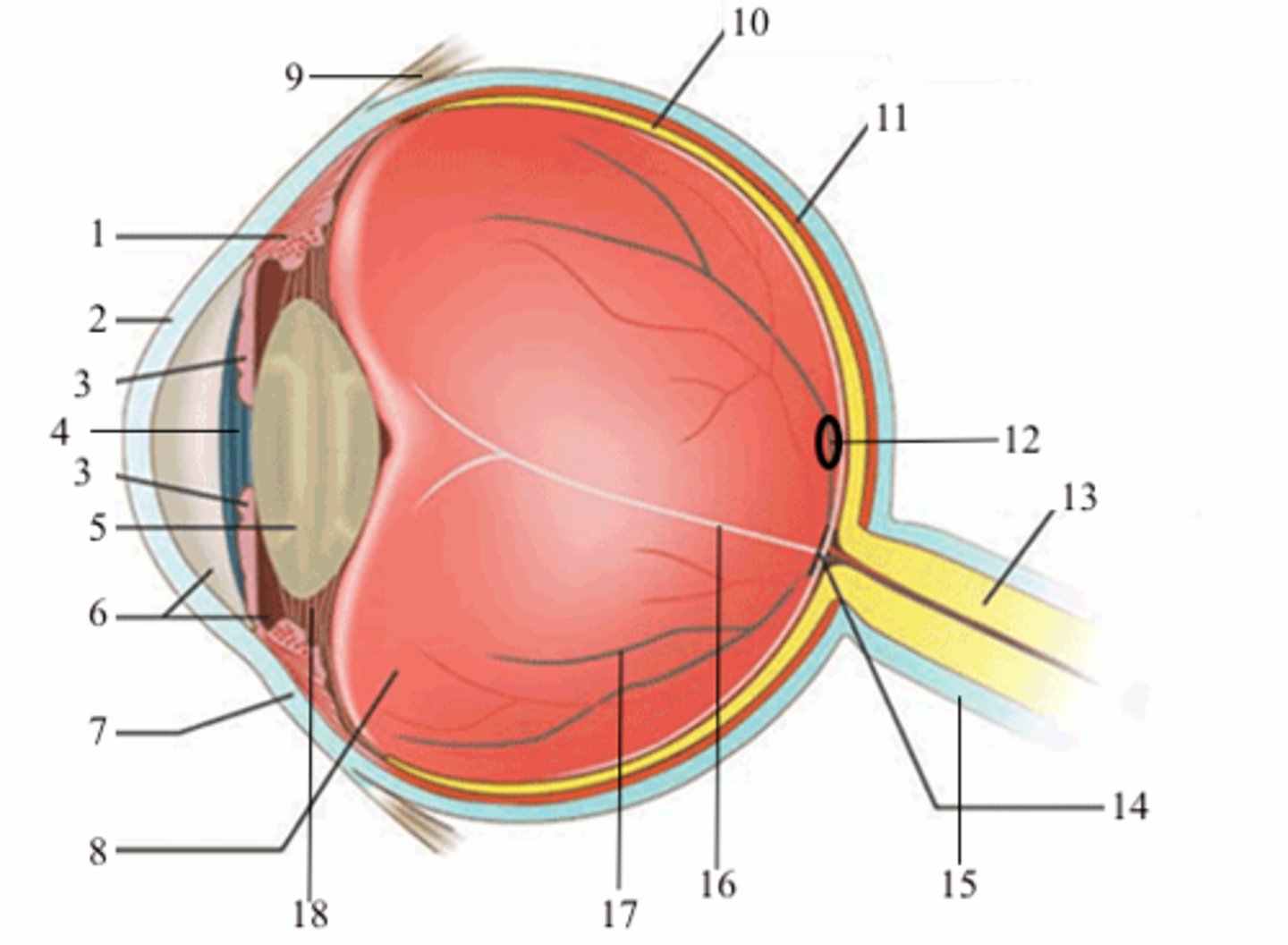
blind spot
16; medial view
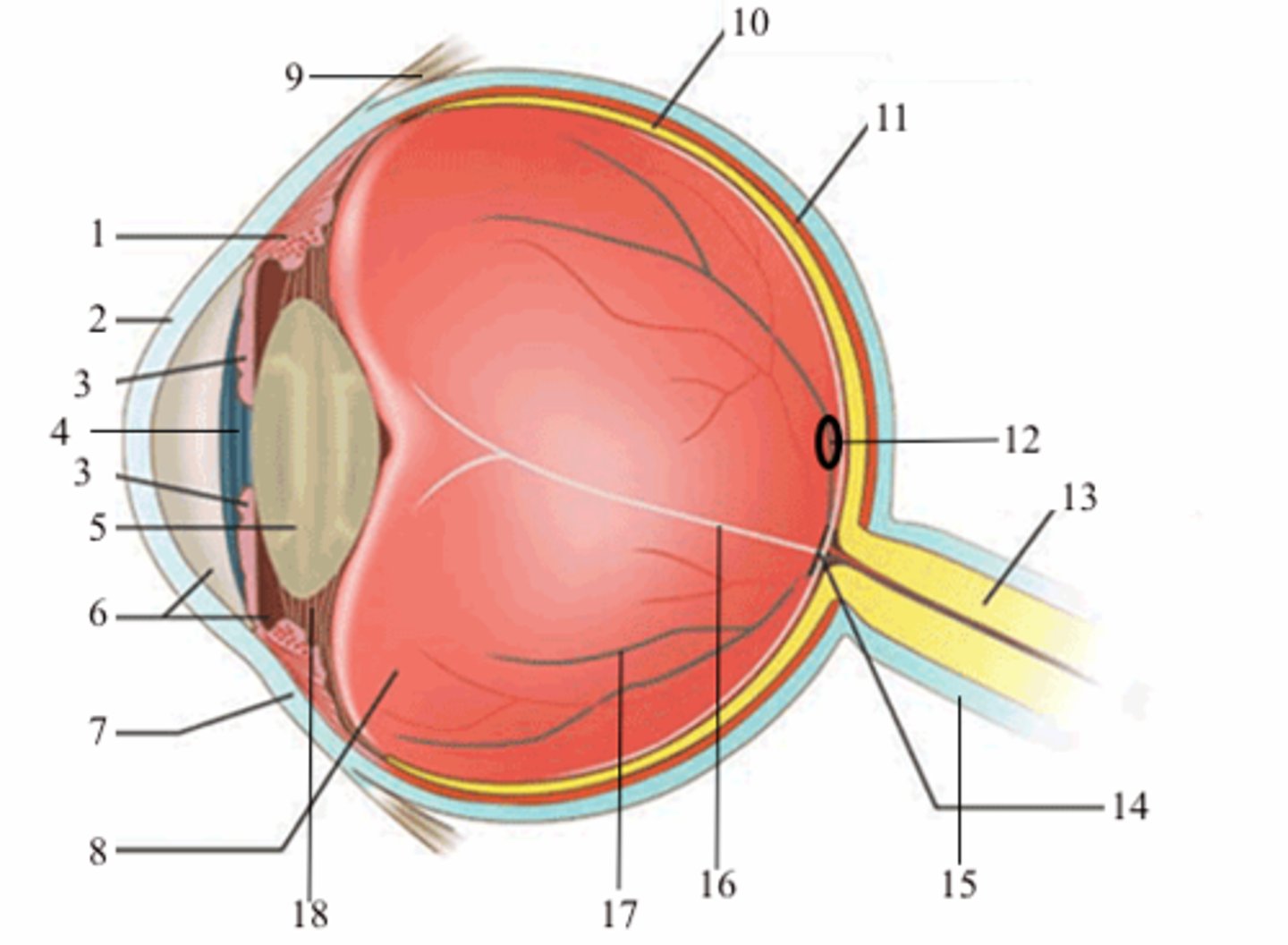
suspensatory ligaments
black arrows; medial view
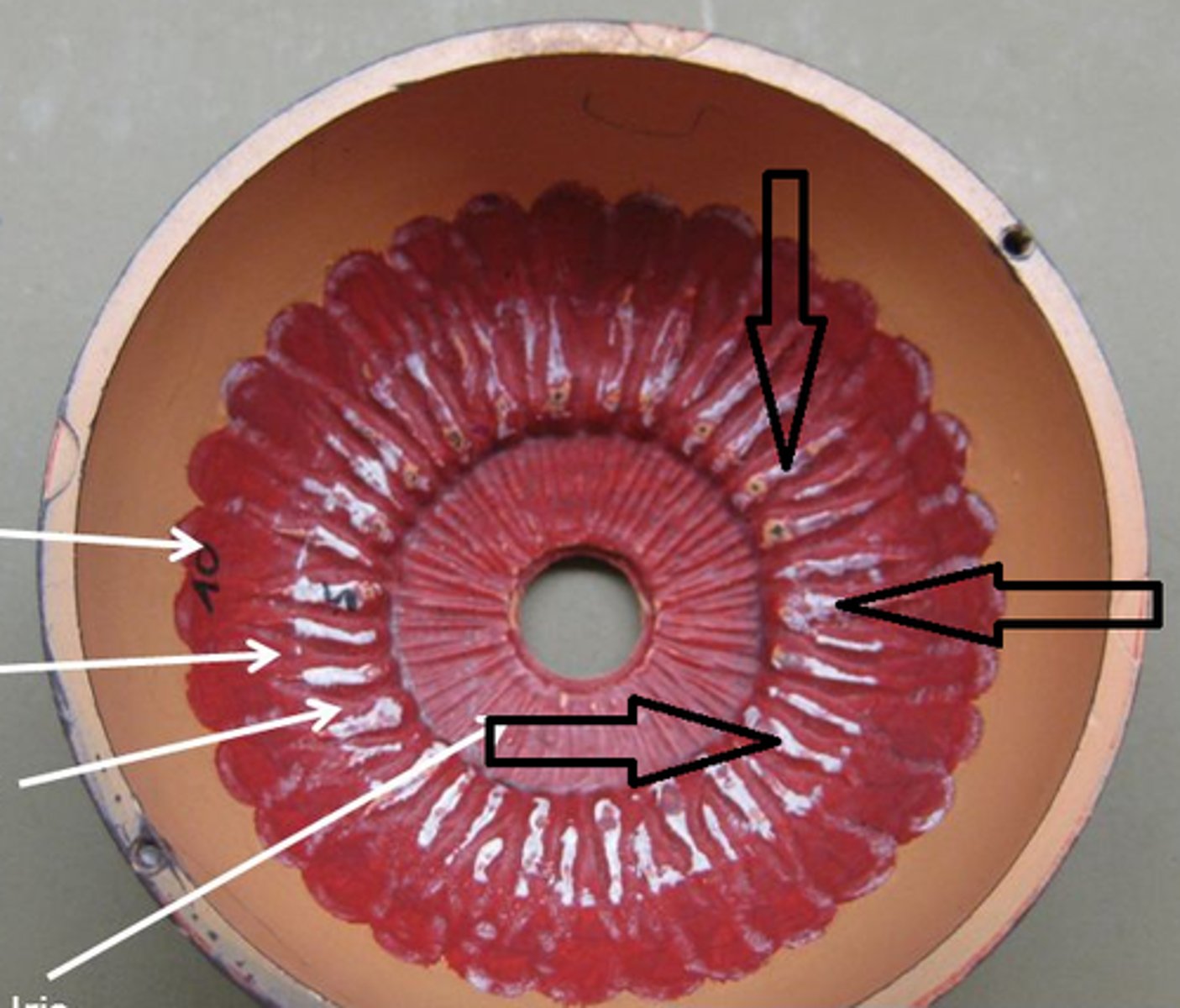
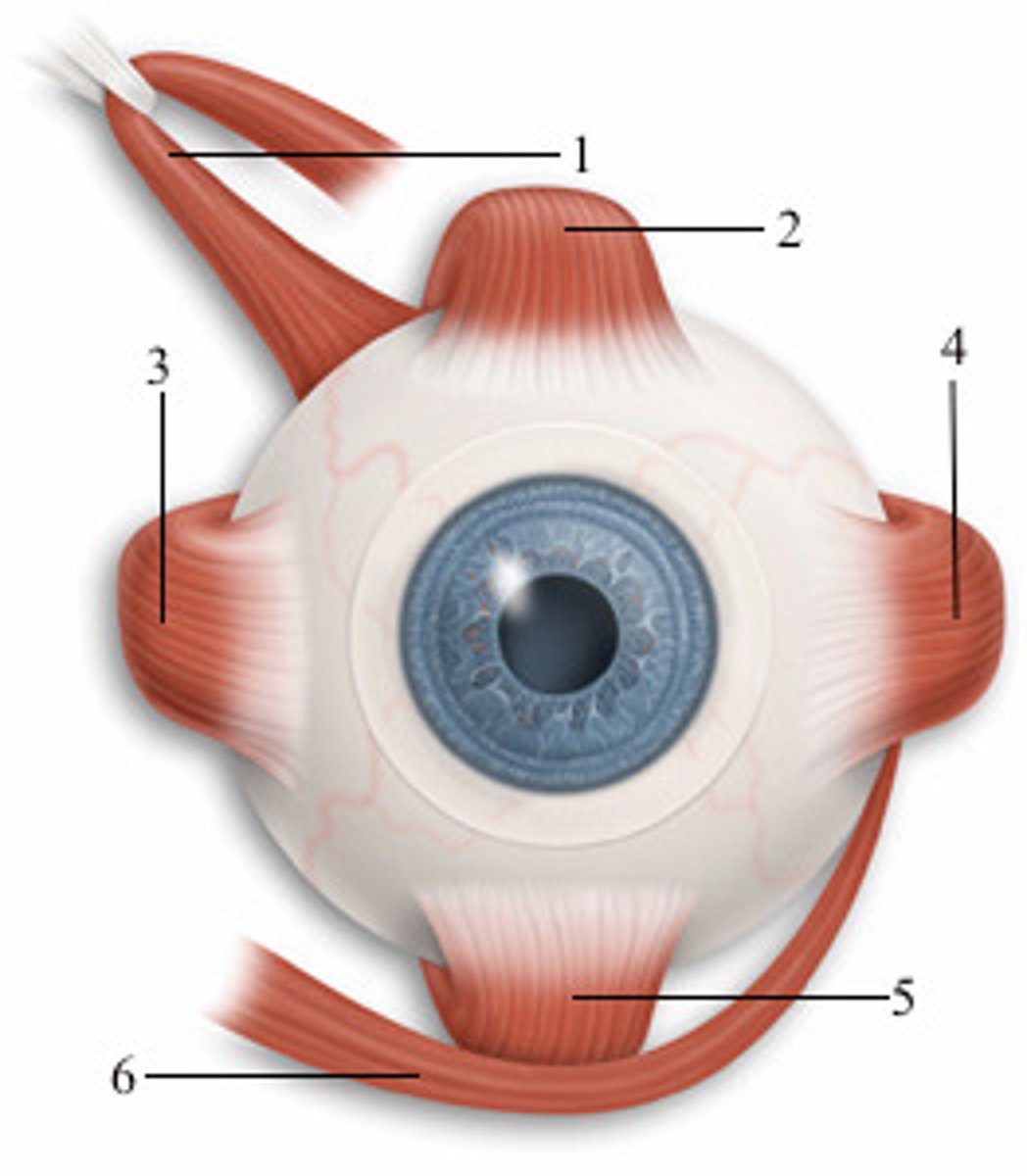
left superior oblique
1; medial view
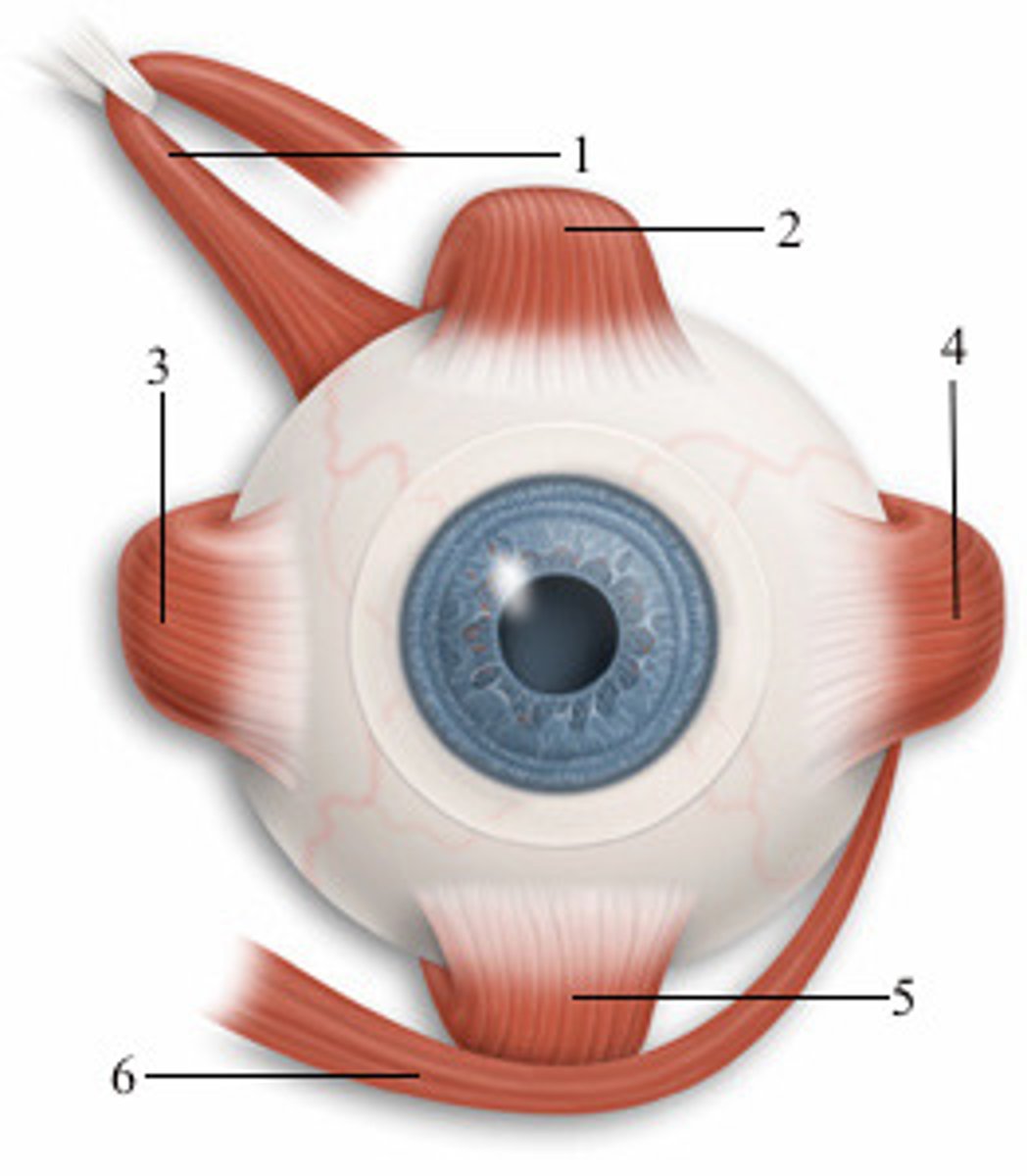
left superior rectus
2; anterior view
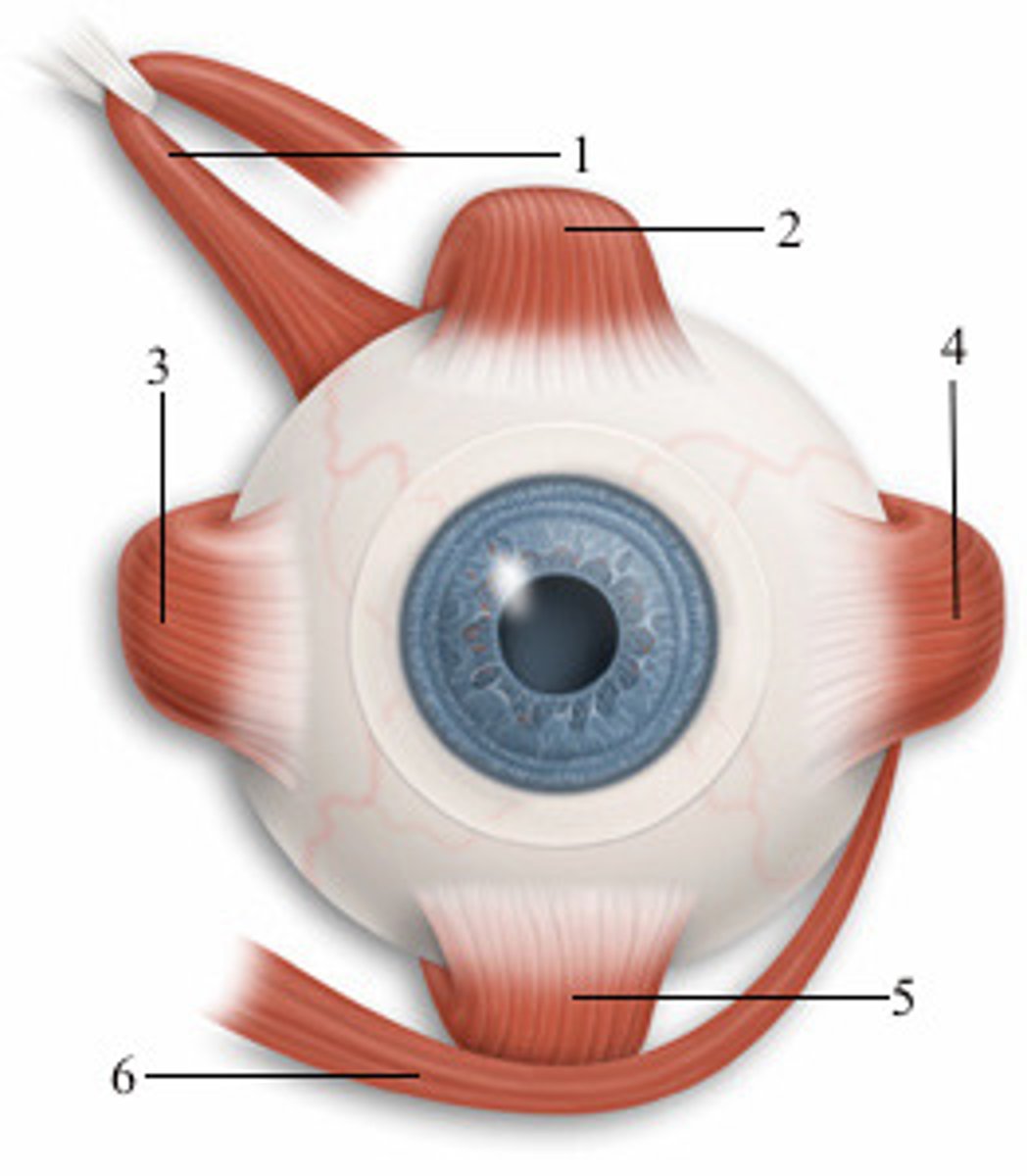
left medial rectus
3; anterior view
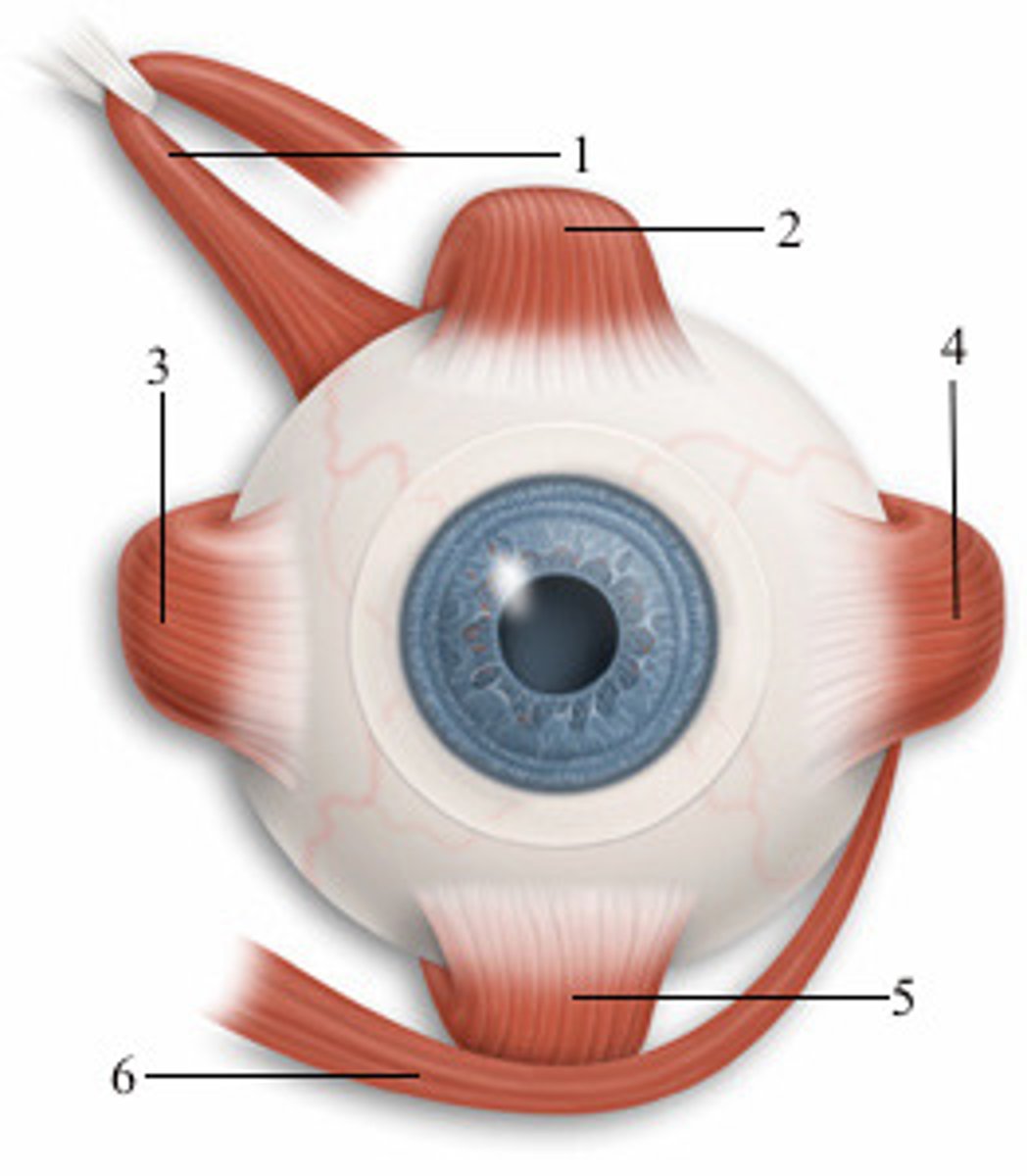
left lateral rectus
4; anterior view
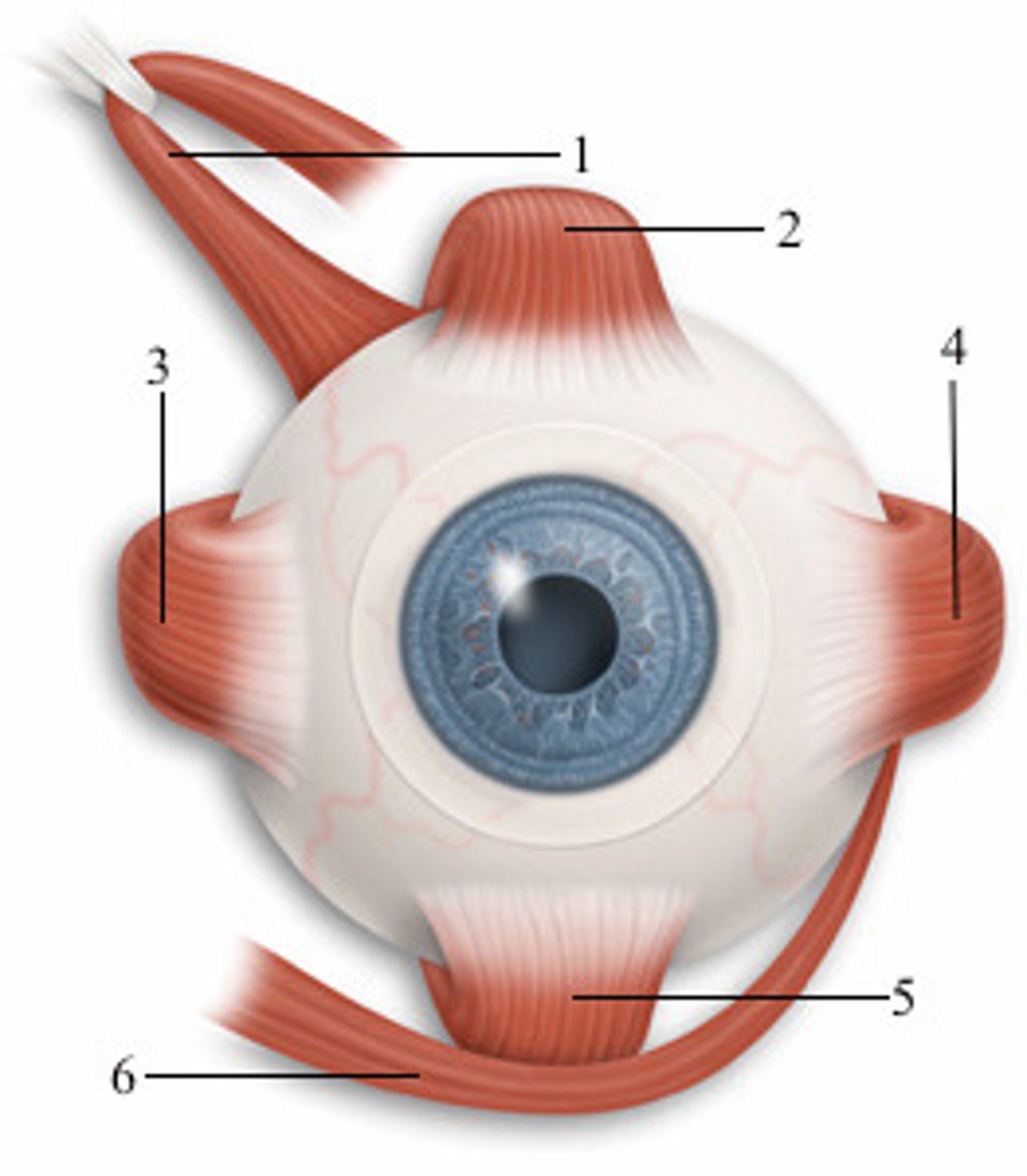
left inferior rectus
5; anterior view
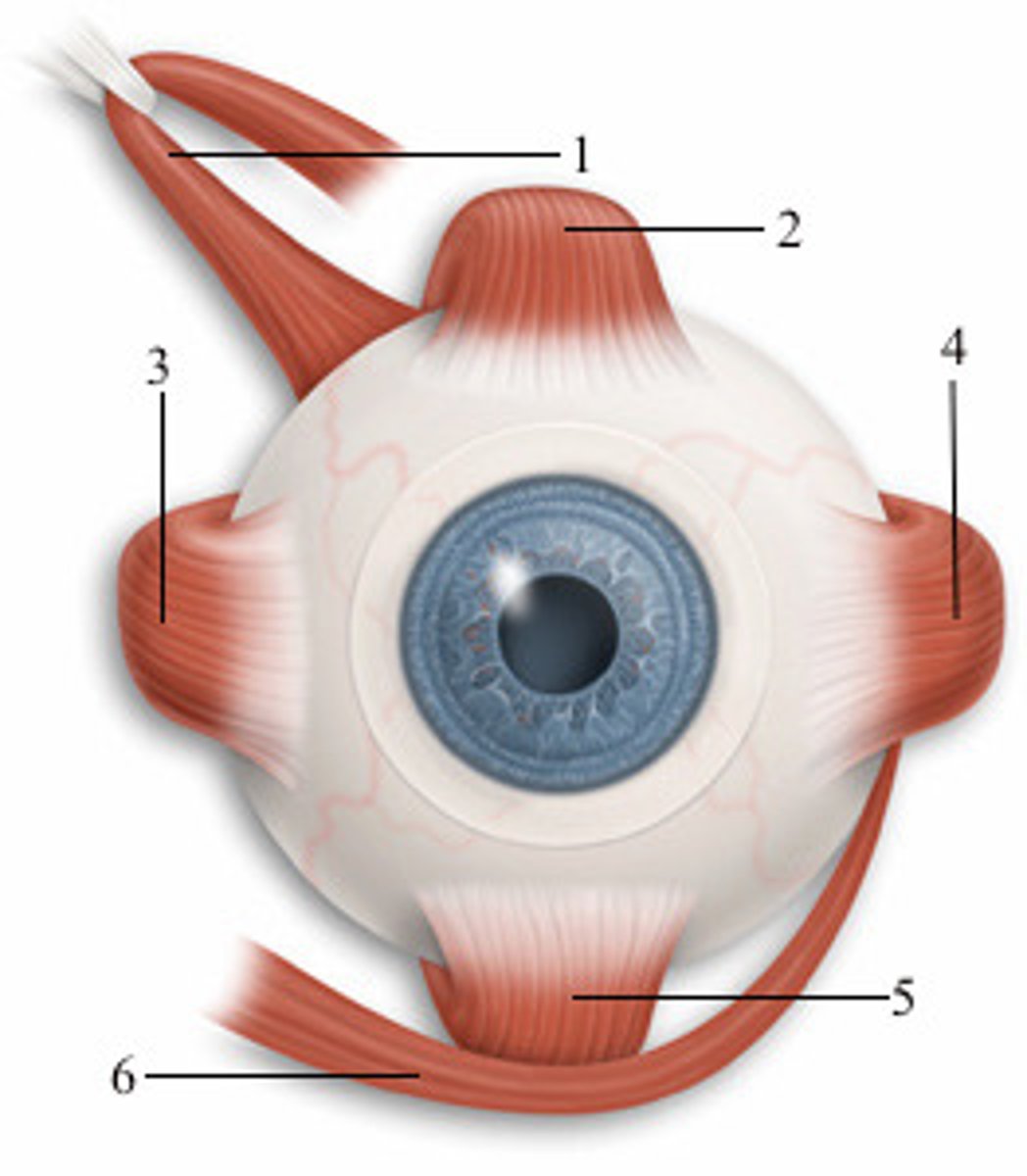
left inferior oblique
6; anterior view
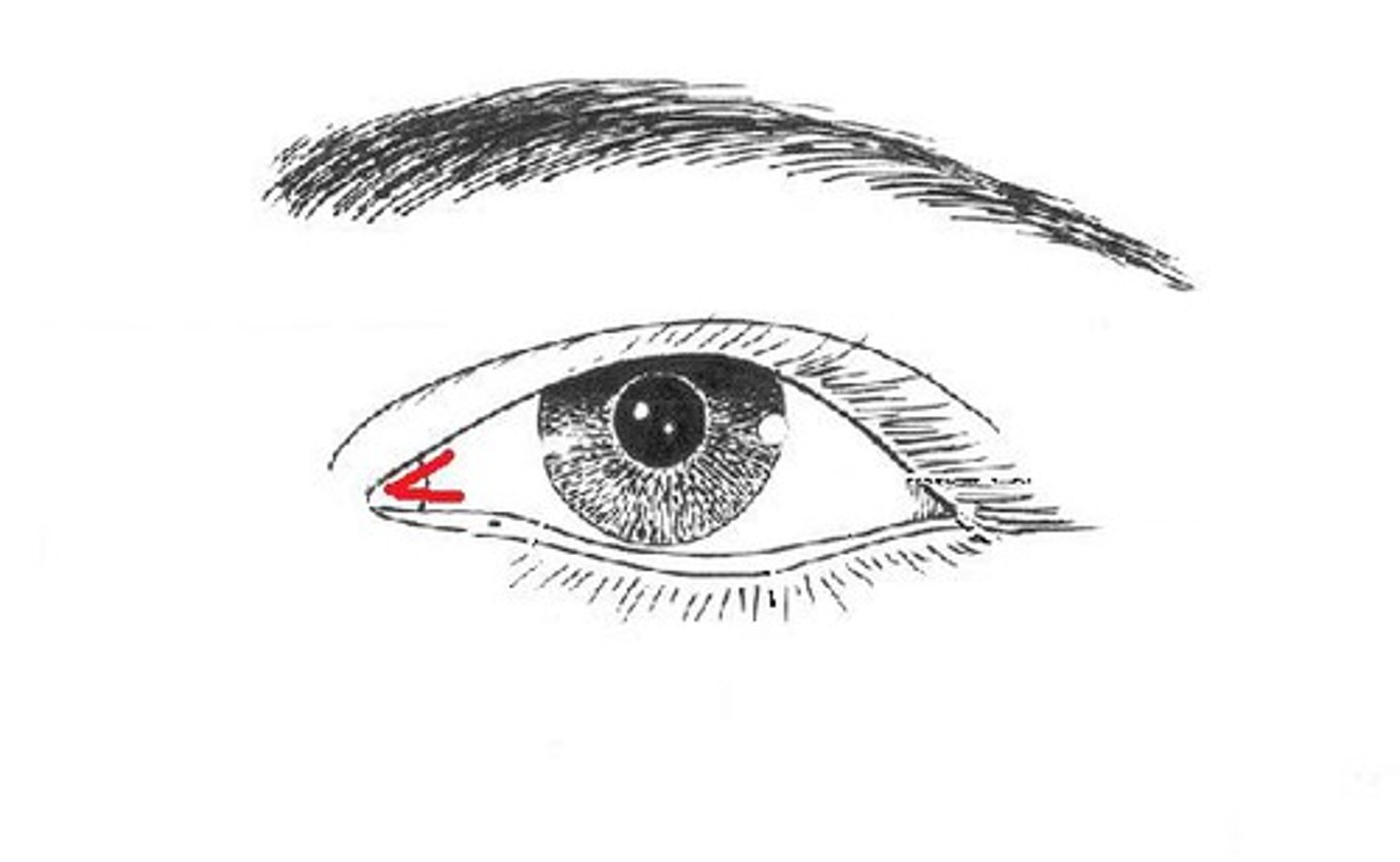
medial canthus
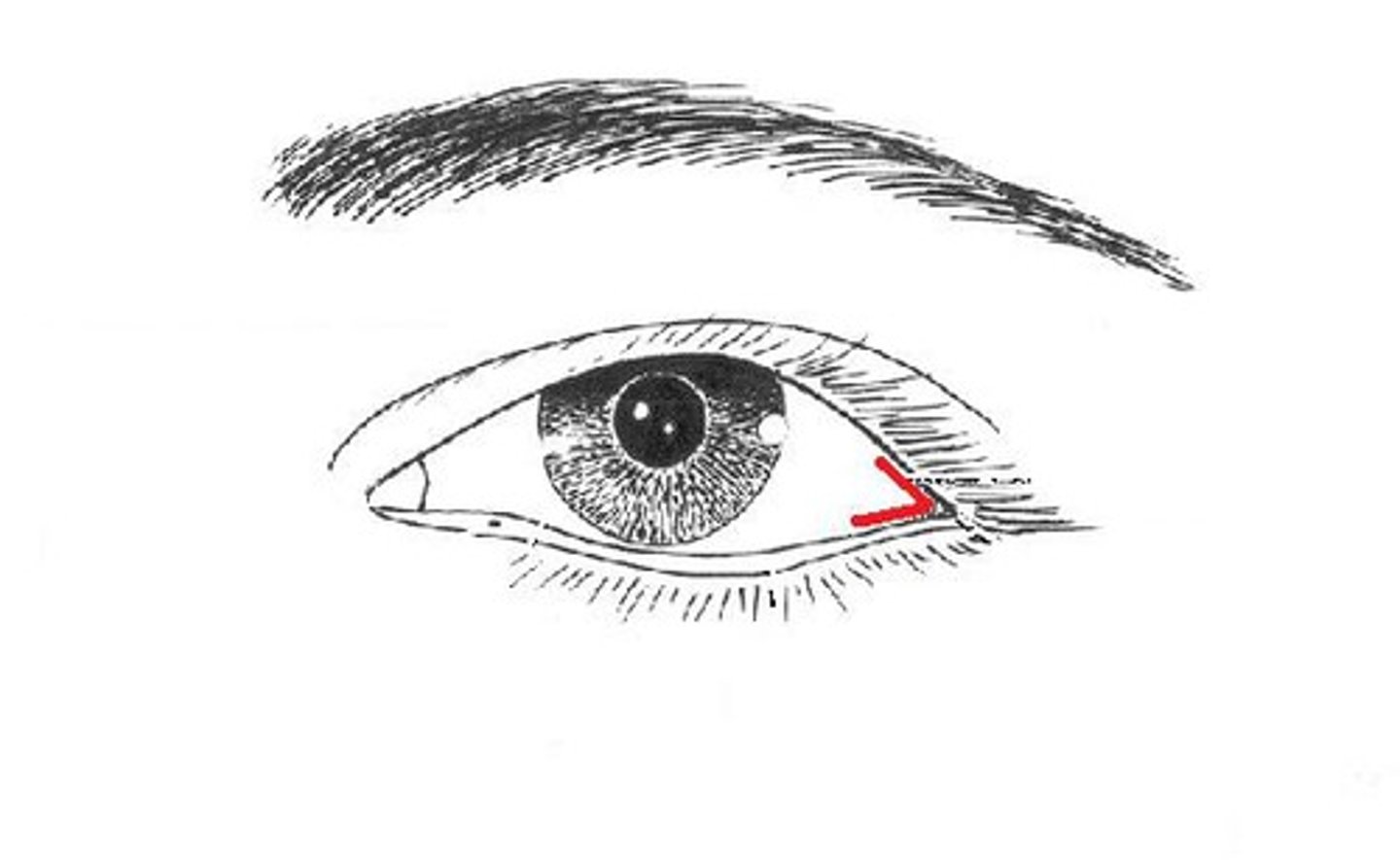
lateral canthus
lacrimal gland
1
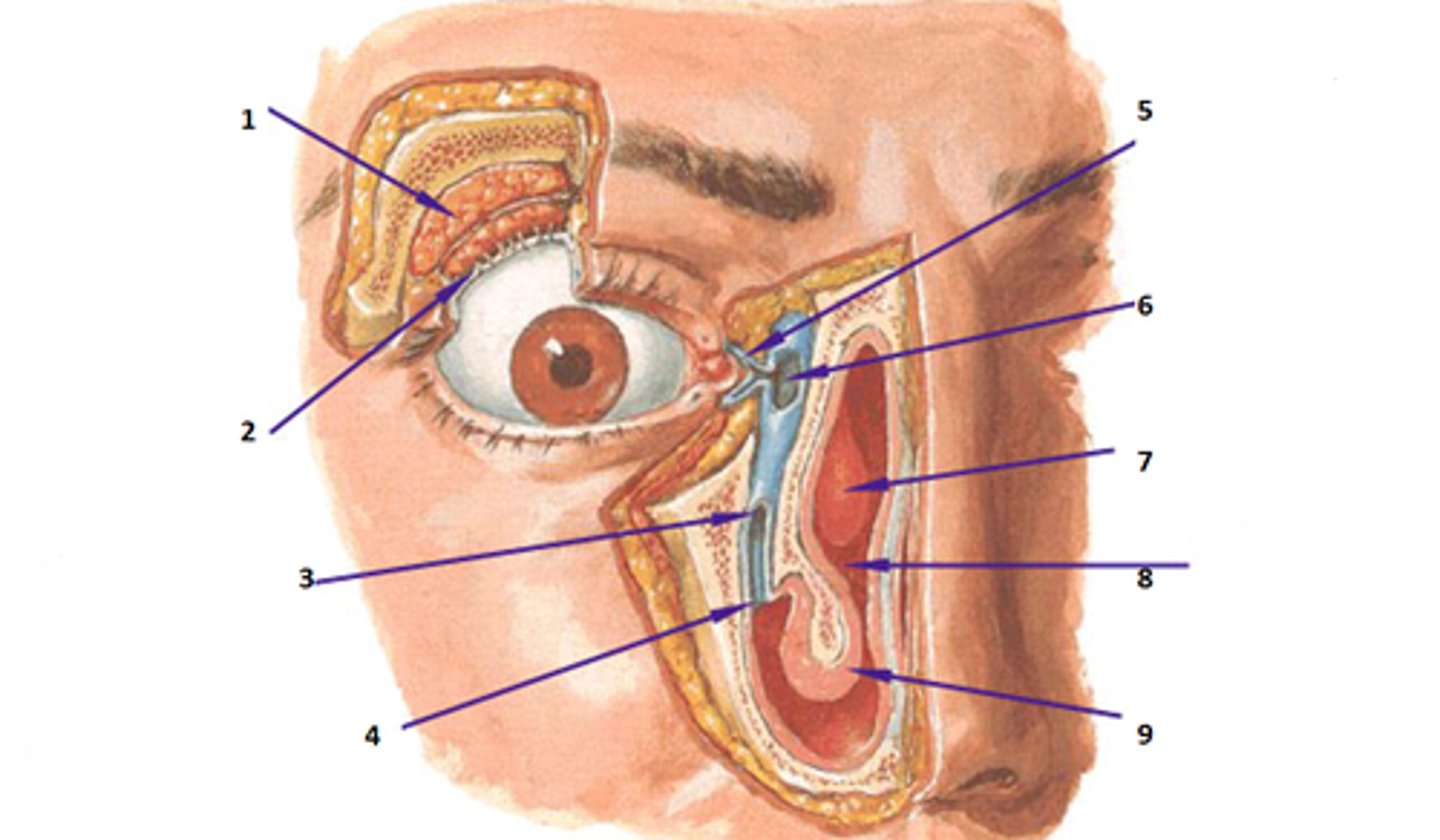
lacrimal canals
5
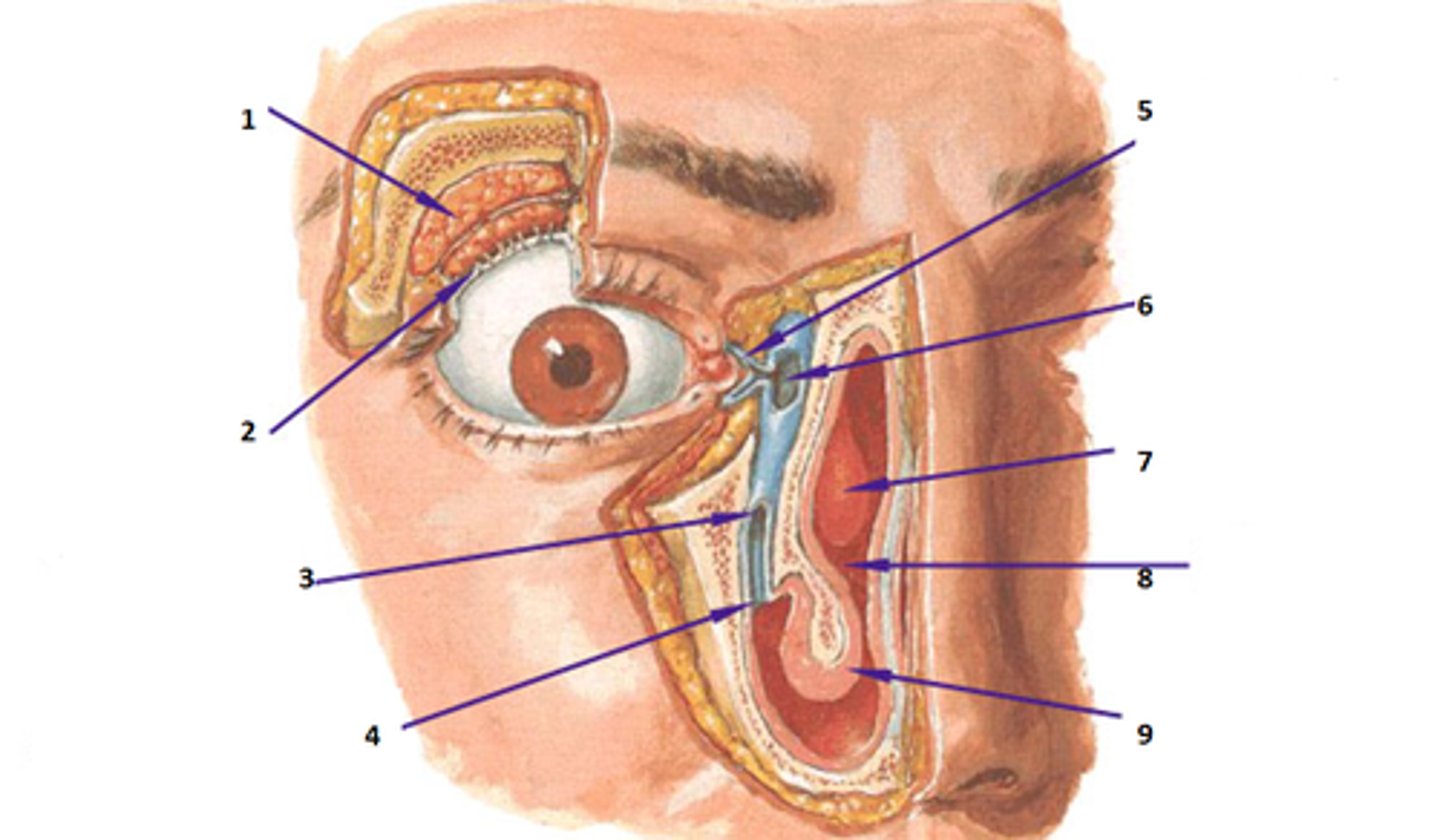
lacrimal sac
6
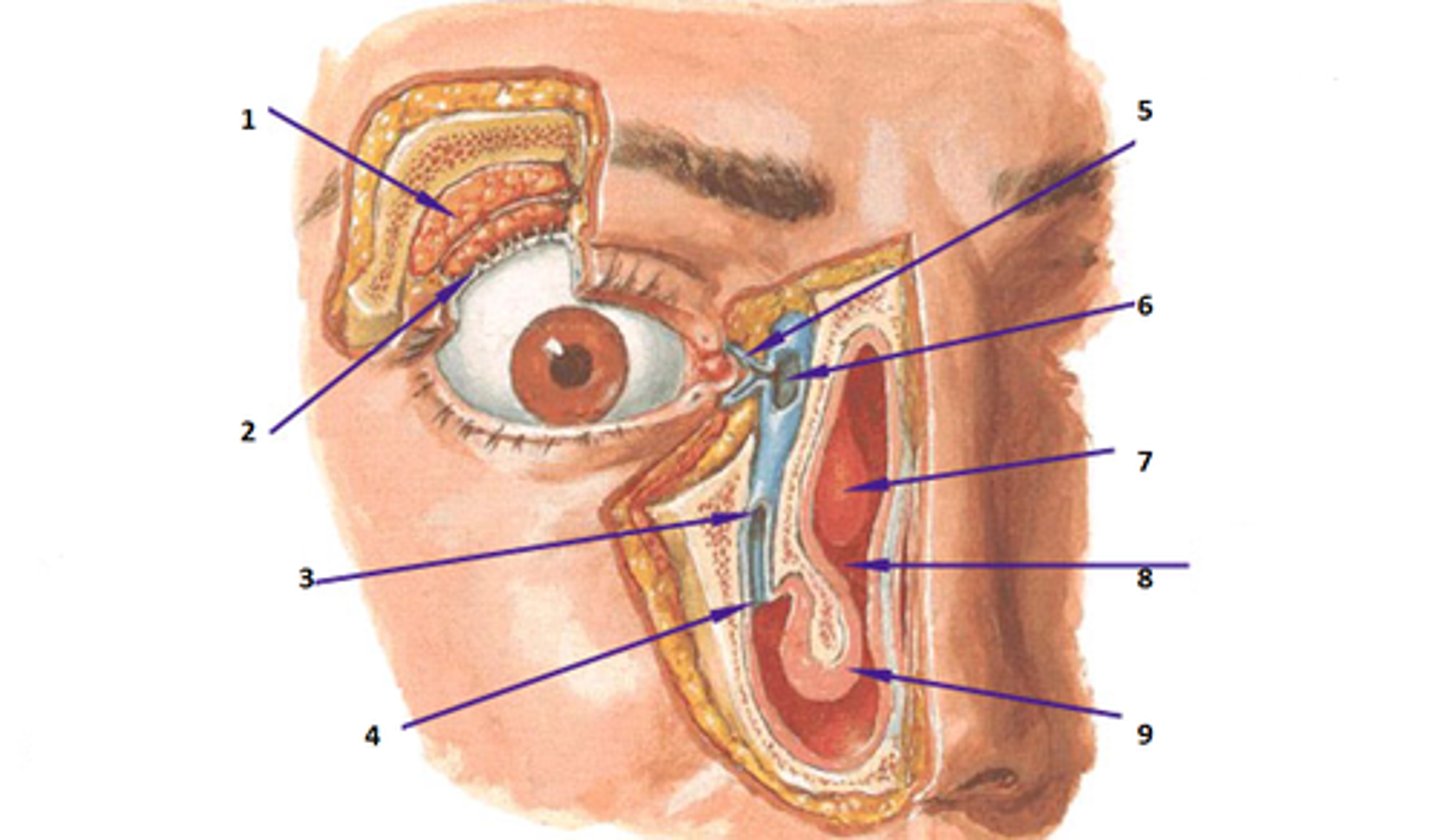
nasolacrimal duct
3
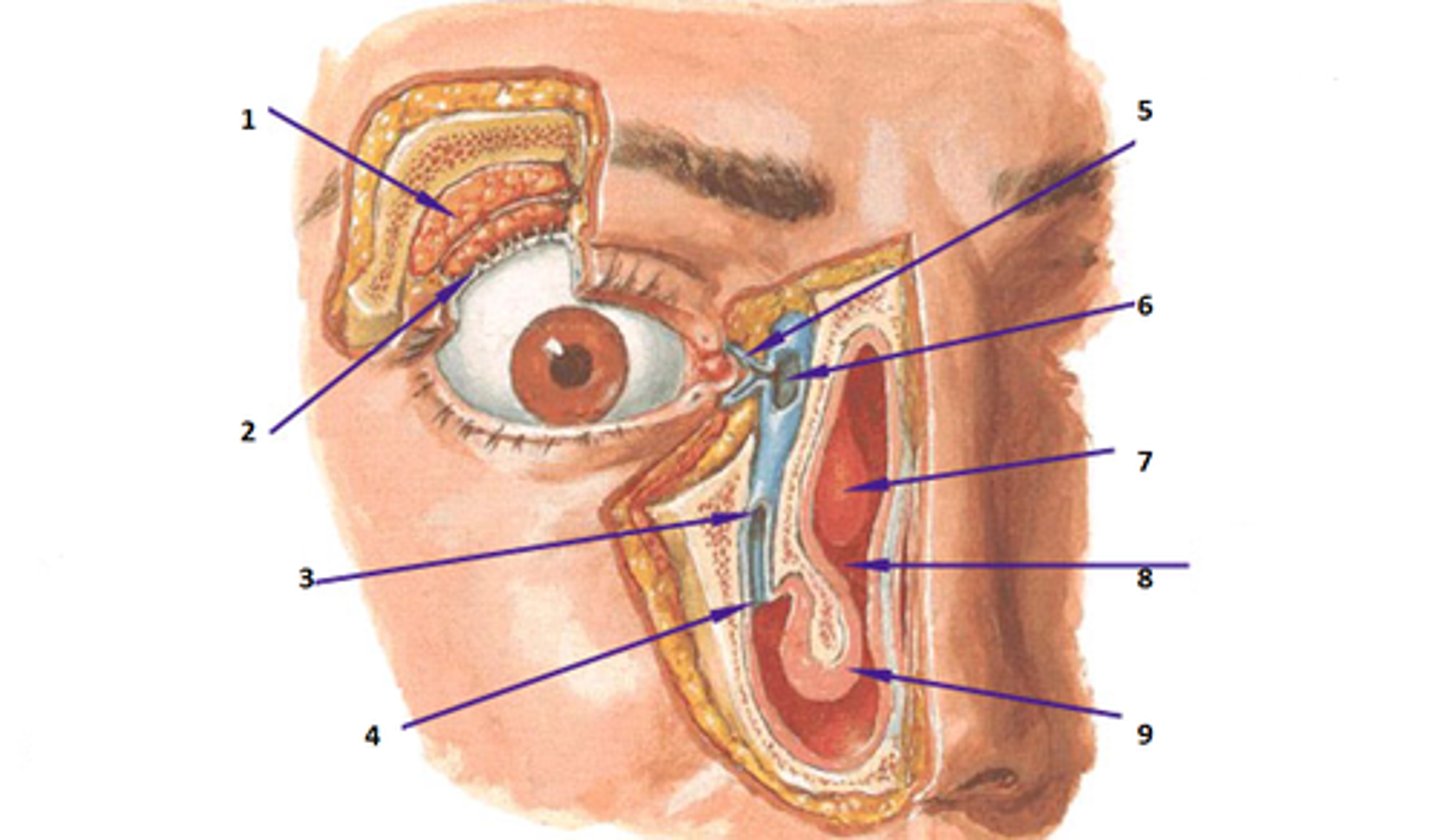
optic nerve
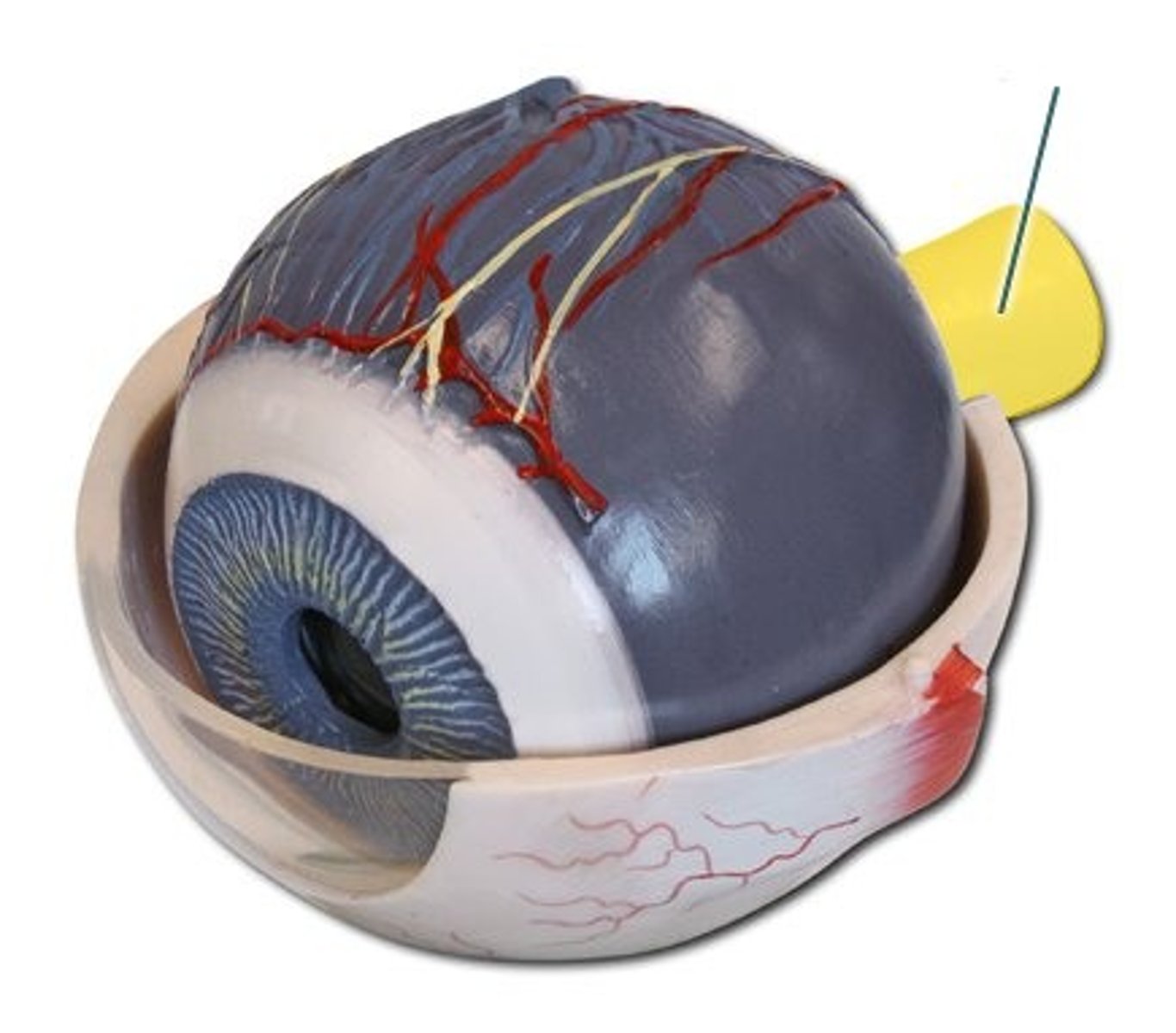
macula lutea
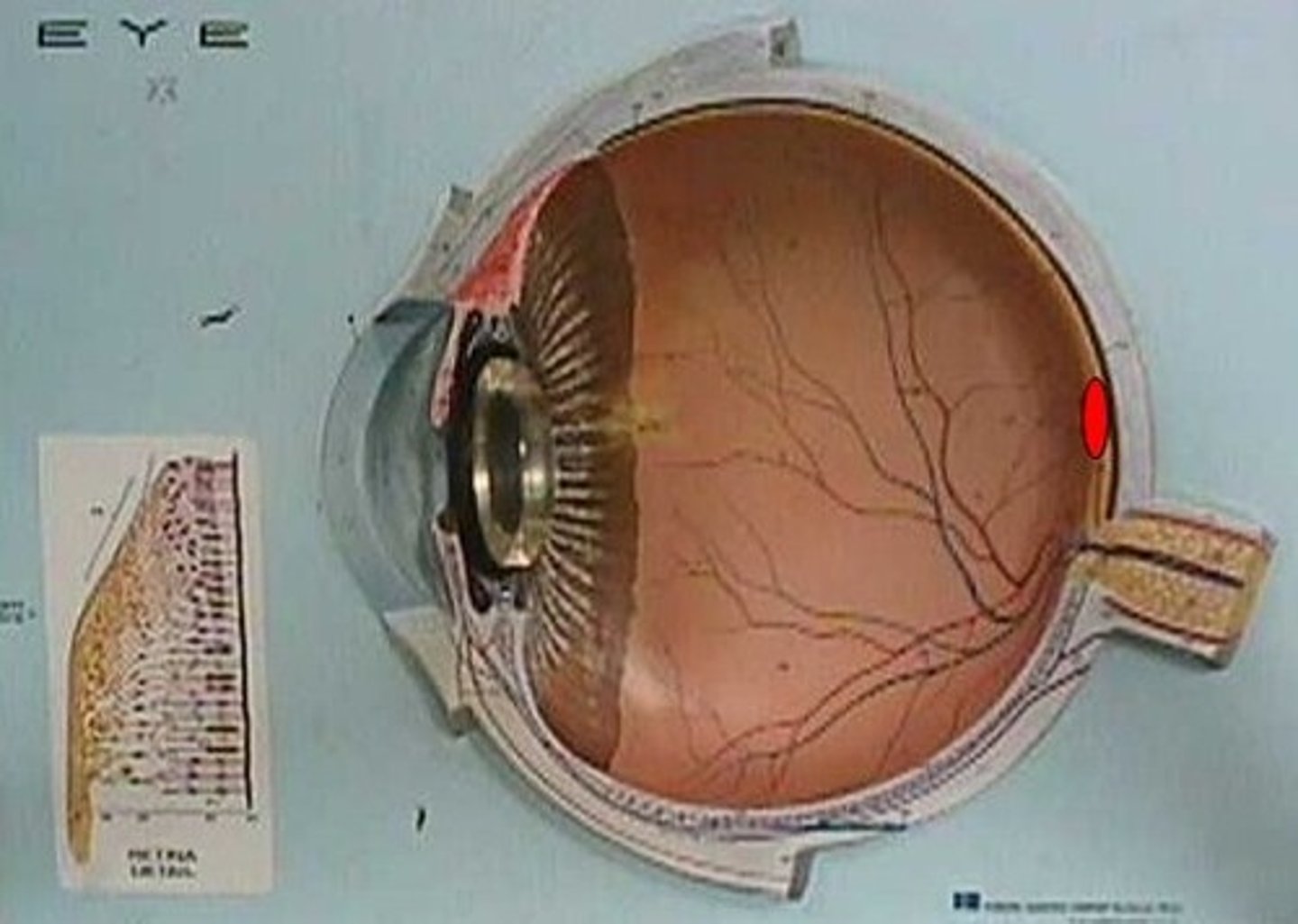
accommodation
Changing the shape of the lens using the ciliary body. This allows us to focus on objects at varying distances.
refraction
The change in speed and direction of light when it passes from one kind of material to another.

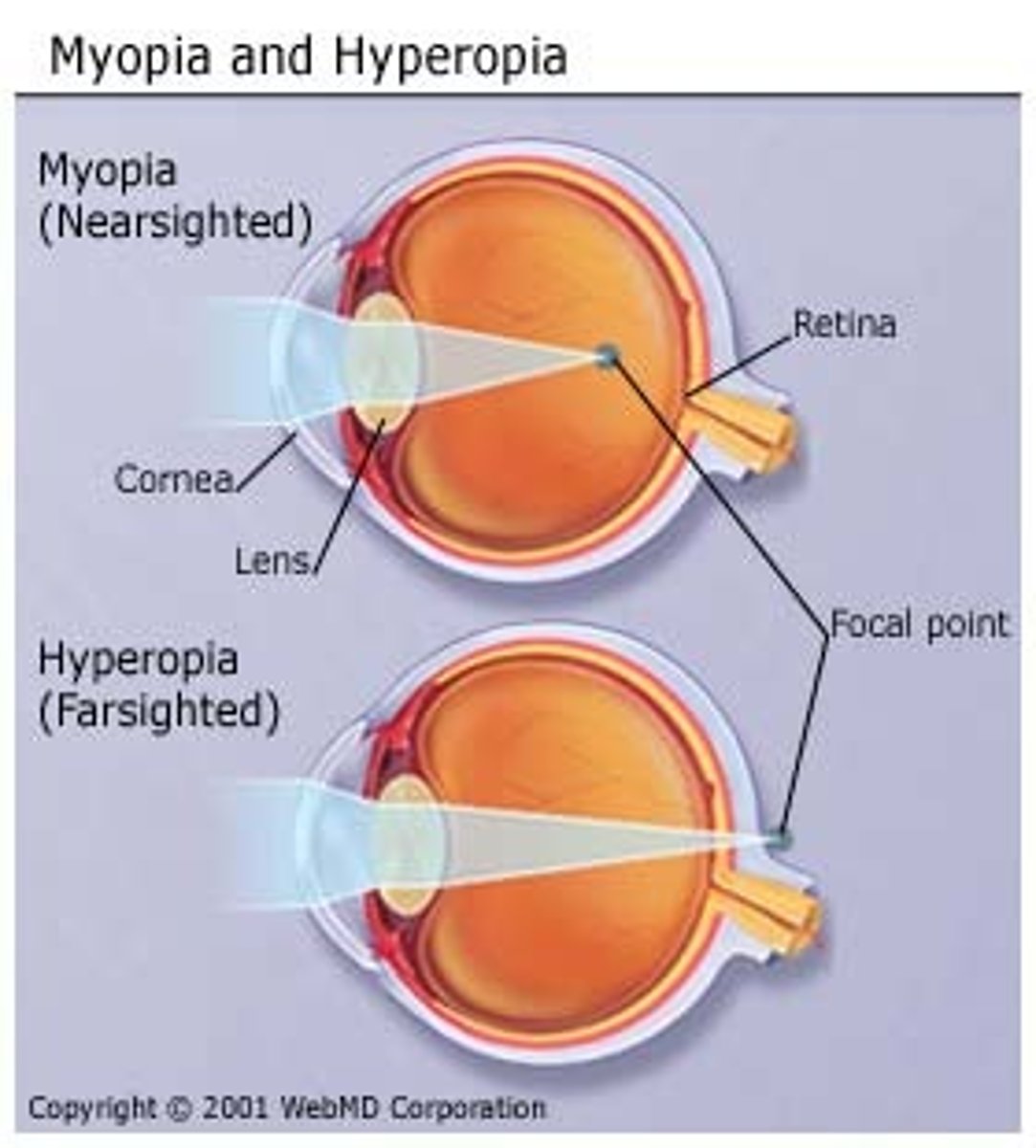
myopia
nearsightedness
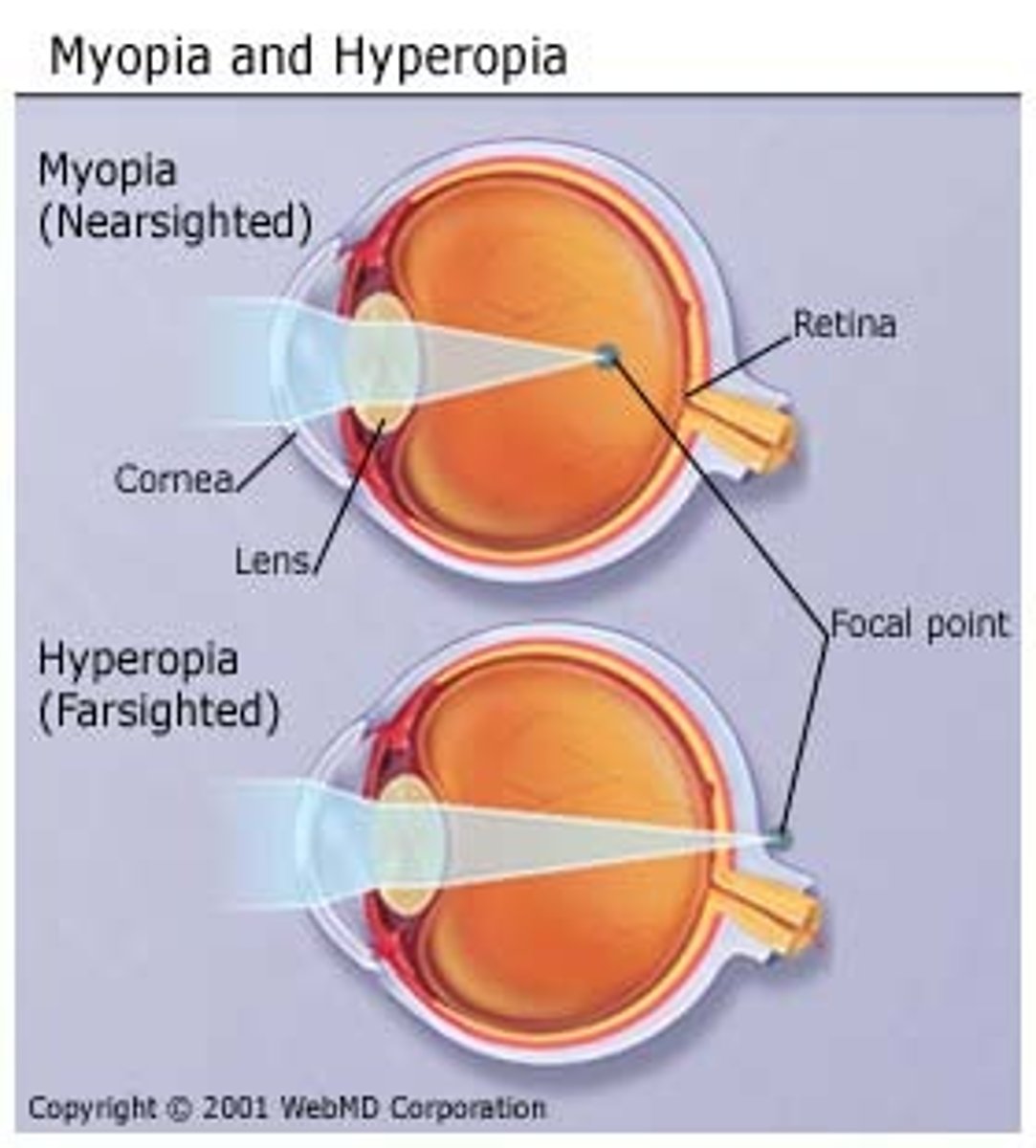
hyperopia
farsightedness
astigmatism
a defect in the eye or in a lens caused by a deviation from spherical curvature, which results in distorted images, as light rays are prevented from meeting at a common focus
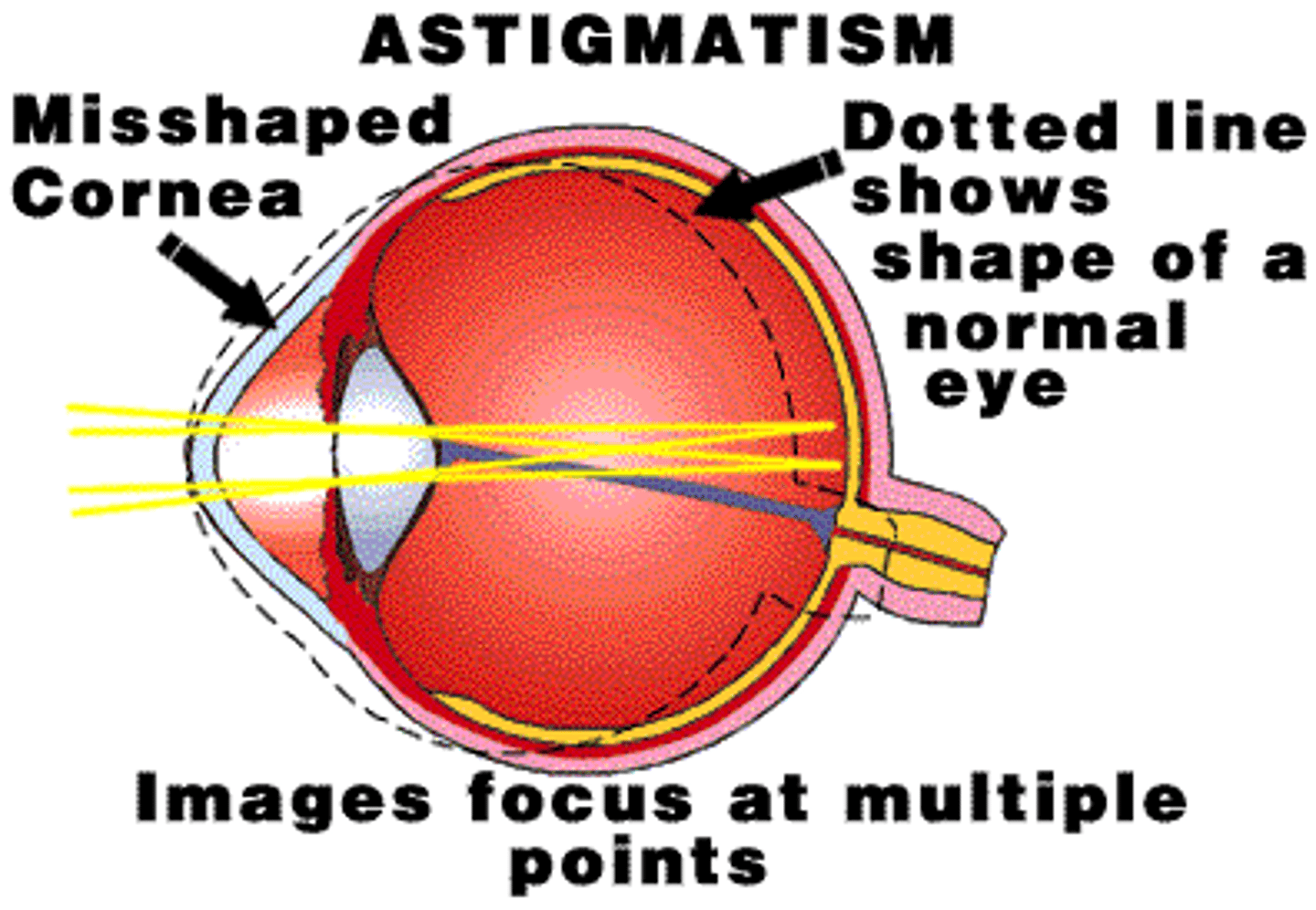
presbyopia
farsightedness caused by loss of elasticity of the lens of the eye, occurring typically in middle and old age.
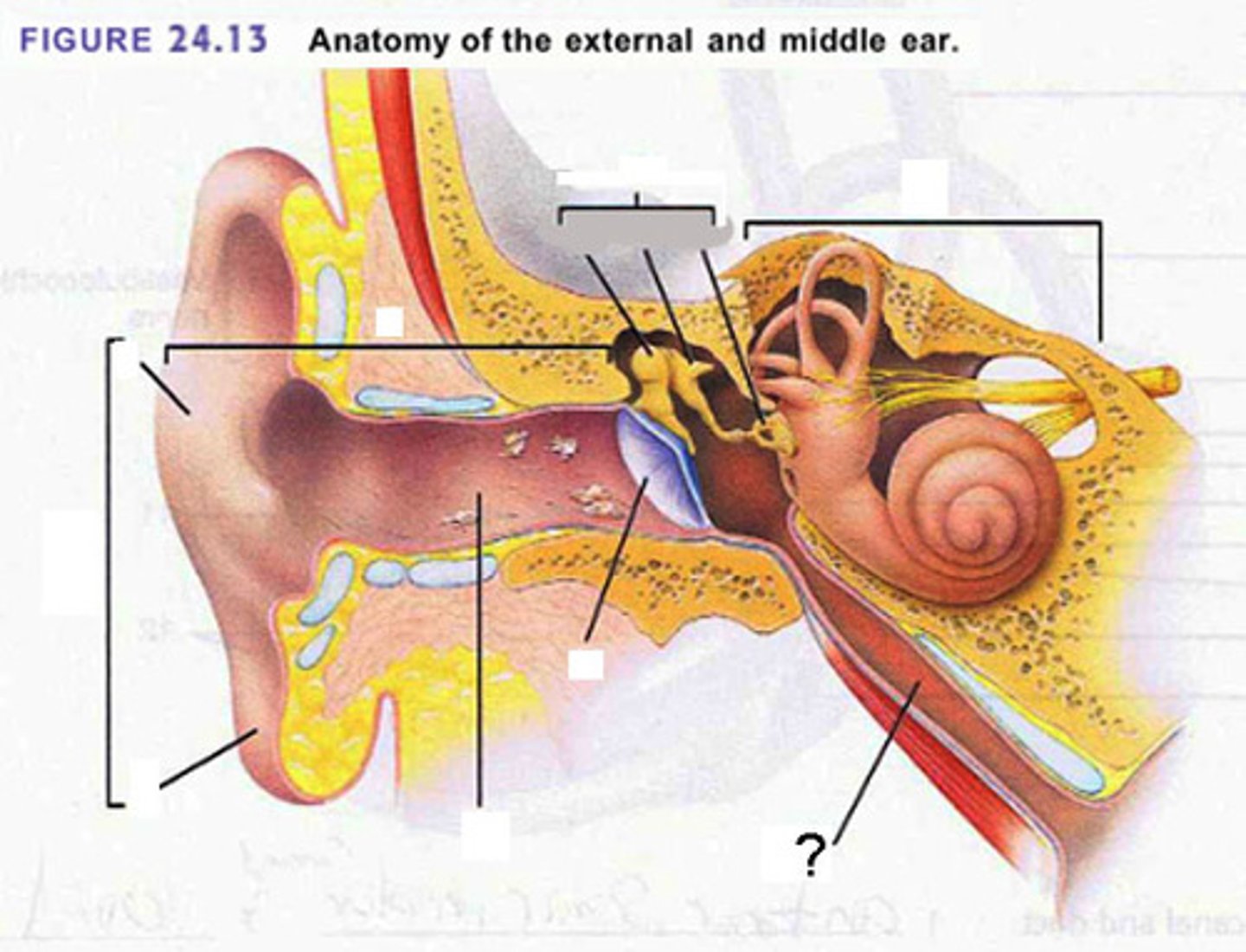
Auricle (pinna)
flap of the ear; the protruding part of the external ear, or pinna
External acoustic meatus
Canal in the exteral surface of the temporal bone, bounded internally by the tympanic membrane
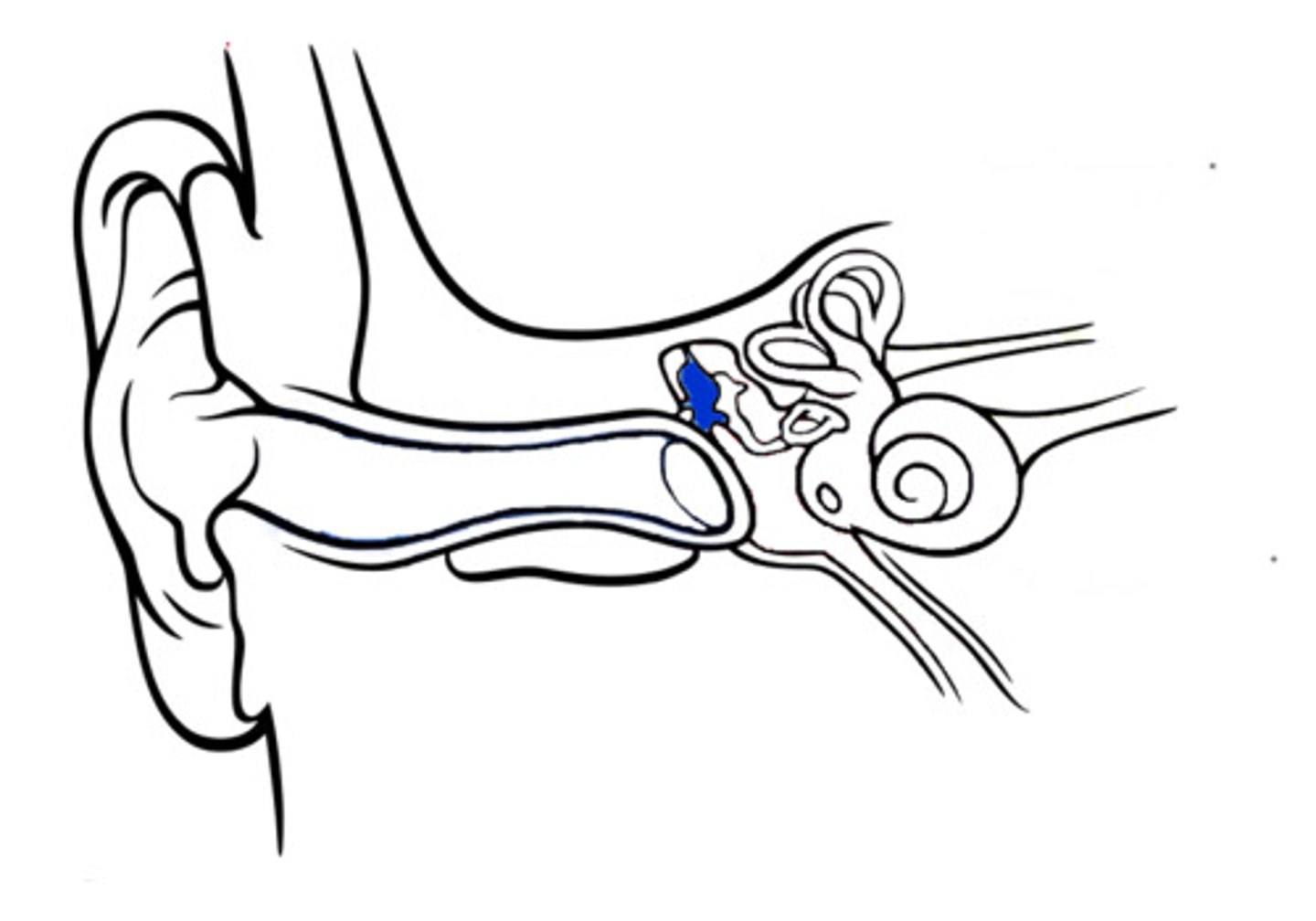
external ear
outer structures of the ear that collect sound
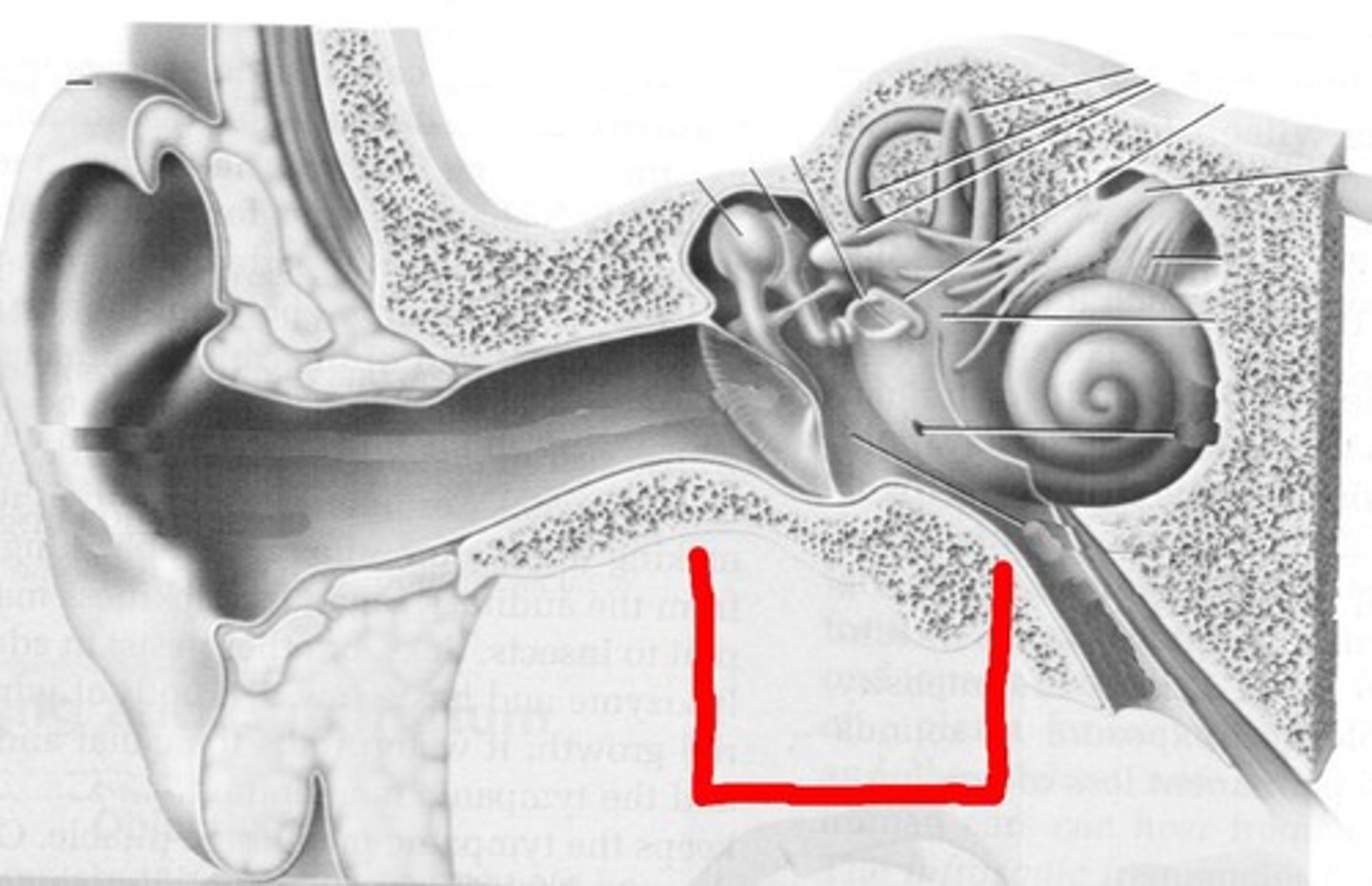
middle ear
the chamber between the eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea's oval window
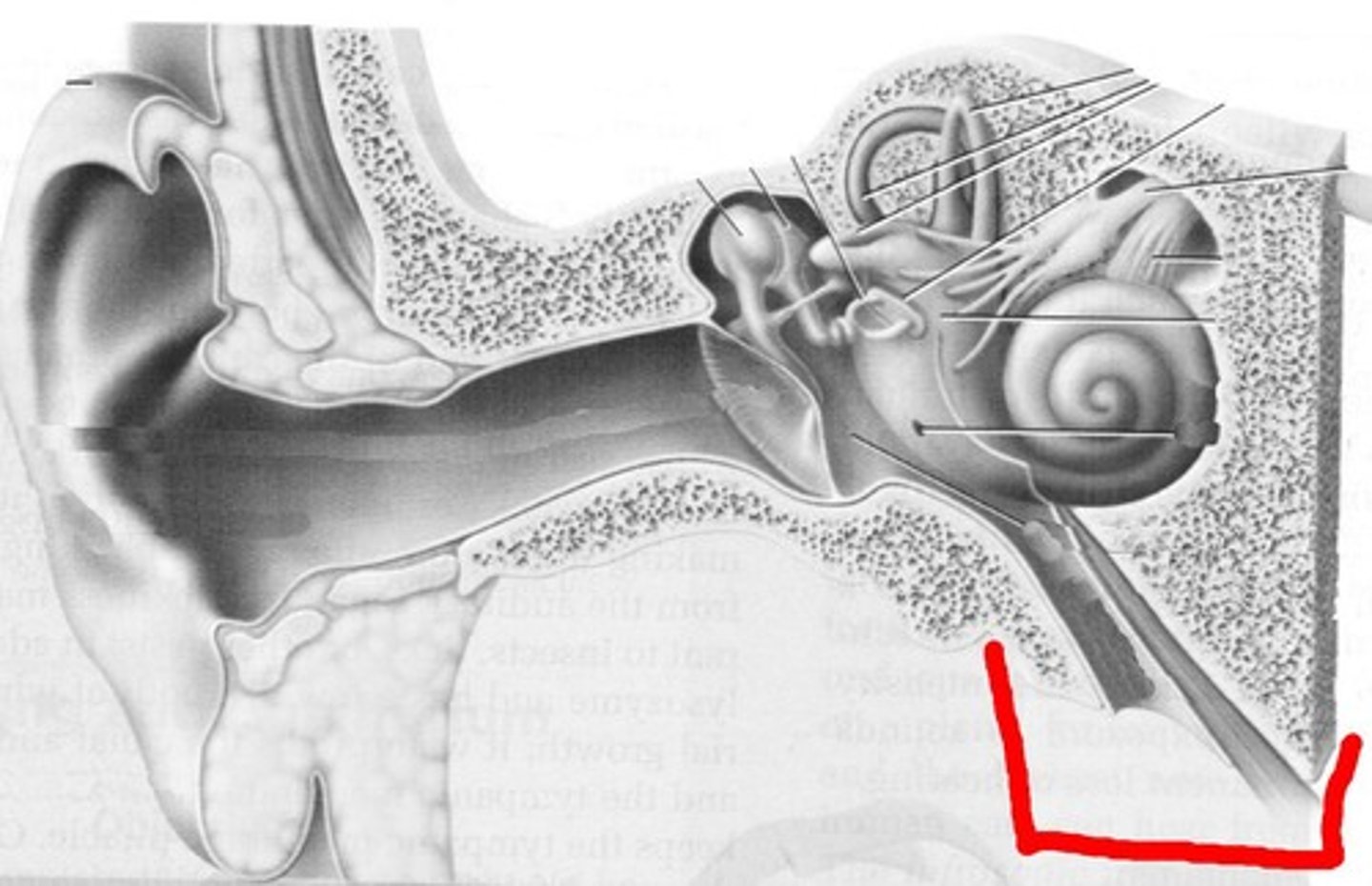
inner ear
the innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibule
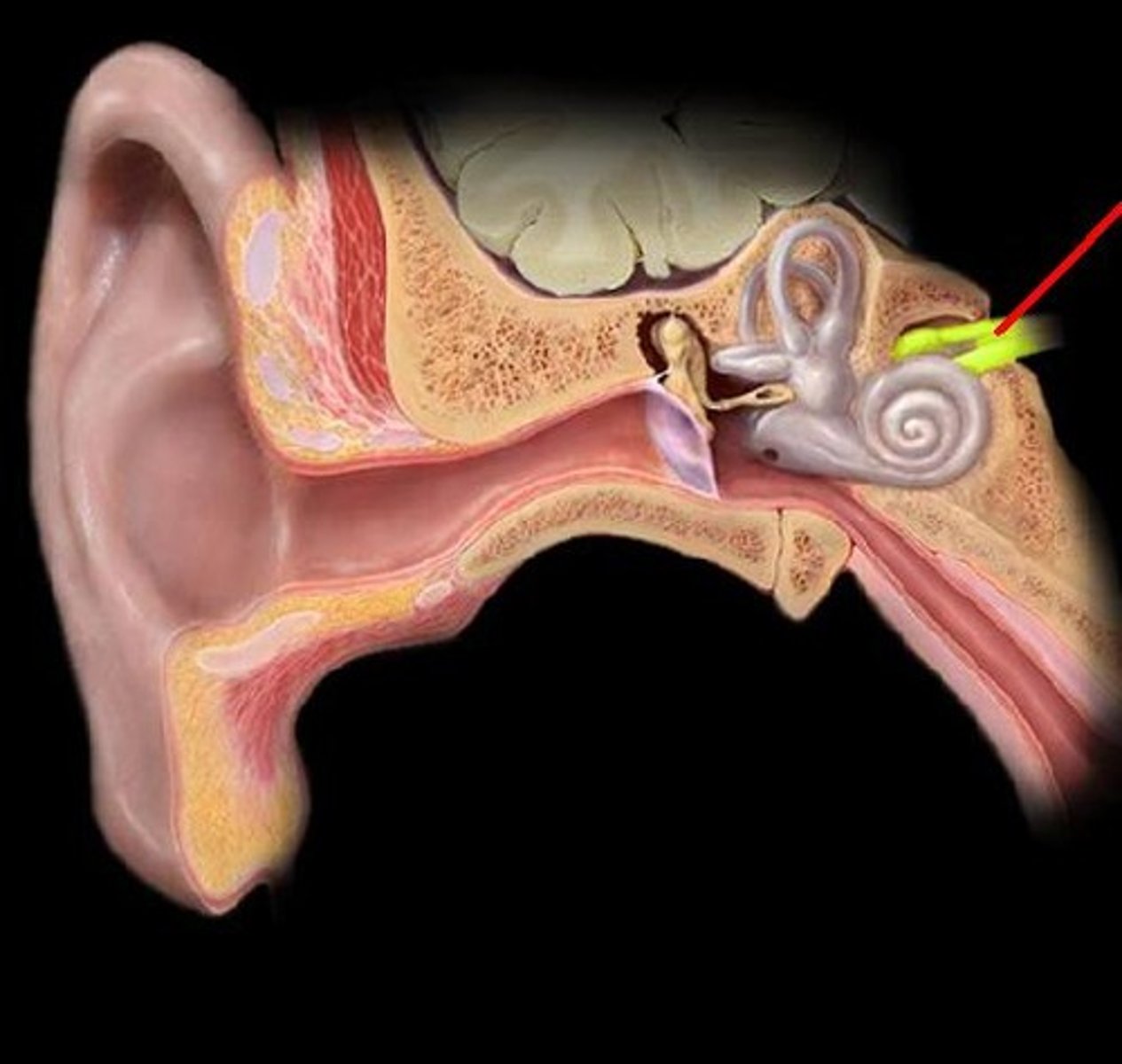
vestibulocochlear nerve
It's made of the vestibular nerve, which monitors sensations of balance, position, and movement and the cochlear nerve, which monitors hearing receptors.
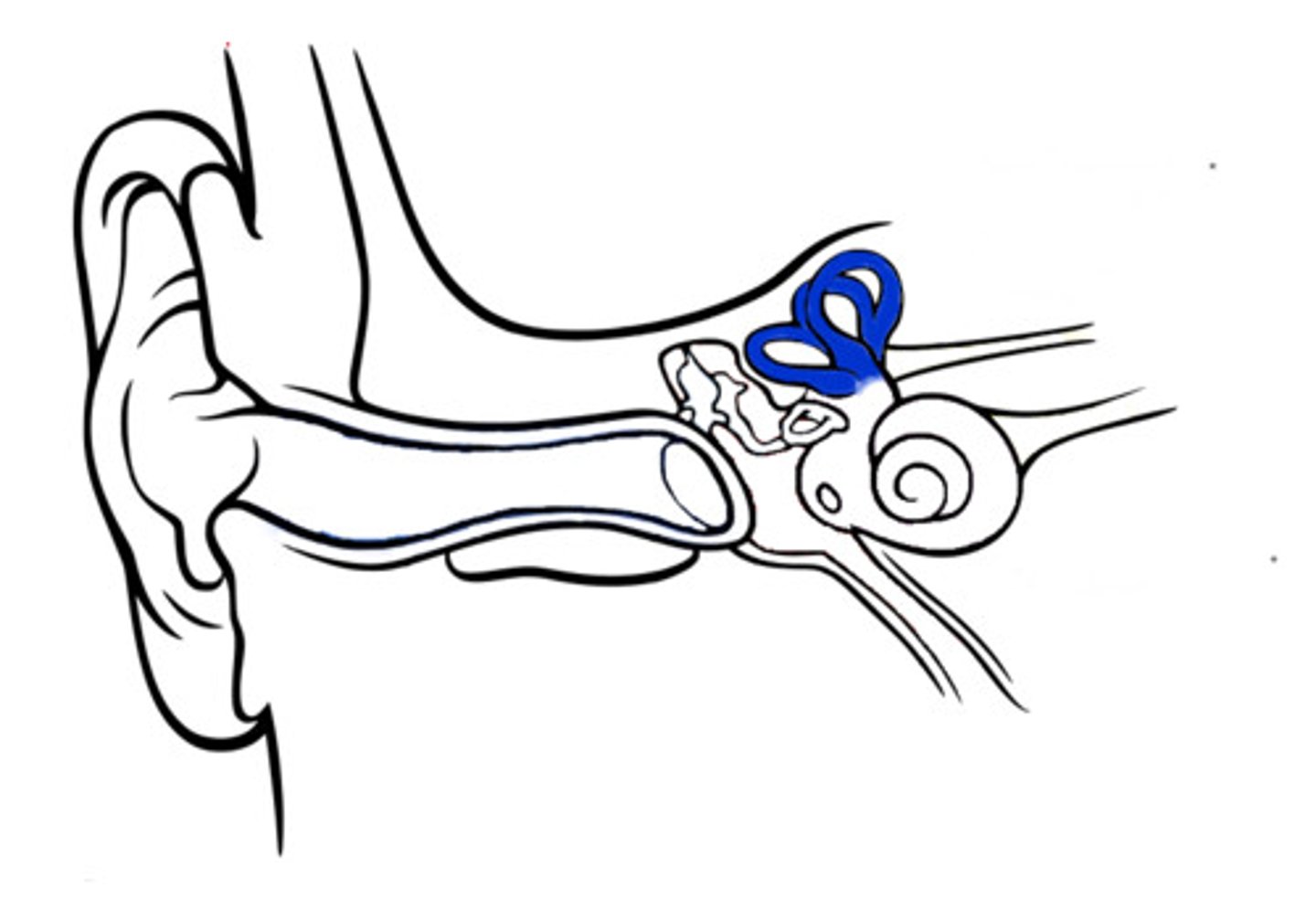
semicircular canals
fluid-filled structures in the inner ear that are associated with the sense of balance
vestibule
middle part of the inner ear, in front of the semicircular canals and behind the cochlea, that contains the utricle and the saccule; functions to provide body balance and equilibrium
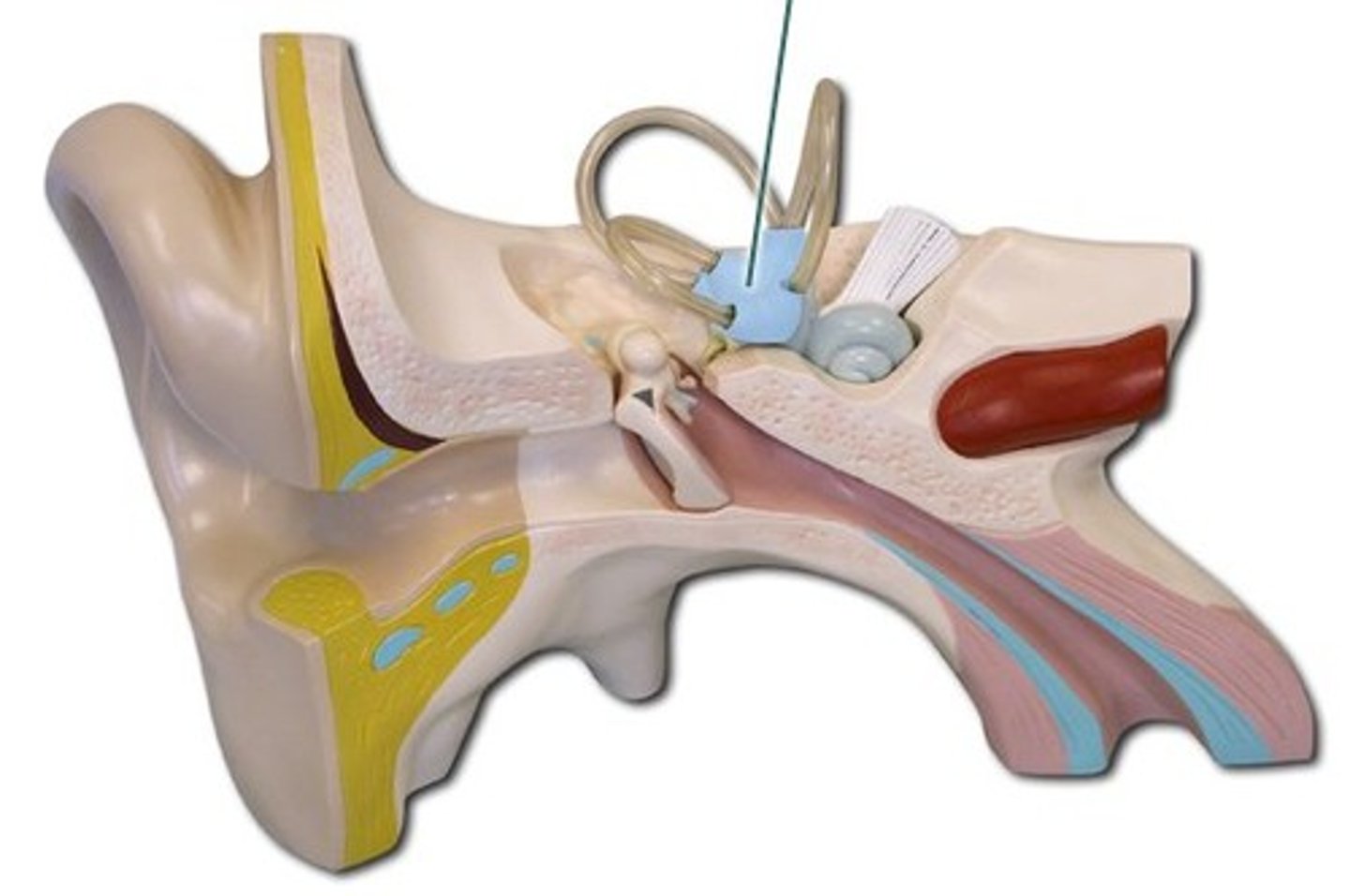
cochlea
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
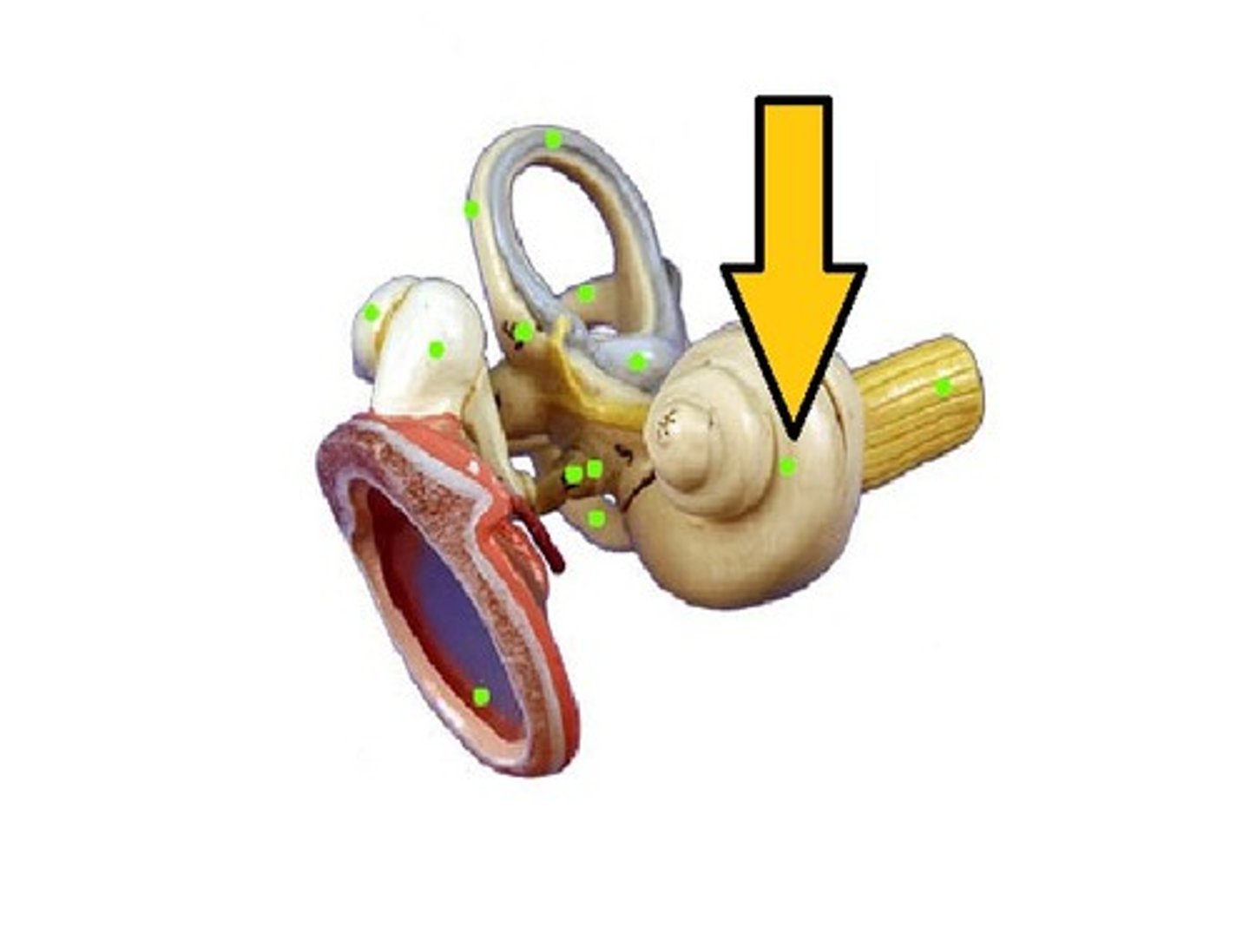
Scala vestibuli
Scala media
Scala tympani
Organ of corti
vestibular membrane
tectoral membrane
basilar membrane
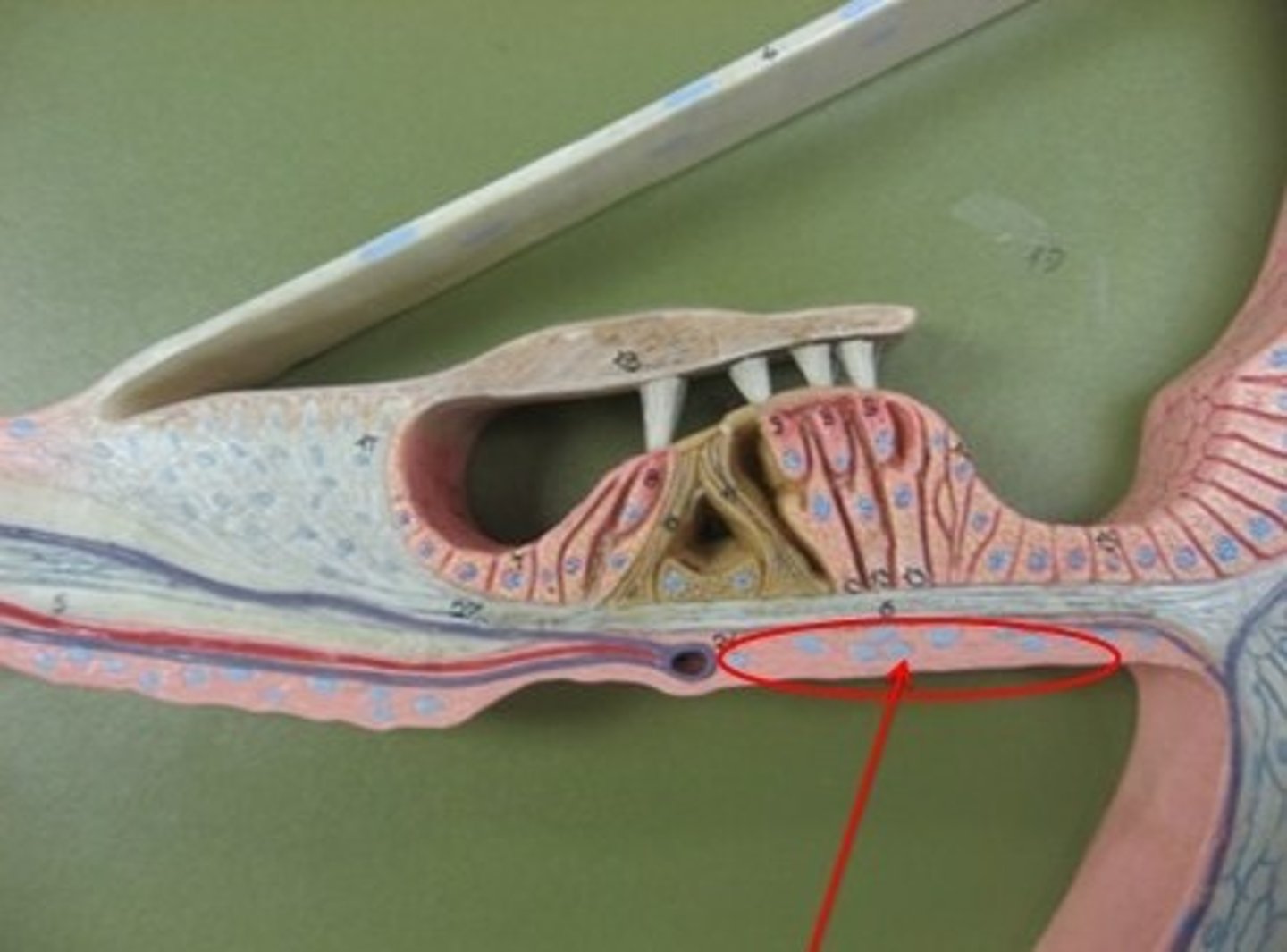
Hair receptor cells
oval window
membrane at the enterance to the cochlea through which the ossicles transmit vibrations
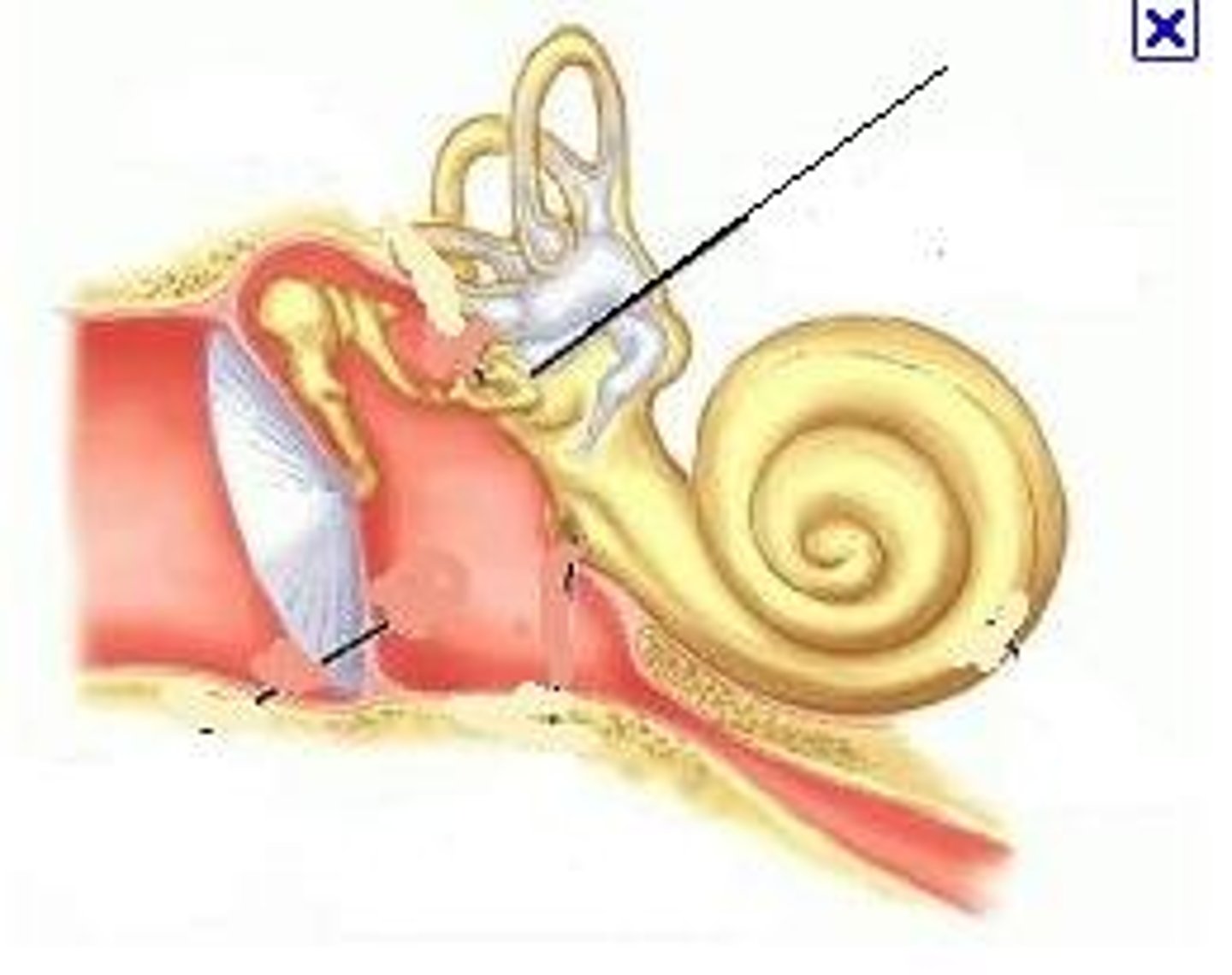
malleus
hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
incus
anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
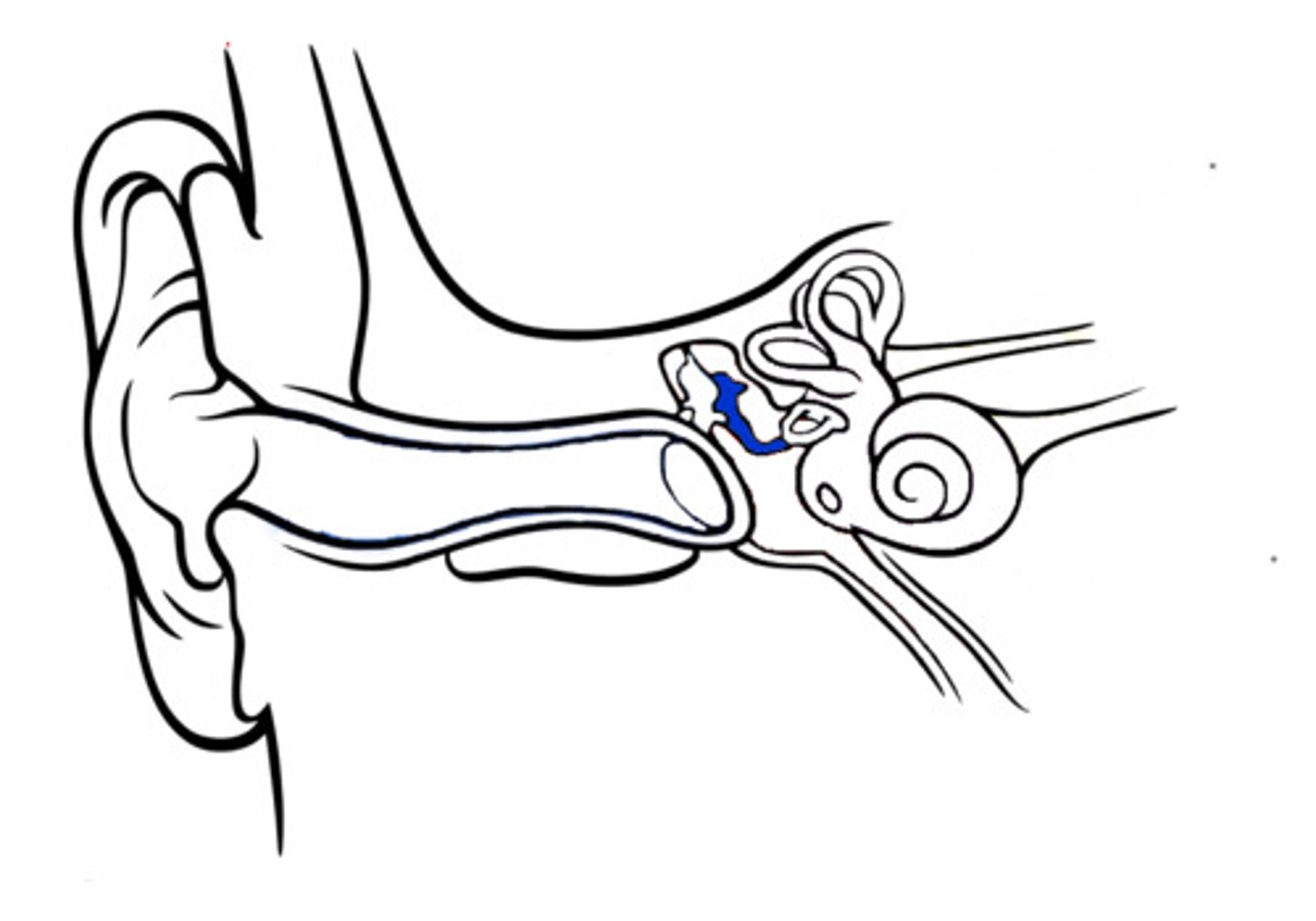
stapes
stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
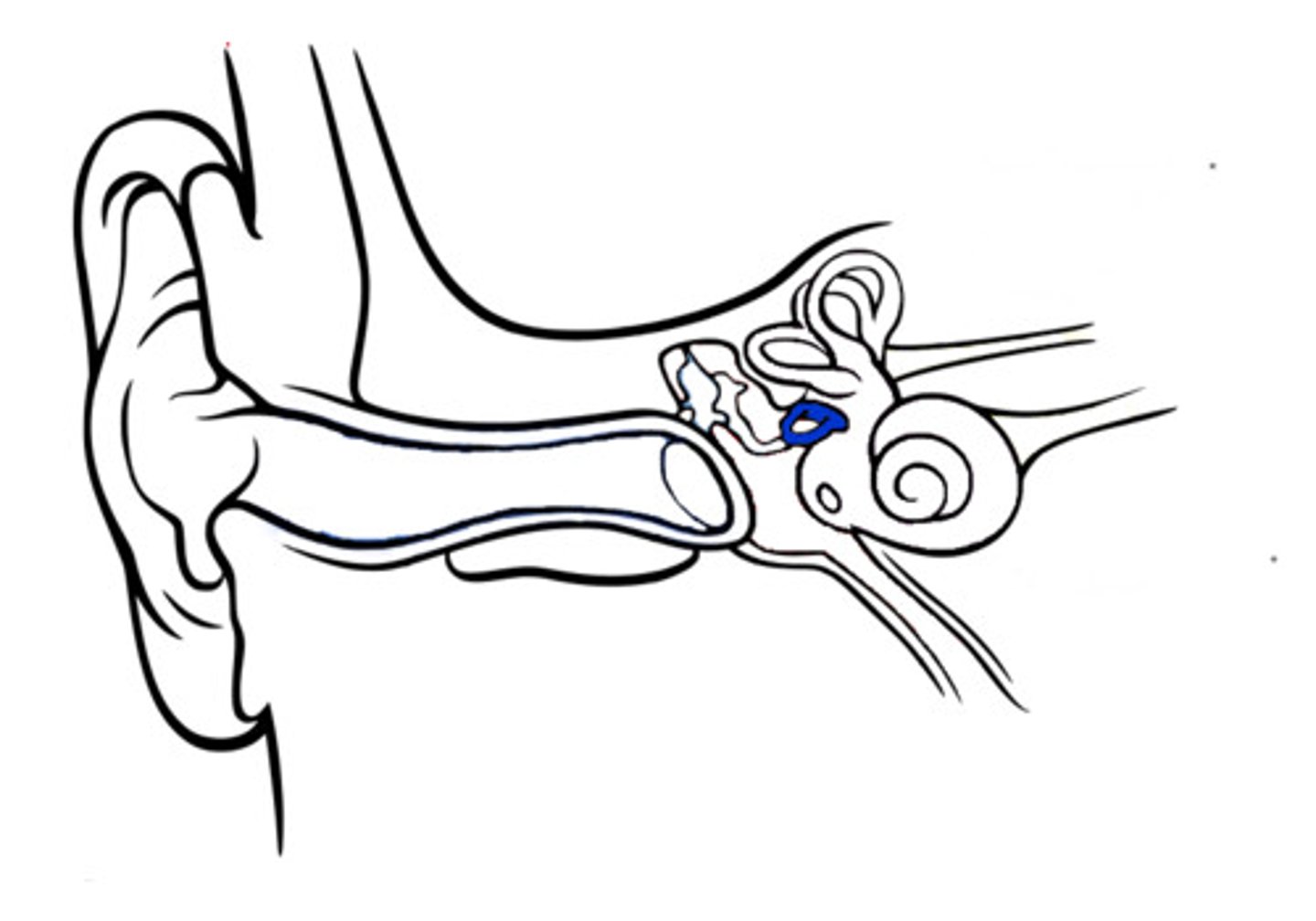
auditory/eustation tube
Connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx.
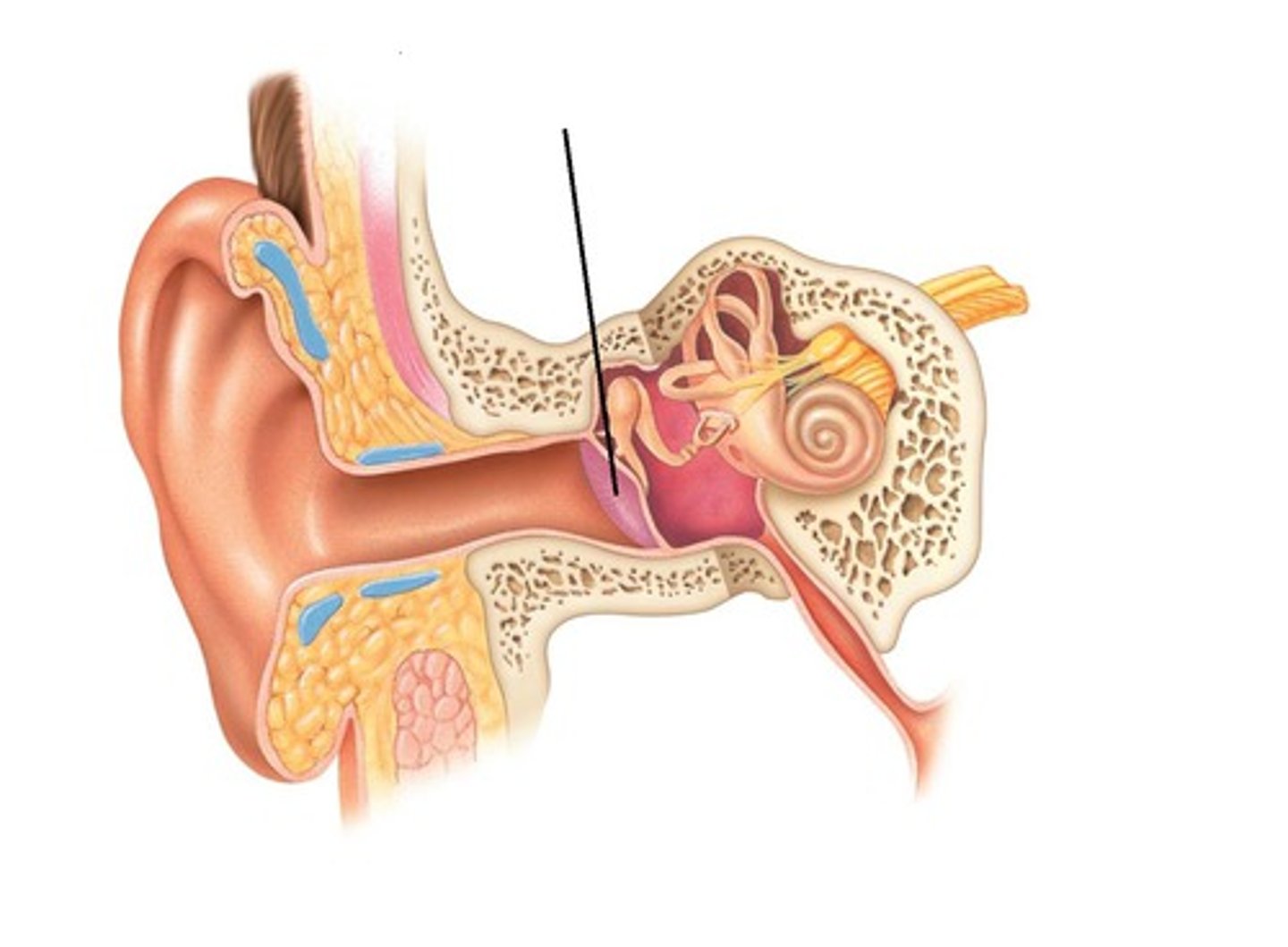
tympanic membrane
The eardrum. A structure that separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves.
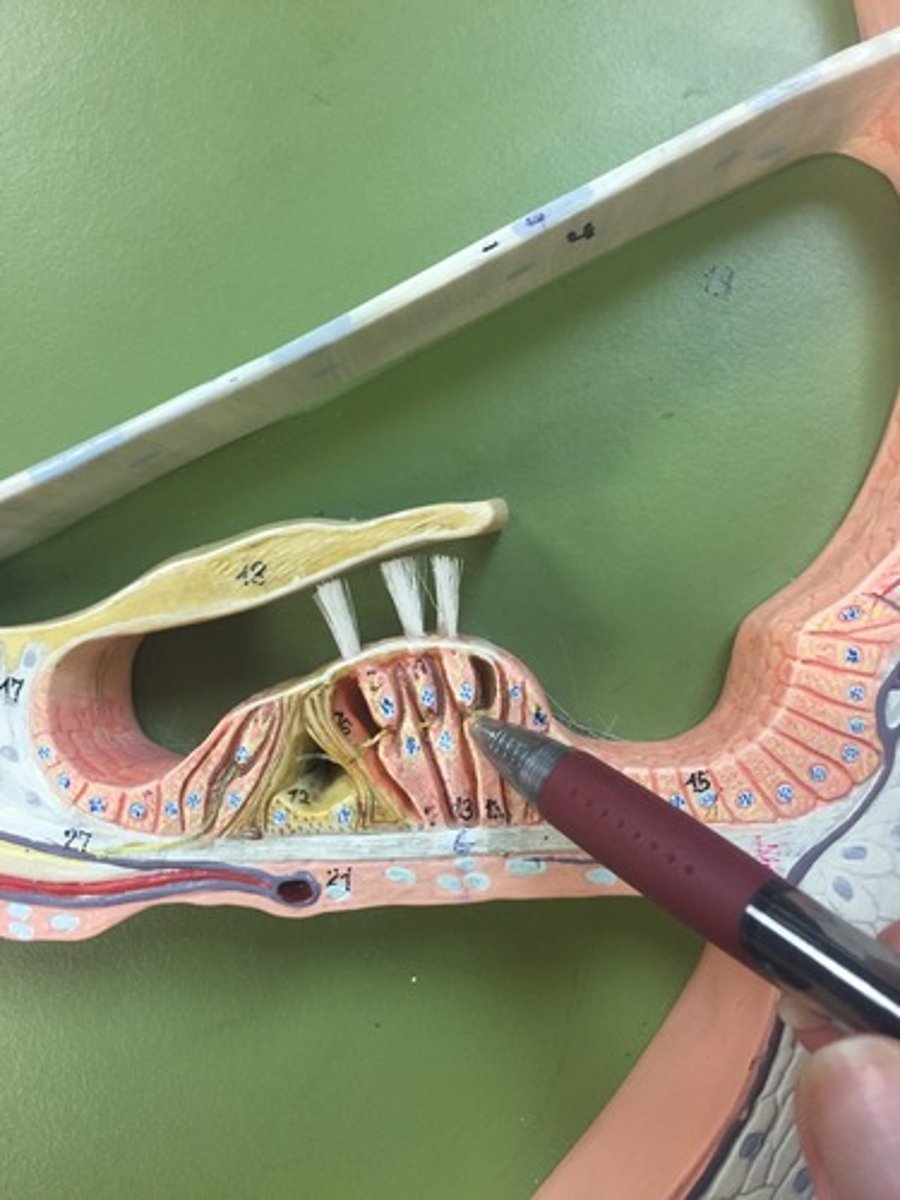
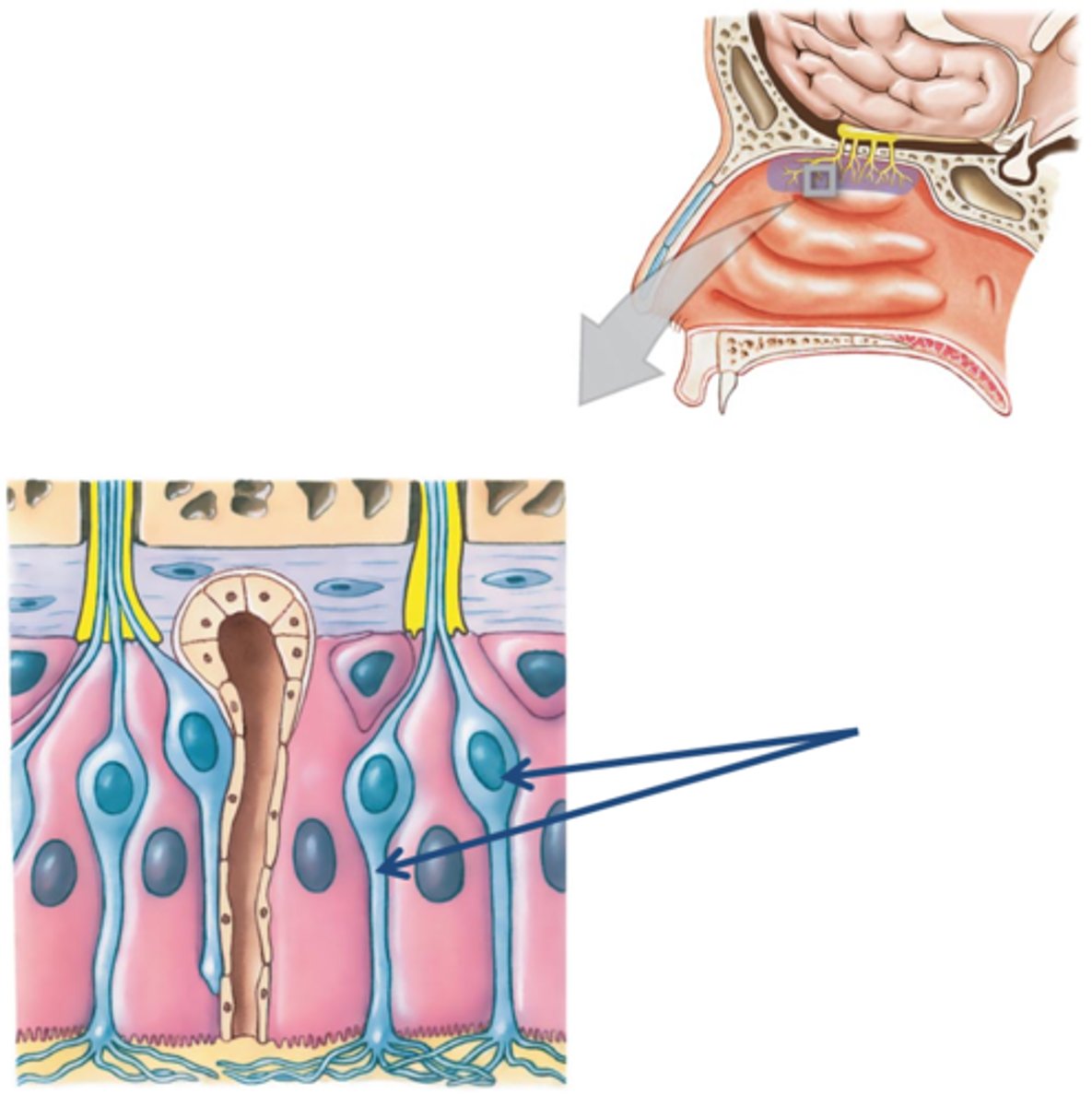
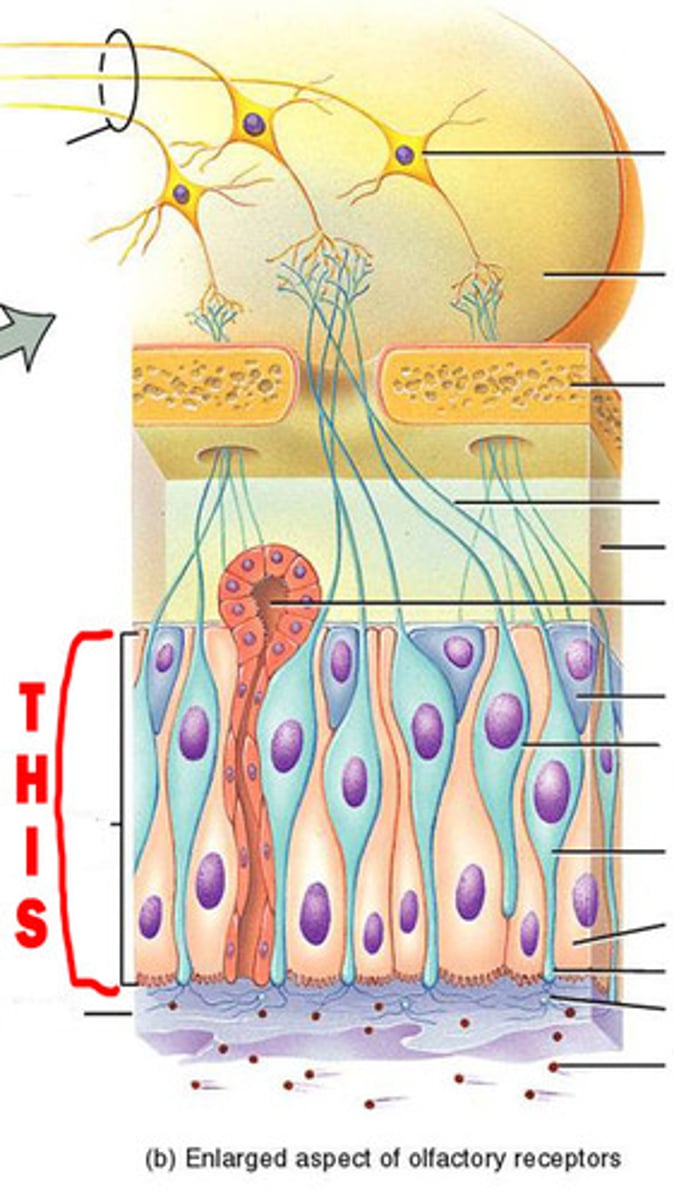
Olfactory receptor
nerve endings that act as the receptors for the sense of smell
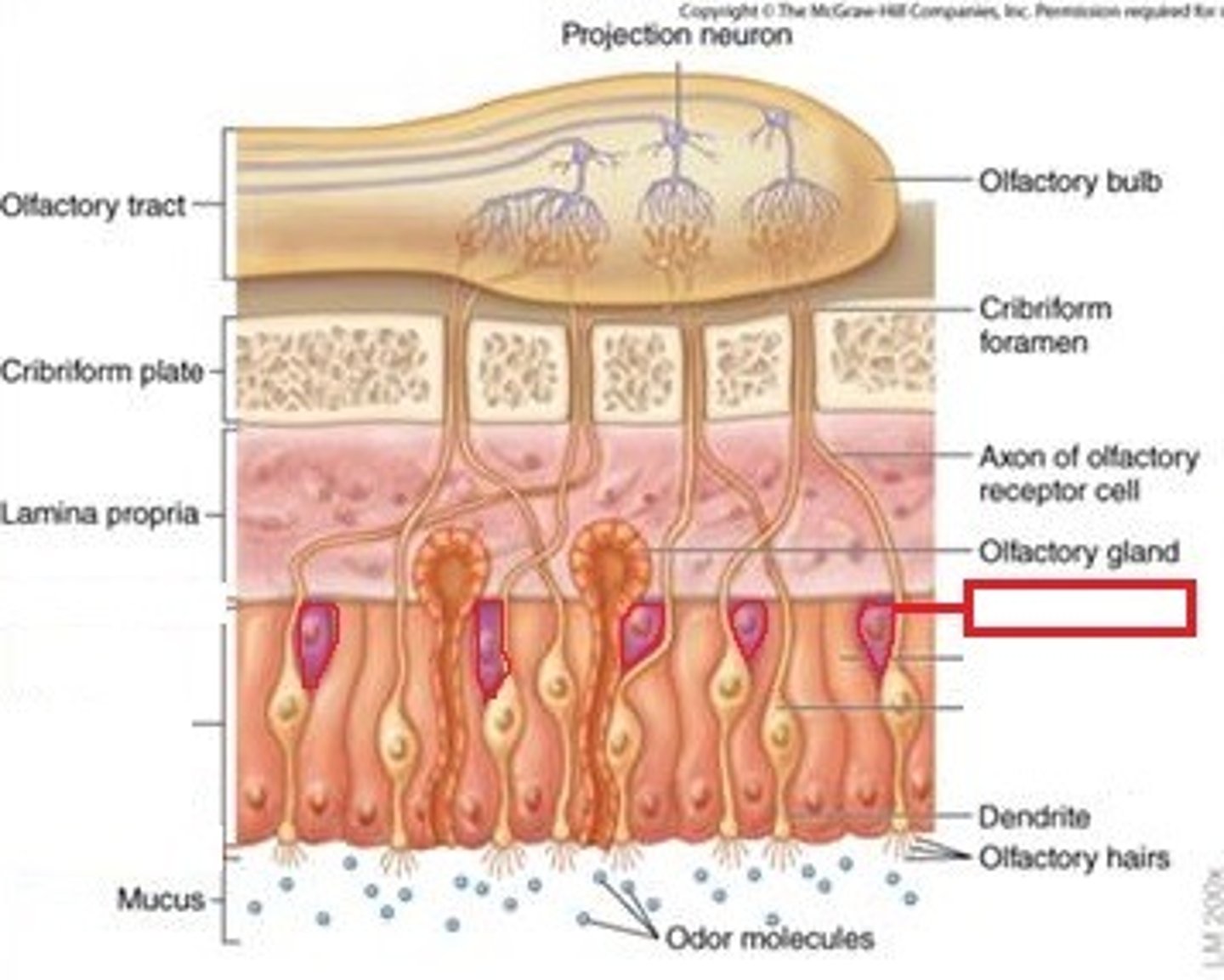
Basal Cell (Olfactory Epithelium)
cells capable of division and differentiation into either supporting or olfactory cells.
Supporting cells (olfactory epithelium)
J.
non-neural cells in the olfactory epithelium that function as metabolic and physical support for the olfactory epithelium.
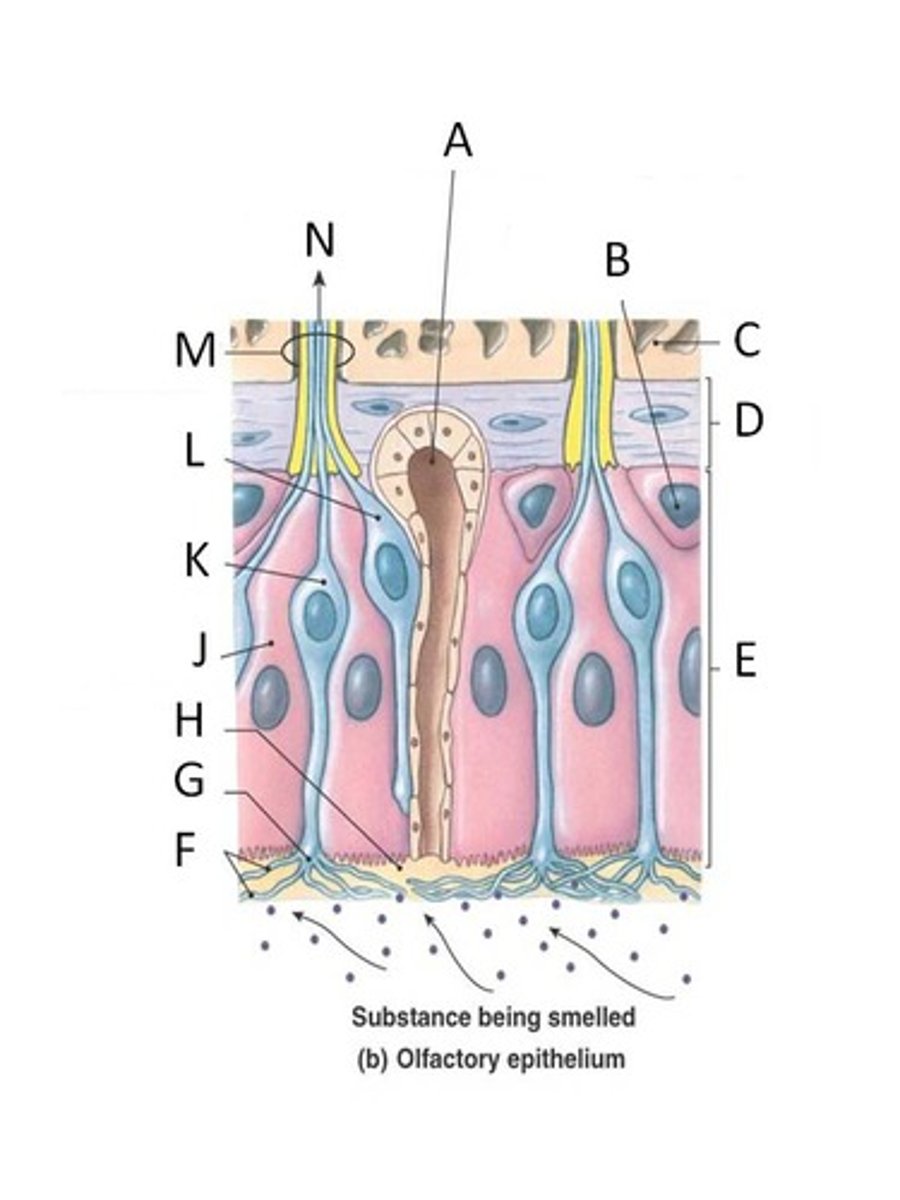
Olfactory epithelium
Layer of epithelium below the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone responsible for detecting odors.
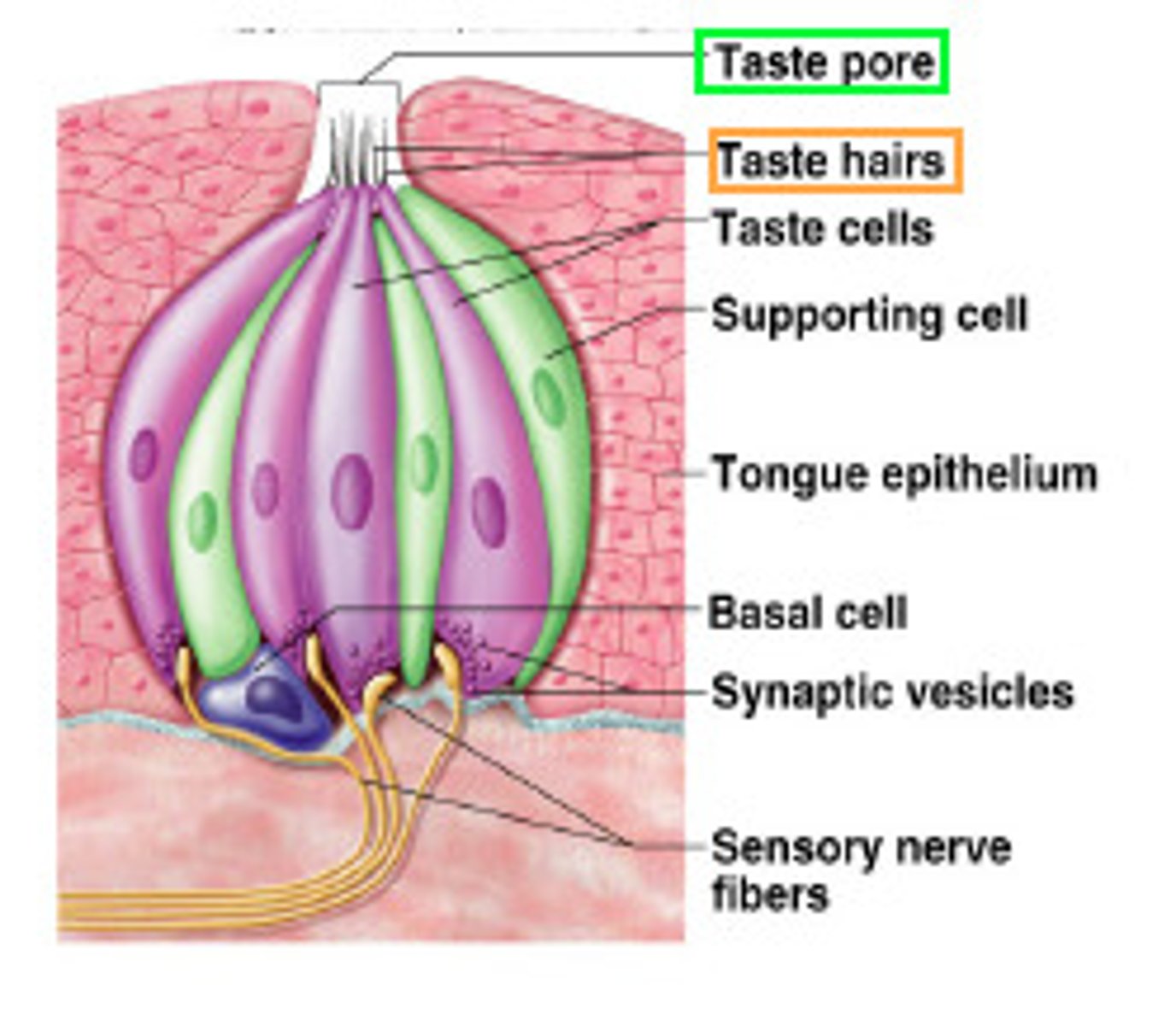
papillae (taste buds)
Receptor organ for detecting taste
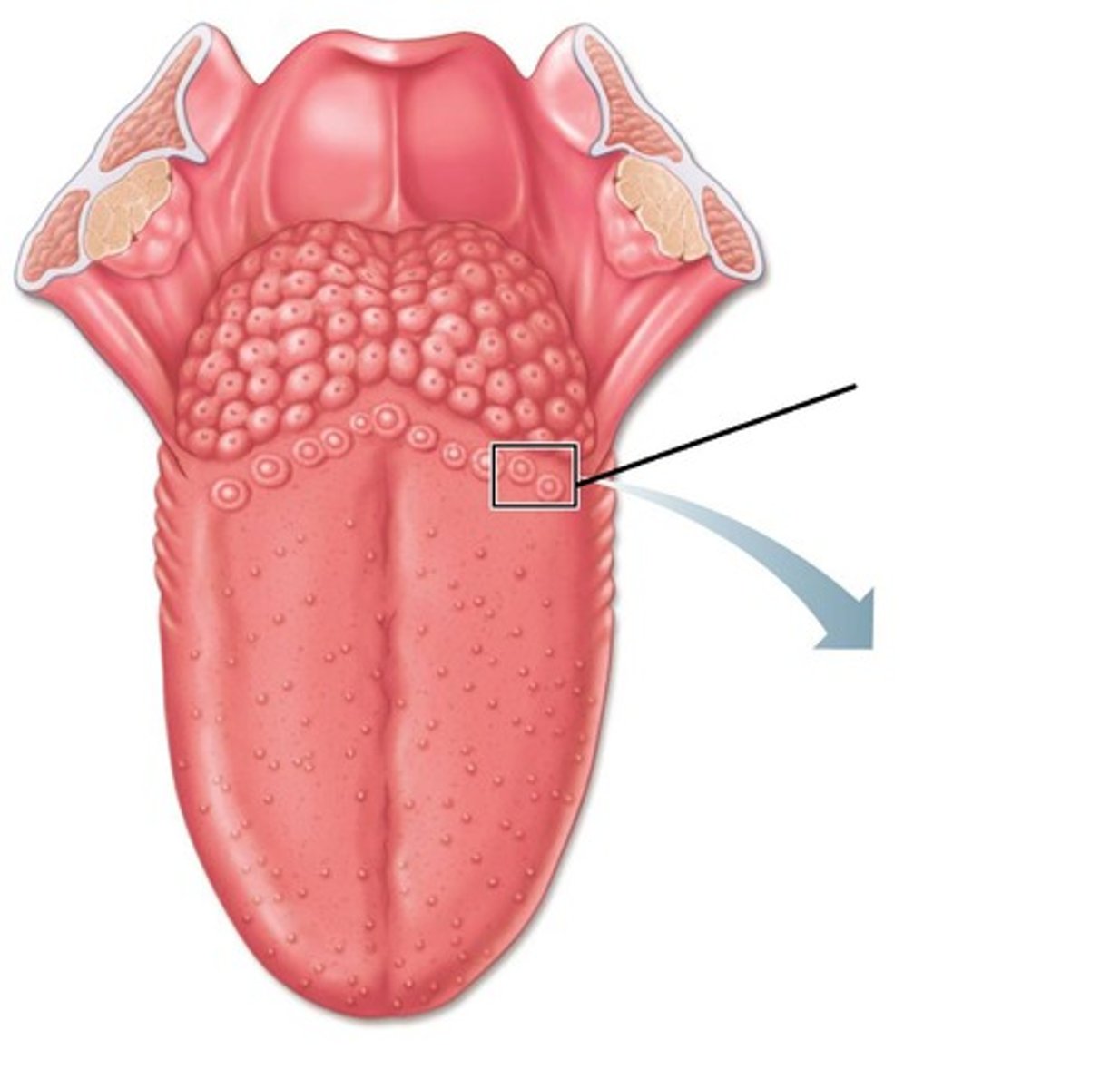
Taste receptor cell
Sensory cells within the taste bud that respond to tastents.