Unit 4 Bio
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Last updated 2:01 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
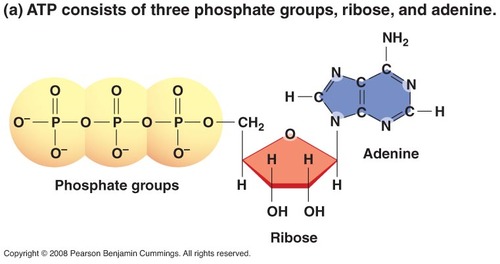
ATP
adenosine triphosphate; energy is stored in the bonds from breaking down organic compounds (glucose) during cellular respiration; energy for cell activities
2
New cards
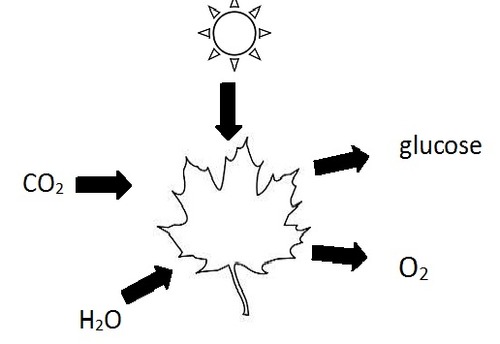
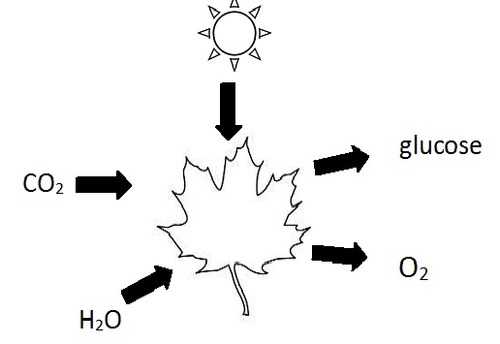
Reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide and water
3
New cards
Products of photosynthesis
glucose and oxygen
4
New cards
Reactants of cellular respiration
glucose and oxygen
5
New cards
Products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
6
New cards
Alcohol fermentation
Glycolysis then production of alcohol and CO2; anaerobic respiration; done in yeasts and bacteria
7
New cards
Lactic acid fermentation
Glycolysis then production of lactate; occurs in muscle cells of animals
8
New cards
Types of anaerobic respiration
alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
9
New cards
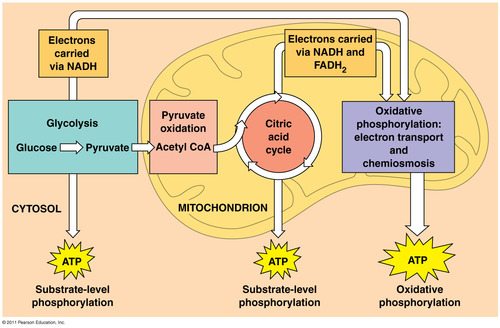
Aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen; more effective at making ATP; occurs in the mitochondria
10
New cards
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen; no mitochondria needed
11
New cards
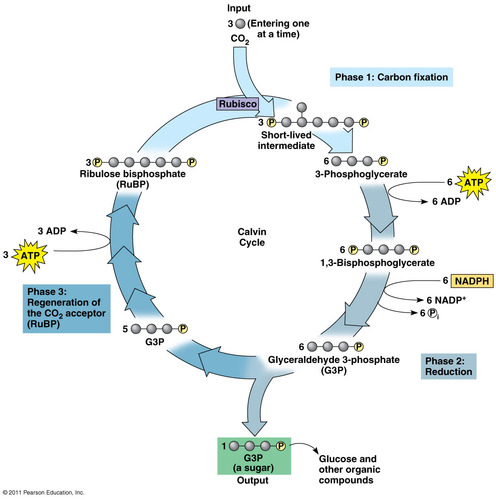
Calvin cycle
a pathway of photosynthesis in which carbon dioxide (the carbon source for glucose) is converted into glucose using ATP
12
New cards
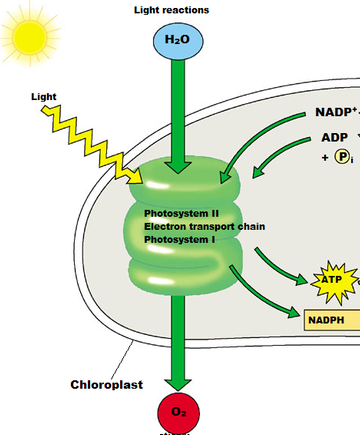
Light reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH (for the Calvin Cycle)
13
New cards
Formula for aerobic respiration
Glucose + 6 oxygen -> 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water
14
New cards
Organelle where aerobic respiration occurs
mitochondria
15
New cards
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
16
New cards
Organelle where photosynthesis occurs
Chloroplast
17
New cards
What gas did we measure in the photosynthesis lab?
oxygen
18
New cards
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
19
New cards
How many ATP produced in glycolysis?
2 ATP
20
New cards
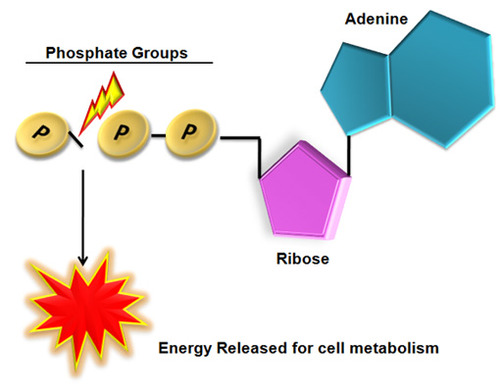
What happens when ATP has a phosphate removed?
energy is released
21
New cards
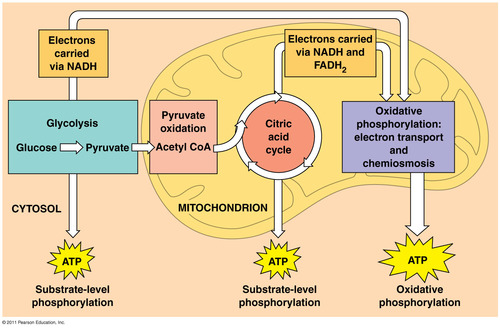
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
22
New cards
Where do the Krebs cycle and electron transport take place?
in the mitochondria
23
New cards
ADP
adenosine diphosphate, only has two phosphates
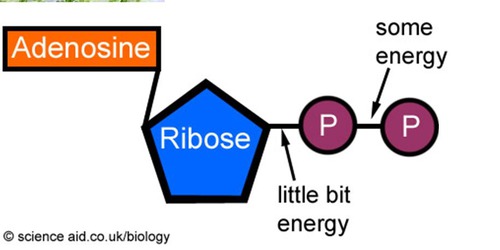
24
New cards
If oxygen is present, what happens after glycolysis?
Krebs Cycle
25
New cards
Products of the light reactions used in Calvin Cycle
ATP, NADPH
26
New cards
What living things do aerobic respiration?
any cell with a mitochondria (all eukaryotes)
27
New cards
Carbohydrate structure
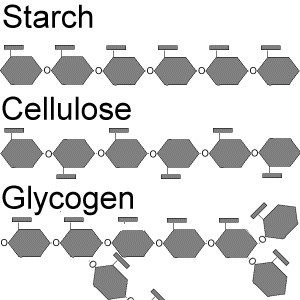
28
New cards
What is ALWAYS the first step of cellular respiration?
glycolysis (with or without oxygen)
29
New cards
Which type of respiration makes the most energy?
aerobic respiration