Unit #1 test review 🌟
5.0(1)Studied by 32 people
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:45 PM on 10/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
What is ordinary matter made from?
Made from the atoms from the 92 elements.
2
New cards
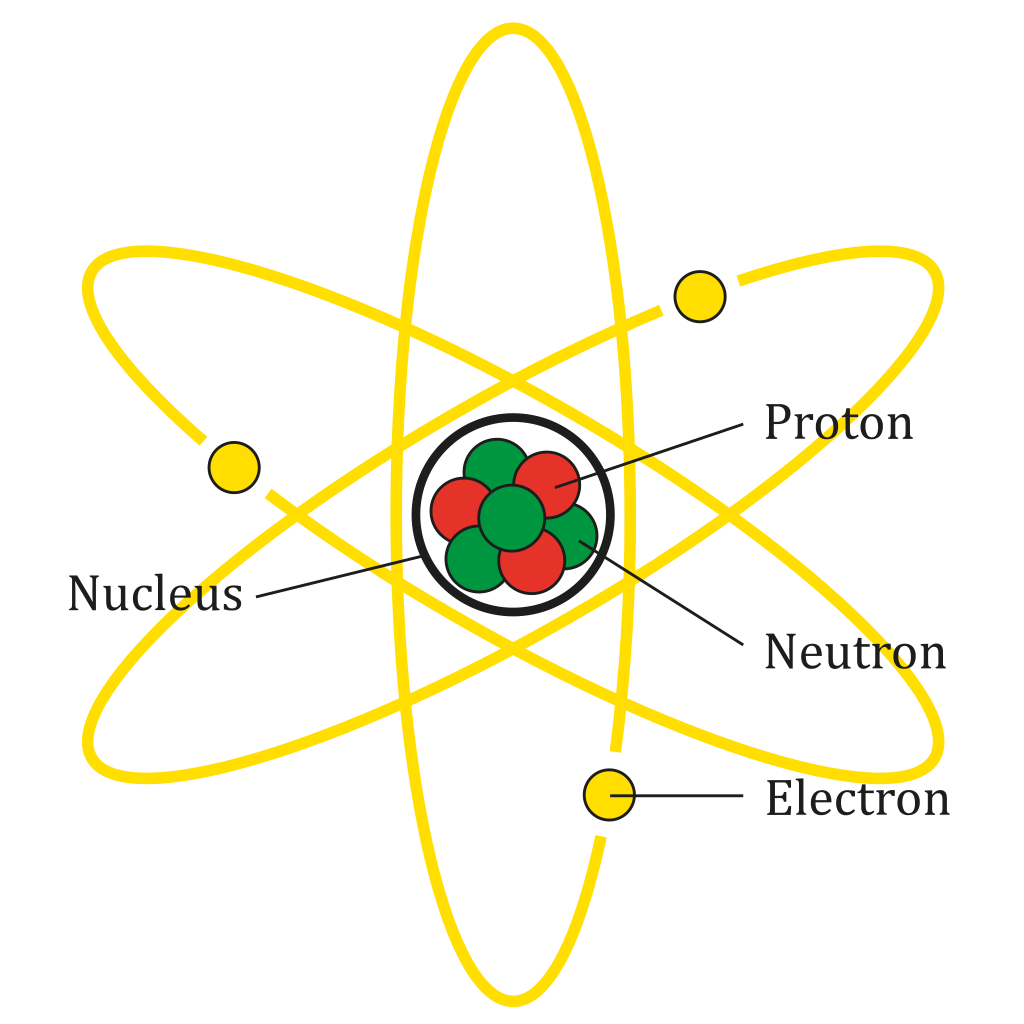
What are atoms made of?
Smaller particles: protons, neutrons, electrons.
3
New cards
What did Dalton discover?
1. "Atoms cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged through chemical reactions."
2. All elements are made from atoms.
3. Compounds are made from combining atoms in whole # ratios.
2. All elements are made from atoms.
3. Compounds are made from combining atoms in whole # ratios.
4
New cards
What charge do electrons have?
Negative, -.
5
New cards
Do atoms have a charge?
No, most are neutral.
6
New cards
Are the # of protons and electrons equal in a neutral atom?
Yes.
7
New cards
True/False: The number of protons determines the element.
True! (ex. Hydrogen H has 1, Tin Sn has 50)
8
New cards
How do atoms interact with each other?
Via their electrons.
9
New cards
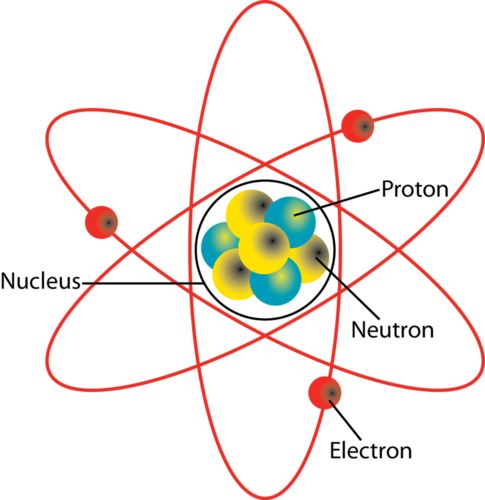
Is the nucleus the center of the atom? And what is it made of?
Yes! Made from neutrons and protons.
10
New cards
What was Democritus' model of the atom?
A hard sphere.

11
New cards
What was Democritus' main idea?
Matter is made of very small and invisible particles, "atomos."
12
New cards
What was Dalton's model and thinking? And was was cool about it?
Same thinking as Democritus! Matter was made up of atoms. Model = hard sphere
13
New cards
What did JJ Thomson discover and HOW?
The electron! Through cathode ray experiments.
14
New cards
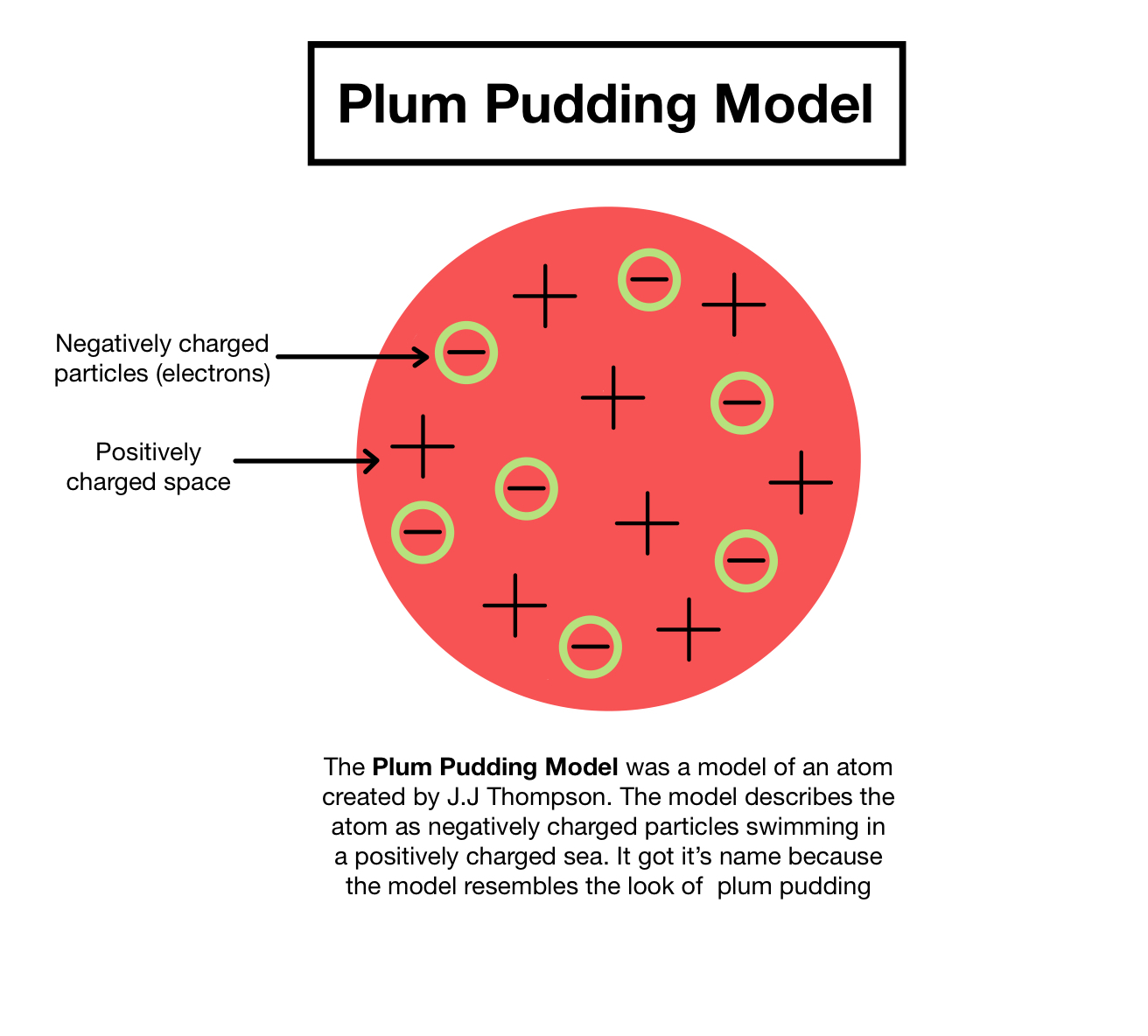
What was JJ Thomson's model of an atom?
Plum-pudding model. The + must exist to cancel the -, in order to create neutral atom. NO NUCLEUS IN THIS MODEL!
15
New cards
Who did the gold foil/alpha scattering experiment?
Rutherford!
16
New cards
What did the gold foil/alpha scattering experiment show?
1. There is a nucleus in the atom and it is positively charged (because sometimes the alpha particle would shoot back, instead of going through. It would hit the nucleus = the nucleus has a very big impact).
2. The atom is mostly empty space (most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold foil without any problem).
2. The atom is mostly empty space (most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold foil without any problem).
17
New cards
What was Rutherford's model of the atom?
Tiny, dense, and positively charged nucleus. Light, negative electrons surrounding it.

18
New cards
What did Rutherford discover?
All atoms have most of their mass concentrated in a tiny, dense, and positively charged nucleus.
19
New cards
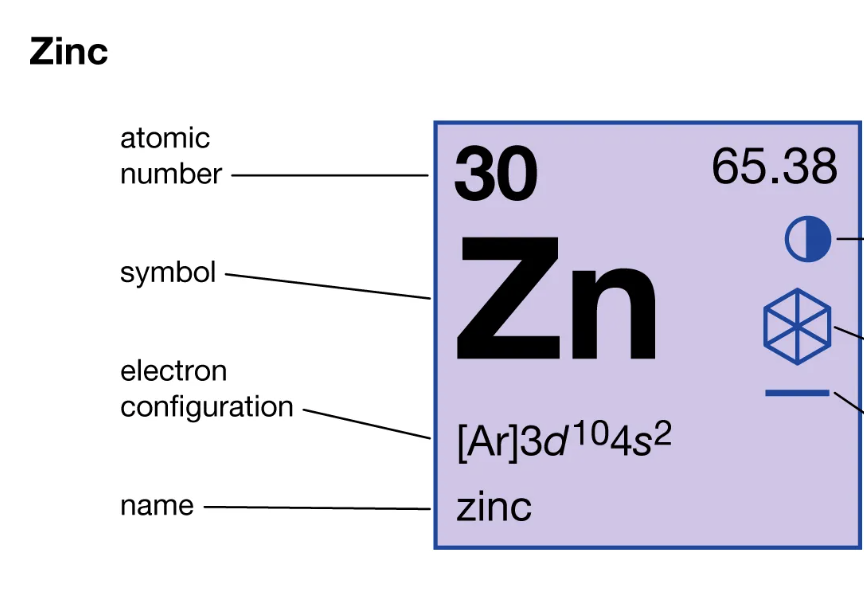
What is the atomic number of an element? And where is it on the periodic square?
The # of protons in the nucleus. Located TOP right in the square: it determines the element. (ex. Zinc's atomic number is 30).
20
New cards
Do all the atoms of the same element have the same # of protons?
Yes. All Helium atoms = 2 protons, Carbon atoms = 6 protons.
21
New cards
How does the nucleus stay together?
Neutrons and protons (+) repel each other.
22
New cards
True/False: Atoms of the same element won't necessarily have the same # of neutrons.
True!
23
New cards
What is this number represent: (Carbon-12, Carbon-13)
The # of neutrons.
24
New cards
Atomic mass
The weighted average mass of all isotopes of an ELEMENT, (amu = units).
25
New cards
What process is when atomic nucleus decays or gives off energy?
Radioactivity.
26
New cards
What is the lightest particle in the nucleus?
The electron- they are very very fast!
27
New cards
In reality, what is the electron cloud the size of?
An atom!
28
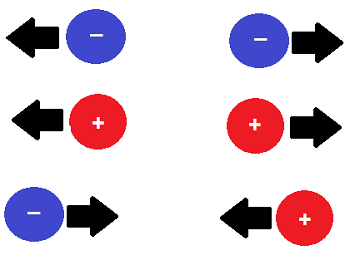
New cards
How is electromagnetic force LIKE and UNLIKE gravity?
LIKE: acts of electric charge
UNLIKE: electromagnetic force can attract/repel
UNLIKE: electromagnetic force can attract/repel
29
New cards
What are ions?
Charged atoms. They have an uneven # of protons to electrons.
30
New cards
Difference between Na & Na^1+
Na = 11 protons, 11 electrons
Na^1+ = 11 protons, 10 electrons.
Na^1+ = 11 protons, 10 electrons.
31
New cards
True/False: if an atom has over 97 protons, it is radioactive.
Sort of! It must have OVER 83 PROTONS.
32
New cards
What is a chemical reaction?
Creates new compounds (something that is >2 elements) FROM elements.
33
New cards
What is a nuclear reaction?
Creates new elements FROM other elements. 2 MAIN TYPES.
34
New cards
2 types of nuclear reactions.
1. Decay reactions (nucleus spontnsly. breaks up).
2. Bombardment reactions (nucleus is struck by another nucleus/proton/neutron).
2. Bombardment reactions (nucleus is struck by another nucleus/proton/neutron).
35
New cards
What is radiation?
Transmission of matter, energy, waves through space. CAN BE DANGEROUS when it has high energy (breaks chem. bonds in molecules).
36
New cards
Atomic mass equation.
(mass of iso. #1)x(abundance of iso. #1 in DECIMAL FORM) + (however many isotopes you have).
37
New cards
Atomic # vs Atomic mass.
(Atomic weight is the same thing as atomic #).
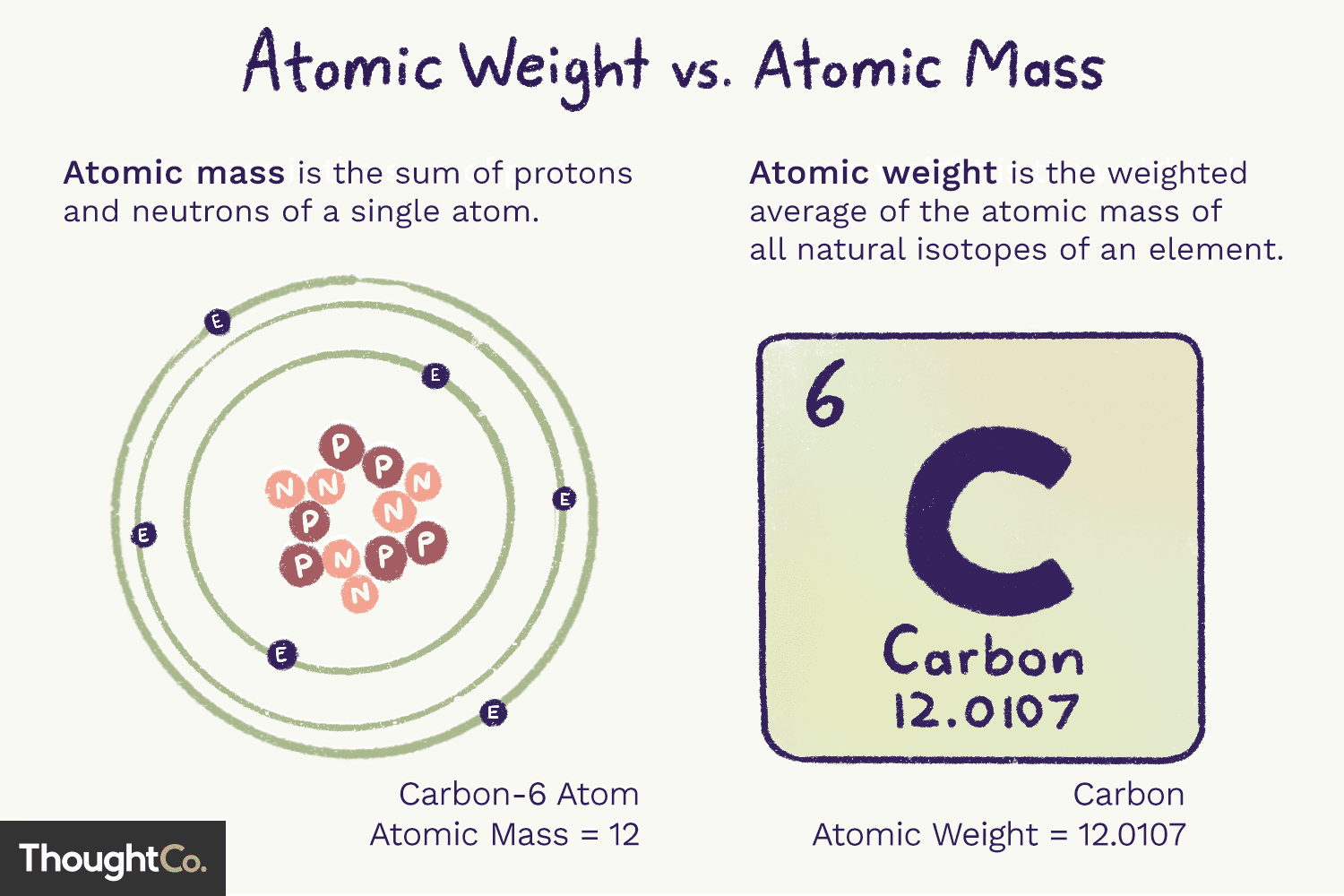
38
New cards
Alpha decay.
- Unstable nucleus shoots out 2 PROTONS + 2 NEUTRONS = to
create new daughter nucleus.
- 42He is the alpha particle that is shoots out.
create new daughter nucleus.
- 42He is the alpha particle that is shoots out.
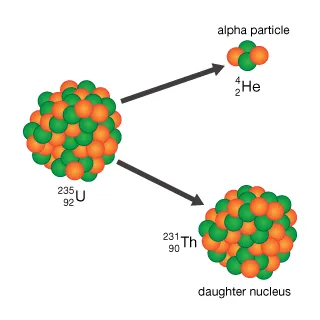
39
New cards
How do the # of protons/neutrons, atomic # and mass # change when ALPHA decay?
Protons: -2
Neutrons: -2
Atomic #: -2
Mass #: -4
Neutrons: -2
Atomic #: -2
Mass #: -4
40
New cards
Beta decay.
when unstable nucleus emits electron (0-1e)
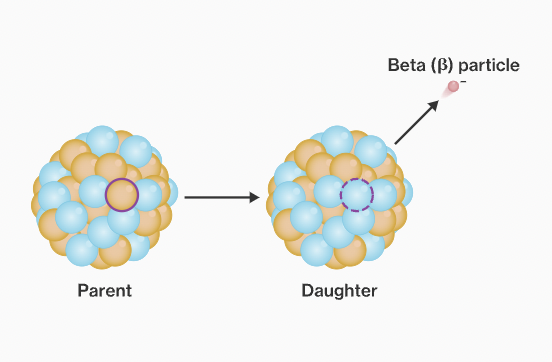
41
New cards
How does the atomic # and mass # change after beta decay?
Atomic #: +1
Mass #: No change.
Mass #: No change.
42
New cards
Gamma decay.
When an excited nucleus decreases its energy by emitting HIGH ENERGY electromagnetic radiation.
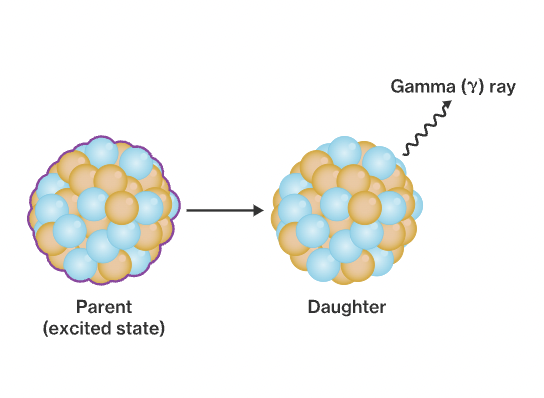
43
New cards
Write the equation for the gamma decay of Cobalt-60.
60,27Co -> 0,0 γ + 60,27Co
44
New cards
How do the protons/neutrons, atomic #/mass # change after going through gamma decay?
ALL STAY THE SAME!
45
New cards
What is a positron?
(0,+1e). A nuclear particle (has the same mass as an electron), but ➕ charge
46
New cards
Positron emission.
When the nucleus releases a proton into 1. a positron, 2. a neutron. Neutron stays inside nucleus.
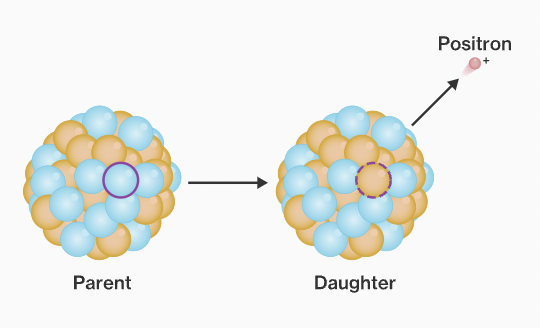
47
New cards
How do the protons/neutrons and atomic#/ mass# change after positron emission?
Protons: -1
Neutrons: +1
Atomic #: -2
Mass #: STAYS SAME
Neutrons: +1
Atomic #: -2
Mass #: STAYS SAME
48
New cards
Equation for positron emission.
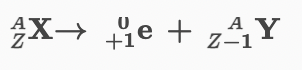
49
New cards
What is half-life?
The time that it takes for half a sample to decay.
50
New cards
Equation for half life.
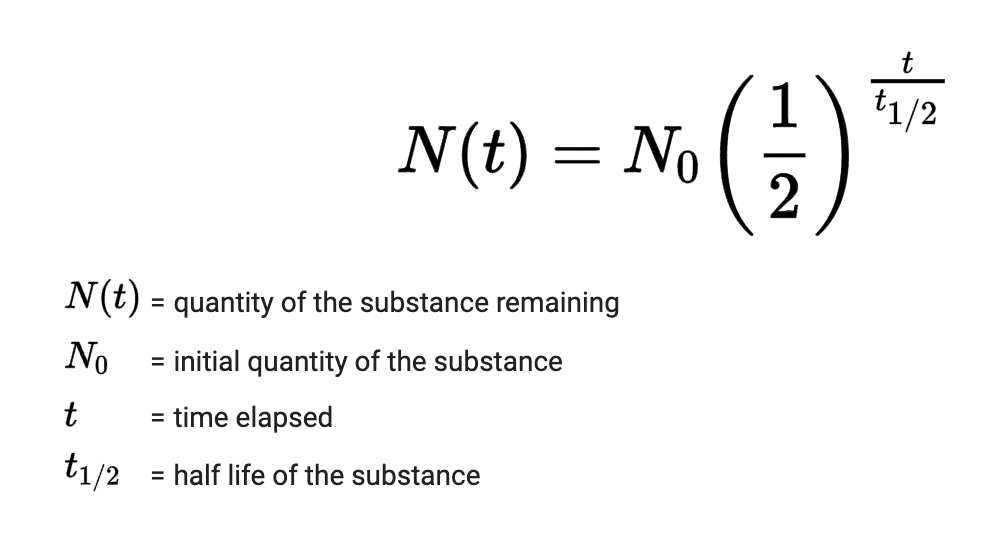
51
New cards
What do you put into a table to find half-life?
# of half lives
time (units)
amount remaining (units)
time (units)
amount remaining (units)
52
New cards
What is radioactive dating?
using the half-life of a radioactive isotope to determine how old something is. LOOKING BACK.
53
New cards
What is nuclear fission?
The forced splitting of a nucleus.
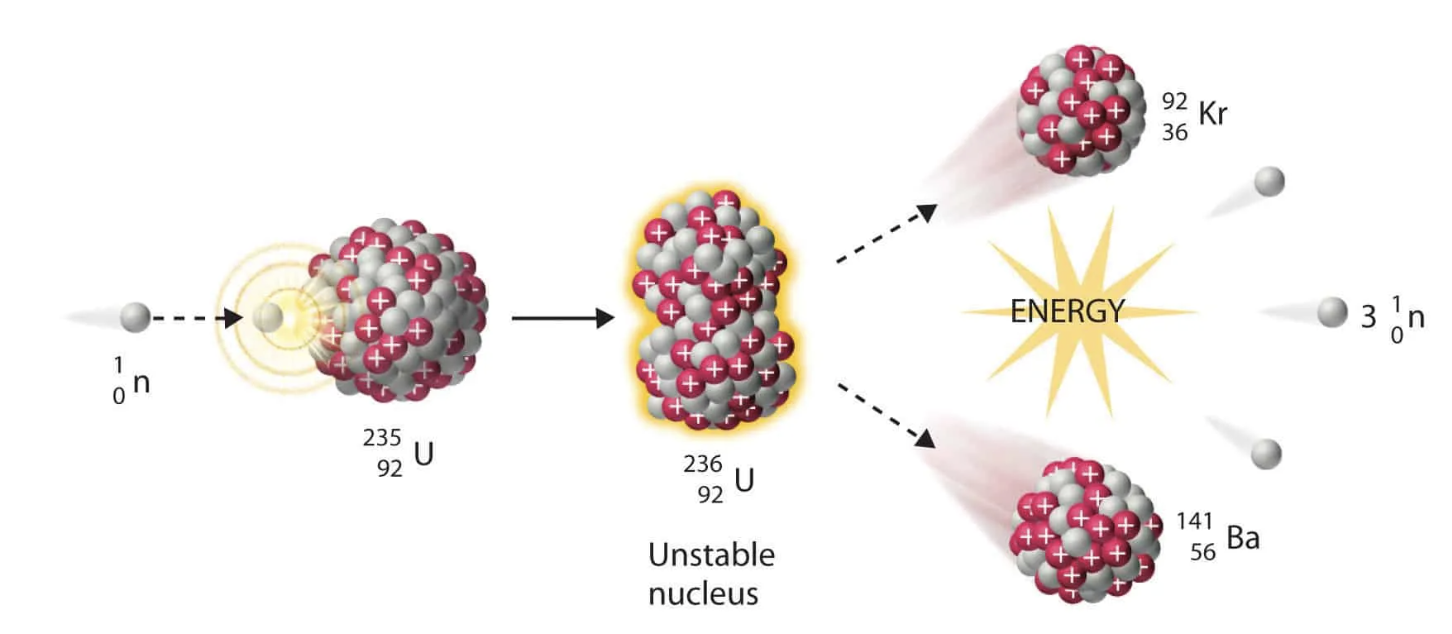
54
New cards
What are some real-world scenarios of nuclear fission?
Atomic bombs.
Nuclear power-plants (control rods keep it under control).
Nuclear power-plants (control rods keep it under control).
55
New cards
What is light? What is its range?
Form of electromagnetic energy, mainly comes from electrons in atoms. Range goes from radio-waves (LOW energy) to gamma rays (HIGH energy).
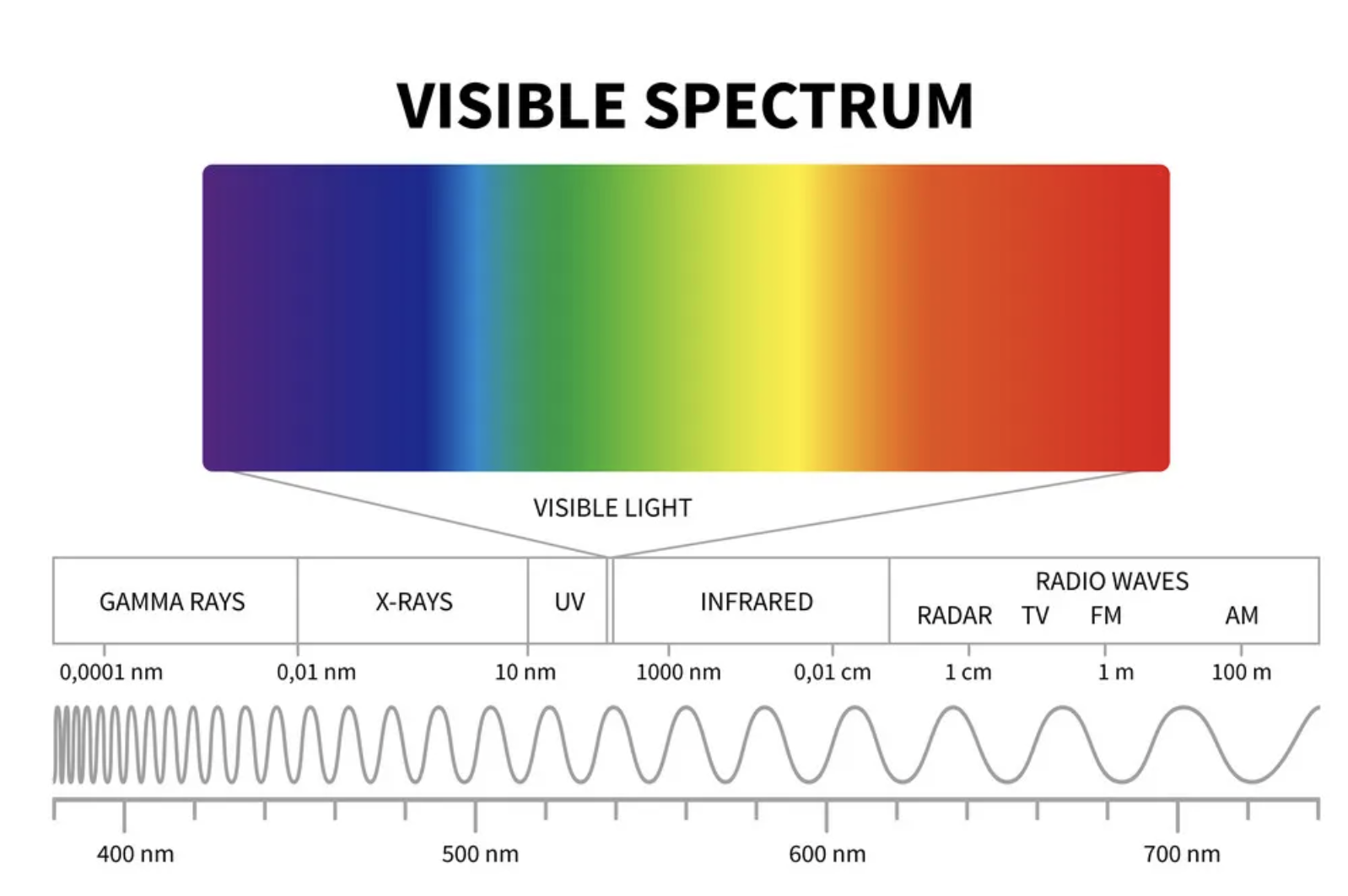
56
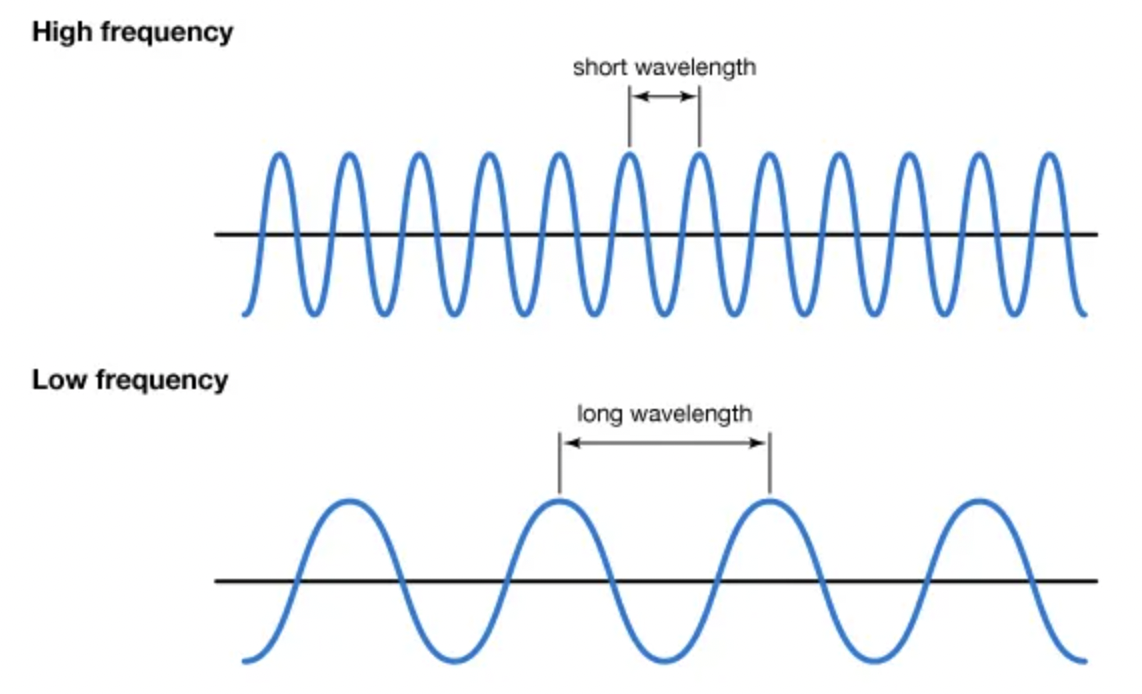
New cards
True/false: Wavelength (λ) and frequency (ν) are DIRECTLY related.
FALSE. They are INVERSELY related.
57
New cards
Units of wavelength (λ)?
Meter (m).
58
New cards
Unit of frequency (v)?
Hertz or 1/s (s^-1).
59
New cards
What is the speed of light? And what is the symbol for it?
3.0 x 10^8 m/s, c
60
New cards
What is the equation for speed?
c = λv
61
New cards
Units of energy (E)?
Joules.
62
New cards
Equation for energy?
E = hv
63
New cards
What is Planck's constant?
h = 6.626 x 10^-34

64
New cards
What is a photon?
Quantum of light.
65
New cards
How is energy quantized?
Looks like a staircase. Jumps of energy are made SO SMALL that energy seems continuous.
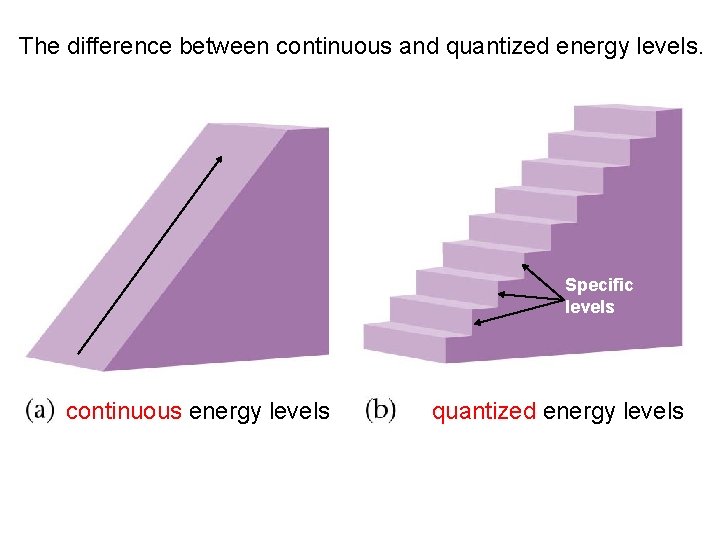
66
New cards
What is Bohr's model of the atom?
- Electrons are in ORBIT around the nucleus @ specific distances with specific amounts of energy
- Each electron has a "ground state"/normal.
- Electrons jump UP to higher state (absorb energy). Higher state = "excited state".
- Electron jumps DOWN to "normal state", releases energy in form of LIGHT.
- Each electron has a "ground state"/normal.
- Electrons jump UP to higher state (absorb energy). Higher state = "excited state".
- Electron jumps DOWN to "normal state", releases energy in form of LIGHT.
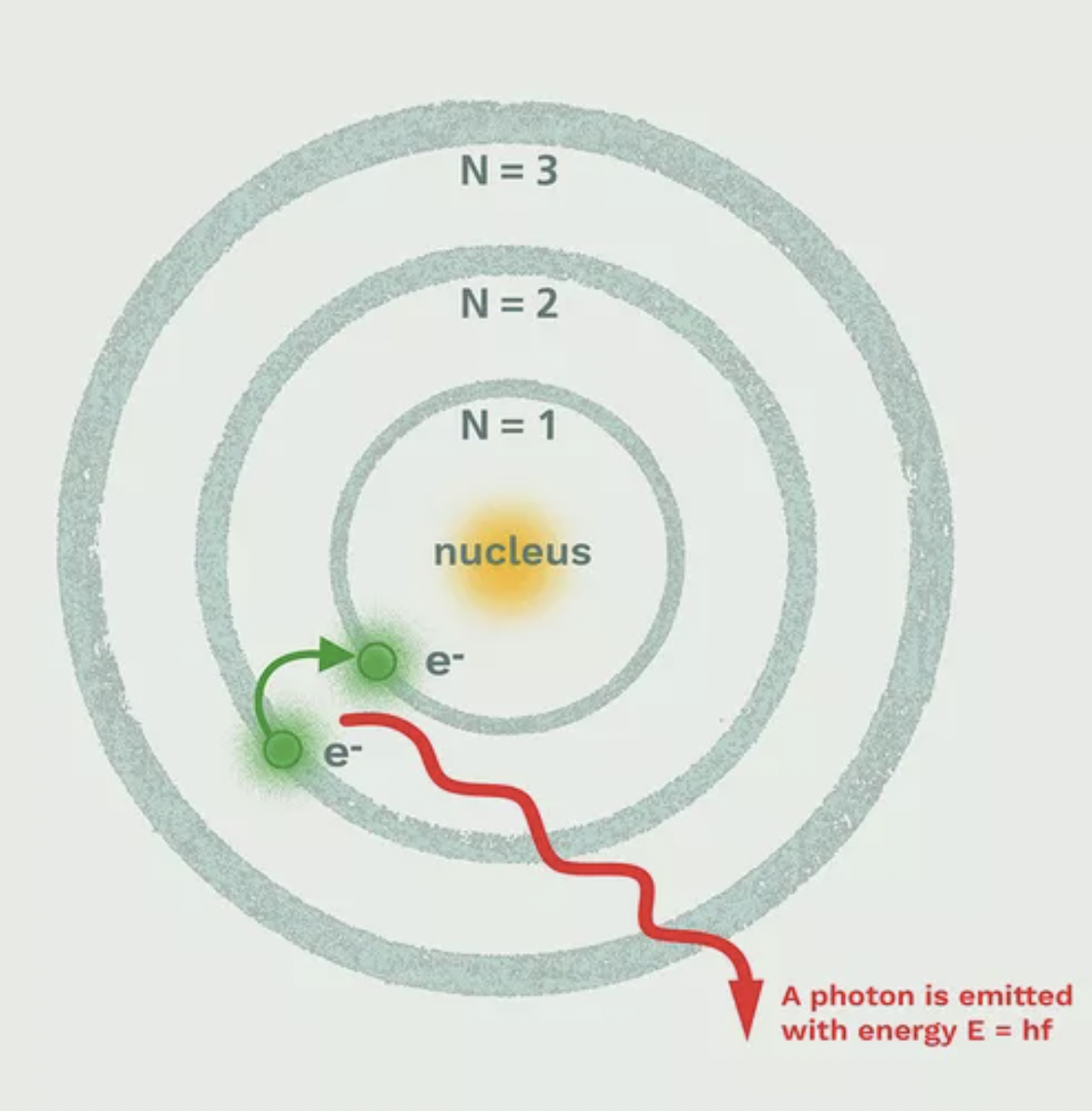
67
New cards
What is the atomic emission spectrum?
specific spectral lines, indicate SPECIFIC wavelengths of light released from an atom. UNIQUE TO EVERY ELEMENT
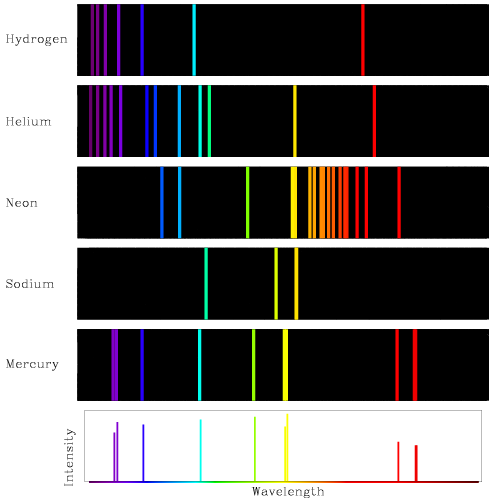
68
New cards
Penetration & mass of alpha decay.
- Alpha particles can be shielded by paper +skin. LEAST harmful.
- MOST mass (8,000x of beta): 4 amu.
- MOST mass (8,000x of beta): 4 amu.
69
New cards
Penetration & mass of beta decay.
- Beta particles shielded by aluminum. INTERMEDIATE harmful.
- INTERMEDIATE mass: 1,200 amu
- INTERMEDIATE mass: 1,200 amu
70
New cards
Penetration & mass of gamma decay.
- Gamma decay shielded by 2inch lead. MOST harmful.
- 0 mass (it's energy).
- 0 mass (it's energy).