LEC 10.1: Comfort & Pain Management
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Pain
Whatever the person says it is and exists whenever he says it does
Highly subjective, based on experience of client
Pain
Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage
Pain is a physical and emotional experience
It is in response to actual or potential tissue damage
It is described in terms of such damage
3 parts have important implication
Pain is a physical and emotional experience
One of the 3 parts that have important implication
Pain is not just all in the body and mind
It is in response to actual or potential tissue damage
One of the 3 parts that have important implication
Example: Radiographic or laboratory result is normal, but the pain is real in the patient
It is described in terms of such damage
One of the 3 parts that have important implication
Pain can be described through location, duration, intensity, etiology
Chemical
Thermal
Mechanical
Types of pain stimuli
Mechanical
Type of pain stimuli
Cuts, Physical Injuries
Thermal
Type of pain stimuli
By cold or heat
Chemical
Type of pain stimuli
In blood vessels, have blocking of blood flow, which can cause pain
Production of lactic acid when muscles tear
Pain Management
Alleviation of pain or a reduction in pain to a level of comfort that is acceptable to the client
Location
Duration
Intensity
Etiology
Types of Pain
Location
Type of pain
Classification of pain based on where it is in the body
Example: Head, Knee, Chest
Radiate
Referred
Visceral
Within Location, what factors needs to be considered?
Radiate
Within Location, factor that needs to be considered
Spread or extend
Radiate
Identify the type of pain based on Location
Severe chest pain that ___ down the left arm and jaw, which indicates a Myocardial Infarction. Pain from the heart __ to other parts of the body.
Referred
Within Location, factor that needs to be considered
Appear to arise in different areas
Referred
Identify the type of pain based on Location
Patient with history of gallstones presents to hospital with intense pain in right shoulder and upper back. Pain is ___ from the irritation of the gallbladder (Biliary Colic). Original source of the pain is the inflammed gallbladder but it is not there where the pain is felt, rather the upper back and right shoulder.
Right Leg
When Kidney Punch Test is conducted, where else can pain be illicited?
Right Neck
Right Shoulder
Other than directly in the liver, pain from the liver can be referred to where?
Visceral
Within Location, factor that needs to be considered
Arising from organs or hollow viscera
Visceral
Identify the type of pain based on Location
Patient is admitted with acute appendicitis, experiencing diffused, poorly localized abdominal pain. Pain is all over the abdomen. Arises from the inflammation of the appendix and is described as deep, cramp-like pain.
Duration
Type of pain
Either Acute or Chronic
Acute
Chronic
Classifications for Duration
Acute
Classifications for Duration
Lasts only through the expected recovery period; whether it has a sudden or slow onset and regardless of intensity.
Less than 3 months
Less than 3 Months
What is the duration of Acute Pain?
Chronic
Classifications for Duration
Prolonged, usually recurring or persisting over 3 months or longer, and interferes with daily functioning
From injury or illness
More than 3 Months
What is the duration of Chronic Pain?
Intensity
Type of pain
Classified as either Mild, Moderate, or Severe
1-3
What is the pain rating for Mild Pain?
4-6
What is the pain rating for Moderate Pain?
7-10
What is the pain rating for Severe Pain?
Etiology
Type of Pain
Classified as either Physiological or Neuropathic
Nociceptive Pain
What is Physiological Pain also known as?
Physiological/Nociceptive Pain
Classification of Etiology
Experience when intact properly functioning nervous system sends signals that tissues are damaged, requiring attention and proper care
Subcategories: Somatic or Visceral
Somatic
Visceral
What are the subcategories of Physiological Pain?
Somatic
Subcategory of Physiological Pain
Originates in the skin, muscles, bone, or connective tissues
Visceral
Subcategory of Physiological Pain
Pain wherein it arises from organs or hollow viscera
Neuropathic Pain
Classification of Etiology
Damaged or malfunctioning nerves
Subcategories: Peripheral, Central, or Sympathetic
Peripheral
Central
Sympathetic
What are the subcategories of Neuropathic Pain?
Pain Threshold
Pain Tolerance
Hyperalgesia & Hyperpathia
Allodynia
Dysesthesia
Concepts Associated with Pain
Pain Threshold
Concept Associated with Pain
Least amount of stimuli to feel pain
Wala pa ang pain. You have the stimulus and when you start to recognize it as painful
Pain Tolerance
Concept Associated with Pain
Maximum amount of pain stimuli that a person is willing to withstand without seeking avoidance of the pain or relief
Pain is already there.
Pain Tolerance
The following is an example of what:
Mother giving birth is experiencing Labor Pain but refuses to take medications to have a greater drive to push and to avoid the baby from becoming drowsy, withstanding the pain.
Hyperalgesia & Hyperpathia
Concept Associated with Pain
Use interchangeably to denote a heightened response to a painful stimuli
Intense reaction to pain stimuli
Hyperalgesia & Hyperpathia
The following is an example of what:
A person may experience intense pain to a painful stimuli that typically illicits only a mild response or no response.
Allodynia
Concept Associated with Pain
Non-painful stimuli produce pain
Exaggerated response to a painful stimuli
Allodynia
The following is an example of what:
A person receives light touch and experiences pain.
Dysesthesia
Concept Associated with Pain
Unpleasant abnormal sensation
Either spontaneous or evoked
Nociception
Physiologic process related to pain perception
Transduction
Transmission
Perception
Modulation/Descending System
4 Processes of Nociception
Transduction
Part of the process of Nociception
Injury
Harmful stimuli triggers release of biochemical mediators/neurotransmitters, including prostaglandins, histamine, serotonin, substance P, which synthesize the nociceptors
Causes movement of ions across the cell membrane, exciting the nociceptors (pain receptors)
At this phase, non-opioid medications can work, like those that inhibit prostaglandin release
Transmission
Part of the process of Nociception
Includes 3 segments:
Pain impulses travel from peripheral nerve fibers to dorsal horn of spinal cord – substance P serves as a neurotransmitter that enhances the movement of impulses across the nerve synapse from the primary afferent neuron to the second order neuron in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
Pain signals transmit through an ascending pathway in the spinal cord to the brain
Transmission of the information to the brain where pain perception occurs
Opioids can especially work in this phase, which block the release of neurotransmitter, Substance P, which stops the pain at the spinal level
Perception
Part of the process of nociception
Client becomes conscious of the pain; how they interpret pain
Sum of complex activities in the CNS that may shape the character and intensity of pain perceived
Example: Sharp, burning pain, intense pressure
Gives meaning to the pain
Modulation
Part of the process of nociception
Part of descending system/often described as the descending system
Final process that occurs when neurons in the brain send signals back down to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and the descending fibers release substances like endogenous opioids, serotonin, and norepinephrine which can inhibit or reduce the ascending pain pulses in the dorsal horn
Modulates/reduces the pain
Since the released substances are absorbed back, there is still pain felt, it is just modulated
Melzack & Wall
Who proposed the Gate Control Theory?
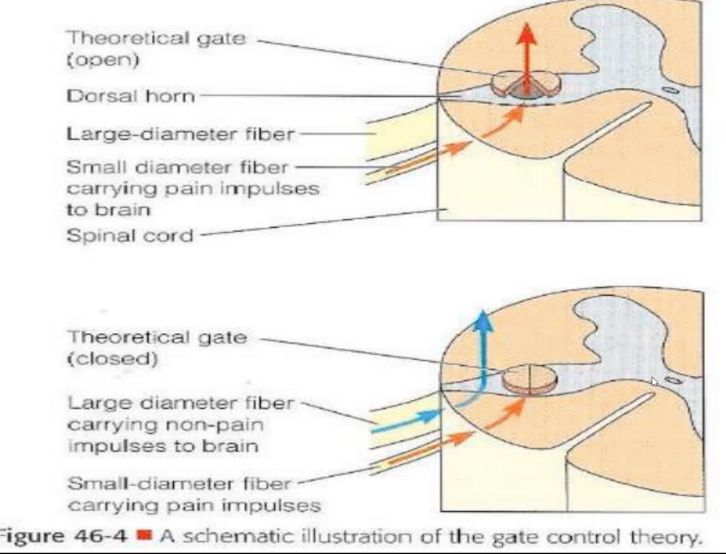
Gate Control Theory
Theory that proposes non-painful sensations can block painful ones, helping to reduce pain perception
Through non-painful sensations, such as rubbing or massage
According to the Gate Control Theory, how is pain alleviated?
Physiologic
Psychosocial
What are the aspects of the human response to pain?
Ethnic & Cultural Values
Developmental Stage
Environment & Support People
Past Pain Experiences
Meaning of Pain
Emotional Response to Pain
Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
Ethnic & Cultural Values
One of the Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
Behavior related to pain is a part of the socialization process.
Cultural background can affect the level of pain that an individual is willing to tolerate.
Development Stage
One of the Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
An important variable that will influence both the reaction and the expression of pain.
Doesn’t mean that children or the very young infants feel pain - They’re more expressive when they are in pain even though they can’t verbalize it
Environment & Support People
One of the Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
Usually when the person in pain is surrounded by people, they can get distracted and lose their attention to pain
However, a lonely person may perceive pain as severe since they don’t have much of a distraction
A strange ___ can compound pain
New to a certain area in the hospital, sound by machines or other people, may cause more discomfort
Past Pain Experiences
One of the Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
People who have personally experienced pain or who have been exposed to the suffering or someone close are often more threatened by anticipated pain than people without a pain experience.
Because they have experienced it before, they anticipate it and the anxiety will build up causing more discomfort
Meaning of Pain
One of the Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
A client who associates pain with a positive outcome may withstand the pain well.
Client with unrelenting chronic pain may suffer more intensely.
Emotional Response to Pain
One of the Factors Affecting the Pain Experience
Anxiety often accompanies pain. If anxiety is prolonged, depression, difficulty coping, the fear of the unknown, fear of inability to control pain
That may affect their response to pain, creating fatigue which reduces their ability to cope and increases the pain perception
Infant
Toddler & Preschooler
School-Age Child
Adolescent
Adult
Elder
Age Variation Categories in Pain Experience
Infant
Age Variation Category in Pain Experience
Perceives pain
Respond to pain with increased sensitivity
Older ___ tries to avoid pain for example, turns away and physically resists
Glucose Pacifier
Tactile stimulation/White Noise
Interventions to alleviate pain in Infants
Toddler & Preschooler (1-3 y.o.)
Age Variation Category in Pain Experience
Develops the ability to describe pain and its intensity and location
Often responds with crying and anger because they perceive pain as a threat to security
Reasoning with __ at this stage is not always successful
May consider pain as a punishment
Feel sad
May learn there are gender differences in pain
Tends to hold someone accountable for the pain
Distract with toys, books, pictures
Blow bubbles (“Blow pain away”)
Appeal to child’s belief in magic by using a “magic” blanket to take away the pain
Explore misconceptions about pain
Interventions to alleviate pain in Toddler & Preschooler
School-Age Child
Age Variation Category in Pain Experience
Tries to be brave when facing pain
Rationalizes in an attempt to explain the pain
Responsive to explanations
Can usually identify the location and describe the pain
With persistent pain, may regress to an earlier stage of development
Use imagery to turn off “pain switches”
Provide a behavioral rehearsal of what to expect and how it will look and feel
Provide support and nurturing
Interventions to alleviate pain in School-Age Child
Adolescent
Age Variation Category in Pain Experience
Slow to acknowledge pain
Recognizing pain or “giving in” may be considered as weakness
Wants to appear brave in front of peers and not report pain
Provide opportunities to discuss pain
Provide privacy
Present choices for dealing with pain
Encourage music or TV for distraction
Massage, acupressure
Interventions to alleviate pain in Adolescents
Adult
Age Variation Category in Pain Experience
Behaviors exhibited when experiencing pain may be gender-based behaviors learned as a child
May ignore pain because to admit it is perceived as a sign of weakness of failure
Fear of what pain means may prevent some ___ form taking action
Focus on the client’s control in dealing with the pain
Allay fears and anxiety when possible
Interventions to alleviate pain in Adults
Elder
Age Variation Category in Pain Experience
May have multiple conditions presenting with vague symptoms
May perceive pain as part of the aging process
May have decreased sensations or perceptions of the pain
Lethargy, anorexia, and fatigue may be indicators of pain
May withhold complaints of pain because of fear of the treatment, of any lifestyle changes that may be involved, or of becoming dependent
May describe pain differently, as “ache”, “hurt”, or “discomfort”
May consider it unacceptable to admit or show pain
Thorough history and assessment is essential
Spend time with the client and listen carefully
Clarify misconceptions
Encourage independence whenever possible
Interventions to alleviate pain in Elder
Pain Assessment
What is considered the Fifth Vital Sign?
Pain history to obtain from the client (COLDSPA)
Direct observation
What are the two major components for assessing pain?
Characteristic
Onset
Location
Duration
Severity
Pattern
Associated Signs & Symptoms
COLDSPA
Direct Observation
The following situation exemplified which major components of pain assessment?
Comatose patient cannot speak whether in pain or not so the nurse should take the vital signs and assess other symptoms, like increased HR, increased BP, diaphoretic (increased sweating).
Location
Related Factors
When Known
Either Acute (<3 months) or Chronic (>3 Months)
What should be taken into account when Diagnosing Pain?
Ineffective Airway Clearance related to weak cough secondary to postoperative incisional abdominal pain.
Hopelessness related to feelings of continual pain
Anxiety related to past experiences of poor control of pain and anticipation of pain.
Ineffective Health Maintenance related to chronic pain and fatigue
Self-Care Deficit (Specify the ADL Affected) related to poor control of pain.
Deficient Knowledge (Pain Control Measures) related to lack of exposure to information resources.
Impaired Physical Mobility related to arthritic pain in knee and ankle joints
Insomnia related to increased pain perception at night
Ineffective coping related to prolonged continuous back pain, ineffective pain management, and inadequate support systems and anxiety related to poor control of pain and anticipation of pain
Examples of Diagnosis related to the problem of pain (Best to Write Out these Diagnoses)
Planning
Established goals will vary according to the diagnosis and its defining characteristics
Pain is on a case to case basis
Depends on the pain’s defining characteristics:
Somatic or Visceral
Somatic pain originates on skin, muscle, bone, like a paper cut. Visceral pain is on the deeper level, like liver pain and angina pectoris, a cardiac pain, or irritable bowel.
Neuropathic
For neuropathic pain, Postherpetic neuralgia is pain felt by patients that have experienced herpes zoster like shingles and chicken pox, which may last longer due to malfunctioning nerves. Can be a painful, numbness, electric shock or burning.
Type of stimulus
Mechanical: trauma, injury, tumor, alteration in the body tissue like edema, blockage of body duct, muscle spasm
Thermal: cold or hot
Chemical: tissue ischemia/blocked coronary artery, muscle spasm like lactic acid being produced
Muscle Spasm
What type of pain stimulus can be considered either Mechanical or Chemical?
Implementation
What portion of nursing management is pain management a part of?
Pharmacologic
Nonpharmacologic
What are the 2 basic types of nursing interventions?
Pharmacologic Interventions
One of the 2 basic types of nursing interventions
Giving medications
Non-Pharmacologic Interventions
One of the 2 basic types of nursing interventions
Interventions that do not rely on medications
Level I: Nonopioid (& Adjuvant)
Component of the Ladderized Treatment of Pain
For pain that is persistant, giving analgesics or OTC medications, like paracetamol, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, acetylsalicylic acid, celecoxib, naproxen, as well as a support.
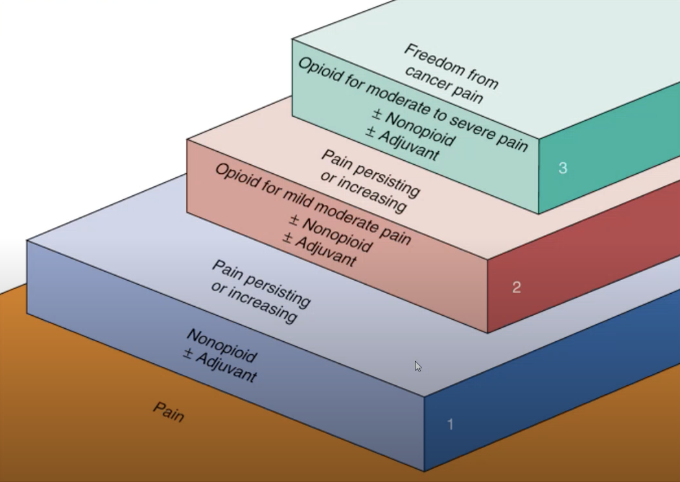
paracetamol
ibuprofen
acetaminophen
acetylsalicylic acid
celecoxib
naproxen
Examples of Nonopioids
Level II: Opioid for mild moderate pain (& Nonopioid + Adjucant)
Component of the Ladderized Treatment of Pain
If pain is mild or moderate wherein it’s persistent, this may be given, including hydrocodone, codeine, tramadol, and buprenorphine.
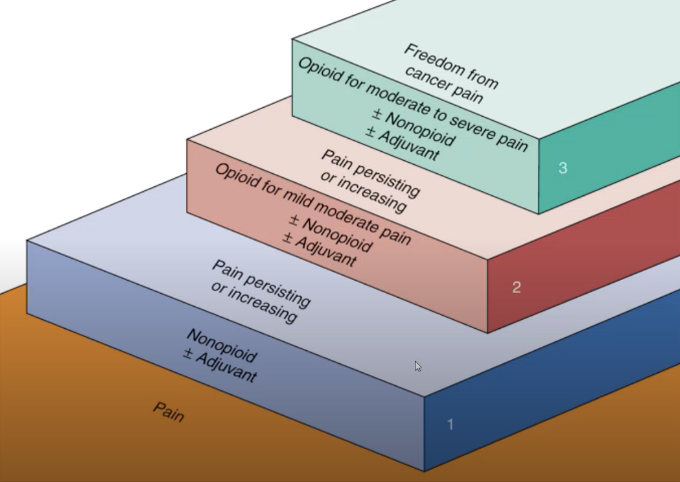
Level III: Opioid for severe pain (& Nonopioid + Adjuvant)
Component of the Ladderized Treatment of Pain
If pain is severe, this may be given, including fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine sulfate, oxycodone, oxymorphone.
fentanyl
hydromorphone
methadone
morphine sulfate
oxycodone
oxymorphone
Examples of Opioids for Severe Pain
Establishing a trusting relationship.
Consider the client’s ability and willingness to participate actively in pain relief measures.
Use a variety of pain relief measures
Provide measures to relieve pain before it becomes severe.
Use pain-relieving measures that the client believes are effective.
Try ineffective pain relief again before abandoning it
Maintain an unbiased attitude
Prevent harm to the client.
Educate the client and caregiver about pain.
Important Factors to Consider in Implementing
Establishing a trusting relationship
Important in Implementing
When a person is pain, there is always anxiety so this must be done to lessen that
Assess client’s ability and willingness to participate
Important in Implementing
Should be done most especially in nonpharmacologic treatment