Chemistry Module 4
5.0(1)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/34
Last updated 2:14 PM on 12/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
wave, particle
light is made of
2
New cards
radiation
the rays and particles (alpha and beta) that are emitted by radioactive material
3
New cards
visible light, x rays, microwaves, tv/radio waves
Examples of electromagnetic radiation
4
New cards
wavelength, frequency, and amplitude
characteristics of waves
5
New cards
wavelength symbol
λ
6
New cards
frequency symbol
V
7
New cards
wavelength
the shortest distance between equal points on a wave
8
New cards
frequency
the number of waves that passes a given point per second
9
New cards
amplitude
Height of a wave from the origin to a crest
10
New cards
Speed of light
(3.00 x 10^8 m/s) c=λV (wavelength x frequency)
11
New cards
Waves models don't explain
why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at a given temp and why some metals emit electrons when light of a specific frequency shines on them
12
New cards
quantum
the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
13
New cards
quantum concept
Matter can gain or lose energy only in small specific amounts called quanta
14
New cards
photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
15
New cards
photon
a massless particle that carries a quantum of energy
16
New cards
Planck's constant
6.626 x 10^-34 Js
17
New cards
Formula for the energy of a photon
E=hv
18
New cards
atomic emission spectrum
the set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of the element
19
New cards
increases
When the wavelength decreases the frequency ____
20
New cards
ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom
21
New cards
Bohr's contribution
Electrons moved in orbits (incorrect), the number assigned to each orbit of an electron is a quantum number
22
New cards
Bohr lacked
his model explained hydrogen's spectral lines but not any other element, although not 100% sure - evidence shows electrons do not move around nucleus in circular orbits
23
New cards
de Broglie equation
λ = h/mv, predicts that all moving particles have wave characteristics
24
New cards
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time, the only quantity that can be known is the probability for an electron to occupy a certain region around the nucleus
25
New cards
4
the quantum mechanical model assigns ____ quantum numbers to atomic orbitals
26
New cards
principal quantum number
symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron, as n increases the orbital becomes larger
27
New cards
1
an atoms lowest principal energy level is assigned a principal quantum number of ___
28
New cards
energy sublevels
principal energy levels contain
29
New cards
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
30
New cards
Pauli Exclusion Principle
two electrons occupying the same orbital must have opposite spins
31
New cards
Hund's rule
single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal-energy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbitals
32
New cards
valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom which are added up
33
New cards
Hund's Rule
example of Whose Rule/principle
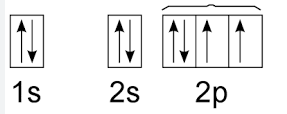
34
New cards
Aufbau Principle
example of whose rule/principle
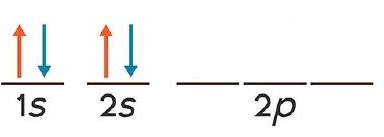
35
New cards
Pauli Exclusion Principle
examples of whose rule/principle