Circuit Analysis Ch.1
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Circuit Analysis Ch.1 HW
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
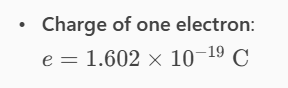
How much charge is represented by the given amount of electrons?
a. For 6.482 × 1017 electrons, the charge q = ___ mC
b. For 4.24 × 1018 electrons, the charge q = ___ mC
c. For 6.46 × 1019 electrons, the charge q = ___ C
d. For 4.628 × 1020 electrons, the charge q = ___ C
a. -103.84 mC
b. -679.25 mC
c. -10.35 C
d. -74.14 C

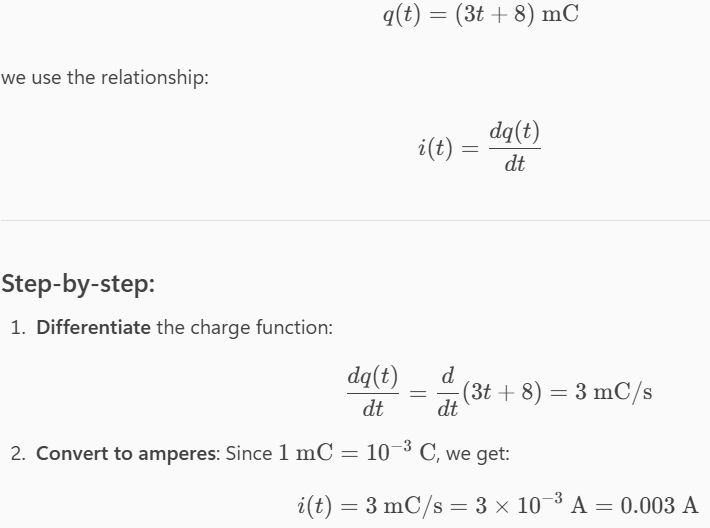
Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by the following equation.
q(t) = (3t + 8) mC
3 mA
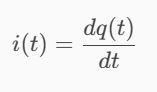
Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by the following equation.
q(t) = (6t2 + 4t – 2) C
i = (12t + 4) A

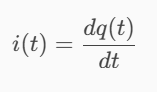
Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by the following equation.
q(t) = (5e–t – 9e–2t) nC
i = (-5e-t + 18e-2t) nA

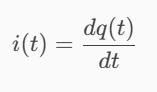
Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by the following equation.
q(t) = 10sin (120πt) pC
i = 1200πcos(120πt) pA
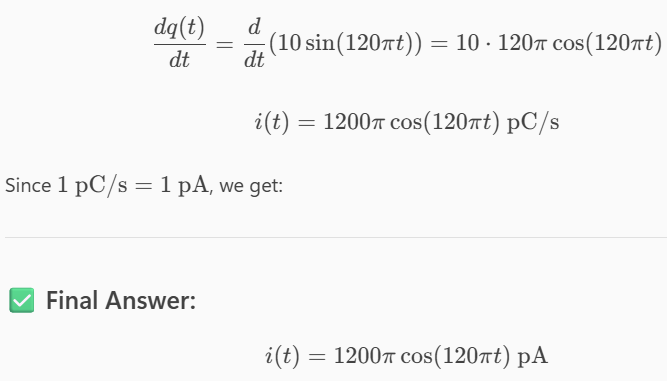

Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by the following equation.
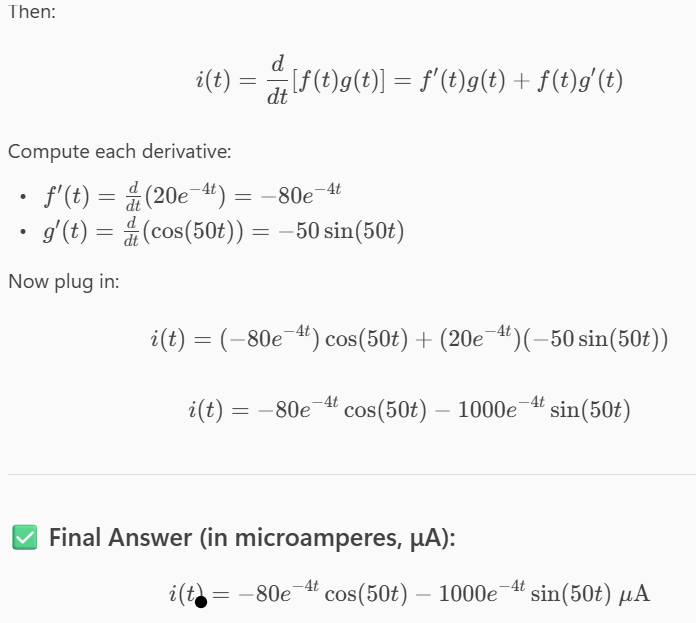
q(t) = 20e–4t cos (50t) μC
i = -80e-4t cos (50t) - 1000e-4tsin(50t) μA
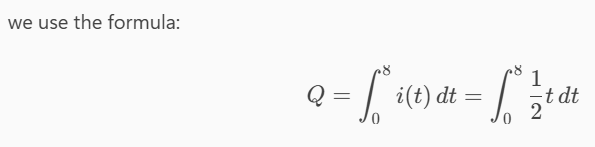
Determine the total charge transferred over the time interval of 0 ≤ t ≤ 8 s when i(t) = (1/2)t A.
16 C
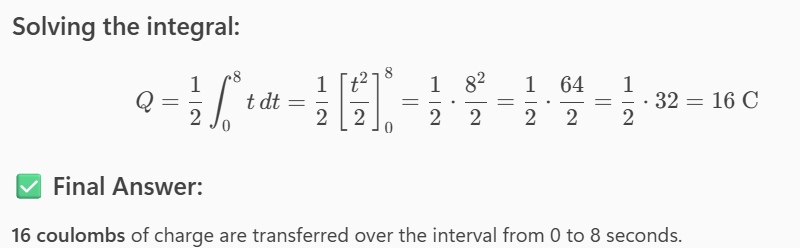
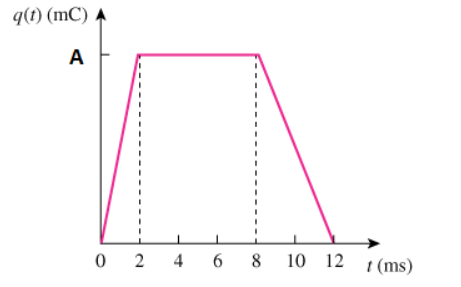
The charge entering a certain element is shown in the given figure, where A = 50. Find the current at 1 ms, 6 ms, and 10 ms.
The current at 1 ms is ____ A.
The current at 6 ms is ____ A.
The current at 10 ms is ____ A.
25 A, 0 A, -12.5 A

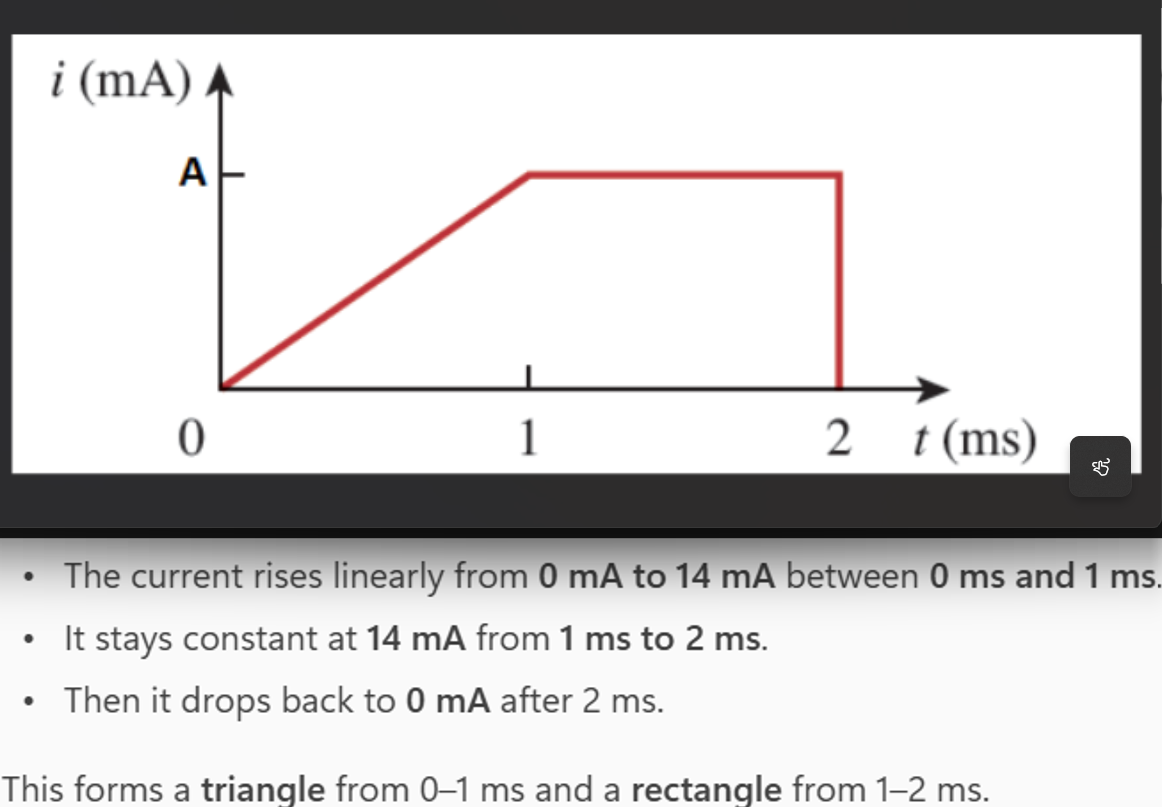
The current flowing past a point in a device is shown in the given figure, where A = 14. Calculate the total charge through the point (μC).
21 μC
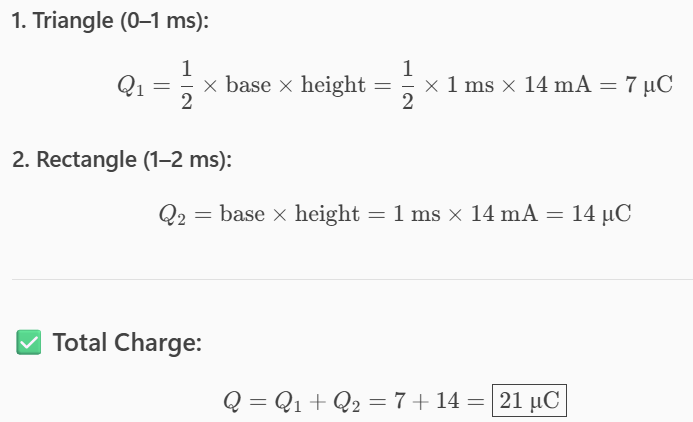
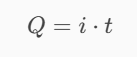
A lightning bolt with 6 kA strikes an object for 10 μs. How much charge is deposited on the object (mC)?
mC


The voltage v(t) across a device and the current i(t) through it are v(t) = 24cos(2t) V, and i(t) = 27(1 − e−0.5t) mA.
Calculate the total charge in the device at t = 1 s, assuming q(0) = 0 (mC).
5.75 mC
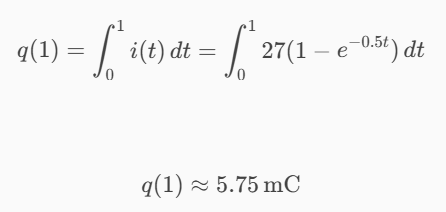
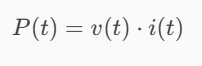
The voltage v(t) across a device and the current i(t) through it are v(t) = 24cos(2t) V, and i(t) = 27(1 − e−0.5t) mA.
Calculate the total charge in the device at t = 1 s, assuming q(0) = 0 (mW).
-106.10 mW

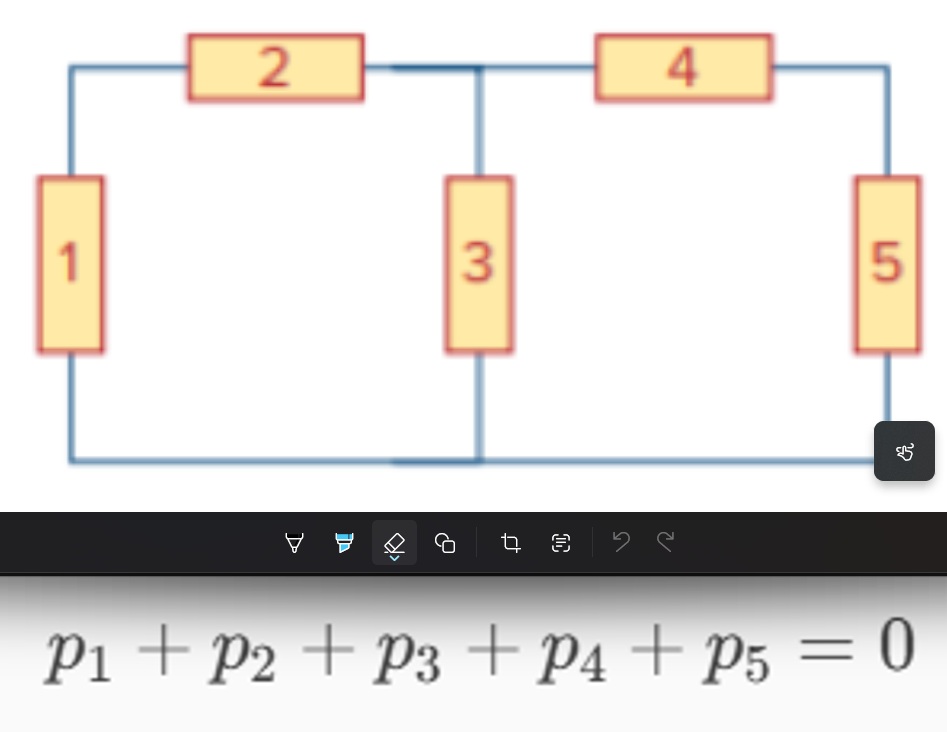
The figure below shows a circuit with five elements. If p1 = –220 W, p2 = 75 W, p4 = 60 W, and p5 = 45 W, calculate the power p3 absorbed by element 3.
40 W
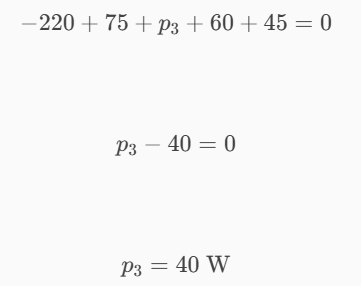
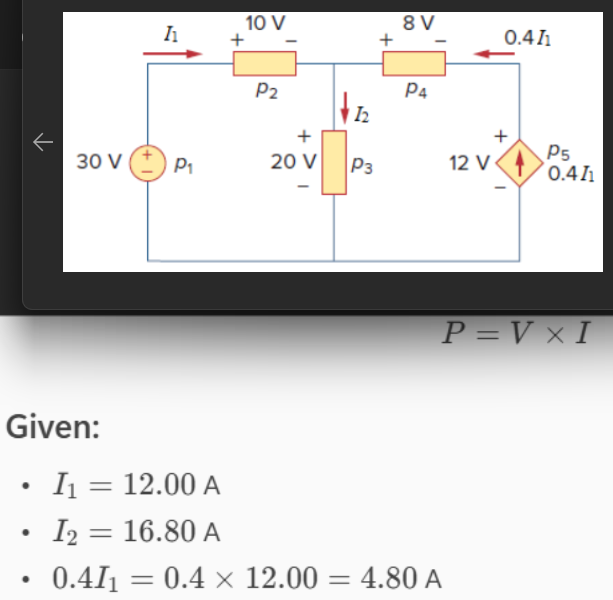
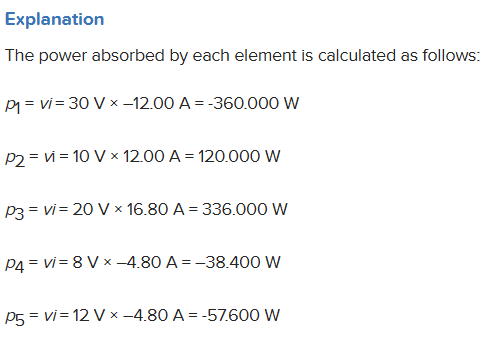
Find the power absorbed by each of the elements in the given figure, where I1 = 12.00 A and I2 = 16.80 A.
p1 = ____ W
p2 = ____ W
p3 = ____ W
p4 = ____ W
p5 = ____ W
-360 W, 120 W, 336 W, -38.4 W, -57.6 W
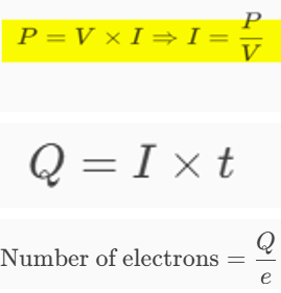
A 76-W incandescent light bulb operates at 120 V. How many electrons and coulombs flow through the bulb in one day?
The number of electrons that flow through the bulb in one day is ____×1023 electrons.
The number of coulombs that flow through the bulb in one day is ____ kC.
3.42×1023, 54.7 kC

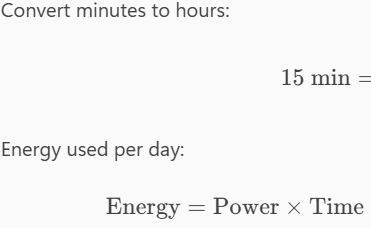
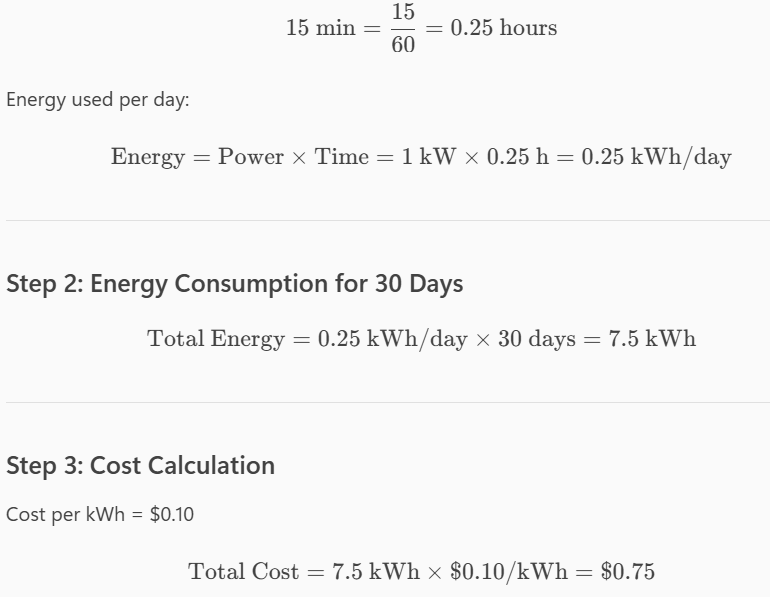
A 1-kW electric heater takes 15 min to boil a quantity of water. If this is done once a day and power costs 10 cents per kWh, what is the cost of its operation for 30 days?
The cost of the operation for 30 days is $____
$0.75 or $0.8