Nursing of Adults Unit One
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
what do the lungs regulate
regulates acid base
what do the kidneys regulate
balance bicarbonate levels
pH range
7.35-7.45
HC03 Normal range
22-26 (bicarb)
PaCO2 normal range
35-45 (carbon dioxide)
Pa02
80-100 (if lower than 80 pt is hypoxic)
Causes of respiratory acidosis
respiratory depression
anesthesia overdose
increased ICP
airway obstruction
decreased alveolar capillary diffusion
pneumonia: COPD, ARDS, PE
What is happening to labs during respiratory acidosis?
decreased pH, increased PC02, increased carbon dioxide
S/S of respiratory acidosis
-Hypoventilation -> Hypoxia
-Rapid, shallow breaths
-Decreased BP
-Skin - pale or cyanotic
-Headache
-Hyperkalemia
-Dysrhythmias
-Drowsiness, dizziness, disorientation
-Muscle weakness
Causes of respiratory alkalosis
hyperventilation (anxiety, PE, fear), mechanical ventilation
What is happening to labs during respiratory alkalosis?
increased pH, decreased PC02, "blowing off carbon dioxide"
s/s respiratory alkalosis
Hyperventilation
tachycardia
decreased of normal BP
Hypokalemia
Numbness & Tingling of Extremities
Hyper reflexes & muscle cramping
seizures
anxiety
irritability
Causes of metabolic alkalosis
increased HCO3 (antacids, admin of sodium bicarbonate)
decreased H+ (NG suctioning, prolonged vomiting, hypercortisolism)
what happens to labs when during metabolic alkalosis
increased pH, increased HC03
S/S of metabolic alkalosis
-Confusion
-Dysrhythmias (tachycardia from decreased K)
-Compensatory hypoventilation
-Dizziness, increased irritability
-Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
-Increased anxiety, seizures
-Tremors, muscle cramps, tingling of fingers and toes (decreased Ca)
causes of metabolic acidosis
-increased H+ production (DKA, hypermetabolism)
-decreased H+ elimination (renal failure)
-decreased HCO3 production (dehydration, liver failure)
-increased HCO3 elimination (diarrhea, fistulas)
what happens to labs during metabolic acidosis
decreased pH, decreased HC03
too much H+ (acid) and too little bicarb
S/S of metabolic acidosis
- headache
- decreased BP
- hyperkalemia
- muscle twitching
- warm, flushed skin
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- changes in LOC
- kussmaul respirations
indications for IV therapy
-promote fluid balance
-promote electrolyte balance
-administer medications
-provide nutrition
-replacement of blood/blood products
crystalloids
-water + dissolved solutes
-isotonic solutions (0.9% NS, LR, D5W)
-same osmotic pressure as blood
-cells undergo no change
-expands intravascular space
-maintain fluid balance
hypotonic solutions
-0.45% NS, D5 0.45% NS)
-lower osmotic pressure than blood
-fluids flows into cells
-cells swell-caution
-given to correct fluid volume deficit
hypertonic solutions (D5LR or 3% saline)
-greater osmotic pressure than the blood
-fluid shift out of cells
-can dehydrate cells- caution TPN or treatment of cerebral edema
colloids
used to replace circulating blood volume
blood
whole blood and packed red blood cells.
blood products
plasma, platelets, albumin, granulocytes, cryoprecipitate
why is plasma given?
clotting, anticoag reversal, hemorrhage
why are Platelets given?
low platelet count, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage
why is albumin given?
burn victims, ascites
why are granulocytes given?
low WBC
why are cryoprecipitates given
clotting factors, low hemoglobin, low RBC, anemia, hemorrhage
infiltration
nonvesicant fluid
extravasation
when the fluid is a vesicant
nonvesicant
non irritating
vesicant
irritating to skin
phlebitis
irritation/inflammation of the vein
infection
introduction to growth and microbes- can go into blood stream cause overall changes, lowered LOC, tachycardia, fever, ect. often caused by MDR.
Circulatory overload
rapid infusion, impaired kidney or heart function, elderly patients, getting bolus's
S/S of circulatory overload
crackles, edema, dyspnea, SOB, cough, tachycardia
nursing actions for circulatory overload
slow down infusion, diuretics, sit pt up
thrombus
stasis of blood ("clot") in the IV catheter or vein, can break loose can cause an embolus
thrombus s/s
redness, warm, swelling, unilateral
thrombus prevention
flushing, ambulation, avoid IV's in points of flexion
pulmonary embolus
thrombus becomes mobile and travels to the lungs
pulmonary embolus s/s
SOB, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxia, chest pain
air embolism
failure to prime tubing or disconnection of CVC tubing, if tube travels to brain=stroke
air embolism causes
no priming, improperly using caps/clamps
how are blood/blood products administered?
through special tubing along with isotonic saline. requires large bore IV catheter (16g-20g).
universal donor
Type O, can give to anyone
universal recipient
type AB can receive any type of blood
Blood compatibility
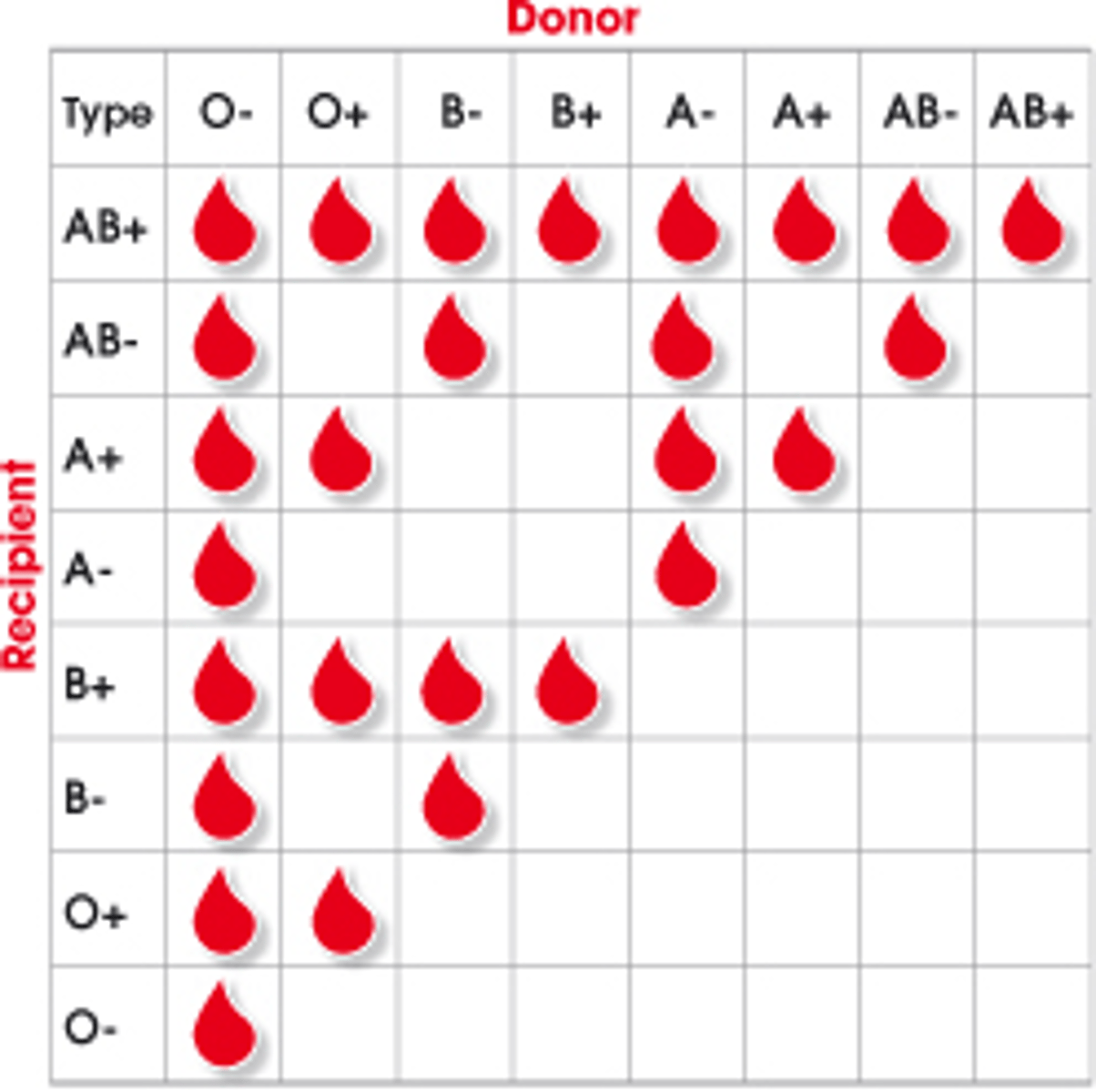
When do most blood reactions occur?
first 15 minutes
Things to check before administering blood
-ABO group
-RH type
-patients name
-ID blood band
-hospital #
-expiration date
how long should you start a blood transfusion after receiving it from the blood bank?
30 min
Can you add medications to blood products?
NO
transfusion reactions: acute hemolytic
due to wrong type of blood.
hypotension, tachycardia, lower back pain, anxiety, fever/chills, chest pain, tachypnea
transfusion reactions: febrile nonhemolytic
due to antibody reaction to leukocytes in blood.
fevers, shakiness, chills, tachy
transfusion reaction: bacterial contamination
sepsis, fever, chills, hypotension
transfusion reactions: allergic reactions
due to plasma protein or IgA response.
rash, itchy, flushing
transfusion reactions: fluid volume excess (circulatory overload)
hypertension, SOB, moist lung sounds, bounding pulse
equation for calculating pt's intake needs
100ml/kg for first 10kg PLUS
50ml/kg for next 10kg PLUS
15ml/kg for remaining kg
diffusion-passive movement
particles/electrolyte move from area of high concentration to low.
osmosis-passive
movement of water from area of high particle concentration to low
filtration
effect of hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmatic pressure
active transport
requires energy (ATP), sodium potassium pump
Osmoreceptors
triggers thirst
baroreceptors
measures pressures
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
compensatory process that leads to increased blood pressure and blood volume to ensure perfusion of the kidneys; important in the continual regulation of blood pressure
ADH
antidiuretic hormone, hold onto fluid
aldosterone
hold onto salt and fluid
ANP
atrial natriuretic peptide
fluid volume deficit
too little in the extracellular space
fluid volume excess
too much fluid in the extracellular space
client risks for fluid volume deficit
decreased oral intake, vomiting/diarrhea, fever, laxative/diuretic use, adrenal insufficiency, hemorrhage
fluid volume deficit assessment findings
sudden weight loss, postural hypotension, tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, flat neck veins when supine, dark yellow urine, thirst, hemo concentration
fluid volume excess causes
rapid IV admin, heart failure, kidney failure, hormonal fluctuations, excess intake of sodium, cirrhosis, aldosterone/glucocorticoid excess, cushing's disease, overuse of ADH
fluid volume excess assessment findings
weight gain of 1kg or more in 24 hours, rapid bounding pulse, full/distended neck veins, crackles in dependent lobes of lung, progressive dyspnea, edema, demodilution, increased blood pressure
third spacing
fluid goes from vascular or cellular space to tissue compartments. fluid is trapped and unable to be used by the body.
causes of third spacing
burns, liver failure, hypoalbuminemia, ascites
treatment of third spacing
-restore circulating volume (IV fluids, albumin)
-may also require a diuretic
assessment for third spacing
-hypovolemia symptoms (without weight loss), ascites, generalized edema
-can progress to hypotension, hypovolemic shock and circulatory failure
sodium range
135-145
potassium range
3.5-5
calcium range
8.4-10.5
magnesium range
1.5-2.5
Hypernatermia assessment findings
thirst, dry sticky membranes, fever, decreased urine output, lethargy, coma
Hypernatremia causes
water diarrhea, excessive salt intake, high fever, severe burns, decreased fluid intake
Hypernatremia management
oral intake increased, iv admin of hypotonic fluids, sodium restriction
Hyponatremia assessment findings
anorexia, tachycardia, nausea/vomiting, nausea/vomiting, personality changes, confusion, convulsions, and coma
Hyponatermia management
oral admin of sodium, iv admin of hypertonic fluids
Hyponatremia causes
SIADH, psychogenic polydipsia, GI losses, profuse diaphoresis, addison's disease, admin of non electrolyte fluids
Hyperkalemia assessment findings
muscle twitching, weakness, irritability and anxiety, low BP, ECG changes (tall peaked T waves), dysrhythmias (irregular rhythm, brady), abdominal cramping
hyperkalemia causes
renal failure, sever burns or tissue damage, potassium sparing diuretics, overuse of salt substitute, addison's disease, rapid IV admin of potassium
Hyperkalemia management
mild- restrict potassium or hold potassium supplements, increase fluids
severe-
1. IV calcium (protects heart from dysrhythmias)
2. IV insulin and glucose (shift potassium into cells)
3. polystyrene sulfonate (kayexalate) (excrete potassium through stool)
4. diuretic (excrete potassium in urine)
hypokalemia assessment findings
alkalosis, shallow respirations, irritability, confusion, drowsiness, weakness, fatigue, arrhythmias (flat T wave, presence of U wave, heart block), thready pulse, nausea, vomiting
hypokalemia causes
potassium wasting diuretics, vomiting/diarrhea, GI suctioning, IV glucose and insulin, excessive admin of non electrolyte fluids, large glucocorticoid doses
Hypokalemia management
mild- oral admin of potassium
severe- IV admin of potassium, potassium sparing diuretic
Hypercalcemia assessment findings
deep bone pain, constipation, anorexia, nausea vomiting, pathological fractures, thirst, polyuria, chronic kidney stones
Hypercalcemia causes
parathyroid tumors, multiple fractures, Paget's disease, prolonged immobilization, chemotherapy agents, multiple myeloma
Hypercalcemia management
mild- oral fluids & calcium restriction
severe- IV saline and diuretic, oral phosphates, calcitonin admin
hypocalcemia assessment findings
chvostek's sign, trousseau's sign, convulsions, circumoral numbness, arrhythmias, tetany, twitching, stridor, spasms