MECH2305 - Powder Metallurgy
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Power metallurgy
Metal is formed through heating compacted metals
Applications of powder metallurgy
Offers cost effective alternative
Materials that are too difficult to form other ways
Materials with better performance
5 Steps of powder metallurgy
Blending - Mix powders, lubricants and binders
Compaction - Form green part
Burn out - Part is heated to remove lubricants and binders
Sintering - Heated to high temperatures to diffuse
Secondary operations - Machine etc if neccessary
5 Powder characteristics
Morphology (smallest particle to largest)
Size
Density
Flowability
Compressability
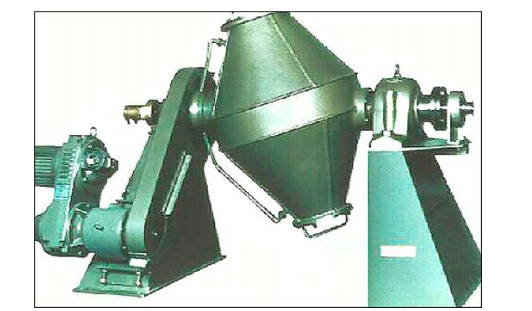
Blending
Powers are all blended together
Compaction
High pressure applied to form the “green part” which has enough strength to be handled
Sintering
Heat treatment to bond particles, increasing strength and hardness
Ceramic vs Metal Powders
Ceramic powders do not deform, need additives to ensure bond.
PM advantages
Can have better properties
High material efficiency
Can form from difficult materials (ceramics)
PM disadvantages
High tooling and equipment costs
Metal powders are dangerous
Variations in density of the part
Expensive metallic powders required