Palliative & End of Life Care
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 255 - Introduction to Oncology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
True or False: Palliative care is the same as end-of-life care.
False:
While palliative care includes end-of-life care, it is appropriate at any stage of a serious illness and can be provided alongside curative treatment.
What is the misconception about palliative care and treatment options?
That palliative care is only offered when "nothing else can be done." In reality, it can be provided alongside active treatments to improve quality of life.
Is palliative care only for cancer patients?
No. A common misconception is that palliative care is only for people with cancer, but it is beneficial for anyone with a serious illness.
Where does palliative care take place, contrary to common belief?
A misconception is that it only happens in hospice, but palliative care can occur in hospitals, homes, long-term care, and outpatient clinics.
What is the main goal of palliative care?
To improve the quality of life of patients and their families facing life-threatening illness.
How does palliative care address suffering?
By preventing and relieving it through early identification, correct assessment, and treatment of pain and other problems.
What three issues does palliative care aim to treat?
Physical, psychosocial, and spiritual problems.
Who benefits from palliative care?
Both patients and their families dealing with life-threatening illnesses.
Palliative care definition
An approach tocare that focuses on QoL, prevents and relieves suffering, and addresses physical, psychosocial and spiritual concerns
whole person care
Palliative Care pathway of illness
occurs in junction with disease modification care that attempts to extend life
palliative care can be started as soon as illness is diagnosed
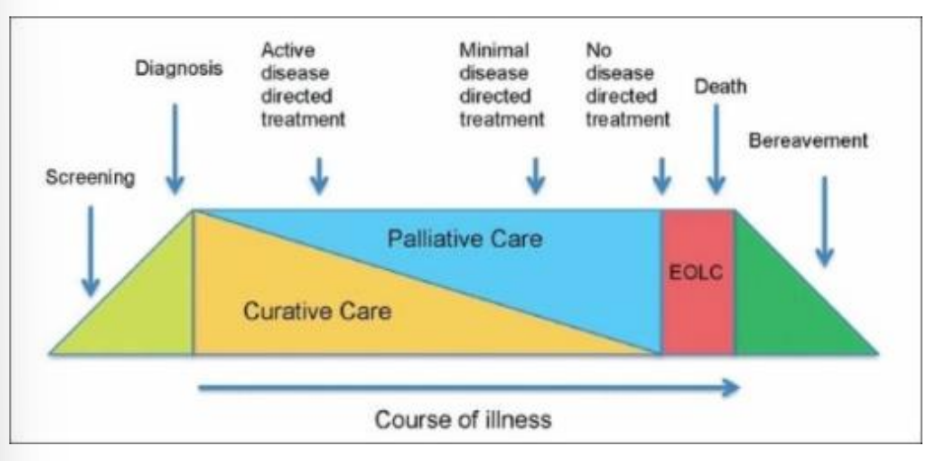
Palliative care bow tie model
What language should we use for patients in palliative care
listen to the words the patient is saying
try and limit words like battle, survivor, and warrior
may may patient feel guilty when they are dying
How was death traditionally approached in the past?
It was a familial, religious, and communal event, with end-of-life care usually occurring at home.
What was the typical cause and nature of death in the past?
Most people died from communicable diseases, and death was often swift and sudden.
How was disease perceived in earlier times?
As a normal part of life that often led to death.
How is death typically approached in the present day?
It is institutional, medical, and handled by professionals.
What is the typical experience of death today compared to the past?
Death is often prolonged, with most people dying in advanced stages of disease and outside the home.
What are common emotional or social responses to death today?
Denial, avoidance, procrastination, and separation.
What is the hoped-for approach to death and dying in the future?
A balanced "happy medium" between past and present approaches
What are key future goals in end-of-life care?
Early integration of palliative care in chronic disease/cancer management and routine advanced care planning.
What improvements are expected in the future of end-of-life care?
More options for care location and better grief support/resources.
Who can receive palliative care?
Anyone with a life-limiting illness experiencing symptoms or needing help with care planning.
Does palliative care depend on age, diagnosis, or goals of care?
No. It is for all ages, all diagnoses (cancer and non-cancer), and all goals of care (R, M, C).
resuscistative care
medical care
comfort care
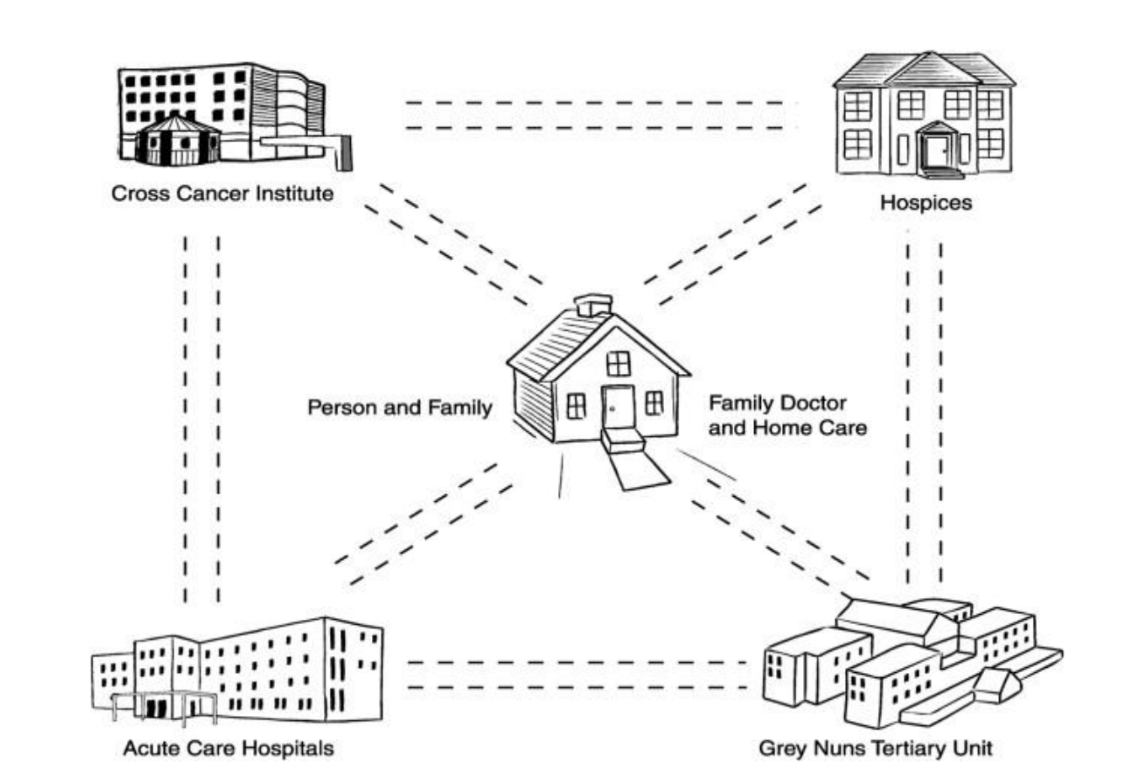
Edmonton Zone Palliative Care Program
consultative team works at all parts of the healthcare system
can do in home consults or within hospital
have their own unit in the Grey Nuns for more complex cases
What is the main goal of the patient’s agenda in care?
To provide patient-centered care by understanding what matters most to the patient.
Give two examples of patient-centered questions a provider might ask.
“How do you think I can be most helpful to you today?”
“What’s the most important thing for me to address today?”
What is the patient dignity question?
“What should your healthcare provider know about you (or your family member) to give the best care possible?”
gets a sense of the patient’s personhood
What is the full form of ESAS-r?
Edmonton Symptom Assessment System Revised.
What is the main purpose of the ESAS-r?
It is used for screening and longitudinal monitoring of symptoms.
How is pain defined?
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience that is multi-dimensional.
What factors contribute to the experience of pain?
Pain is shaped by factors including tissue damage caused by disease and underlying psycho-spiritual suffering.
What are the two main categories of pain classification?
Nociceptive and Neuropathic pain.
What is nociceptive somatic pain and where does it come from?
Somatic pain is well-localized pain resulting from damage to bone or soft tissues.
What is nociceptive visceral pain and how is it characterized?
Visceral pain is poorly localized pain caused by organ involvement.
What causes neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is caused by damage to the central, peripheral, or autonomic nervous system.
What details should be taken into account when taking a pain history
location, radiation, severity, quality
onset, duration, pattern
exacerbating and alleviating factors
impact on function and mood
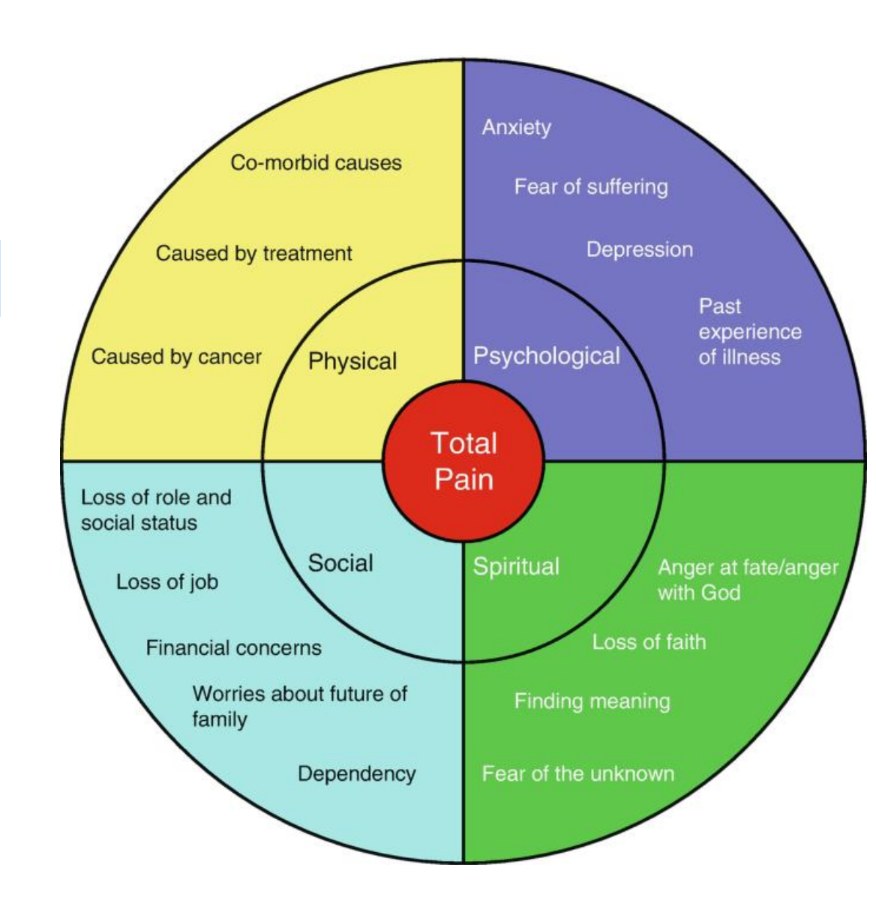
What does total pain syndrome refer to?
refers to the total suffering experienced by a patient, often expressed primarily as pain.
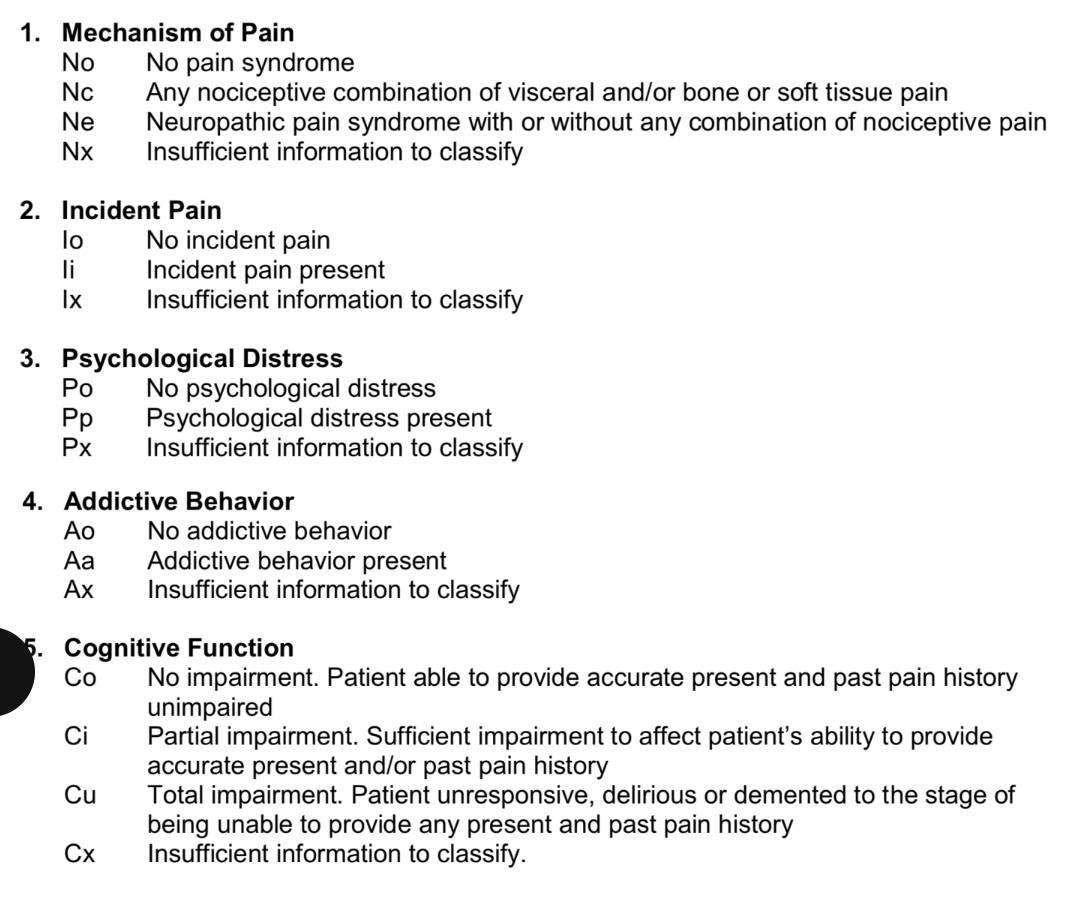
NIPAC Pain Control Profile
NIPAC stands for Neuropathic/Nociceptive, Incident, Psychological , Addictive , and Cognitve Function. It helps healthcare providers categorize pain based on these characteristics to guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Additional Considerations for MGMT of Cancer Pain
patient prognosis
psychological distress
alternative explanations of pain
pt at risk for opiod use disorder
Why is it important to acknowledge fatigue in patients?
It's important to acknowledge the loss or grief associated with changes in functioning and the impact on identity and sense of self.
Who can assist with managing fatigue in patients?
Rehabilitation colleagues can be helpful in managing fatigue.
What are some common causes of nausea?
Causes include constipation, gastroparesis, abdominal involvement, medications, bowel obstruction, metabolic abnormalities, esophagitis, intracranial abnormalities, and treatment-related factors.
Why is knowledge of the emesis centers and pathways important?
Understanding emesis centers, pathways, and associated neurotransmitters/receptors is key for selecting the appropriate anti-emetic treatment.
What is the difference between anorexia and cachexia?
Anorexia is appetite loss, while cachexia refers to weight loss
What is Cachexia Syndrome?
Cachexia Syndrome is a complex catabolic state driven by the release of inflammatory cytokines.
How does anorexia/cachexia affect patients?
It can be a major source of distress for both the patient and their family.
How is dyspnea defined?
Dyspnea is an uncomfortable, subjective awareness of breathing.
Is there a direct correlation between dyspnea and SpO2, PFTs, or imaging?
No, there is no direct correlation between dyspnea and SpO2, pulmonary function tests (PFTs), imaging, etc.
How is psychological distress in palliative care described?
Psychological distress is a spectrum, ranging from normal to pathologic/maladaptive responses.
What is a common myth about psychological distress in palliative care patients?
The myth is that all palliative patients are depressed/anxious and that it's a normal response, so it doesn’t require treatment.
What are key strategies to address psychological distress?
Listen, validate, empathize, and explore the patient’s feelings.
What percentage of patients develop delirium in the final weeks of life?
Up to 90% of patients develop delirium in the final weeks of life.
Why is delirium important to address in palliative care?
Delirium interferes with optimal symptom assessment and management.
What is delirium often mistaken for in palliative care?
It is often mistaken for poorly controlled pain, so clinicians need to be on high alert.
In terms of communication, do most patients want to be kept in the loop?
yes, most patients ‘want to know’
Is care planning a one time conversation
No, discussions should take place over time
normalize the discussion as standard practice
Why is cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) often ineffective in patients with advanced incurable illnesses?
CPR in these patients is typically ineffective and unlikely to improve outcomes.
even if recussitated, QoL after the fact is worse due to broken ribs
success rate <10% in palliative care settings
What is the main difference between palliative care and hospice?
Hospice is a physical location where palliative care is provided, typically for patients in the last few months of life.
What is the philosophy of care in hospice?
The philosophy of care in hospice is comfort-focused care.
What is the primary goal of palliative care?
Palliative care aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life, helping people live and die well. It does not hasten death.
What is the primary goal of MAiD (Medical Assistance in Dying)?
MAiD aims to relieve suffering by helping an eligible person intentionally end their life through the administration of a lethal dose of medication.