Chapter 16 and 17 part 1
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
S. aureus, pyogenes, agalactiae, pneumoniae, Viridans Streptococcus
gram positive cocci
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, meningitidis, Moraxella catarrhalis
gram - staphylococci
gram +, catalase + cocci, spherical cells, non-motile, non-spore forming
general characteristics of staphylococcus
staphylococcus
aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, although few strains can be obligate anaerobes colonies produced after 18-24 hours, able to grow in the presence of high salt concentration and at temperatures ranging from 18 to 40
anterior nares, nasopharynx, perineal area, skin, colonizer of mucosa
habitat or reservoir for S. aureus (5)
skin, mucous membrane
habitat for S. epidermidis (2)
Skin, mucous membranes
habitat for S. haemolyticus and lugdunesis (2)
skin, genitourinary tract, mucosa
habitat for S. saprophyticus (3)
skin, mucosa, oropharynx
habitat for micrococcus spp, kocuria spp, kytococcus spp.
S. aureus
mode of transmission:
Endogenous strain: sterile site by traumatic introduction (surgical wound or microabrasions)
Direct contact: person - to - person, fomites
Indirect contact: aerosolized
S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, and S. lugdunesis
Mode of transmission: Endogenous strain: sterile site by implantation of medical devices ( e.g shunts, prosthetic devices)
Direct contact: person to person
S. saprophyticus
Mode of transmission: Endogenous stain: sterile urinary tract, notably in young, sexually active females
Micrococcus spp, Kocuria spp, Kytococcus spp.
Mode of transmission: Endogenous strain: uncertain, rarely implicated in infections, immunocompromised hosts: brain abscess, meningitis, pneumonia, endocarditis.
Staphylococcus
Epidemiology:
Shedding of bacteria is common; responsible for many hospital acquired (nosocomial) infections
Susceptible to high temperatures, and disinfectants and antiseptics solutions; can survive on dry surfaces for long periods
Can be transferred to a susceptible person through direct contact or contact with fomites (contaminated clothing, bed linens)
coagulase
an enzyme that clots plasma
Staphylokinase
an enzyme that breaks down clots to help the bacteria spread
TSST - 1
A toxin: toxic shock syndrome toxin
Enterotoxins
toxin that causes food poisoning
a-hemolysin
toxin that destroys red blood cells
Panton-Valentine Leukocidin
invasin that kills white blood cells
adhesins
It helps the bacteria stick to host tissues
collagen, fibronectin, elastin
3 types of adhesins
capsule
structure that is:
polysaccharide, covers the outermost layer of the cell wall, inhibits phagocytosis, and chemotaxis by leukocytes
slime layer (biofilm)
structure that is:
loose-bound, water-soluble film, produced at varying amounts, allows the organism to adhere to inorganic surfaces, inhibits the penetration of antibiotics
peptidoglycan
structure that is: half of the cell wall by weight, consist of many cross-linked layers of glycan chains, provide osmotic stability, stimulates production of endogenous pyrogen ( endotoxin-like activitiy), leukocyte chemoattractant
enzymes
these catalyze construction of the peptidoglycan layer, called penicillin-binding proteins because these are targets of panicillin and other beta lactam antibiotics
teichoic acids and lipoteichoic acids
specie- specific, phosphate-containing polymers, bound either covalently to N- acetylmuramic acid residues of the peptidoglycan layer or to the lipids n the cytoplasmic membrane; binds to fibronectin
surface adhesion proteins
most are covalently bound to the cell wall peptidoglycan; they have been designated microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMM)
staphylococcal protein A, Fibronectin-binding proteins A and B, clumping factor protein A and B
3 adehesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMM)
cytoplasmic membrane
complex of proteins, lipids, and a small amount of carbohydrates, serves as an osmotic barrier of the cell and provides and anchorage for the cellular biosynthetic and respiratory enzymes
staphyloccoci
the ability of _ to cause diease depends on the abiity of the bacteria to:
evade immune clearance
produce surface proteins that mediate adherance of the bacteria to host tissues during colonization, produce disease through the elaboration of specific toxins and hydrolytic enzymes leading to tissue destruction
evade immune clearance, adhere to host tissues, produce toxins and enzymes
the ability of staphylococci to cause diseases depends on: (3)
capsule, slime layer, peptidoglycan, teichoic acid, protein A
virulence factors of staphylococcus aureus (5)
capsule
virulence factor of staphylococci: inhbits chemotaxis and phagocytosis; inhibits mononuclear cell proliferation
slime layer
virulence factor of staphylococci: facilitates adherance to foreign bodies
peptidoglycan
virulence factor of staphylococci: provides osmotic stability; endotoxin-like activity
teichoic acid
virulence factor of staphylococci: binds to fibronectin
protein A
virulence factor of staphylococci: bound to the cytoplasmic membrane, binds to immunoglobulins → decrease immune mediated clearance of organisms from the sites of infection
coagulase
mainly produced by S. aureus (+), coagulase + CRF (coagulase reacting factor) from plasma form thrombin-like factor
staphylokinase
converts fibrinogen to fibrin (clot),
fibrin clot
coats staphylococci and protects them from phagocytosis, localizes the infection and protects the organisms from phagocytosis
bound coagulase
can directly convert fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin and cause staphylococci to clump
cell-free coagulase
accomplishes the same result by reacting with a globulin plasma factor to form staphylothrombin
catalase
produced by al staphylococci, catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to H2O and O2, protects the organism from toxic H2O2 that accumulates during bacterial metabolism and is released during phagocytosis
hyaluronidase
virulence factor: hydrolzes hyaluronic acid in connective tissues, promoting spread of staphylocci in tissue
firbrinolysis
virulence factor: dissolves fibrin clots
lipases
virulence factor: hydolyzes lipids
nucleases
virulence factor: hydrolazes DNA
cytotoxins
virulence factor: toxic for many cells, including erythrocytes, fibroblasts, leukocytes, macrophages, and platelets
exfoliative toxin
serine proteases that split the intracellular bridges in the stratum granulosum epidermis
enterotoxin
stimulates release of inflammatory mediators in mast cells, increasing peristalsis and fluid loss, as well as nausea and vomitting
toxic shock syndrome toxin
produces leakage or cellular destruction of endothelial cells
alpha hemolysin, beta hemolysin, delta toxin, gamma toxin and PV leukocidin
4 types of cytotoxins
alpha hemolysin
Cytotoxin
• 33,000 Da polypeptide
• Disrupts the smooth muscle in blood vessels
• Toxic to erythrocytes, leukocytes, hepatocytes, and platelets
• Binds to the cell surface, aggregates into a heptamer forming 1-2 nm pore
and allows the rapid reflux K+ and influx Na+ and Ca+ and other small molecules
• Leads to osmotic swelling and cell lysis
Beta hemolysin
cytotoxin:
35,000 Da heat-labile protein produced by most strains of S. aureus
• Also known as Sphingomyelinase C
• Works in conjunction with the alpha toxin
• Catalyzes the hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids in susceptible cells
• Acts on Sphingomyelin in the plasma membrane of erythrocyte
• Enhanced hemolytic activity on incubation on 37°C and subsequent
exposure to cold temperatures such as 4°C
• "Hot - Cold Lysin
Delta toxin
cytotoxin:
3,000 Da polypeptide produced by almost all strains of S. aureus and other Stpahylococci
Considered less toxic to alll cell than either alpha or beta hemolysin
Acts as a surfactant (reduces surface tension)
Disrupts cellular membrane by means of detergent-like action
found in higher percentage of S, aureus strains and some CoNS
Gamma toxin
Bicomponent toxin composed of 2 polypeptide chains
• S (slow-eluting proteins) component - HIgA, HIgC and LuKS-PV
• F (fast-eluting proteins) component - HIgB and Lukf- PV
HIgA, HIgC and LuKS-PV
S( slow -eluting proteins) component
HlgB and LuKf- PV
F (fast-eluting proteins) component
Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL)
endotoxin lethal to polymorphonuclear leukocytes
exfoliative toxin
also known as epidermolytic toxin
exfoliative toxin A
type of exfoliative toxin:
heat-stable, gene is phage-associated
exfoliative toxin B
type of exfoliative toxin: heat-liable, located on plasmid
serine proteases
Exfoliative toxins A and B act as _, which are enzymes that cut specific proteins
Serine proteases
spit cell adhesion structures responsible for forming the intracellular bridges in the stratum granulosum epidermis; protective neutralizing antibodies develop, leading to resolution of the toxic processes
Toxic shock syndrome toxin - 1 (TSTT-1)
22,000 Da, heat- and proteolysis-resistant
• Previously referred to as Enterotoxin F
• Chromosomal-mediated toxin that causes the majority of cases of
menstruating-associated TSS and approximately 50% of non-menstruating
c a s e s
• At low concentrations, causes leakage by endothelial cells, and is cytotoxic
to these cells at higher concentrations
• absorbed through the vaginal mucosa, leading to systemic effects as seen with prolonged tampon use
cutaneous infections, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) or ritter disease, toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning, bacteremia, endocarditis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis and septic arthritis
infections cause by staphylococcus aureus (9)
cutaneous infections
typically the abscess is filled with pus
and surrounded by necrotic tissues
and damaged leukocytes
• Usually occurs as a result of previous
skin infections such as cuts, burns, and surgical incisions
folliculitis
type of cutaneous infection: mild inflammation of a hair follicle or oil gland; base of the folllicle is raised and reddended with small collections of pus beneath epidermal surface
furnucles (boils)
extensions of folliculitis, large, painful, raised nodules with underlying collection of dead and necrotic tissue, can drain spontaneously or through surgical incisions
carbuncles
type of cutaneous infection:
carbuncles: occurs when furnucles coalesce and extend to deeper subcutaneous tissue, multiple sinus tracts are usually present, chills and fevers
wound infections
type of cutaneous infection: occur after organisms on skin or external source enter wound from a surgical procedure or trauma; characterized by edema, erythema, pain, accumulation of purulent material
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome or ritter disease
Bullous exfoliative dermatitis that occurs primarily in newborns and previous healthy young children
Characterized by:
Abrupt onset of localized perioral erythema
Slight pressure displaces the skin (+ Nikolsky sign)
Large bullae or cutaneous blisters form, followed by desquamation of epithelium
Bullous impetigo
localized form of SSSS
specific strain of toxin producing S. aureus are associated with formation of superficial skin blisters, S. aureus is present in the localized blisters, erythema does not extend beyond the borders of the blister ( nikolsky sign not present), occurs primarily in infants and young children, highly communicable
toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
• rare but potentially fatal multisystem disease
• Characterized by:
• F e v e r
• Hypotension y
• Diffuse, macular, erythematous rash
• Desquamation of the entire skin
• Multiple organ system involvement
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome or ritter disease
Cutaneous blisters contain clear fluid but no organisms or leukocytes
• Epithelium becomes intact again within 7-10 days, when antibodies against
the toxin appear
• Scarring does not occur as only the top layer of epidermis is affected
• Primarily affects neonates and young children (<5% mortality rate, deaths
caused by secondary bacterial infection of denuded skin)
• Infections in adults - occur in immunocompromised hosts or patients with
renal disease (60% mortality rate)
toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
first desvribed in 1978 and was associated with women using highly absorbent tampons, although some cases appeared in men, children, and non-menstruating women; initial fatality rate - 5%, risk of recurrent diease - as high as 65% unless patient is treated with effective antibiotic
purpura fulminans
Characterized by:
• Large, purpuric skin lesion
• F e v e r
• Hypotension
• Disseminated intravascular coagulation
• A s s o c i a t e d w i t h overwhelming
meningitidis infections
food poisoning
Enterotoxins, most commonly
• A (78%)
• D (38%)
• B (10%)
• Characterized by:
• N a u s e a
• Vomiting
- abdominal pain
severe cramping
food poisoning
• Results from ingestion of a toxin formed outside the
body
• D i s e a s e o c c u r s w h e n f o o d b e c o m e s c o n t a m i n a t e d
with enterotoxin-producing strains of S. aureus
• F o o d s u c h as:
• Salads with mayonnaise and eggs
• Meat or Meat products
• Poultry
• Egg products
• Food kept at room temperature
bacteremia
presence of bacteria in the blood, most likely originated from skin infections, more than 50% are nosocomial, commonly observed among intravenous drug users, prolonged episodes are associated with dissemination to other body sites
endocarditis
50% mortality rate unless promply diagnosed, initally have nonspecific influenze like symptoms that can deteriorate rapidly to include disruption of cardiac output and peripheral evidence of septic embolization
pneumonia
occur secondary to influenza virus infection, can develop after aspiration of oral secretion or from hematogenous spread of the organism from a distinct site; develops as a contigious, lower respiratory tract infection or a complication of bacteremia;
characterized as:
multiple abscesses and focal lesions in pulmonary parenchyma
aspiration pneumonia
seen in the young, elderly, and patients with cystic
fibrosis, influenza, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and bronchiectasis
hematogenous pneumonia
common for patients with bacteremia or endocatditis
necrotizing pneumonia
caused by community acquired MRSA; massive hemoptysis, septic shock, and high mortality rate
Empyma
occurs in 10% of patients with pneumonia, pus-filled pockets that develops in pleural space S. aureus responsible for ½ of cases
Osteomyelitis
results from hematogenous dissemination to bone or
by secondary infection resulting from trauma or
extension of disease from an adjacent area
• Occurs as a manifestation secondary to bacteremia
• Children - results from cutaneous infection and
involves long bone
• Sudden onset of localized pain and high fever
• Adults - Vertebral osteomyelitis, intense back pain with fever
septic arthritis
occurs in children and adults who are receving intraarticular injections or who have mechanically abnormal joints, usually seen in large joints, characterized by: painful erythematous joint with purulent material obtained on aspiration, childre: patients with trauma to the extremities, adults: histor of rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, joint surgery, skin infections, or intravenous drug abuse
endocarditis, Catheter and Shunt infections, prosthetic joint infections, urinary tract infections
two coagulase negative S. (4)
Catheter and Shunt infections
more than 50% causes by CoNS, leads to persistent bacteremia as CoNshave continual access to the blood
native valve endocarditis
S. lugodunesis, otherwise more commonly caused by streptococci
artificial valve endocarditis
more commonly caused by staphylococci;
CoNS are introduced at time of valve replacement
indolent course of infection, clinical signs and symptoms not developing up to 1 year after procedure
infection occurs at site where valve is sewn to heart tissue - abscess formation can lead to separation of valve at suture line and to mechanical heart failure( heart valve replacement),
infections have high mortality rate
immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis
occurs in patients with long-standing diease
prosthetic joint infections
characterized by: localized pain, mechanical failure of joint; treatment: joint replacement and antimicrobial therapy
urinary tract infections
S. saprophticus - most common staphylococcal pathogen in young sexually active women; characterized by: dysuria; pyuria, bacteriuria
Staphylococci
Recovery of ___ requires no special procedure; specimens should be taken from the site of infection after appropriate cleaning of surrounding area to avoid contamination by skin microbiota
stain, staining reaction, shape, arrangement in clusters
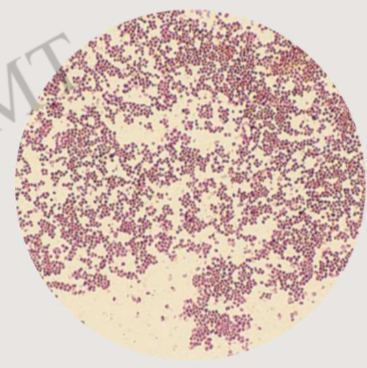
Sheep's Blood Agar
staphylococci produce round, smooth, white, creamy colonies _ after 18- 24 hours of incubation at 35° to 37° C
what is the agar used
staphylococci
they can produce hemolytic zones around the colonies and may rarely exhibit pigment production