Electronic Components Found in Medical Devices
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Types of Electronic Components
Resistors
Capacitors
Inductors
Diodes
Transistors
Integrated Circuits
Resistors definition + symbol (photo + 2)
Limit or control the flow of electric current in a circuit
fx.: thermistors, photoresistors/LDRs

Resistors Unit
[Ω] = ohms
mains cable 0.1Ω/m, human arm 1000Ω
Resistors Types
wire-wound
carbon film
metal oxide
variable resistors - LDRs (light dependent resistors)
Thermistors

Wire-Wound Resistors (3)
Constructed by winding a metal wire (nichrome) around a ceramic or insulating core
high power handling
precise
Carbon Film Resistors (2)
Made by depositing a thin layer of carbon on a ceramic substrate
Good stability
Metal Oxide Resistors (3)
Composed of a metal oxide film
High-temperature stability and reliability
Used in high-power applications bc/ thermal properties
Variable Resistors (2)
Allow adjustment of resistance
fx.: LDRs (Light Dependent Resistors)
LDRs (Light Dependent Resistors) (3)
made from semiconductor materials that change resistance based on light intensity
semiconductor based
used as light sensors
Thermistors (2)
Semiconductor-based resistors whose resistance changes significantly with temperature
Used as temperature sensors
Uses of resistors (2)
set currents and voltages in circuits
thermistors and LDRs: used as light and temperature sensors
Power and Voltage Ratings of a resistor (2)
Maximum values that resistors can handle without damage.
Important for ensuring safe operation in circuits.
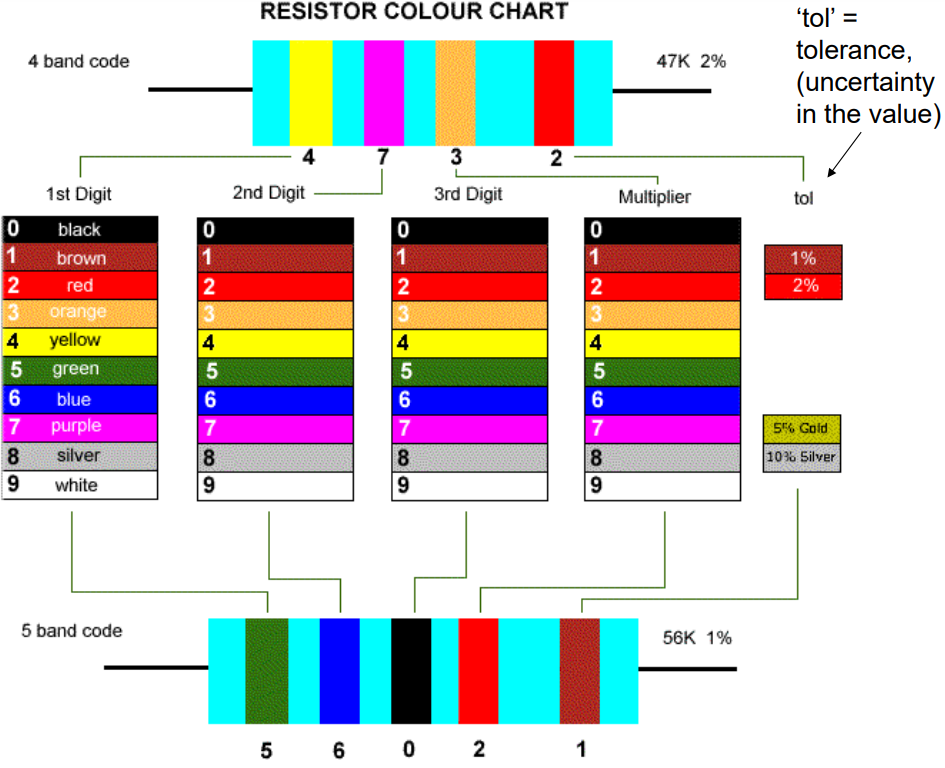
Carbon Film Resistor Colour Code (6)
Colour Code: A system of colored bands on resistors indicating their resistance value, tolerance, and reliability.
Typically consists of 4 or 5 bands
the first two or three represent significant digits
the next indicates the multiplier
the last band shows tolerance
uncertainty in the value
Capacitors symbol + unit + extra note (photo +2)
[F] = Farad
The patient-earth system has a capacitance of approximately 100 pF (pico = 10-12)
![<p>[F] = Farad</p><p>The <strong>patient-earth system</strong> has a capacitance of approximately <strong>100 pF</strong> (pico = 10<sup>-12</sup>)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/981d4995-432b-40f2-8646-3b49b1fc2234.png)
Capacitors uses (3)
Store and release electrical energy
Timing Circuits
create time delays or oscillations w/ resistors
smooth voltages by removing low unwanted frequencies from signals
Types of Capacitors (Based on Dielectric) (3)
Paper Capacitors
Air Capacitors
Mica Capacitors etc.

Paper Capacitors (3)
Use paper as the dielectric material
Stable
Reliable
Air Capacitors (2)
Use air as the dielectric
Found in tuning circuits due to their variable capacitance
Mica Capacitors (3)
Utilize mica as the dielectric
High precision and stability
Used in high-frequency applications
Inductors symbol and unit
[H] = Henry
![<p>[H] = Henry</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/535a5559-a7cf-4ac3-81fb-75261392637e.png)
Inductors uses (2)
Store energy in a magnetic field when current flows through them
Smooth voltages by removing high unwanted frequencies from signals

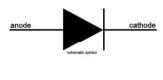
Diodes definition + symbol
Allow current to flow in one direction only
Diodes uses
Rectification
LEDs as Indicators
Photodiodes as Light Sensors
Zener Diodes in Regulated Power Supplies
Rectification
Convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) in power supplies
LEDs as Indicators
Provide visual feedback in devices (e.g., power indicators)
Photodiodes as Light Sensors
Detect light levels for applications like automatic lighting and camera exposure
Zener Diodes in Regulated Power Supplies
Maintain a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions
Types of Diodes
Generic Diodes
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes)
Photodiodes
Zener Diodes

Generic Diodes
Standard diodes that allow current to flow in one direction only; used for rectification
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes)
Emit light when current passes through; commonly used as indicators in electronic devices
Photodiodes
Function as light sensors; generate current or voltage when exposed to light
Zener Diodes
Allow current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific voltage (Zener voltage) is reached; used for voltage regulation in power supplies.
Transistors symbols
it has 3 terminals
Transistors Uses (3)
very fast switching
amplifiers
filter circuits
Integrated Circuits (ICs) (2)
Complex circuits with multiple components in a single package
consist of thousands of miniature resistors, diodes, transistors and capacitors
Integrated Circuits Uses (7)
amplifiers
filters
RAM, ROM
counters
timers
comparators
microprocessors
Semiconductors (9)
fx.: Silicon (Si) and Germanium (Ge)
Found in resistors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits
Act as insulators in their natural state
Become conductors when energy is applied
heat, light E
Conductivity increases with more energy exposure
Used as energy sensors for measuring heat and light energy
Heat E: thermometers
Light E: spectrophotometers, digital microscopes
Power Supplies
Mains voltage 240V AC but most instruments need few volts
constant DC
every electronic medical device which is connected to the mains supply needs to have a ‘power supply’
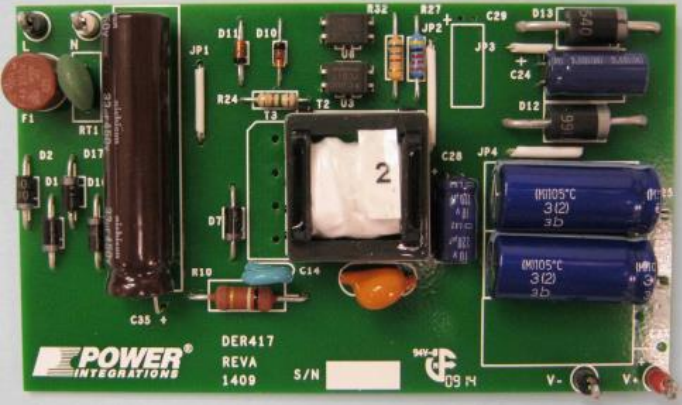
Power supplies consist of
step-down transformer
4 diodes for full-wave rectificatio
smoothing capacitors and inductors
zener diodes for voltage regulation (essential when voltage supply is erratic)