AP Computer Science Principles
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Logic error
An error in a program that makes it do something other than what the programmer intended.
Pair programming
Involves two programmers at a single workstation. At any given point in time, one is writing code and the other is actively observing, watching for possible errors
but also thinking about the overall approach.
Runtime error
An error that occurs when the program is run using certain sets of data that result in some illegal operation, such as dividing by zero.
Syntax error
An error that occurs because a program statement fails to follow the correct rules of syntax.
Open source
Software whose source code is freely available and may be used, distributed, or modified by anyone.
Ethics
The study of how to decide if something is morally right or wrong.
Infinite loop
The repetitive execution of a block of operations that will never end. This is a fatal error when it occurs in an algorithm.
Sequential operation
An algorithmic operation that carries out a single task and then moves on to the next operation in sequence.
Conditional statements
a block of code that performs different actions or computations based on the value of a Boolean expression, or condition (same as selection - represented by if-else)
Input
the data or information that a computer receives to perform a task or process
Iteration
The repetitive execution of a block of operations.
Output
the information or data that a computer system generates as a result of processing input data
Pseudocode
a simplified, English-like way of writing code or algorithms before translating them into a specific programming language
Sorting
The task of putting a list of values into numeric or alphabetical order.
Boolean expression
An expression that can evaluate only to true or false.
Program
a set of instructions written in a programming language that a computer executes to perform a specific task
Event Driven Programming
a programming approach whereby the program's behavior is controlled by writing code that responds to various events that occur, such as Button clicks.
Hardware
the large and small physical components that make up a computers such as the computer's keyboard or its processor.
Software
the computer programs that make up a computer system such as the mobile apps we will be creating in this course.
Abstraction
the process of simplifying complex systems or concepts by hiding unnecessary details and focusing on relevant aspects
Binary Number
a number written in the binary system, a system that uses only two digits, 0s and 1s.
Data
is distinct information that is formatted in a special way. It exists in a variety of forms, like text on paper or bytes stored in electronic memory
Intellectual Property
refers to any property that is created using original thought. Including patents, copyrights, and trademarks.
Network
a group of two or more computer systems linked together
Social Networking
the use of dedicated websites and applications to interact with other users, or to find people with similar interests to oneself.
Analog
a device or system that represents changing values as continuously variable physical quantities
ASCII
a code for representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127
Cloud Computing
the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.
Cryptography
the art of protecting information by transforming it into an unreadable format, called cipher text
Digital
any system based on discontinuous data or events.
Spam
electronic junk mail or junk newsgroup postings
Bit
Single unit of information on a computer represent as a 0 or 1
Bit Rate
The number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time
Latency
The time it takes for a signal to arrive (lag)
WiFi
A wireless networking technology that utilizes radio waves to transmit information/data
Bandwidth
The maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time.
IP Address
A number assigned to any item that is connected to the Internet.
Packets
Small chunks of information that have been carefully formed from larger chunks of information.
Router
a device that forwards data packets between computer networks
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of packets on the internet.
Domain Name System (DNS)
the Internet's system for converting alphabetic names into numeric IP addresses.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
The protocol used by the World Wide Web. It describes how messages are formatted and interchanged, and how web servers respond to commands.
Server
A computing device that awaits and responds to requests for data.
Client
A computing device that requests data stored on a server.
Net Neutrality
The principle that Internet service providers should enable access to all content and applications regardless of the source, and without favoring or blocking particular products or websites.
Internet Censorship
The control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet.
Routing Table
A data table stored in a router that lists the routes to particular network destinations
Algorithm
A precise sequence of instructions for processes that can be executed by a computer
Function/Procedure
A piece of code that you can easily call over and over again.
Application Programming Interface (API)
a collection of commands made available to a programmer
Documentation
a description of the behavior of a command, function, library, API, etc.
Parameter
Variables defined in the heading of the function/procedure, if required, that allow input values to be sent into the function in its calling statement.
Loop
The action of doing something over and over again.
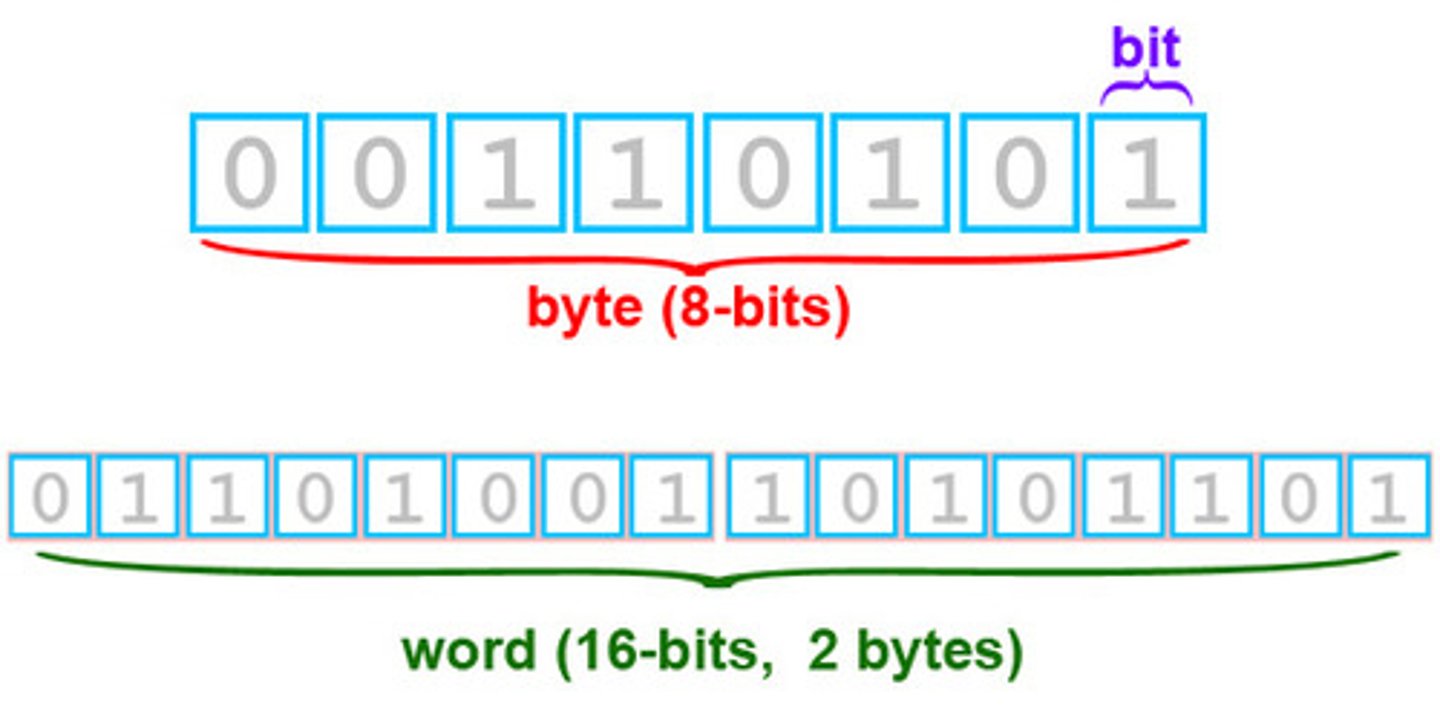
Byte
technical term for 8 bits of data
Heuristic
a problem solving approach (algorithm) to find a satisfactory solution where finding an optimal or exact solution is impractical or impossible.
Metadata
Data that describes other data. For example, a digital image my include metadata that describe the size of the image, number of colors, or resolution.
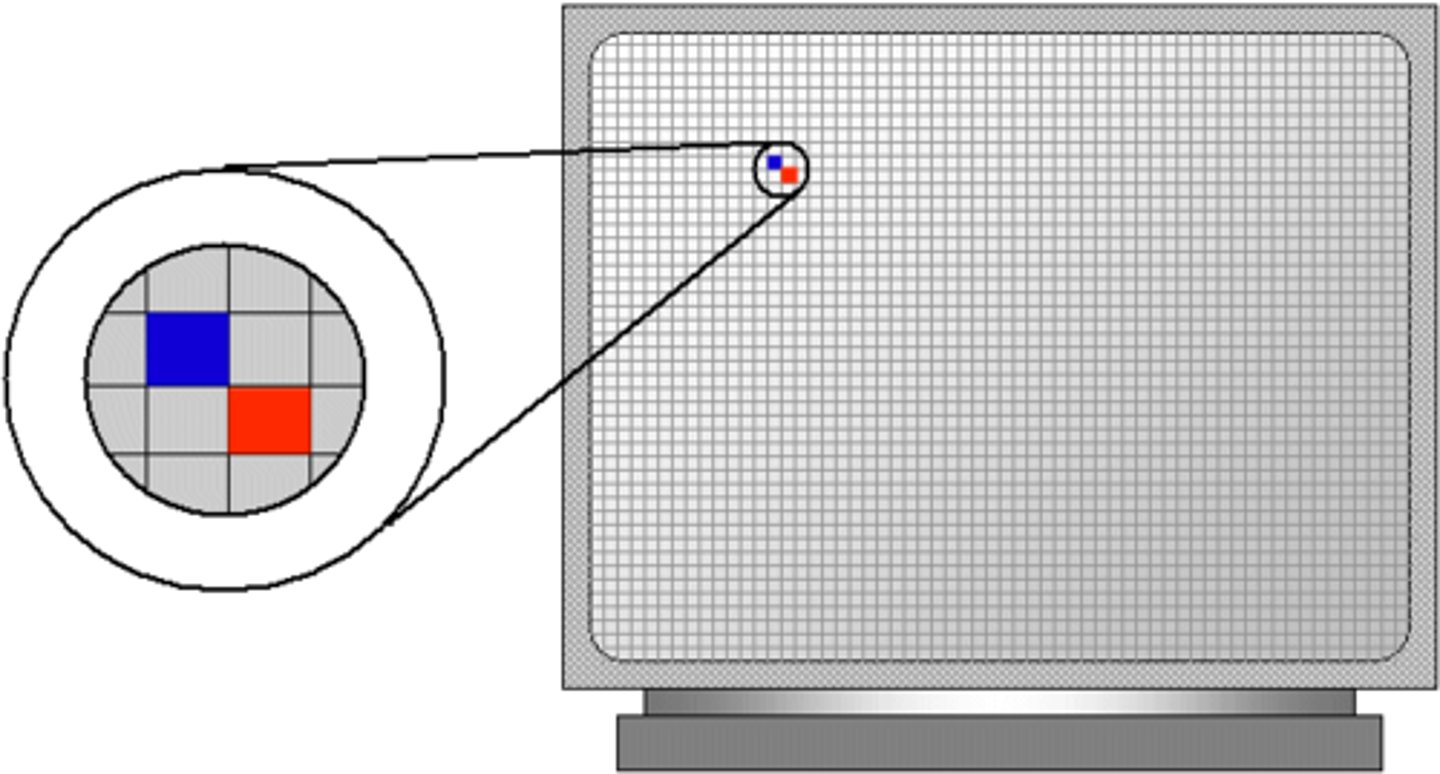
Pixel
Short for "picture element" it is the fundamental unit of a digital image, typically a tiny square or dot which contains a single point of color of a larger image.
Lossless Compression
A compression scheme in which every bit of the original data can be recovered from the compressed file.

Lossy Compression
A compression scheme in which "useless" or less-than-totally-necessary information is thrown out in order to reduce the size of the data. The eliminated data is unrecoverable.

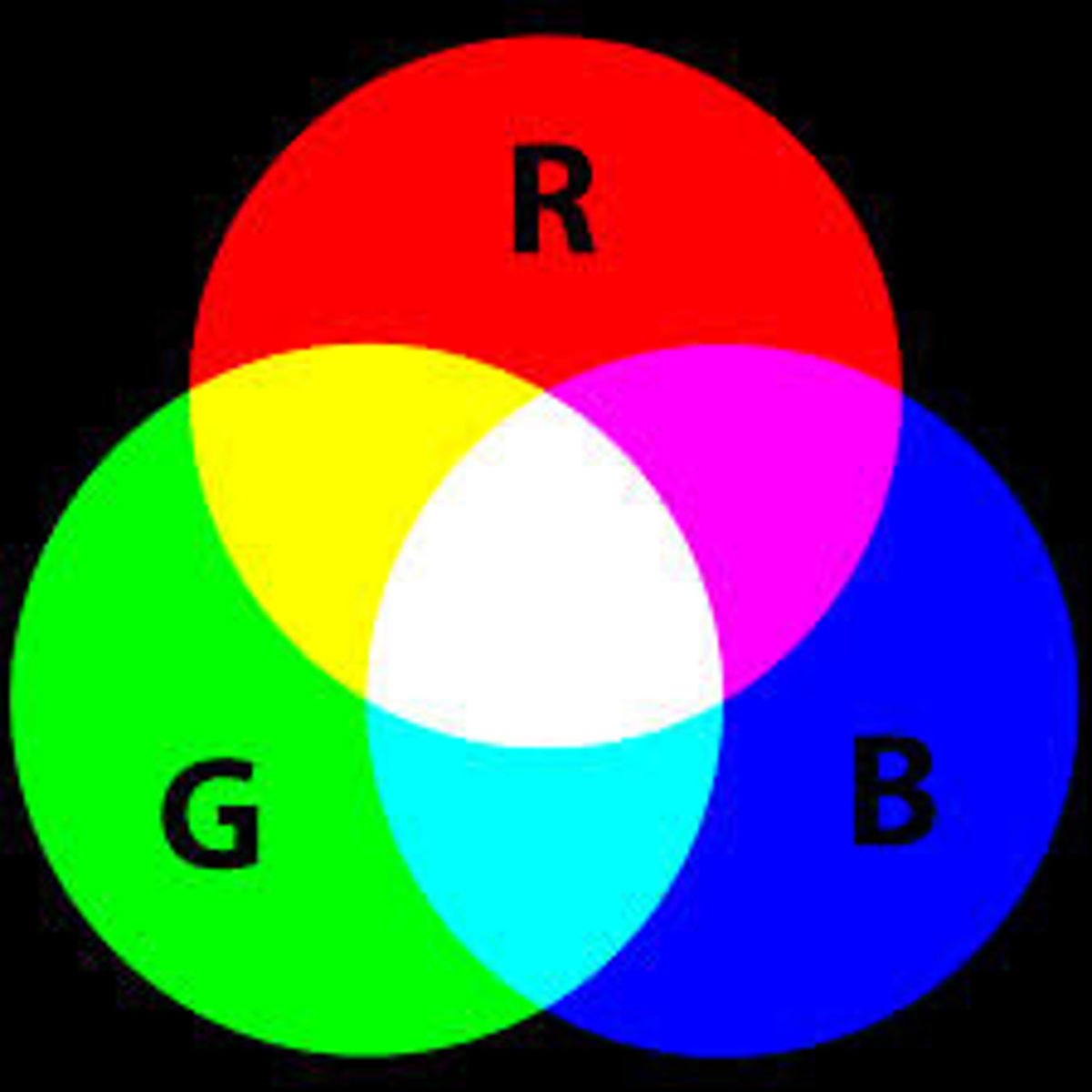
RGB
the color model that uses varying intensities of (R)ed, (G)reen, and (B)lue light added together in order to reproduce a broad array of colors.
Heuristic
A problem that can not be solved in a reasonable amount of time. Often used to create an approximate or good enough solution.
Innovation
A novel or improved idea, device, product, etc. or the development thereof
Big Data
a broad term for datasets so large or complex that traditional data processing applications are inadequate.
Cipher
the generic term for a technique (or algorithm) that performs encryption
Decryption
a process that reverses encryption, taking a secret message and reproducing the original plain text
Encryption
a process of encoding messages to keep them secret, so only "authorized" parties can read it.
Public Key Encryption
An asymmetric encryption scheme in which the encryption key is made public, but the decryption key is kept private.
Digital Divide
the gulf between those who have ready access to computers and the Internet, and those who do not.
Filter
tool/technique using dynamic parameters for reducing a data set to viewing only similar items in a row or column.
Protocol
A set of rules governing the exchange or transmission of data between devices.
ASCIII
The universally recognized raw text format that any computer can understand
Redundancy
the presence of duplicated or unnecessary data, components, or functions within a system. This duplication is often intended to improve reliability and resilience, allowing the system to continue functioning even if some components fail
HTTPS
the secure version of HTTP, the standard protocol for transferring data on the web. The "S" signifies that the connection between a web browser and a website is encrypted and secure, protecting data transmitted between them
TCP
provides reliable, ordered and error checked delivery of a stream of packets in the internet
URL
an easy to remember address for calling a web page
Decimal
Traditional number system using digits 0-9.
Creative Commons
one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted work. A CC license is used when an author wants to give people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that they have created.

High Level Programming Language
A programming language that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of a particular type of computer. Such languages are considered high-level because they are closer to human languages and further from machine languages. Examples: JavaScript, Java, FORTRAN
Low Level Programming Language
A programming language that provides little or no abstraction from a computer's instruction set architecture—commands or functions in the language map closely to processor instructions. Generally this refers to either machine code or assembly language.
Fault tolerant network
a system's ability to continue operating correctly even in the presence of errors, faults, or failures in its components
Global Variable
A variable whose scope is "global" to the program, it can be used and updated by any part of the code. Its global scope is typically derived from the variable being declared (created) outside of any function, object, or method.
If Statement
The common programming structure that implements "conditional statements".
Local Variable
A variable with local scope is one that can only be seen, used and updated by code within the same scope. Typically this means the variable was declared (created) inside a function; includes function parameter variables.
User Interface
The visual elements of an program through which a user controls or communications the application. Often abbreviated UI.
Data Type
(ex: Number, Boolean, or String) a value's property that dictates how the computer will interpret it.
Variable
A placeholder for a piece of information that can change.
Debugging
Finding and fixing problems in your algorithm or program.
Conditionals
statements that run under only certain conditions
Selection
uses a Boolean condition to determine which of two or more parts of an algorithm are to be executed.
Concatentate
to link together or join. Typically used when joining together text Strings in programming (e.g. "Hello, "+name)
Binary Search
a search algorithm that starts at the middle of a sorted set of numbers and removes half of the data; this process repeats until the desired value is found or all elements have been eliminated.
Linear Search
a search algorithm which checks each element of a list, in order, until the desired value is found or all elements in the list have been checked.
Cleaning Data
a process that makes the data uniform without changing its meaning (replacing all equivalent abbreviations, spellings, and capitalizations with the same word).
Transforming Data
editing or modifying data (doubling every number/graphing data points)
Data Mining
the application of statistical techniques to find patterns and relationships among data for classification and prediction
Sampling
A process for creating a digital representation of analog data by measuring the analog data at regular intervals called samples.
Base 2
The name given to the counting system for Binary (0-1)
Base 10
The name given to the counting system for Decimal Values (0 - 9)
Citizen Science
scientific research conducted in whole or part by distributed individuals, many of whom may not be scientists, who contribute relevant data to research using their own computing devices.
Crowd Sourcing
A subfield of computer science that attempts to solve problems by using the ability of many humans to solve small subproblems and then using computers to combine those solutions into some meaningful results.