Physiology XA: flashcards
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PHYL 1011 Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
Physiology
THe study of normal functioning of a living organism and its component parts, including all of its chemcial and physical processes
Levels of Organization
atoms-molecules-cells-tissues-organs-systems-organisms-populations-ecosystems-biosphere
Circulatory (cardiovascular)
transport of materials between all cells of th body
Digestive System
Conversion of food into particles that can be transported into the body and the elimination of some waste
Endocrine
Coordination of body function through synthesis and release of regulatory molecules
Immune System
Defense against foreign invaders
Integumentary
Protection from external enviornment
Musculoskeletal System
Support and movement
Nervous System
Coordination of body function through electrical signals and release of regulatory molecules
Reproductive System
Perpetuation(continuing) of the species
Respiratory System
Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the internal and external enviornments
Urinary System
Maintanence of water and solutes in the internal enviornment and waste removal
External enviornment
The enviornment the organism lives in (the atmosphere)
External enviornment examples
digestive tract, respiratory tract excluding the lungs, ureters, bladder, fallopian tubes
Internal Enviornment
The enviornment the cell lives in divided into the extracellular and the intracellular fluid
Internal Enviornment examples
lungs, kidneys, ovaries, skin, blood in the blood vessels
Extracellular fluid
fluid outside our cells
Intracellular fluid
Fluid inside our cells
Homeostasis
The ability of the human to monitor its internal enviornment and to take actions to correct or minimize disruptions that threaten its normal function
Homeostasis Examples
body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, O2 in blood
Negative Feedback
Feedback are designed to keep the body in homeostasis
Negative Feedback example
thermoregulation, and blood sugar regulation
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback loops temporarily sends the body out of homeostasis and requires outside intervention to shut off the positive feedback loop.
Positive feedback examples
Contractions in childbirth
Local Control
Homeostatic control that takes place within a tissue
Reflex Control
Homostatic control that requires long distance signalling and involves many different organs
Plasma membrane is made of what
A phospholipid bi layer and proteins
Plasma Membrane functions
barrier between ICF and ECF, regulation of exchange between ICF and ECF via proteins, communication between ICF and ECF via proteins and structural support with proteins and carbohydrates.
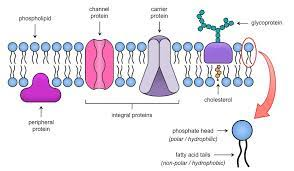
Fluid Mosaic Model
Nucleus
It boundary, or nuclear envelope is a two membrane structure that seperates the nucleus from the cytoplasmic compartment Communication goes through the nuclear pores
Cytoplasm
Consist of a fluid portion called the cytosol, insoluble particles called inclusions, insoluble particles called inclusions and membrane bound strucutres collectively known as organelles
Cytosol
AKA intracellular fluid. A semi gelatinous fluid seperated from the extracellular fluid by the cell membrane.
Organelles
Membrane bound compartments that play specific roles in the overall function of the cell.
Mitochondria
Plays an important role in ATP production. Mitochondria are the site of most ATP synthesis in the cell. Spherical with a double wall that create two seperate compartments.
Rough ER
The main site of protein synthesis. Granular appearance due to the rows of ribosomes.
Smooth ER
synthesizes lipids and stores calcium ions. lacks ribosomes and appears as smooth membrane tubes
Golgi Apparatus
Consist of a series of hollow curved sacs called cisternae stacked on top of one another and surrounded by vesicles. Participates in protein modification and packaging.
Lysosomes
Act as the digestive system of the cell
Peroxisomes
Storage vesicles that are smaller than lysosomes.
Gap Junctions
Allow direct and rapid cell to cell communication between cytoplasm of neighboring cells
Tight Junctions
Restrict movement of material between the cells they link
Desosomes
Attach neighboring cells together and holds cells in place within tissue
ECF
1/3 of the total body water volume and consist of Interstitial fluid and blood plasma
Interstitial Fluid
Lies between the circulatory system and the cells
Blood plasma
Liquid matrix of blood
Osmotic equilibrium
Water is able to move freely between the ICF and the ECF therfore water distributes itself until the water concentration is equal
Chemical disequilibrium
The nature of the soultes is strikingly different between the ICF and ECF
Osmosis
Passive movement of water across a membrane in response to a solute concentration gradient
Osmotic Pressure
The pressure that the piston must exert to stop the movement of water when the osmotic pressure is high then the water movement is quicker
Osmolarity:
Calculates the number of particles in a solution
Hyperosmotic
greater osmolarity than
Isosmotic
same osmolarity than
hyposmotic
lower osmolarity than
Tonicty
describes the volume change of a cell considering only the non penetrating solutes
hypertonic
more tonic than
isotonic
same tonicty as
hypotonic
less tonic than
hypotonic cell
water will move into the cell
hypertonic cell
water will move out of the cell
osmosis movement
Water moves from areas of low concentration of solute to areas of high concentration of solute
Diffusion
Passive movement of solutes from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Energy for diffusion
inherent kinetic energy from movement and potential energy from concentration gradient
Factors that determine rate of diffusion
concentration gradient (higher gradient higher rate), molecule size (bigger molecule, slower rate), and temperature (higher temp faster rate)
Membrane permeability
the ability of a membrane to let molecules pass through
Membrane permeability factors
lipid solubility (high lipid solubility high rate), size of molecule (big low rate), exact composition of the lipids within the membranes
How do liphophobic solutes move through the plasma membrane
They use proteins inserted in the plasma membrane called protein mediated transport
Two different types of proteins
Channel and Carrier Proteins
Create a water filled pore, direct link between ECF and ICF, no confirmation change, fast and used for small molecules
Channel Proteins
Confirmation change
change in protein shape
Require confirmation change to transport molecules and can carry one or molecules at once
Carrier proteins
Uniport
Move one specific molecule GLUT transporters
Symport
Moves 2 or more specific molecules in the same direction SGLT transporter
Antiport
Moves 2 or more specific molecules in the opposite direction Na+ ATPase
Transportation that uses protein carriers
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of molecules across cell membranes in repsonse to a concentration gradient with the aid of a membrane protein, Passive transport and goes from high to low concentration
Active Transport
requires input of ATP and transports solutes, ,low to high concentration and goes away from equilibrium
Carrier proteins
Bind to their substrate require conformation change, it is slower and used for larger molecules.
Protein carrier role in primary active transport
acts as an enzyme to break down ATP
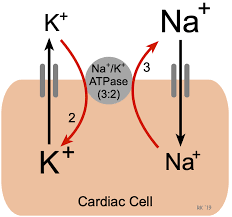
Na+ K+ ATPase pump
What type of active transport is Na+ K+ ATPase
primary active transport
Steps of Na+/K+ ATPase
3Na+ from ICF bind to affinity sites
ATPase is phosphorylated with P1 from ATP
Na+binding sites lose their affinity and release 3Na+ into ECF
2K+ from ECF bind to high affinity sites
K+ binding sites lose their affinity for K+ and release 2K+ into ICF.
what type of active transport is the SGLT
secondary active transport
Steps for SGLT
Na+ binds to carrier
Na+ bidnign creates a high affinity site for glucose
Glucose binding changes carrier confirmation so that binding sites face the ICF
Na+ is released into cytosol, where Na+ is low. Release changes glucose bidning site to low affinity and glucose is released.
Specificity
Transporters can only move one specific molecule
Competition
When transporters can move more than one substrate, these molecules compete with one another
Saturation
ALl transporters work at their maximal capacity, transport rate can no longer increase
Endocytosis
Moves large molecules into the cell
Exocytosis
Moves large molecules out of the cell
Electrical Disequilibrium
Body is electrically neutral which means that there are an equal amount of cations and anions but they are unevenly distributed between the ICF and ECF
Resting membrane potential
-70mV
Electrochemical Equilibrium
The movement caused by concetration gradient is matched exactly by the movement caused by the electrical gradient
Equilibrium potential of K+
-90mV
Equilibrium Potential of Na+
60mV
WHat ion pulls harder on membrane potential
K+
WHat ion is more permeable to the cell
The cell membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+
How is cell membrane potential is determined
concentration of K+ and Na+ in the ICF and ECF, the cell membrane permeability to K+ and Na+
Ways to change membrane potential andn why?
adding more channels which makes ions more permeable therfore causing more movement
hyperpolarization
dropping below -70mV
depolarization
moving above -70mV
repolarization
dropping back to -70mV