Chemistry
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/41
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
Properties of Metals
* Malleable
* Conduct electricity
* Conduct heat
* Ductile (can be stretched)
* Shiny
* Conduct electricity
* Conduct heat
* Ductile (can be stretched)
* Shiny
2
New cards
Properties of Non-Metals
* Low melting and boiling points
* Do not conduct heat
* Do not conduct electricity
* Brittle
* Dull
3
New cards
Metalloids
Both physical properties of metals and non-metals
4
New cards
Periodic table patterns
* The period is the row and is determined by the number of energy levels (shells)
* The group is the column down and it is determined by the number of valence electrons
5
New cards
Ionisation energy
The amount of energy required to remove and electron from an isolated atom or molecule
6
New cards
Atomic Radius
The total distance from an atom's nucleus to the outermost orbital of an electron
7
New cards
Electronegativity
A measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons to itself
8
New cards
Relationships down the groups of the PT
Ionisation is less, the electronegativity is less, but the atomic radius is more.
9
New cards
Relationships across the periods of the PT
Ionization is more, the electronegativity is more, but the atomic radius is less.
10
New cards
Formation of an ion
* An atom has an equal number of protons and electrons so they are electrically neutral
* The number of electrons can change in an atom and a chemical reaction can change the number of electrons in the outer shell (valence shell)
* Atoms will generally follow the octet rule where they are more stable when they have a full valence shell
11
New cards
Formation of a cation
* When an atom loses electrons they are losing negative charge and therefore become positive
* A positive ion is called a cation
* E.g., Magnesium goes from 2.8.2 and loses 2 electrons to form 2.8
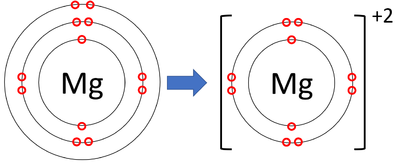
12
New cards
Formation of an anion
* When an atom gains electrons into the outer shell it is gaining negative charge so it becomes a negatively charged ion
* A negative ion is called an anion
* E.g., Sulphur has an electron configuration of 2.8.6 and it becomes 2.8.8
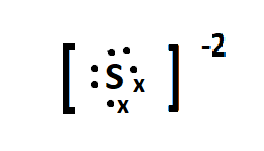
13
New cards
Polyatomic ions
Polyatomic Ions are an ion that contains two or more atoms joined together and it has an overall positive or negative charge
14
New cards
Ionic compounds
* Ionic compounds contain oppositely charged ions which are organised in a regular 3 dimensional lattice
* Each ion is held in the crystal lattice by strong electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions around it
* These are called ionic bonds
15
New cards
Naming ionic compounds
**CATION FIRST**
* Potassium fluor==ide==
* Copper ox==ide==
* Magnesium hydrox==ide==
* Barium carbon==ate==
* Iron chlor==ide==
* Aluminium brom==ide==
* Potassium fluor==ide==
* Copper ox==ide==
* Magnesium hydrox==ide==
* Barium carbon==ate==
* Iron chlor==ide==
* Aluminium brom==ide==
16
New cards
Writing ionic fomulae
* Identify the positive and negative ions
* Look at the charges they need to cancel out
* Swap them over and place at the bottom or if a ration of one to one put together
17
New cards
Physical properties of ionic compounds
* Hard
* Brittle
* Non-conductors of electricity as a solid
* Conductors of electricity in solution or molten
* High melting and boiling points
18
New cards
Isotope
Two or more forms of the same element that contain equal number of protons but different number of neutrons in their nuclei
19
New cards
Relative atomic mass definition
A weighted average of the masses of atoms of the isotopes
20
New cards
Carbon isotopes
* Almost all carbon atoms found in living things, and in the rocks, seas, and atmosphere of our planet have the number symbol 12C6
* The is called Carbon-12
* A fraction of the carbon atoms on Earth have the nuclear symbol 14C6
* This is called Carbon-14
* The is called Carbon-12
* A fraction of the carbon atoms on Earth have the nuclear symbol 14C6
* This is called Carbon-14
21
New cards
Relative atomic mass
The relative atomic mass we see written on the periodic table is an average.
* E.g., Only a tiny fraction of carbon atoms have a mass number of 13 or 14. All the rest have a mass number of 12.
* This means that the average mass of carbon atoms is 12.01
* This is called the relative atomic mass of carbon
22
New cards
Relative atomic mass calc
1. Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its % abundance
2. Add these values together
3. Divide by 100 to get the average
* E.g., Boron
1. 10x20=200, and 11x80=880
2. 200+880=1080
3. 1080/100=10.8
23
New cards
Properties of an Acid
* Corrosive
* Taste sour
* Turn blue litmus red
* React with active metals
* React with bases
* Contain hydrogen ions
* Taste sour
* Turn blue litmus red
* React with active metals
* React with bases
* Contain hydrogen ions
24
New cards
Properties of a Base
* Corrosive
* Taste bitter
* Turn red litmus blue
* Feel soapy or slippery (react with fats to make soap)
* React with acids
* Alkalis = soluble base
* Contain hydroxide ions
* Taste bitter
* Turn red litmus blue
* Feel soapy or slippery (react with fats to make soap)
* React with acids
* Alkalis = soluble base
* Contain hydroxide ions
25
New cards
Acid + Base → __________
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
E.g, Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water
E.g, Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water
26
New cards
Oxidation
Loss of electrons
* Element gains oxygen
* Element gains oxygen
27
New cards
Reduction
Gain of electrons
* Element loses oxygen
* Element loses oxygen
28
New cards
A successfull collision means a chemical reaction occurs, two things must be true:
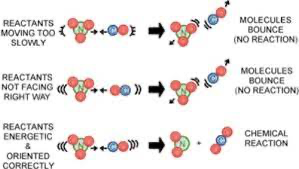
29
New cards
Controlling rate of reaction
* Temp
* Concentration
* Surface area
* Agitation
* Catalysts
* Concentration
* Surface area
* Agitation
* Catalysts
30
New cards
Temp
* Increased temp = increased ROR
Reasons:
1. Increased speed of particles in liquids and gases leads to particles colliding more frequently
2. Gives particles more energy, when ,molecules collide, chemical bonds are more likely to break (activation energy)
Reasons:
1. Increased speed of particles in liquids and gases leads to particles colliding more frequently
2. Gives particles more energy, when ,molecules collide, chemical bonds are more likely to break (activation energy)
31
New cards
Rate of Reaction
How fast a chemical reaction occurs
32
New cards
Concentration of the reactants
* Concentrated - more solute to solvent
* Dilute - less solute to solvent
* Increased concentration = increased ROR
Reason:
1. Reactant particles are more likely to collide if there is a lot of them in a small space
* Dilute - less solute to solvent
* Increased concentration = increased ROR
Reason:
1. Reactant particles are more likely to collide if there is a lot of them in a small space
33
New cards
Surface area
* Increased SA = increased ROR
Reason:
1. More reactant particles are exposed
Reason:
1. More reactant particles are exposed
34
New cards
Agitation
* Mixing and stirring
* Increased agitation = increased ROR
Reason:
1. More reactant particles are exposed
* Increased agitation = increased ROR
Reason:
1. More reactant particles are exposed
35
New cards
Catalysts
* Chemicals that speed up reactions but are not consumed (used up) during the reaction
* Catalysts = increased ROR
Reasons:
1. Reduce the activation energy that is required to convert the reactants into products
2. Provides an alternate pathway for reaction
3. Easier for reactant molecules to collide
E.g., Enzymes are biological catalysts
* Catalysts = increased ROR
Reasons:
1. Reduce the activation energy that is required to convert the reactants into products
2. Provides an alternate pathway for reaction
3. Easier for reactant molecules to collide
E.g., Enzymes are biological catalysts
36
New cards
Mole
Avogadros number, 6.022 x 10^23
* Used to count atoms, molecules, ions etc.
* Used to count atoms, molecules, ions etc.
37
New cards
The mole equation
* n = number of moles (mol)
* m = mass of the sample (grams, g)
* M = molar mass of the sample (grams per mole, g/mol)
* Molar mass is the no. of grams making up 1 mole of a substance
n=m/M
* m = mass of the sample (grams, g)
* M = molar mass of the sample (grams per mole, g/mol)
* Molar mass is the no. of grams making up 1 mole of a substance
n=m/M
38
New cards
When is a substance said to be soluble?
If it dissolves in solution
39
New cards
Metal + Acid → ________
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen
40
New cards
Metal carbonate + Acid → _________
Metal carbonate + Acid → Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
41
New cards
Types of Chemical Reactions
1. Decomposition
2. Single displacement
3. Double displacement
4. Combination (synthesis)
5. Combustion
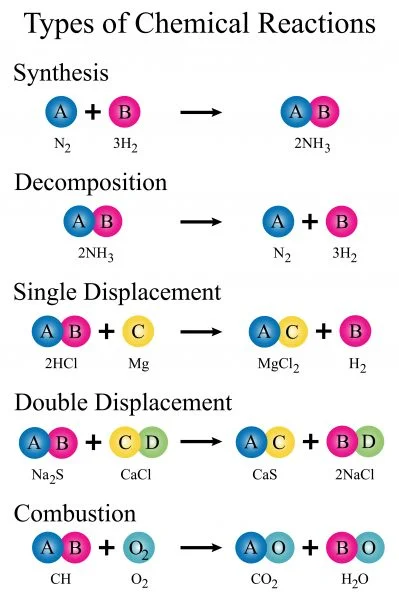
42
New cards
Precipitate reactions
* Reaction occurs when two soluble reactants combine to form an insoluble product known as the precipitate
* Particles from two soluble compounds mix together and some stick to form an insoluble solid
* Solid precipitates out of the solution, making it murky
* Usually the solution clears as the precipitate settles on the bottom or rests at the top
* Particles from two soluble compounds mix together and some stick to form an insoluble solid
* Solid precipitates out of the solution, making it murky
* Usually the solution clears as the precipitate settles on the bottom or rests at the top