Amplitude, Power, and Intensity
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Where is amplitude, power, and intensity found on the graph of a wave? Y or X axis?
Y axis (vertical axis).
If amplitude, power, and intensity are properties found on the vertical axis, are they related to things on the horizontal axis?
No. They are unrelated.
Amplitude, power, and intensity, are three ways of describing what characteristic of a wave?
The strength of a wave. (In terms of sound, the “loudness” or the “volume”)
What is amplitude?
The loudness of a wave.
What is the definition of amplitude?
The maximum variation that occurs in the value of an acoustic variable.
What are the four acoustic variables?
Pressure
Density
Temperature
Particle Motion
How can amplitude be calculated?
Maximum - baseline = amplitude.
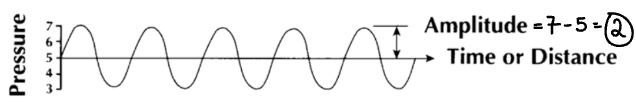
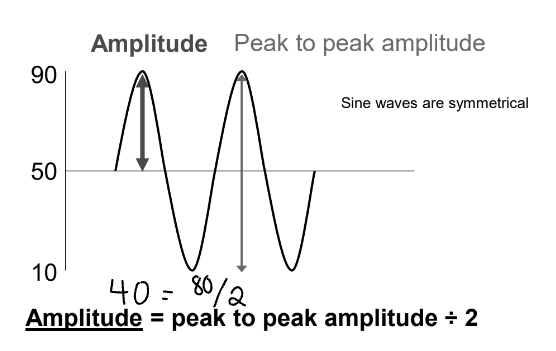
What is another way amplitude can be measured? (hint: peak to peak).
Using the peak to peak method and dividing by two.
What determines the initial amplitude of an ultrasound pulse?
The excitation of the voltage produced by the pulser of the ultrasound system.
What is the definition of power?
The rate at which work is performed or energy is transferred.
What are the two different equations for calculating power?
Power = work/time
Power = energy/time
What is the equation of power using the units that are involved?
SI unit (power) = joule (work/energy) / seconds (time)
1 joule/sec is equal to what?
1 Watt (1 unit of power)
What is the absolute unit for power?
Watt.
The “Watt” unit is named after who?
James Watt, the Scottish inventor of the steam engine and the father of the industrial revolution.
What is the relative unit of power?
Decibels.
What is the typical value of power?
10 miliwatts (10 mW)
Diagnostic ultrasound uses very high or very low power?
Very low.
What is the major reason for increase output power on an ultrasound machine?
To get better penetration which will also result in an improved image quailty,
What is the main clinical principal when it comes to power?
Use As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA).
What is the typical power for B-scan imaging (greyscale ultrasound)?
18 mW.
What is the typical power for M-Mode?
3.9 mW.
What is the typical power for Pulsed Doppler?
30.7 mW.
What is the typical power for Colour Flow?
80.5 mW.
The standard greyscale imaging power (B-scan) is what?
10-20 mW.
Pulsed Doppler and Colour Doppler will be higher or lower power than greyscale (B-scan) imaging?
Higher.
What is the power control labelled as on the ultrasound machine?
Output power or acoustic output.
Can power of the ultrasound system be manipulated by the operator?
Yes.
What are the three different scales that are used to indicate the amount of power being used on an ultrasound machine?
Decibels (dB; 0dB = maximum)
max-min
% (0-100%)
Increased power means what in terms of penetration?
Increased penetration.
Increased power means what in terms of exposure?
Increased exposure.
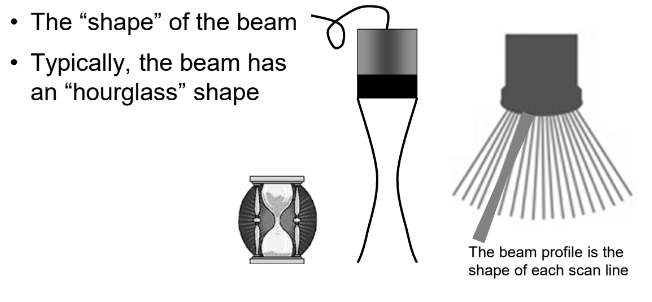
What is beam profile?
The “shape” of the beam.
Typically, what is the shape of the average beam profile?
Hourglass.
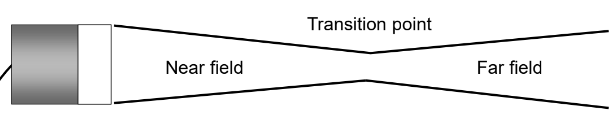
What are the three parts of an unfocused beam?
Near field
Transition point
Far field
Where is the near field, the transition point, and far field on an unfocused beam?
(see picture)
What is the beam diameter?
The diameter of the ultrasound beam. This varies along the length of the beam.
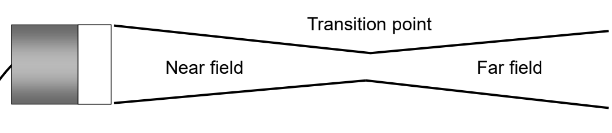
Where is the beam diameter the smallest?
At the transition point.
Beam diameter is measured in what?
cm or mm.
What is the beam diameter?
The cross-sectional 2D area of the beam. This varies along the length of the beam.
Where is the beam area the smallest?
At the transition point.
In what units is the beam area measured in?
cm² or mm².
What are the two types of intensity?
Spatial intensity
Temporal intensity
What is the definition of spatial intensity?
The concentration of energy in a sound beam.
What is the equation for spatial intensity?
Intensity = Power/Area
Intensity = mW/cm²
What is the absolute unit for spatial intensity?
mW/cm²
What is the relative unit of spatial intensity?
Decibels.
What is the typical value of spatial intensity?
100 mW/cm²
For a given power, the smaller the beam are means what for intensity?
The higher the intesity.
What can be done to power and/or area to increase intensity?
Power can be increased, or area can be decreased.
True or False: Intensity and power are indirectly proportional to one another.
False. They are DIRECTLY proportional.
True or False: Power is directly proportional to amplitude².
True.
If power is directly proportional to amplitude², and power is directly proportional to intensity, how are intensity and amplitude related?
Intensity is directly proportional to amplitude².
If amplitude and voltage are directly proportional to one another, this means that power is also directly proportional to what?
Voltage².
If amplitude and voltage are directly proportional to one another, this means that intensity is also directly proportional to what?
Voltage².
Spatial intensity is measured in an attenuating medium or a non-attenuating medium?
A non-attenuating medium.
Spatial intensity varies along the beam. Where it is the highest?
In the narrowest part of the beam and the centre of the beam.
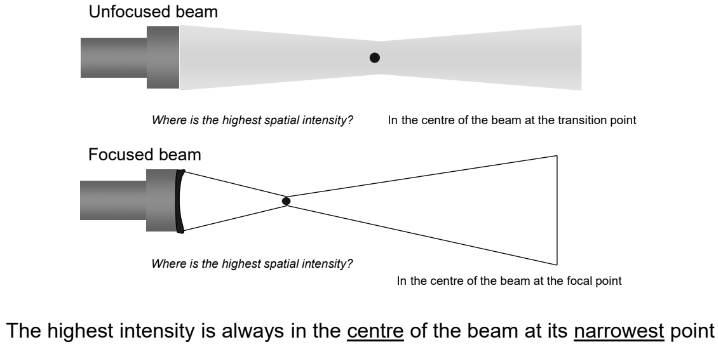
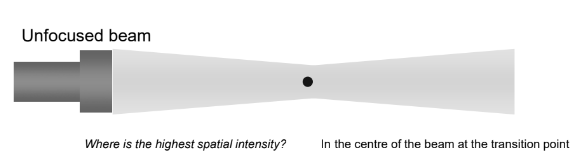
In an unfocused beam, where is the highest spatial intensity?
At the centre of the beam at the transition point.
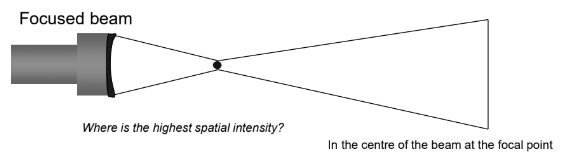
In a focused beam, where is the highest spatial intensity?
In the centre of the beam at the focal point.
True or False: The highest intensity is always where?
The centre of the beam at its narrowest point.
What are the two parameters of spatial intensity?
Spatial peak (SP)
Spatial average (SA)
True or False: Peaks are always lower than averages.
False. Peaks are higher than averages.
Describe spatial peak. (2)
The highest intensity
Found in the centre of the beam at the focal/transition zone.
Describe spatial average. (4)
Average intensity
Obtained across the beam at the transducer face
Lower than SP
Measured at the transducer face
Spatial peak intensity is higher or lower than SA intensity?
Higher.
Spatial peak intensity is much higher or lower than SA intensity in highly focused beam?
Higher.
What two factors affect spatial intensity?
Power (increase in power, increase SP)
Focusing (increase in focusing, increase SP)
What is the two clinical importance of spatial peak?
Understanding bioeffects
Improving image quality
Is temporal intensity related or unrelated to the x axis?
Related (the only one out of amplitude, power, spatial intensity, and temporal intensity that is related to the x axis, the rest are unrelated)
What is the definition of temporal intensity?
The intensity measured during a period of time.
In continuous wave, the temporal intensity varies or is constant?
Constant.
Temporal intensity in pulsed waves varies with and within what? (2)
With each pulse
Within each pulse
There are three types of temporal intensities in pulsed wave ultrasound, what are they?
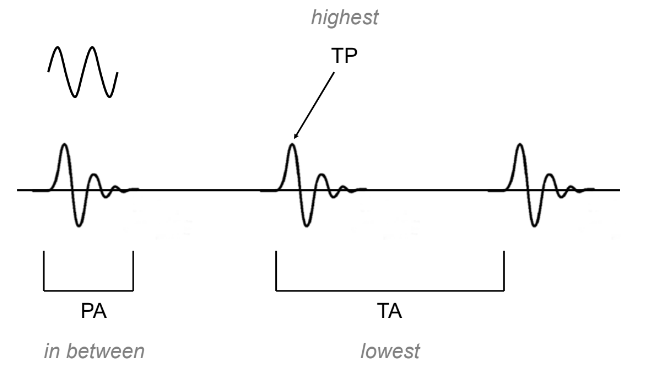
Pulsed average intensity (PA)
Temporal average intensity (TA)
Temporal peak intensity (TP)
What is the definition of pulsed average intensity (PA)?
The average temporal intensity during the time sound is on. (During the pulse duration, PD)
The pulse average intensity (PA) can be increased by what?
Increasing power.
What is the definition of temporal average intensity (TA)?
The average temporal intensity during the entire on and off time. (During the pulse repetition period, PRP).
The temporal average intensity is greatly influenced by what?
The duty factor.
The temporal average should be very high or very low in comparison to the pulse average?
Very low.
TA is always lower than the PA by what factor?
By the duty factor.
What is the equation for temporal average intensity?
TA = PA x DF
TA increases with either stronger pulses or…?
More frequent pulses.
What is the definition of temporal peak intensity (TP)?
The instantaneous absolute highest intensity within a real pulse.
Is TP higher than the PA?
Yes.
Where are the PA, TAM and TP of a wave?
(see image)
For CW, does TP, PA, and TP vary?
No. They are equal to one another. (TA = TP = PA)
What are the six combined intensity values?
SPTP: spatial peak-temporal peak
SPPA: spatial peak-pulsed average
SATP: spatial average-temporal peak
SAPA: spatial average-pulsed average
SPTA: spatial peak-temporal average
SATA: spatial average-temporal average
Out of the six combined intensity values, what is the highest?
SPTP
Out of the six combined intensity values, what is the lowest?
SATA
What is the importance of the combined intensity values?
Research and comparison of bioeffects data in literature.
What are two uncommon terms that are used to describe the SPTP and SPPA?
SPTP - ip - instantaneous peak
SPPA - im - maximum intensity (time avg half maximum)