Learning approaches: The behaviourist approach
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What are the assumptions of the behaviourist approach?
The behaviourist approach is only interested in studying behaviour that can be observed and measured
Behaviourists maintain control and objectivity within their research and rely on lab studies to achieve this
They believe that all behaviour is learned from the environment through classical or operant conditioning. They describe a baby’s mind as a ‘blank slate’ and is written on by experience.
They suggest that the basic processes that govern learning are the same in all species. Thus, animals replace humans as experimental subjects
What is classical conditioning?
Learning through association
What was the aim of Pavlov’s research?
To show how dogs could be classically conditioned to salivate the sound of a bell if that sound was repeatedly presented at the same time as they were given food.
What was the procedure of Pavlov’s research?
Food (US) → Salivation (UCR)
Bell (NS) → No salivation (NCR)
Bell + Food → Salivation (UCR)
Bell (CS) → Salivation (CR)
What is operant conditioning?
Learning through consequences
In operant conditioning there are 3 types of reinforcement: (consequences) of behaviour
Positive reinforcement
Negative reinforcement
Punishment
What did Skinner suggest about learning?
Skinner suggested that learning is an active process whereby humans and animals operate on their environment.
What is positive reinforcement?
Receiving a reward when a behaviour is performed. Thus, the behaviour getting rewarded is more likely to be repeated.
E.g. praise from a teacher when getting an answer correct
What is negative reinforcement?
Occurs when an animal or human avoids something unpleasant
E.g. when a student hands in an essay to avoid being told off
What is punishment?
An unpleasant consequence of behaviour. Thus, this behaviour is less likely to be repeated.
E.g. Being shouted at by a teacher for talking
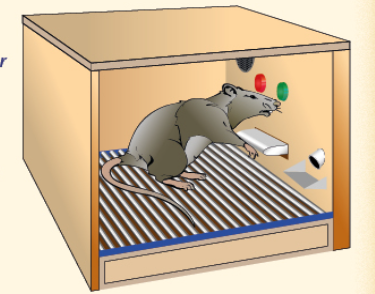
What was the Skinner Box experiment?
Skinner placed rats in specially designed cages called Skinner Boxes
Every time the rat pressed the lever it got a food pellet
After many repetitions, the animal continued the behaviour (positive reinforcement)
Skinner also showed how rats could be conditioned to perform a behaviour to avoid an unpleasant stimulus e.g. electric shocks (negative reinforcement)
What is a strength of the behaviourist approach?
It is based on well-controlled research
Behaviourists focused on the measurement of observable behaviour within highly controlled lab settings.
By breaking down behaviour into basic stimulus response units, all other possible extraneous variables were removed thus allowing cause-and-effect relationships to be established.
E.g. Skinner was able to demonstrate how reinforcement influenced an animal’s behaviour
This suggests that behaviourists experiments have scientific credibility
What is another strength of the behaviourist approach?
REAL WORLD APPLICATION - The principles of conditioning have been applied to real-world behaviours and problems
E.g. operant conditioning is the basis of token economy systems that have been used successfully in institutions such as prisons and psychiatric wards.
These work by rewarding appropriate behaviour with tokens that can be exchanged for privileges.
This increases the value of the behaviourist approach because it has widespread application.
What is a limitation of the behaviourist approach?
ENVIRONMENTAL DETERMINISM - It sees all behaviour as conditioned by past conditioning experiences
Skinner suggested that everything we do it the sum total of our reinforcement and conditioning history.
This ignores any possible influence that free will may have on behaviour (Skinner said free will is a illusion!)
This is an extreme position and ignores the influence of conscious decision-making processes on behaviour.
What is another limitation of the behaviourist approach?
Ethical issues
The rats in the Skinner Box experiment were housed in harsh, cramped conditions and were deliberately kept below their natural weight so they were always hungry.