2.6.3 supply-side policies
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Supply-side policies
Focus on improving the structural long-term performance of an economy
Policies that increase productive potential (LRAS) of economy
*Focus is on LRAS, but can affect SRAS
Why can supply-side policies be good?
Lead to more possible production whilst also lowering PL IF productivity improves
May also improve some of the other macro objectives
What are the 2 different approaches to supply-side policies?
Market-based
Interventionist
Interventionist supply-side policies
Gov actively intervenes to correct market failure + improve economic efficiency
→ more spending, more tax, more control
e.g. investment in education + training, infrastructure spending
Market-based supply-side policies
Policies that aim to increase efficiency by removing barriers + letting free-market forces work better
→ less spending, less tax, less control
e.g. tax cuts, removing unemployment benefits, deregulation
Key difference between market-based + interventionist policies?
Market-based policies reduce government involvement and rely on competition
Interventionist policies involve active government spending + planning to boost supply
5 SSPs that I need to know
Change visa rules to encourage more skilled overseas workers
Cut corporation tax
Cut unemployment benefits
Increase spending on railway network
More relaxed rules for smaller firms on meeting health + safety requirements
Supply-side policies can either be fiscal/regulatory
→ What does this mean?
Fiscal: Gov is spending more or spending less OR increasing tax or reducing tax
Regulatory: Adding to/taking away gov laws + rules
Is ‘change visa rules to encourage more skilled overseas workers’ interventionist or market-based?
Fiscal or regulatory?
Interventionist
→ Gov is doing more to encourage number of potential workers in economy
Regulatory
→ Adding gov laws + rules on immigration
Is ‘cut corporation tax’ interventionist or market-based?
Fiscal or regulatory?
Market-based
→ Less gov taxation compared to before
Fiscal
→ Reduction of a tax
Is ‘cut unemployment benefits’ interventionist or market-based?
Fiscal or regulatory?
Market-based
→ Gov is intervening less in income payments
Fiscal
→ Decrease in gov spending
Is ‘increase spending on railway network’ interventionist or market-based?
Fiscal or regulatory?
Interventionist
→ More spending + more control
Fiscal
→ Increase in gov spending
Is ‘more relaxed rules for smaller firms on meeting health + safety requirements’ interventionist or market-based?
Fiscal or regulatory?
Market-based
→ Less control of firms
Regulatory
→ Change of a gov law
What is the economic effect of changing visa rules to allow more skilled overseas workers?
→ Improves labour force skills
→ By bringing in new, better quality resources
How does cutting corporation tax improve economic performance?
→ Increases incentives
→ Firms have more profit to invest in capital goods
Why might cutting unemployment benefit help the labour market?
→ Reforms the labour market
→ Encourages unemployed workers to search harder for work
What’s the benefit of increasing spending on the railway network?
→ Improves infrastructure
→ Helps firms transport raw materials + finished goods
What’s the impact of relaxing health & safety rules for small firms?
→ Promotes competition
→ Reduces costly regulations, helping smaller firms compete
All SSPs aim to? (3 things)
→ Increase productive potential: This is because the policy will lead to either more resources of a certain type (FoP)/better resources of a certain type
→ Lower the price level: If resources are also more productive, firms see lower costs, which they pass on in the form of lower prices
→ Maybe improve other macro objectives: E.g. there might be an increase in GDP growth/lower unemployment/lower inequality
Why does higher productivity lead to lower prices?
→ Firms can produce more with the same resources, their cost per unit falls
→ This allows them to cut prices while still earning profits, which reduces the overall price level in the economy
Which diagram links well to SSPs?
Draw it
→ Keynesian diagram
Increase productive potential
Lower PL
Maybe improve other macro objectives
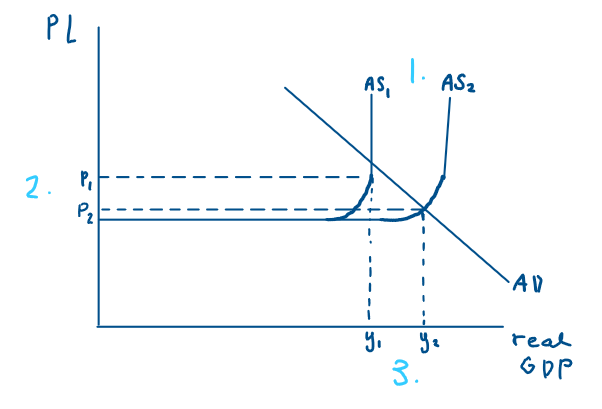
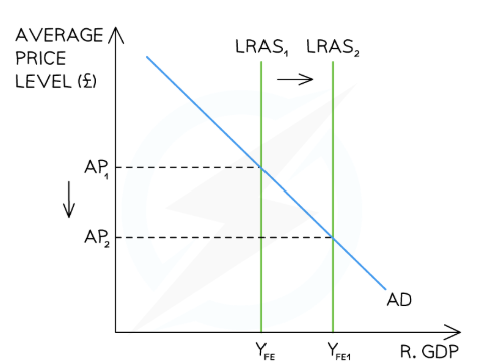
SSPs classical diagram
Draw it
Evaluation points for the 5 SSPs
Negatively affects gov finances - p 2, 4
Takes a long time to work - p 1, 4, 5
Overly complex - p 1, 4
Bad for workers - p 1, 3, 5
May only have a short-term effect - p 2, 5
Strengths of SSPs?
Promote long-run economic growth
Reduce unemployment (structural)
Control inflation in long term
Improve balance of payments
Encourage enterprise + investment
Weaknesses of SSPs?
Very slow to have an effect
Expensive
No guarantee of success
May increase inequality
Can’t fix demand-side issues