Chapter 9: Mid-Latitude Cyclones, Fronts, and Forecasting
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What type of air replaces cold, marine polar air in a warm front?
Warm, humid subtropical air from the Gulf of Mexico.
What is overrunning in meteorology?
The rising of warm air over cold air.
What is a dryline?
A boundary where dry air meets moist air, causing a significant decrease in dew-point temperatures.
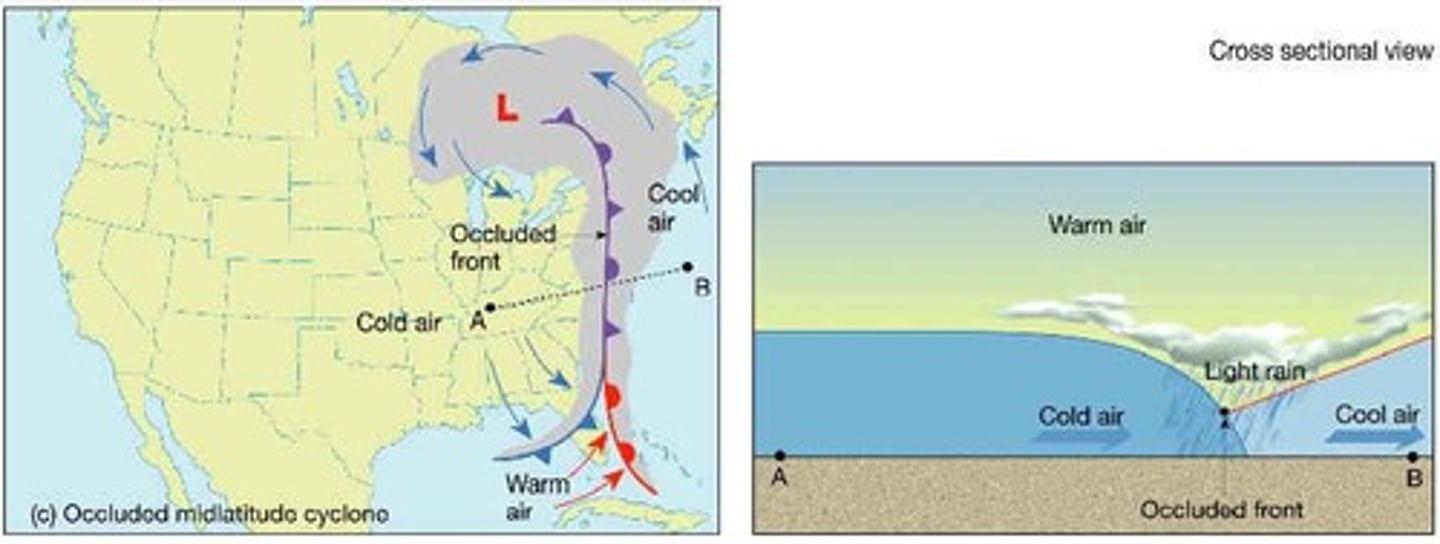
What occurs at an occluded front?
A cold front catches up to and overtakes a warm front, leading to widespread precipitation.
What is cyclogenesis?
The development or strengthening of a mid-latitude cyclone.
Where do mid-latitude cyclones tend to form?
Regions such as the Gulf of Mexico, Atlantic Ocean east of the Carolinas, and eastern slopes of the Rocky and Sierra Nevada mountains.
What is the role of convergence in cyclone development?
Convergence refers to the piling up of air, which can lead to the formation of cyclonic circulation.
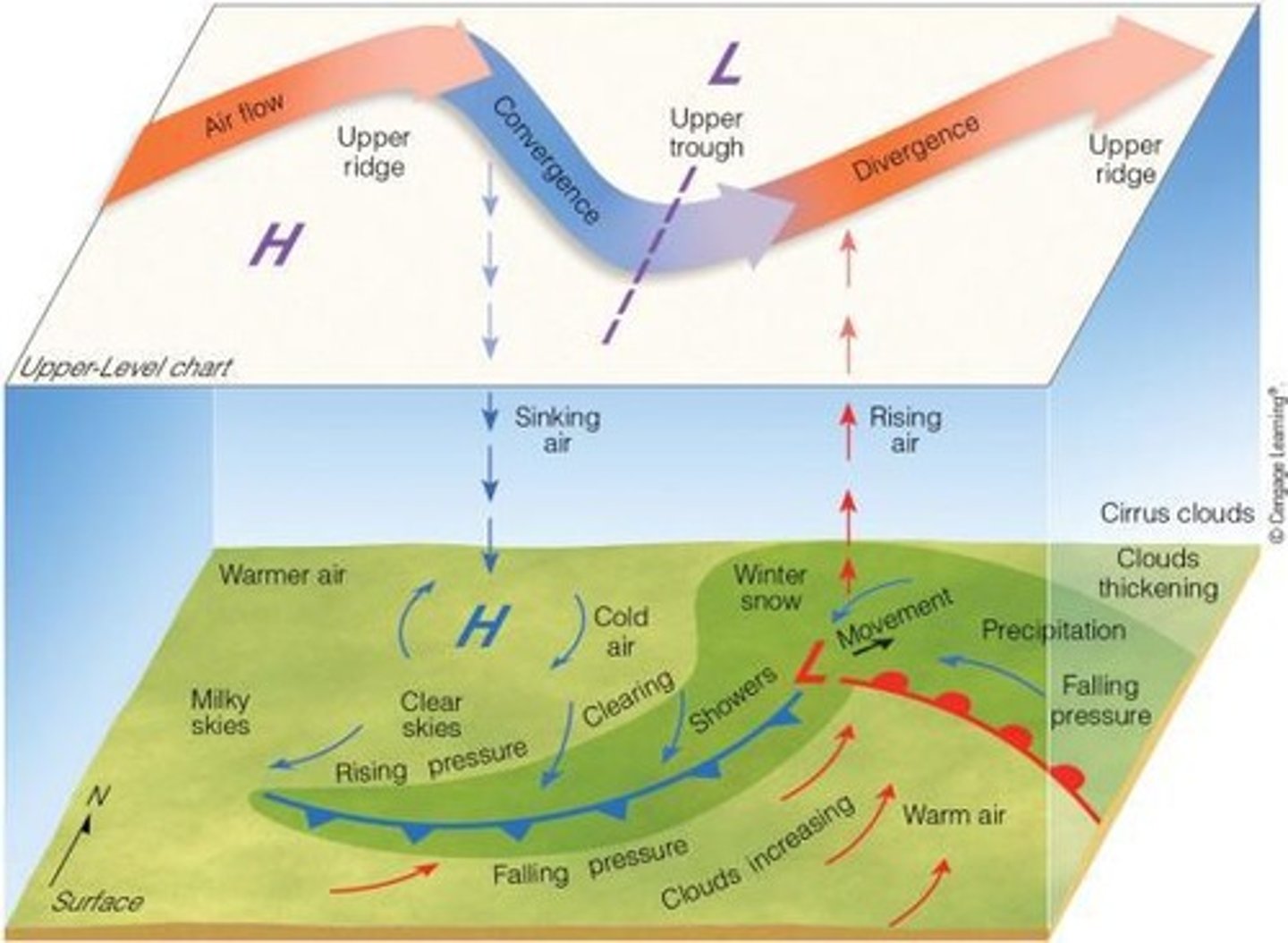
What is divergence in meteorology?
The spreading of air, which is essential for the development of mid-latitude cyclones.
What is the significance of the polar jet stream?
It provides upper-level diverging air necessary for the development of middle-latitude cyclones.
What tools do forecasters use for weather observations?
Maps, charts, soundings, satellite images, Doppler radar, and atmospheric models.
What is a meteogram?
A graph displaying the evolution of meteorological variables at a station over time.
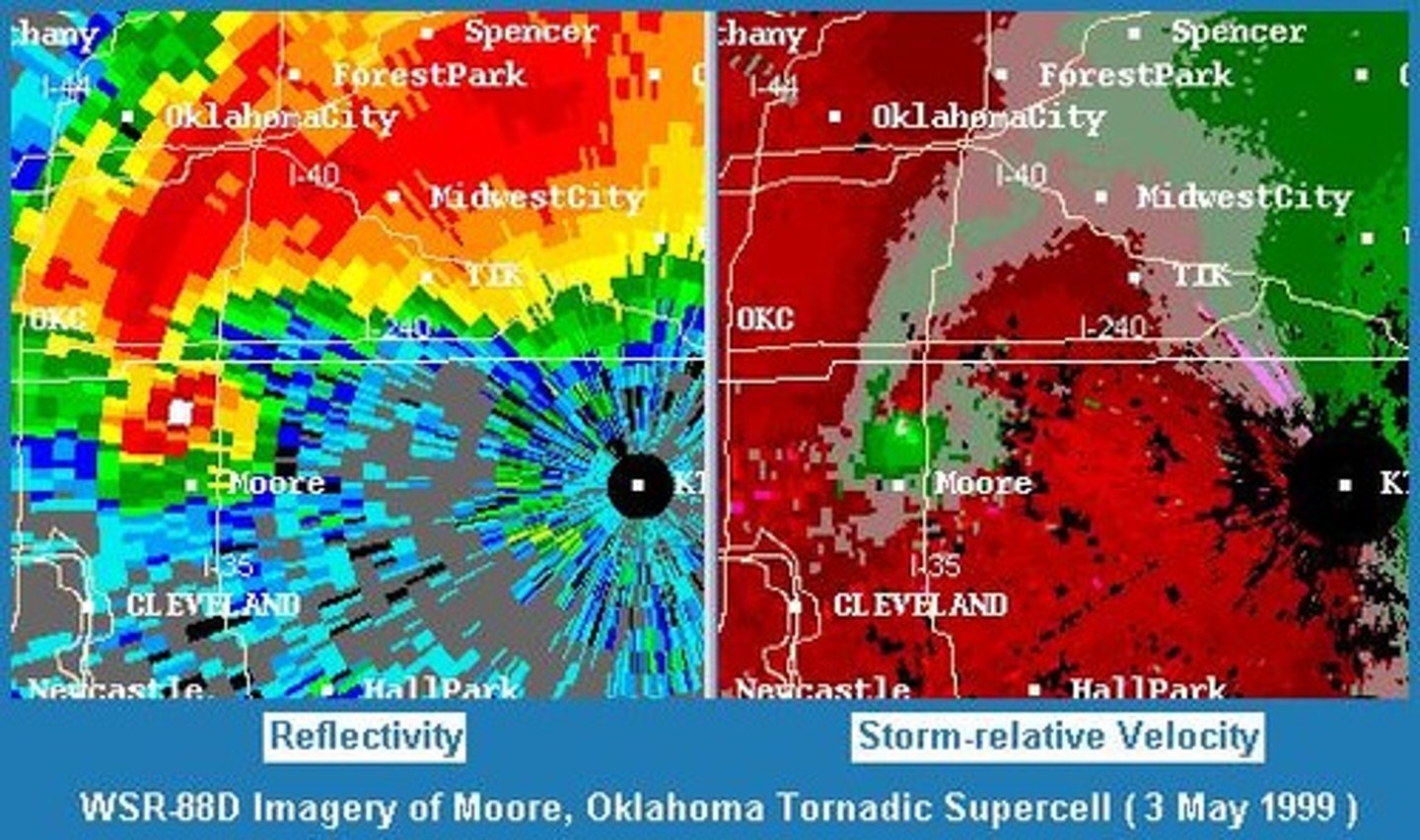
What does Doppler radar measure?
Wind speed in precipitating regions by detecting changes in frequency of waves from moving precipitation particles.
What is numerical weather prediction?
The use of mathematical equations to forecast daily weather.
What is a persistence forecast?
The simplest weather forecast method that assumes current weather conditions will continue.
What is the time range for a nowcast?
Usually under six hours.
What is a medium-range forecast?
A weather forecast that spans three to eight days.
What is the accuracy of national weather service forecasts for 12-24 hours?
Usually quite accurate.
How do mid-latitude cyclonic storms and fronts move?
They move in the same direction and speed as they have for the past six hours.
What is the significance of isobars in weather forecasting?
They indicate areas of pressure change, helping to determine the movement of low and high-pressure systems.
What is the function of the Advanced Weather Interactive Processing System (AWIPS)?
It is a tool used for weather forecasting that integrates various meteorological data.
What does a prognostic chart represent?
The final forecast chart showing the atmosphere at a specified future time.
What is the role of ensemble forecasts?
They create a spaghetti plot based on multiple prediction models or iterations of a single model.
What is a climatological forecast?
A forecast based on historical weather patterns for a specific region.
What is the purpose of soundings in meteorology?
To provide a vertical profile of temperature, dew point, and winds.

What is the typical duration of a long-range forecast?
Beyond eight days.
What is the primary purpose of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)?
To facilitate the international exchange of weather data and certify observation procedures.