Week 10: Bacterial Aerotolerance
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
Respiration
involves oxidation of substrates for energy necessary for life
2
New cards
Oxidation
when a substance LOSES a hydrogen ion and electron
3
New cards
Reduction
when a substance GAINS a hydrogen ion and electron
4
New cards
Oxidation Reduction Potential
measure of the tendency of a chemical substance to gain or lose electrons
5
New cards
obligate aerobes
an organism that REQUIRES oxygen to grow
* uses **cellular respiration**
* uses **cellular respiration**
6
New cards
Obligate **an**aerobes
microorganisms **killed** by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen
* uses **anaerobic respiration/fermentation**
* uses **anaerobic respiration/fermentation**
7
New cards
Facultative anaerobes
does not require oxygen for growth, BUT grows better in its presence
* oxygen present = ATP by aerobic respiration
* no oxygen present = fermentation/anaerobic respiration
* oxygen present = ATP by aerobic respiration
* no oxygen present = fermentation/anaerobic respiration
8
New cards
Aerotolerant anaerobes
ignores oxygen and grows equally well whether it’s present or not
9
New cards
Microaerophiles
requires **lower levels** of oxygen within an environment
10
New cards
Capnophiles
thrives in presence of high concentration of **carbon dioxide**
11
New cards
Biofilm
* when cells stick to e/o and also to surface
* more resistant to antibiotics
* more resistant to antibiotics
12
New cards
Dental caries
cavities
* breakdown of teeth due to acids made by bacteria
* breakdown of teeth due to acids made by bacteria
13
New cards

What type of aerobe or anaerobe is this? (extra points if u can name the bacteria used)
Obligate anaerobe
* \*clostridium sporogenes
* \*clostridium sporogenes
14
New cards

What type of aerobe or anaerobe is this? (extra points if u can name the bacteria used)
Obligate aerobe
* \*psuedomonas **aero**ginosa
* \*psuedomonas **aero**ginosa
15
New cards

What type of aerobe or anaerobe is this? (extra points if u can name the bacteria used)
Facultative anaerobe
\*staphylococcus aureus
\*staphylococcus aureus
16
New cards

What type of aerobe or anaerobe is this? (extra points if u can name the bacteria used)
Microaerophile
* \*steptococcus pyogenes
* \*steptococcus pyogenes
17
New cards
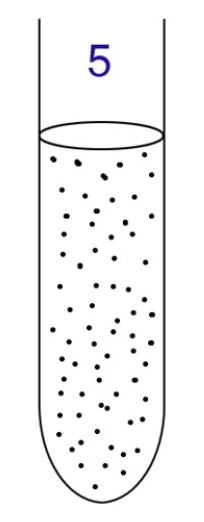
What type of aerobe or anaerobe is this?
Aerotolerant anaerobe
18
New cards
Pellicle
Protein film
19
New cards

What step of **biofilm formation in the mouth** is this?
Pellicle formation
20
New cards

What step of **biofilm formation in the mouth** is this?
Initial adhesion
21
New cards

What step of **biofilm formation in the mouth** is this?
Maturation
22
New cards

What step of **biofilm formation in the mouth** is this?
Dispersion
23
New cards
What two things protect bacteria from harming the mouth?
* Saliva **washes** bacteria away
* Lysozyme **kills** bacteria
* Lysozyme **kills** bacteria
24
New cards
Where are some niches for bacteria in the mouth
* teeth
* tongue
* pockets under gums
* tongue
* pockets under gums
25
New cards
What are the two important bacterias within **dental carries?**
* lactobacillus acidophilus
* streptococcus mutans
* streptococcus mutans
26
New cards
What are the 2 types of sugars **sucrose (strep mutans**) creates in relation to cavities?
* Fructose
* Glucan
* Glucan
27
New cards
What does **fructose** create in relation to cavities?
Lactic acid which breaks down enamel
28
New cards
What does **glucan** create in relation to cavities?
Biofilms
29
New cards
What test do we use to detect the susceptibility to form cavities?
Snyder’s test
30
New cards
Characteristics of **thioglycollate tubes**
* identifies oxygen requirements of bacteria
* medium **consumes** O2 so anaerobes can grow
* medium **consumes** O2 so anaerobes can grow
31
New cards
What percentage of **nitrogen, oxygen and trace gases** are in the atmosphere?
* 78% nitrogen
* 21% oxygen
* 1% trace gases
* 21% oxygen
* 1% trace gases
32
New cards
How much percentage of **O2** and **CO2** is contained within a candle jar?
* 8-10% O2
* 3-5% CO2
* 3-5% CO2
33
New cards
How is oxygen free environment reached in the **candle jar**?
by lighting a small candle in the sealed jar
34
New cards
How is the oxygen consumed?
Flame consumes most of the oxygen which elevates the CO2 levels
35
New cards
How much percentage of **O2** and **CO2** is contained within the anaerobe jar?
* 0% O2
* 10-15% CO2
* 10-15% CO2
36
New cards
How is oxygen free environment reached in the **anaerobe jar?**
* Sealing jar w/ gas generator packet
* chemicals within the packet reacts w/ the O2 to create water and CO2 **(CHEMICALS + O2 → WATER + CO2)**
* chemicals within the packet reacts w/ the O2 to create water and CO2 **(CHEMICALS + O2 → WATER + CO2)**
37
New cards
What does the strip in the jar indicate?
It will turn white when the oxygen in the jar is consumed
* Blue strip = aerobic
* White = anaerobic
* Blue strip = aerobic
* White = anaerobic
38
New cards
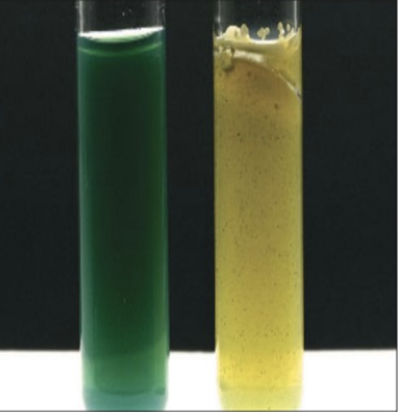

Which is a positive result of the Snyder’s test?
Right tube (yellow)