Parts and Function of Cell
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Active Transport
Requires energy to move molecule; low to high concentration
2
New cards
ATP
energy
3
New cards
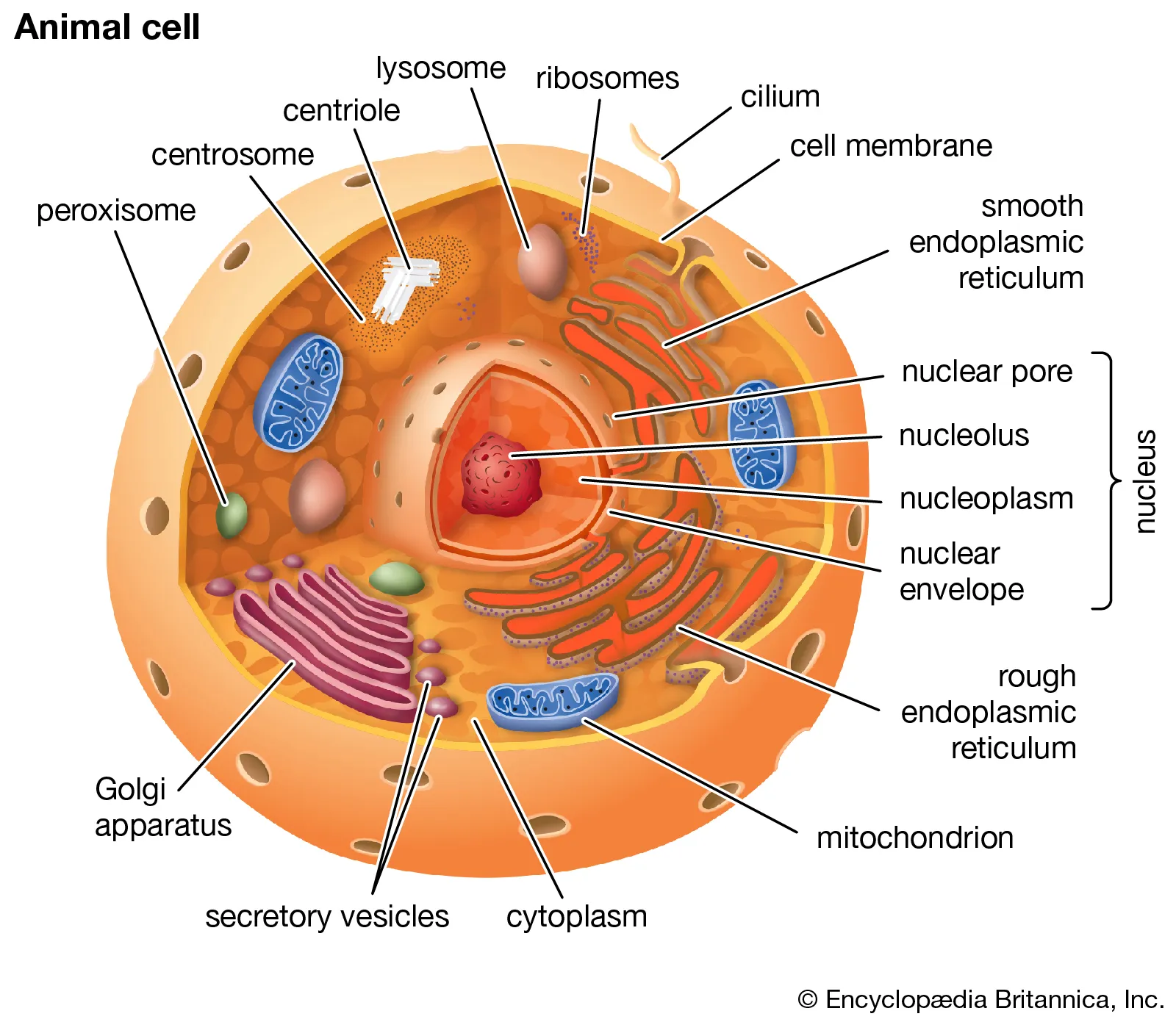
cell
the smallest structural and functional unit of an __organism__,
4
New cards
cell membrane
biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment.
5
New cards
cell theory
1- Every living thing is made of cells
2- the cell is the basic unit of life
3-all cells come from other cells
2- the cell is the basic unit of life
3-all cells come from other cells
6
New cards
cell wall
structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism.
7
New cards
chloroplast
plant cell organelles that convert light energy into relatively stable chemical energy via the photosynthetic process
8
New cards
cytoplasm
the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell
9
New cards
cytoskeleton
a microscopic network of protein __filaments__ and __tubules__ in the __cytoplasm__ of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence.
10
New cards
diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
11
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum
a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
12
New cards
Rough ER
to produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has on it ribosomes
13
New cards
Smooth ER
makes lipids
14
New cards
eukaryote
any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus
15
New cards
facilitated diffusion
In facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into (or out of) the cell by moving down it.
16
New cards
Golgi body
factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion.
17
New cards
hypertonic
any external solution that has a high solute concentration and low water concentration compared to body fluids
18
New cards
hypotonic
any external solution that has a low solute concentration and high water concentration compared to body fluids
19
New cards
isotonic
any external solution that has the same solute concentration and water concentration compared to body fluids
20
New cards
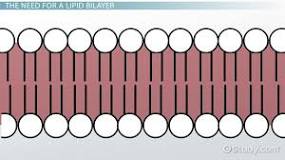
lipid bilayer/phospholipid bilayer
a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules
21
New cards
lysosome
membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids
22
New cards
mitochondrion/mitochondria
generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions
Turns food into ATP(energy)
Turns food into ATP(energy)
23
New cards
nucleus
controls and regulates the activities of the cell (e.g., growth and metabolism) and carries the genes, structures that contain the hereditary information
24
New cards
organ
A part of the body that performs a specific function
collection of tissue
collection of tissue
25
New cards
organ system
\
collection of organs
group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions
collection of organs
group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions
26
New cards
organelle
subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body
(small organ)
(small organ)
27
New cards
osmosis
osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane
28
New cards
passive transport
Passive transport is a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes
29
New cards
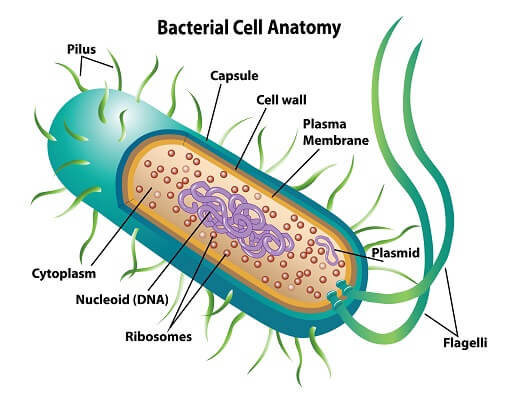
prokaryote
single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
30
New cards
ribosome
micro-machine for making proteins
31
New cards
selectively permeable
Selective permeability of the cell membrane refers to its ability to differentiate between different types of molecules, only allowing some molecules through while blocking others
32
New cards
tissue
group of cells
33
New cards
vacuole
A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products
34
New cards
vesicle
A small sac formed by a membrane and filled with liquid. Vesicles inside cells move substances into or out of the cell
35
New cards
Cytolysis
So much water enters a cell that it explodes
36
New cards
Plasmolysis
water leaves cell so it shrinks
37
New cards
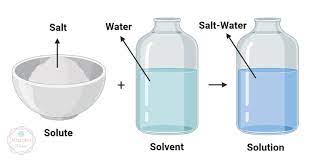
Solute
the substance that dissolves in a solvent to produce a homogeneous mixture.
38
New cards
concentration
amount of molecules in an area (concentration = #molecules/area)
39
New cards
centriole
only in animal cells, required for cell division
40
New cards
Hydrophilic
water-loving
41
New cards
Hydrophobic
water-hating
42
New cards
Active transport happens through…
Protein pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis
43
New cards
Endocytosis
process where molecules are taken into the cell through a vesicle
44
New cards
Exocytosis
process where molecules are put out of cell through a vesicle
45
New cards
Protein pumps
use energy in the form of ATP to move molecules across the membrane against concentration