Biology Chapter 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
Geometric Isomers
isomers in which the order of atom bonding is the same but the arrangement of atoms in space is different (trans and cis)

2
New cards
Structural Isomers/positional isomers
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
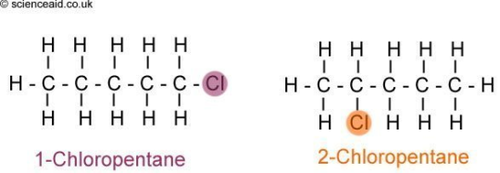
3
New cards
optical isomers (enantiomers)
molecules that are mirror images of each other
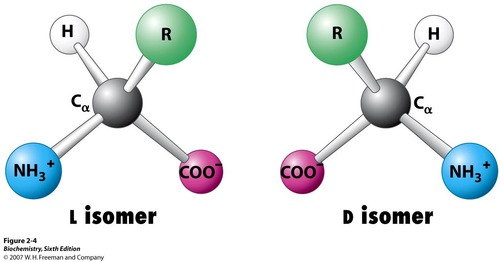
4
New cards
Carbon bonded to 4 different atoms/groups
Why enantiomers occur
5
New cards
Hydrophilic
Polar molecules are...
6
New cards
Hydrophobic
Nonpolar molecules are...
7
New cards
Hydroxyl
OH functional group
8
New cards
Carbonyl
C=O functional group
9
New cards
Carboxyl
COOH Functional Group
10
New cards
Amino
NH2 Functional group
11
New cards
Phosphate
PO4 Functional Group
12
New cards
Methyl
CH3 Functional group
13
New cards
sulfihydryl
SH Functional group
14
New cards
Monomers
building blocks of polymers
15
New cards
Dimer
monomer+monomer
16
New cards
Polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
17
New cards
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
18
New cards
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
19
New cards
Hydrolysis reaction
How to break down a polymer
20
New cards
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
21
New cards
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
22
New cards
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of 3 or more monosaccharides
23
New cards
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
3 monosaccharides
24
New cards
C6H12O6
chemical formula for glucose, fructose, and galactose
25
New cards
Aldehyde
An organic molecule with a carbonyl group located at the end of the carbon skeleton.
26
New cards
Aldose
a monosaccharide that contains an aldehyde group
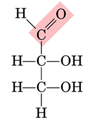
27
New cards
Ketone group
A chemical group consisting of carbonyl (must be in middle of chain) (called a ketose)
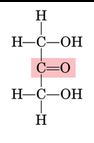
28
New cards
structural isomers
Glucose, galactose, and fructose are...
29
New cards
1:2:1
ratio of C:H:O
30
New cards
Maltose
glucose + glucose
31
New cards
Sucrose
glucose + fructose
32
New cards
Lactose
glucose + galactose
33
New cards
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose. (in leaves, stem, roots)
34
New cards
Glycogen
storage form of glucose in animals (in muscles and liver)
35
New cards
Chitin
Polysaccharide found in arthropod exoskeletons and fungal cell walls.
36
New cards
Cellulose
Carbohydrate component of plant cell walls.
37
New cards
peptidoglycan
A carbohydrate compound that makes the cell walls of bacteria.
38
New cards
lipids, protein, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
macromolecules
39
New cards
storage molecules or structural compounds
Polysaccharides may function as
40
New cards
hydrophilic
all carbohydrates are hydro....
41
New cards
Oxygen
What makes a molecule hydrophilic
42
New cards
Lipids
macromolecule that contains carbon and hydrogen, but very little oxygen(are usually hydrophobic)
43
New cards
long term energy storage
lipids are used for
44
New cards
Fats and Oils(triglycerides), phospholipids, steroids, and waxes
the 4 types of lipids
45
New cards
Monomers
Lipids are not built from
46
New cards
Dehydration reaction
a fatty acid can link to glycerol by
47
New cards
1 glycerol linked to 3 fatty acids
a fat contains...
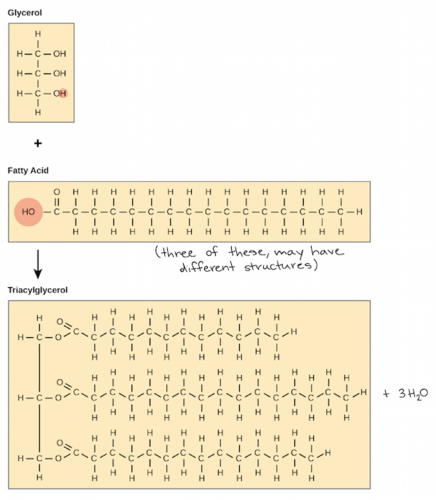
48
New cards
a double bond
unsaturated fats have...
49
New cards
kinks/bends in structure
double bonds in fatty acids lead to
50
New cards
Fatty acid
long chain hydrocarbon
51
New cards
Solid at room temp, mostly seen in animals
Saturated fats are...
52
New cards
Corn oil, peanut oil, olive oil
Unsaturated fats
53
New cards
Hydrogenated
___ means that hydrogen has been added to unsaturated fats.
54
New cards
trans
Hydrogenation creates __ fats
55
New cards
Structurally similar to fats, major component of all cells
Phospholipids are...
56
New cards
Two fatty acids attached to glycerol, phosphate
phospholipids contain...
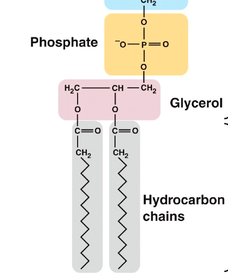
57
New cards
hydrophilic
phosphate in phospholipids are hydro...
58
New cards
saturated
cold adapted organisms have more ___ fat
59
New cards
steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
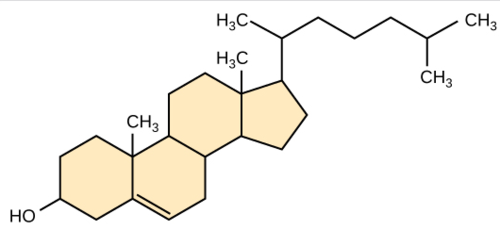
60
New cards
cholesterol
starting material for making steroids and a common component in animal cell membranes
61
New cards
sex hormones
a type of steroid
62
New cards
anabolic steroids
synthetic variants of the male hormone testosterone; causes buildup of muscle

63
New cards
Atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries
64
New cards
wax
A type of structural lipid that forms a waterproof coat and keeps insects or fruits from drying out