Chapter 9 - Money Market and Monetary Policy
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Interest Rate
–The annual rate at which payment is made for the use of money (or borrowed funds)
–A percentage of the borrowed amount
–The price of money (the cost to borrow money) (always on quiz)
Supply of Money
Determined by the Bank of Canada. The supply of money is constant at ant one point and is not affect by the interest rate
Bank of Canada/Central Bank
Gov owned, appointed by federal cabinet, current governor is Tiff Macklem
Five functions of the Bank of Canada
–sole issuer of currency
–government’s bank and manager of foreign currency reserves on behalf of the government
–bankers’ bank and lender of last resort
–auditor and inspector of commercial banks
–regulator of the money supply
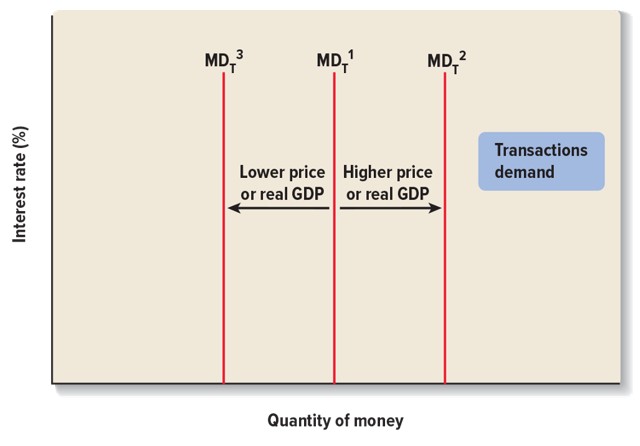
Transactions demand for money
•The desire to hold money as a medium of exchange, that is, to affect transactions
•demand based on the levels of real GDP and prices
•Not related to interest rates
Keep money in chequing account that is in line with what we need to spend on rent, grocery’s…
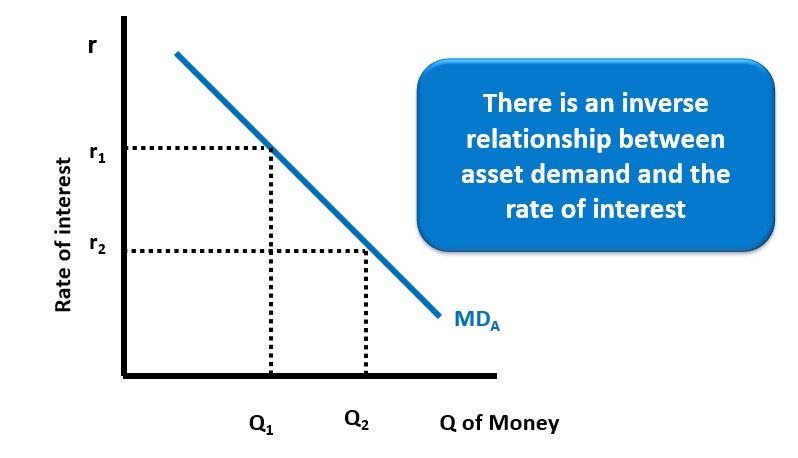
Asset demand for money
•The desire to use money as a store of wealth, that is, to hold money as an asset
•Inversely related to interest rates
•People hold money in savings accounts or other liquid forms to preserve value and maintain purchasing power (stocks)
Transactions demand for money graph
Transactions demand is unrelated to the interest rate
Asset Demand MDa graph
Inverse relationship between asset demand and the interest rate
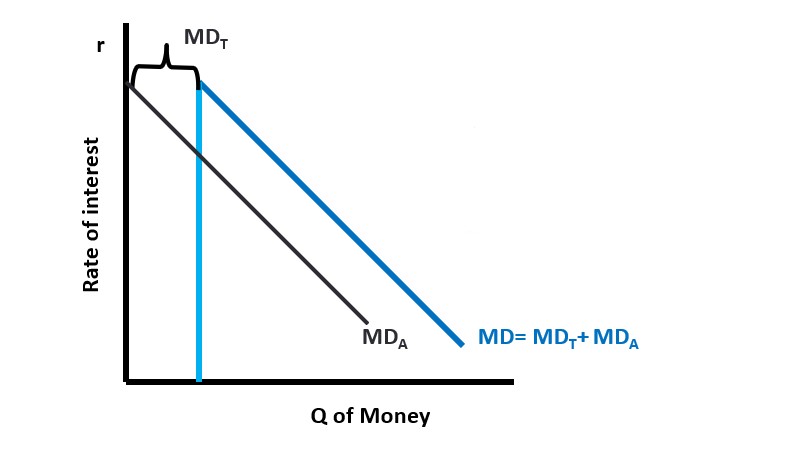
Total Demand for Money
Total demand for money is the sum of transactions demand + asset demand. MD=MDt + MDa
Demand for money is defined by? …
the level of transaction (real GDP), average value of transaction (the price level), the rate of interest
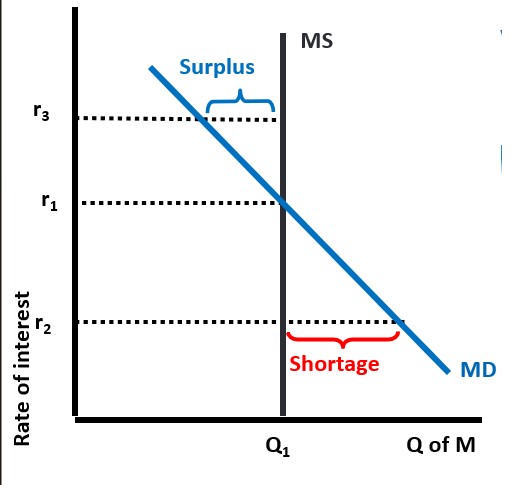
Equilibrium in the Money Market
At the equilibrium interest rate, r1, there is no surplus or shortage of money/demand for money
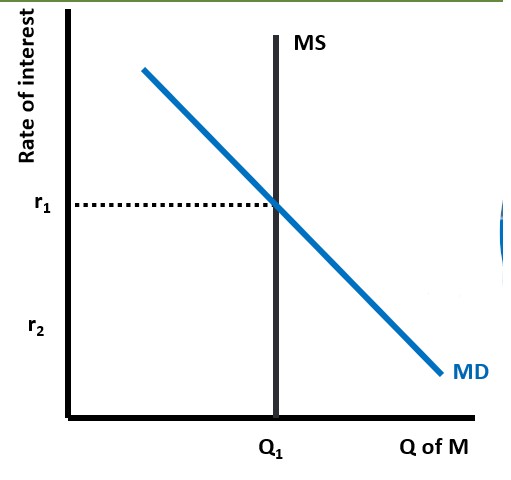
Shortage or surplus in money market
At the equilibrium interest rate, r1, there is no surplus or shortage of money.
At any other rate there is either a shortage or surplus
Info about Bonds …..
–Loans for a set period of time
–Issued by corporations, banks, and various levels of government
–Have a set face value
–Pay a fixed rate of interest (the coupon rate)
–Can be bought and sold in the market
Bond Yields
–The return (“yield”) on a bond depends on:
•the coupon rate
•the profit or loss on its sale
–Bond prices adjust to reflect return on other financial instruments with similar risk
–The higher the price, the lower the return
Surplus of money with bonds
–People choose to buy bonds to reduce their liquidity and earn income
–Bond prices rise, leading to a fall in bond yields and interest rates
–Rates fall until there is no more surplus
Shortage of money with bonds
–People sell bonds in order to increase their liquidity
–Bond prices fall, leading to an increase in bond yields and interest rates
–Rates increase until there is no more shortage
An increase in interest rates can be caused by two things….
Caused by an increase in demand - demand rise, interest rates rise
Caused by an decrease in supply - supply decreases, rates rise
Increase in interest rate caused by:
–Rise in the demand for money
–Fall in the supply of money
Decrease in interest rate caused by:
–Fall in the demand for money
–Rise in the supply of money
Monetary Policy
•Monetary Policy consists of the management of the money supply and interest rates by a country’s central bank.
–It is aimed at achieving certain macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, achieving full employment, or stimulating economic growth
–Bank of Canada plays a major role in the monetary policy
Two monetary targets of the Bank of Canada
money supply and the interest rate. They can not target both at the same time
Expansionary monetary policy
–A policy that aims to increase the amount of money in the economy and make credit cheaper and more easily available
–also called easy money policy
Contractionary monetary policy
–A policy in which the amount of money in the economy is decreased and credit becomes harder and more expensive to obtain.
–also called tight money policy
Two tools Bank of Canada can use to increase or decrease money supply
Open market operations and switching government deposits
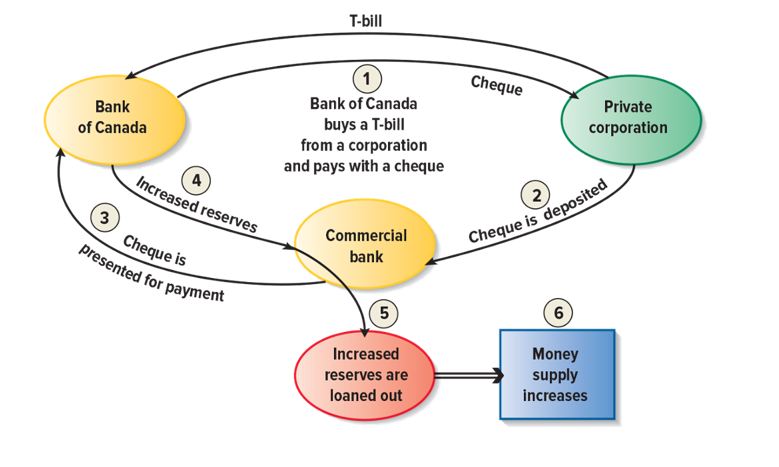
Open Market Operations (OMO)
Buying or selling treasury bills i.e. T-bills (short-term bonds) by BoC in a market that is open to anyone.
•OMO can be initiated at short notice, are impactful and can be done for any amount
Switching government deposits
transferring deposits to/from BoC to commercial banks
•This is getting increasingly popular
There are two reasons why the Bank of Canada no longer targets the money supply:
1.Because it cannot directly affect the loan-creation by the commercial banks.
2.It cannot know for certain what the demand for money is and so cannot predict with certainty what effect a change in the money supply will have.
Bank of Canada has made interest rate its major target in effecting monetary policy, because (2)
–it has much more control over interest rates than it does over the money supply
–it is easier for the Bank to communicate its policy to the general public
Targeting Interest Rates
BoC sets a target for the overnight interest rate at the midpoint of 0.5% operating bank, it than accommodates that supply of money to the demanded quantity
Drop in the bank rate?
Signals expansionary policy, means that credit is more freely available and cheaper
Increase in the bank rate?
Signals contractionary policy, credit is harder to obtain
Monetary Transmission Process
–The way that changes in the money supply affect (transmits) to the real variables in the economy through the interest rate
–The interest rate provides the link between the money market and the product market
Expansionary Monetary Policy
–an increase in the money supply
–which lowers the interest rate
–leading to an increase in investment and therefore aggregate expenditures and demand .
•The result is a multiplied impact on real GDP and a higher price level.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
–a decrease in the money supply
–which increases the interest rate
–leading to a decrease in investment and therefore aggregate expenditures and demand
The result is a multiplied impact on real GDP and a lower price level.
Monetarism
–An economic school of thought that believes that cyclical fluctuations of GDP and inflation are usually caused by changes in the money supply
–Popularized by Milton Friedman
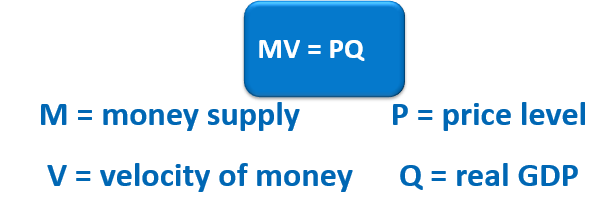
Monetarist View - Equation of Exchange
A formula that states that the quantity of money times the velocity of money is equal to nominal GDP (price level times real GDP
Velocity of Money
•The number of times per year that a unit of currency is spent buying final goods or services
•Sometimes also called the velocity
of circulation
Monetarist View of Velocity of Money
Equation of Exchange: M⋅V=P⋅QM
Assumptions:
Velocity (V) is constant
Full-employment output (Q)
Key Concept: An increase in the money supply (M) leads to a proportional increase in price levels (P), as output (Q) is fixed at full employment
Keynesian View if money supply is increase:
People hold cash’s and do not buy many bonds so interest rates change very little
Keynesian View on when Businesses are not greatly affect by:
interest rate changes, lower interest rate
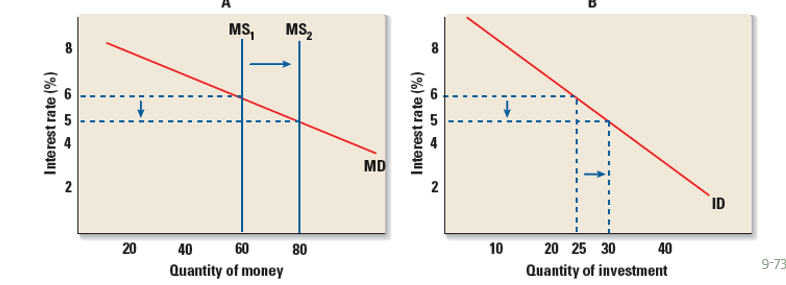
Keynesian view of quantity of money and quantity of investment
–the demand for money is elastic (flat) so a change in money supply only has a small impact on the interest rate; investment demand is inelastic (steep), so the interest change has little impact on investment
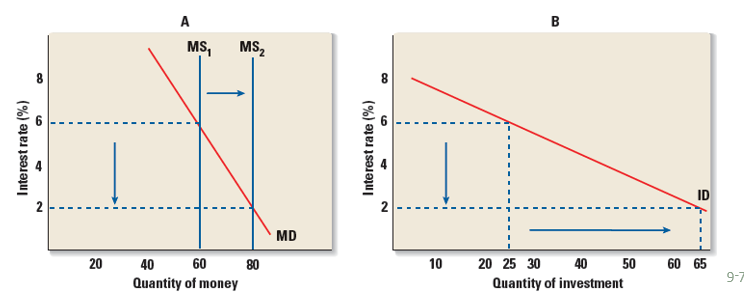
Monetarist View if the money supply is increased
–people are NOT willing to hold much additional cash and therefore buy bonds so the interest rate changes a lot.
Monetarist View on when Businesses are affected by:
–interest rate changes and a lower interest rate will lead to a big increase investment spending.
Monetarists DON’T believe that monetary policy can: (4).
–stimulate economic growth,
–promote full employment
– ensure an acceptable exchange rate
– fight inflation
They feel this hugely overambitious
and thus doomed to fail.
Monetarists feel the sole aim of monetary policy is to
keep prices and the exchange rate stable.
Monetarist view of quantity of money and quantity of investment
–The demand for money is inelastic (steep) so a change in the money supply has a big effect on the interest rate; investment demand is elastic (flat) so the change in the interest rate has a big impact on investment
Anti-Inflationary Monetary Policy
•Bank of Canada approach
“To contribute to solid economic performance and rising living standards for Canadians by keeping inflation low, stable, and predictable”
–Preserve internal and external value of currency which means:
–Keeping inflation rate low (1% - 3%; target is 2%)
Keeping exchange rate stable
Criticisms of Anti-Inflationary Monetary Policy
•Bank of Canada is overly concerned about controlling inflation, resulting in:
– lower economic growth
–higher unemployment
–big budget deficits due to high interest costs