CBNS lecture 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is the CNS?
brain and spinal cord
What is the PNS?
Somatic and autonomic nervous system
Somatic system
controls voluntary muscle movements
Autonomic system
Involuntary moments, and has sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
Sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
Parasympathetic system
rest and digest
Flow of signals
Stimulus (ex: knee hitting a table) —> sensory neurons —> CNS (brain and spinal cord) —> motor neurons —> response
Neurons
nerve cells; transmit chemical and electrical signals around body to brain and other way around (use neurotransmitters)
glia
support and maintain neurons
Soma
cell body (contains mitochondria, nucleus and cytoplasm)
dendrites
recieve neurotransmitters/signals from other neurons
axon
relays neurotransmitters through the neuron to the axon buttons
synaptic terminals
where neurotransmitters leave to another neuron
astrocytes
regulate blood flow
provide structure
maintain chemical balance
oligodendrocytes
build myelin sheath
shwaan cells
build myelin sheath
microglia
immune cells
membrane potential
difference in overall charge outside and inside of the neuron
why is there a membrane potential?
more Na+ outside than inside, more K+ inside than outside, lipid bilayer is impermeable (doesn’t let ions in), the Na+/K+ pump
electrochemical gradient
influences movement of ions in and out of cell
chemical forces
conc. differences (high to low movement)
electrical forces
voltage differences (negative to positive movement)
Does Na+ want to move in or out?
inside because chemical- the conc is lower inside than outside, and electrical- more negative inside, which attracts positive Na
Neuron at rest, is the conc of K+ larger inside or outside?
inside
In a neuron at rest, potassium ions (𝐾+) are more concentrated inside the cell than outside and the cell interior is negatively charged; based on electrochemical gradients, which statement correctly describes the direction of 𝐾+ ion movement?
Both chemical and electrical want it out. Chemical because K+ conc is higher inside, so it wants to go from high to low. Electrical because even though it is negative inside, K+ wants to go outside to make the inside more negative to polarize the cell. The concentration gradient is stronger than the electrical
If a cell has a higher concentration of sodium ions (𝑁𝑎+) outside than inside and also maintains a negative voltage inside, what will be the combined effect of the chemical and electrical forces on sodium ion movement?
both forces drive Na+ inside the cell
Na+/K+ pump and why its important
pumps Na+ out, K+ in. maintains ion gradients
K+ leak channels and why its important
K+ leak passively out of cell. Helps stabilize and make RMP negative
Passive transport
move ions (nonpolar, small) high to low conc. using NO ATP
Diffusion through channel
tunnels that are open that let specific particles through (ex: water or ion channels)
Examples of diffusion through channel
aquaporin (water), K+ channel, Na+ channel
Facilitated diffusion
molecule binds to protein, then changes to it’s shape and carries the molecule through (ex: glucose transport)
is facilitated diffusion passive?
yes, it follows concentration gradient
active transport
going against the gradient, low conc to high conc (high effort)
active pump
Uses ATP to force molecules across the membrane and shoves molecules in and out
A cell needs to move glucose, a large polar molecule, from a high concentration outside to a low concentration inside. Which transport mechanism would be most effective for this process?
facilitated diffusion
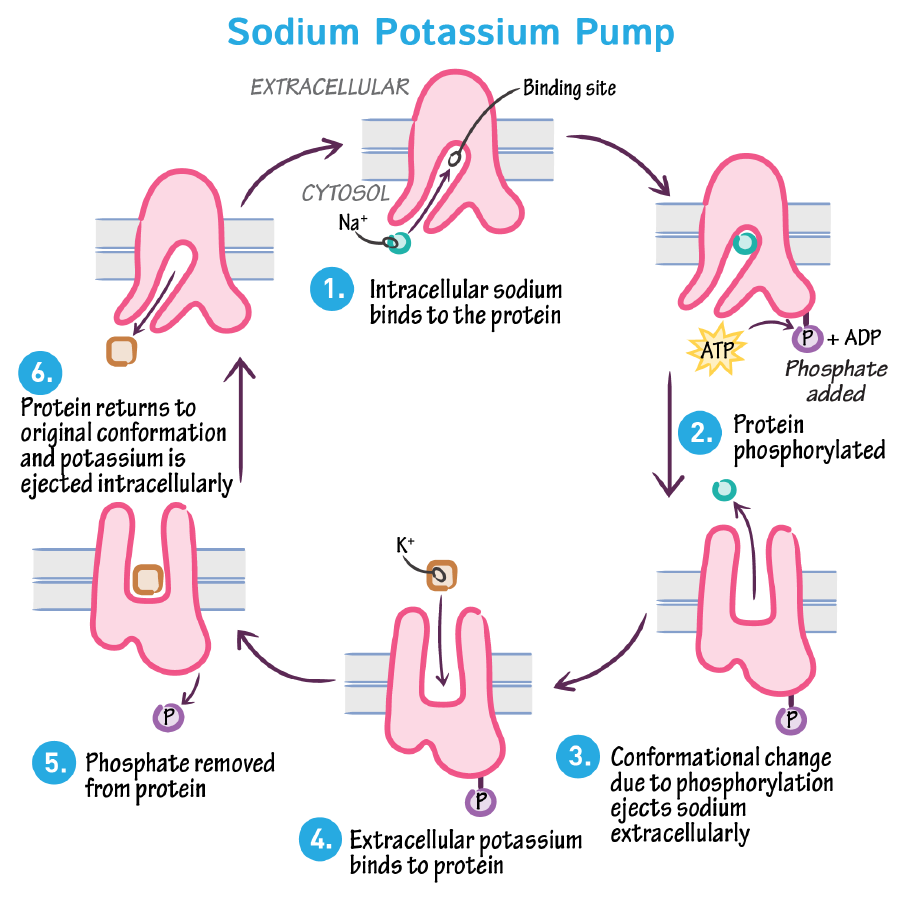
Na+/K+ pump steps in cycle
intracellular Na+ binds to protein
protein undergoes phosphorylation from ATP (phosphate is added)
conformational change ejects NA+ to outside the cell
extracellular K+ binds
phosphate removed
protein returns to regular shape, and the K+ is released inside
when K+ diffuses out, what happens inside the cell?
Becomes more negative
If potassium leak channels in a cell are blocked, what would be the immediate effect on the cell's resting membrane potential?
It would become less negative due to accumulation of potassium ions inside the cell
Nernst equation
calculates the eq potential of an ion across a cell membrane
Resting membrane potential (RMP)
voltage difference inside vs outside when there are no signals firing
If a neuron's potassium leak channels were suddenly blocked while the sodium-potassium pump continued to function normally, what would happen to its resting membrane potential?
less negative since there are lots of K+ being pumped in, not enough passively leaving
If a neuron's sodium-potassium pump stops working properly, what would be the most immediate effect on the resting membrane potential?
The cell would become less negative (more positive)
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
True
CNS glia
Astrocyte, oligodendrocyte
PNS glia
satellite, schwann
ependymal cell
creates CSF
Zone of integration
AP initiated, and has voltage gated ion channels
Zone of input
where neurotransmitters are taken in. ligand gated ion channels
Zone of conduction
AP conduction, moves neurotransmitters, has voltage-gated ion channels
Zone of output
neurotransmitter release, voltage gates ion channels (Na+ and Ca++)
anterograde transport (what direction, what protein, what is in the vesicle)
soma to axon terminal buttons
kinesin
usually enzymes, neurotransmitters, or nutrients
retrograde transport (what direction, what protein, what is in the vesicle)
axon terminal buttons to soma
dynein
usually growth factors
How can pathogens get into the nervous system?
through retrograde traveling of the highway (ex: polio)
Where is myosin?
In the actin in peripheral structures, like the dendrites
How do these proteins move along the ___?
Move along the microtubule through ATP hydrolysis
neurofibrillary tangles
when tau protein fills up and clumps together and tangles
tau proteins
hold microtubules together