Alberta novice drivers training
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
WYLIWYG
Where you look is where you go
Visual lead time
the amount of time that you should be looking ahead for hazards
visual targeting
Looking for an escape route
Horizon method
A method of scanning for hazards
Circle check
A way to scan intersections
Action zone
Where you deal with the hazard
GDL class 7
-learners license
-must be 14 or older
-pass a vision screening and knowledge test
-have parental consent if you are under 18
-provide valid identification
GDL class 7 conditions
-must hold learners license for at least a year
-you must not drive alone
-not permitted to drive between midnight and 5am
-no more passengers than seatbelts
GDL class 5
-probationary driver
-hold your class 7 license for a year
-must be 16 or older
-pass a Alberta class 5 road test
GDL class 5 conditions
-must be a probationary driver for at least 2 years
-no more passengers than seatbelts
-license suspended at 8 demerit points
-zero alcohol level
-not able to re-class your license to 1,2,3 or 4 commercial license
-cannot accompany a learner
Full class 5
-you qualify to re-class your license
-number of demerit points allowed is increased
-zero alcohol tolerance is removed
-you can accompany a learner
Fully licensed class 5 steps
-must be suspension free for the last 12 months
-pass an advanced road test
Class 6
Motorcycle and moped
Class 4
Taxi, ambulance, and small bus of no more than 24 passengers
Class 3
Heavy vehicle with no more than 3 axels
Class 2
Large bus or Motor coach
Class 1
Tractor trailer
Road test pre-requirements
-buy a test permit from a registry agent
-make an appointment for a road test
-have a vehicle that qualifies for the license you are going for
-a vehicle that is mechanically safe
-wear corrective lenses if required
Taking the basic test
-expected to drive in a safe and reasonable manner
-no pets or passengers
-all road tests have a set time frame
-the examiner is not allowed to coach you during the test
Demerit system
-you start with zero points and gain points
-they stay on your record for two years from the offence date
-if you collect enough points you lose your license
How often to change oil
Every 5000Km (check your oil when you fill your gas or twice a month)
Check the power steering fluid
twice a year and only when the engine is cold
Check transmission fluid
Every month or whenever your transmission isn't shifting smoothly
Check engine coolant levels
When the engine is completely cool
Blind spots
Areas of the road that are blocked from your sight by your own vehicle or mirrors. (Areas the driver cannot see)
Exterior walk around
Start by walking to the rear of the vehicle, check the side for damage and tires for inflation, and the lug nuts for damage. Move to the back, check that the trunk is latched, tires are inflated and the plate is visible. At the front check that your lights and signal is visible.
Interior inspection
Look for and secure loose objects and make sure that there is nothing on the ledge of the rear window
Emergency brake
(n) a brake operated by hand, which is often used when parking a car
Exterior mirror
Adjust the mirror and remember that you need to see a slim line of your car
Signal arm
Pull up to turn right and press down to turn left
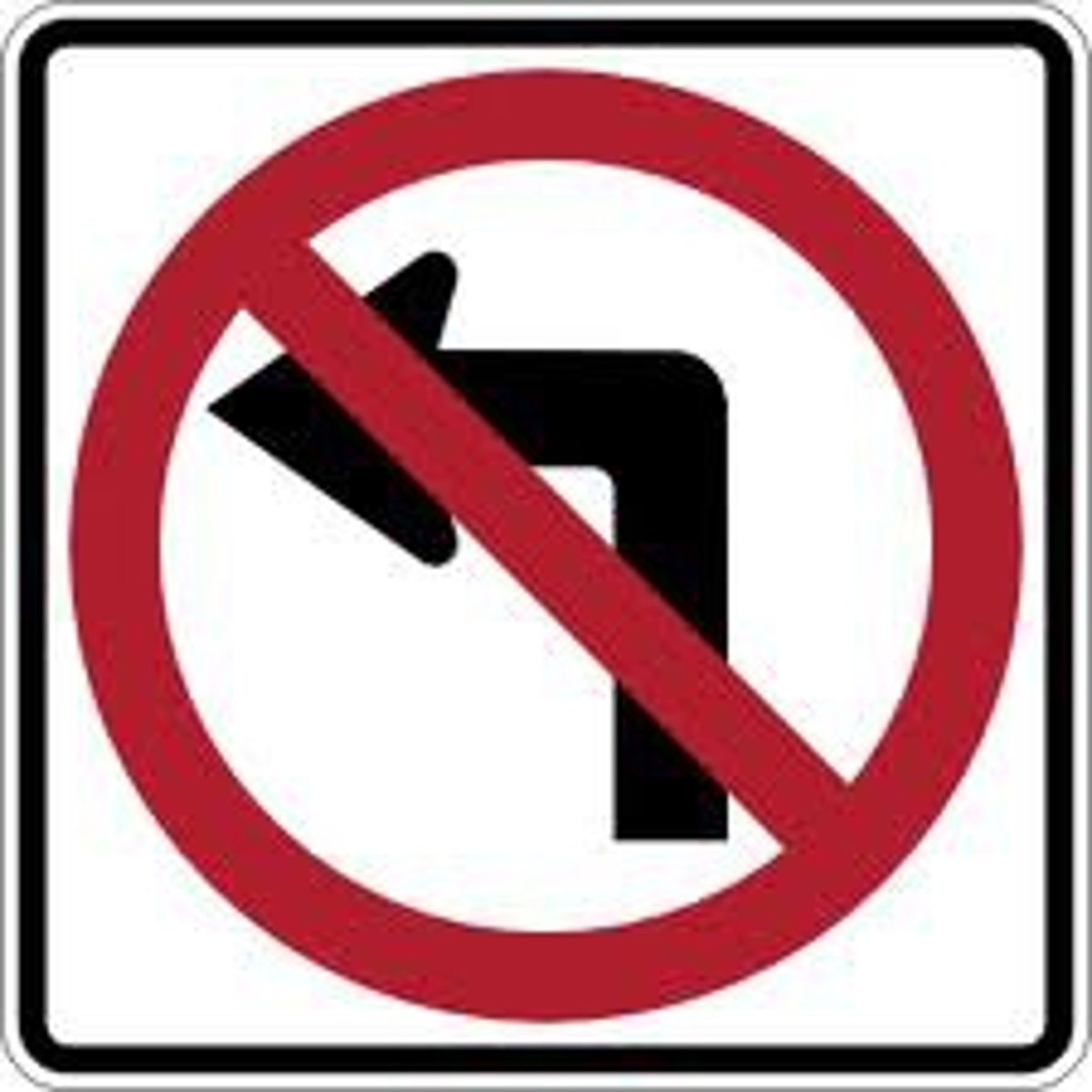
no left turn

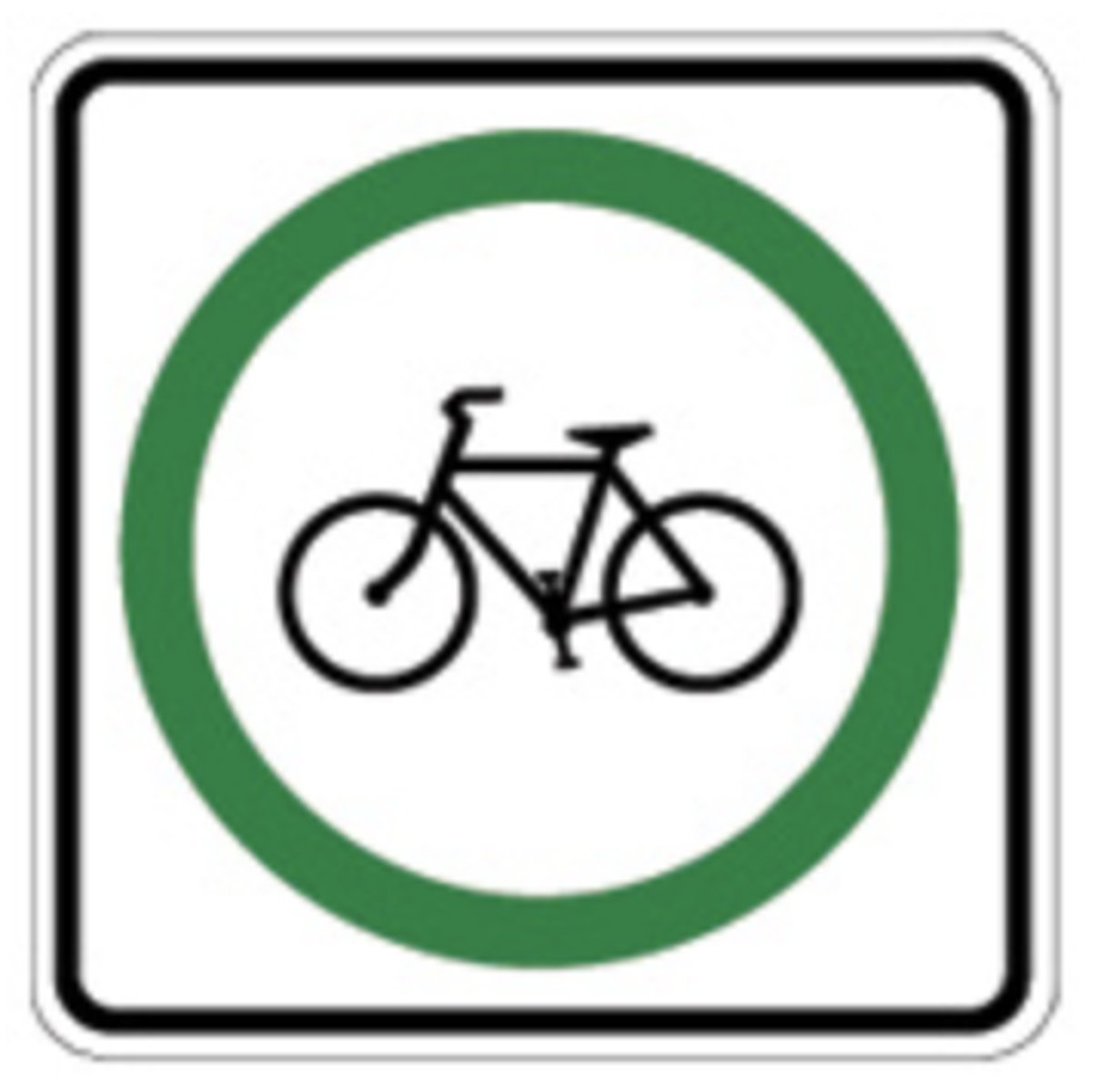
official bike road

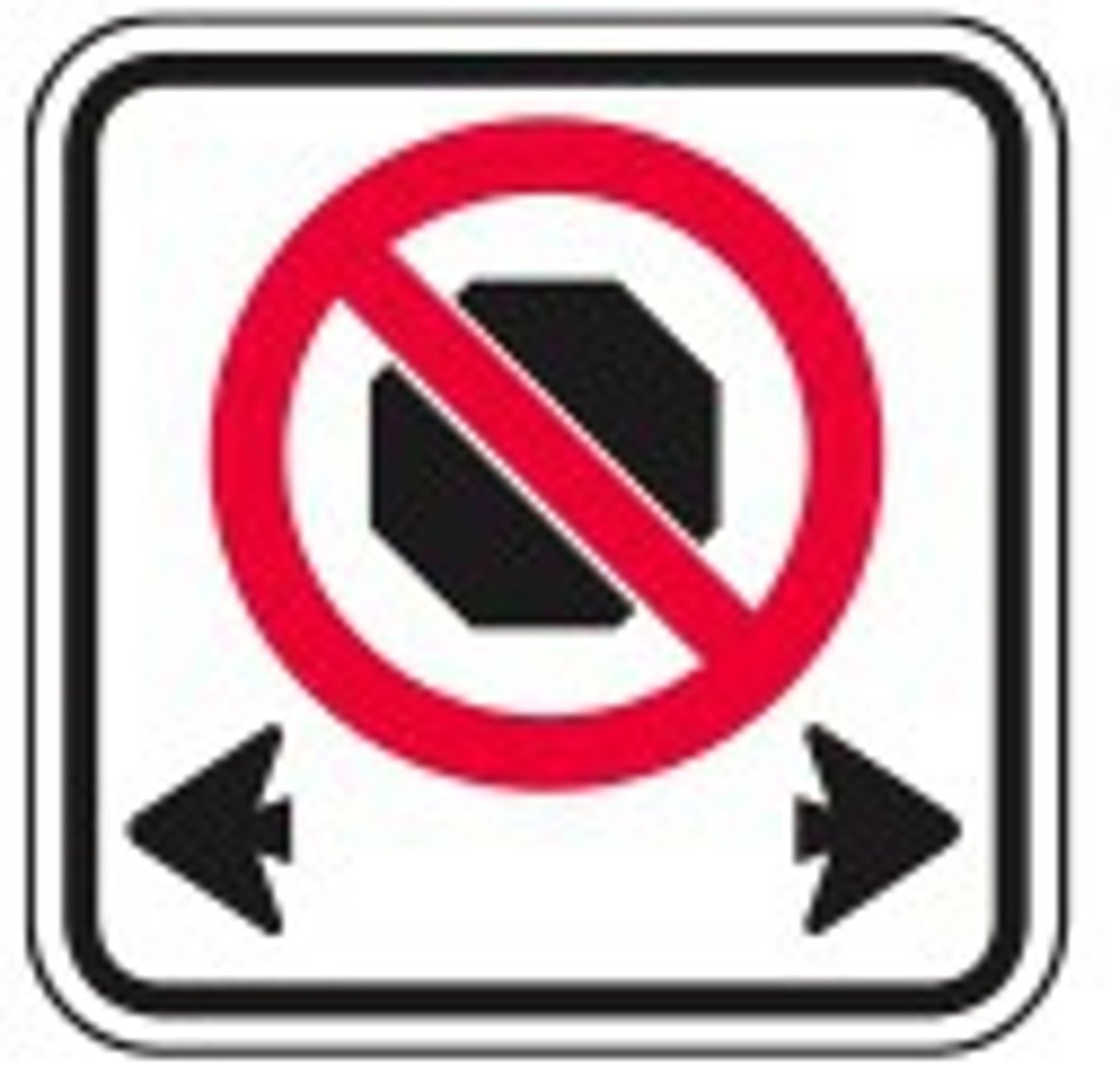
you may not drive straight through the intersection
arrow with a line through it
do not stop in this area

route to passenger railway station
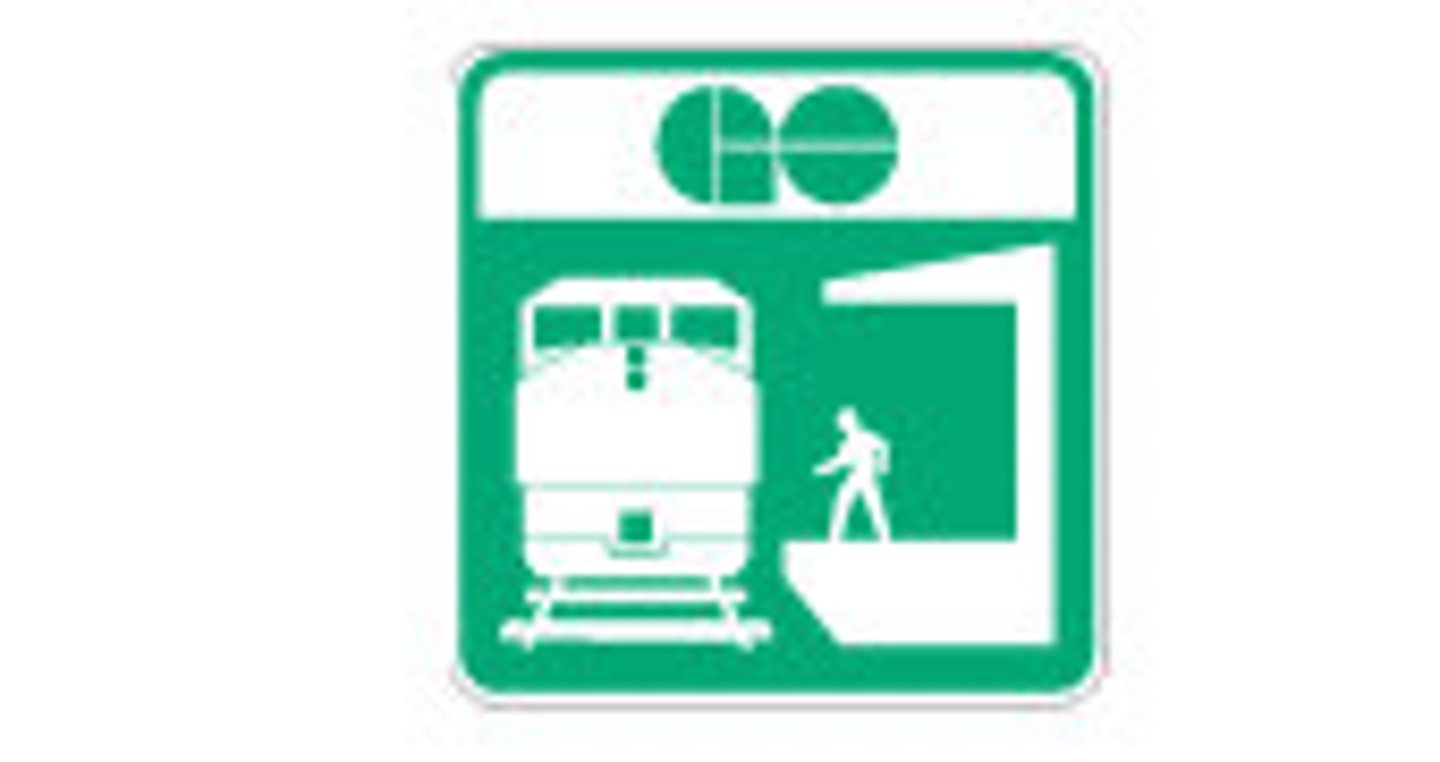
route to airport

no parking

no pedestrians allowed

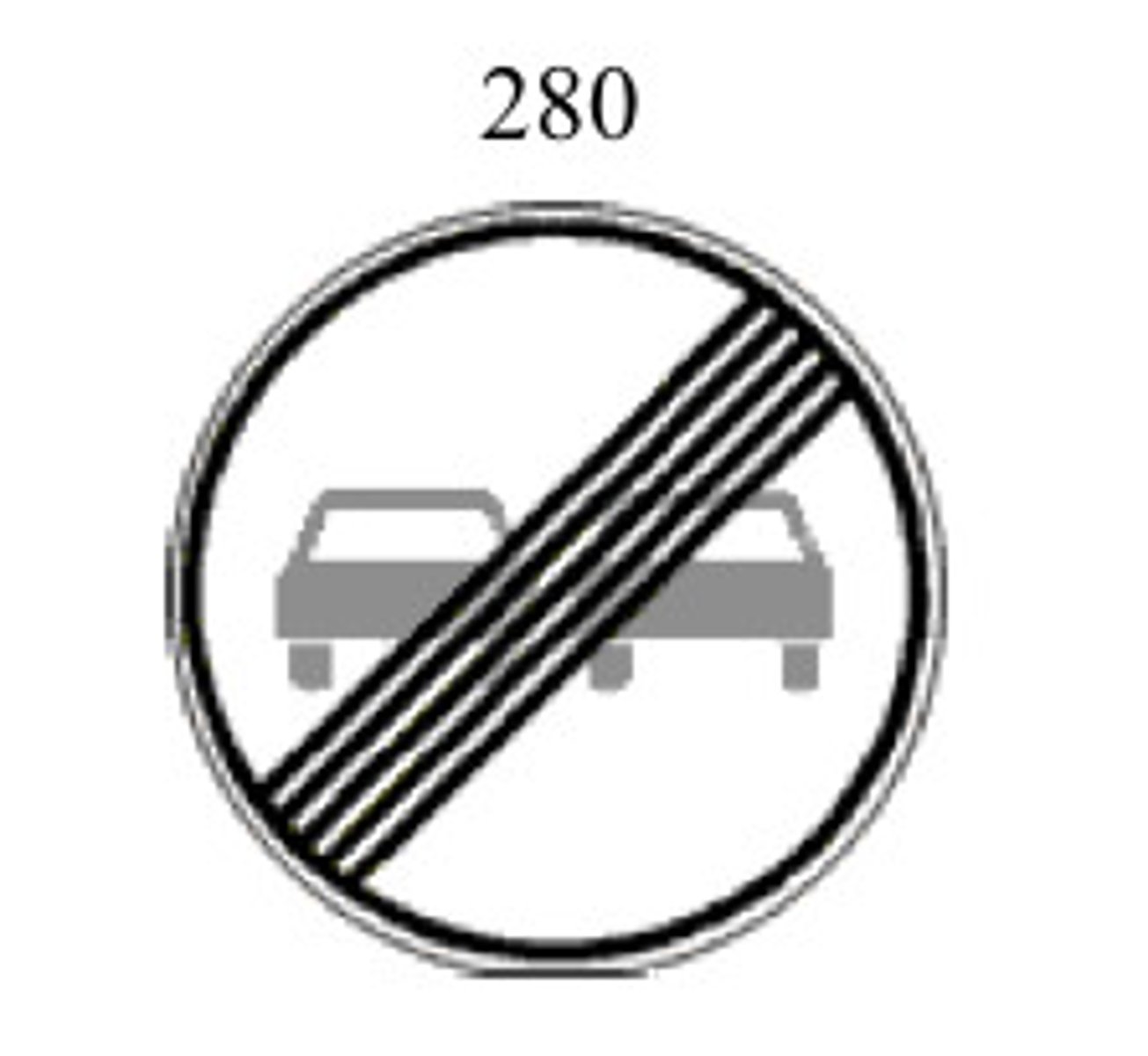
no passing sign
do not enter sign

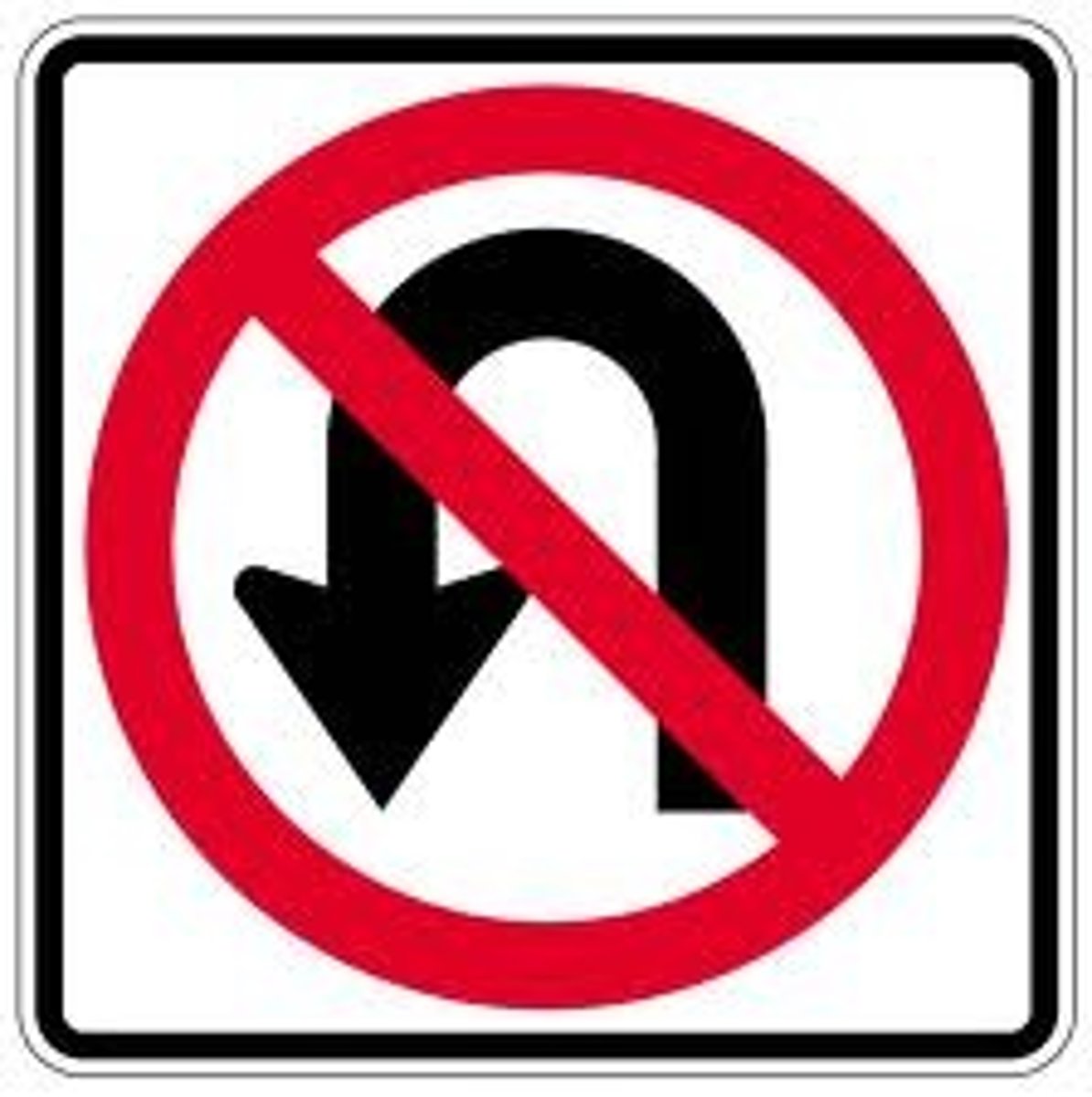
No U-Turn

stop signs
-if there is no stop line stop at the crosswalk
-if there is no crosswalk stop at the edge of the sidewalk
-if there is no sidewalk stop at the edge of the intersection
-wait until it is clear before entering the intersection
information and direction signs
tell you about distances and destinations (usually regtangular with a green background and white letters)
warning or temporary condition signs
warn of dangers or unusal conditions (usually diamond shaped and have a yellow background with black letters or symbols)
slow moving vehicle
the vehicle is traveling 40 Km/h or less

speed limit on trans-canada routes
110 Km/h
speed limit on rural highways and country roads
80 Km/h
speed limit in an alley
15 Km/h
school zone
-reduce speed and watch for children
-may change to municipal bylaws
-you are not premited to pass, or attempt to pass a vehicle traveling in the same direction as you
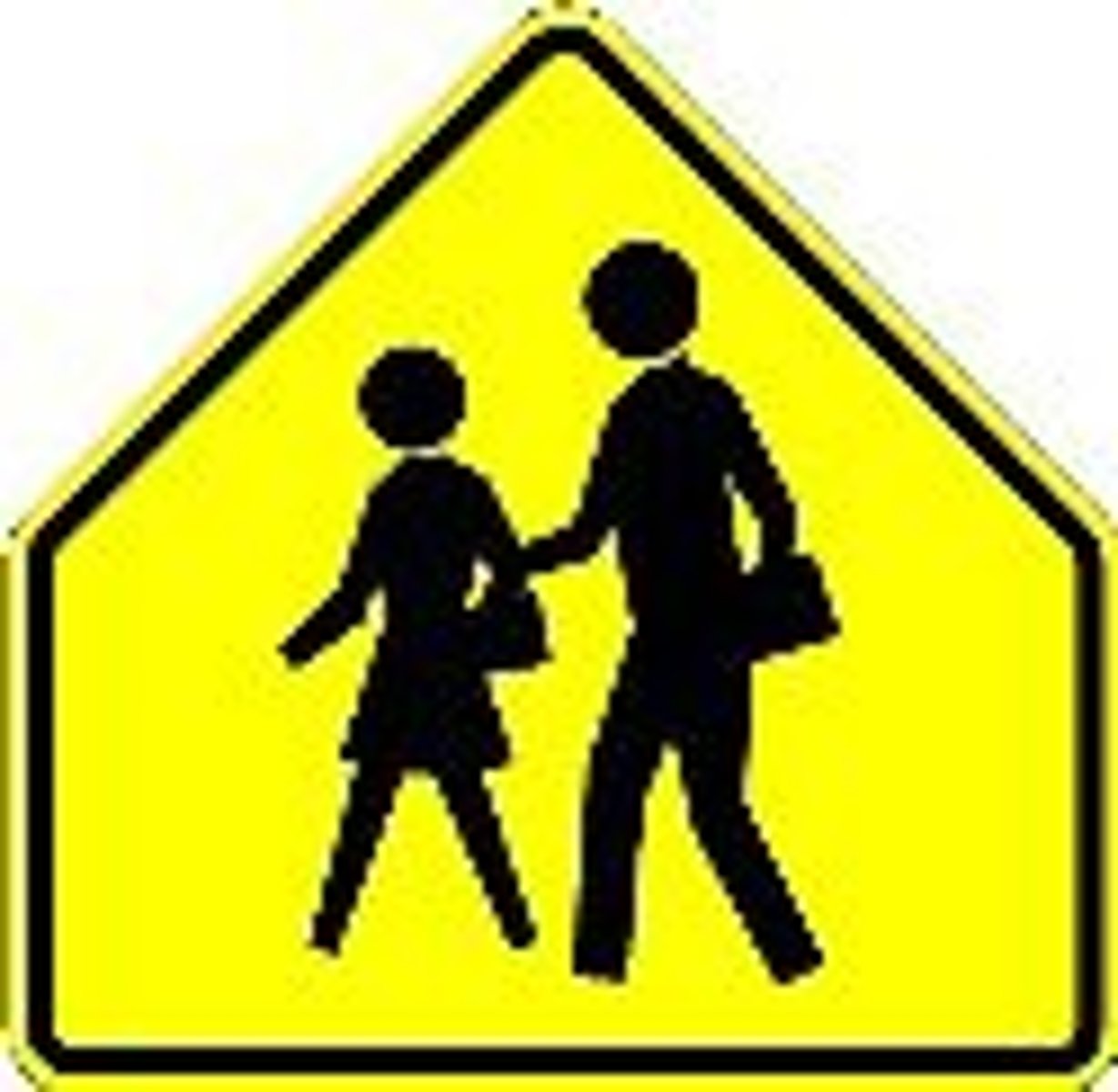

playground zone
-be cautious, children may be close by
-not premitted to pass, or attempt to pass a vehicle traveling in the same direction as you
lane signs

intersection signs
By showing you in advance how the roads join each other, the signs let you know when the road you are traveling on does not continue straight through the intersection. The signs also warn you about possible problems with the movements of other vehicles. Approach all of these intersection types with extra caution by searching ahead and preparing to slow down, if necessary.
steady or solid red light
must come to a stop before crossing the stop line or crosswalk (right turn is premitted after coming to a full stop) (A left turn is premitted from a one way street to a one way street)
flashing red light
Stop-go when the way is clear
Steady Amber Light
red light is coming clear the intersection
flashing amber light
This light means you may proceed with caution after yielding to pedestrians and vehicles in the intersection. If used in conjunction with a Pedestrian sign you must reduce your speed to 30km/h
solid green light
go if safe to do so
flashing green light
proceed through, turn left or right
flashing green arrow
turn left or right as indicated by the arrow
reverse traffic flow
rush arrow strategy designed to ease conjestion
yellow line
Indicates two-way traffic
white line
one-way traffic
single solid line
lane change is not premitted
single broken line
Passing is permitted if it safe.
double solid line
no passing
Single broken yellow line
Stay to the right of the line. You may temporarily cross this line when you are passing a vehicle in front of you.
arrows
What type of pavement marking is used to show you which lane you must use for a turn?
Diamond markings on lane
Usually marked for carpools and buses
X marking
Approach to a railway crossing.
painted island
Pavement Marking: This pavement marking is not allowed to be used for traveling over or for passing.
crosswalk lines
are a pair of white lines or longitudinal lines that mark where a pedestrian will walk.
stop lines
The wide white lines painted across a traffic lane before you enter the intersection are known as
bicycle lane
A designated traffic lane for bicyclists, marked by a solid white line, typically breaking into a dotted line at the corner.
controlled intersection
An intersection where traffic is
regulated by traffic signs or signal lights.
uncontrolled intersections
has no signs or signals to regulate traffic (circle check and yield the right of way to the vehicle on the right)
T intersection
The roadway you are traveling on ends ahead. Signal before turning right or left.
traffic circles
Vehicles entering the traffic circle shall yield to vehicles already in the intersection
U turns are not premitted on
-a roadway between intersections
-where signs prohibit making a U turn
-at an intersection controlled by traffic control signs
- at an alley intersection
lane position
you must drive on the right hand side of the road and drivers should drive as closely as possible to the center line
Shared turn lane
allows vehicles from each direction to turn left using the same lane
passing lane
Lanes: The type of lane that allows someone to go infront of a slower vehicle by accelerating in this lane
multi-lane highway
slow moving traffic should travel in the traffic lane to the far right unless the left lane is required to make a left hand turn
passing is illegal when
-approaching vehicles are too close
-a solid line is on your side
-a sign indicates no passing
-you are in a school or playground zone
-another vehicle has stopped to allow a pedestrian to cross
being passed
-stay to right
-adjust speed to let vehicle move back into lane
merging
adjust speed so you have a gap in traffic (your entry into the flow of traffic should be at or near the speed of other traffic)
weave zone
Lanes: A zone of a highway where traffic is both entering and exiting
Curves and hills
before entering a curve slow down and stay in your lane and accelerate slightly after entering the curve to maintain speed (keep in the right lane as you approach the top of a hill and do nor pass)
school buses
Always stop when approaching a stopped bus. It is a felony to cause the death of a person while passing a stopped school bus that is loading or unloading school children.
emergency vehicles
Pull to the right side and stop
- Do not stop in intersection
- Do not drive or stop in a way that interferes with vehicles
- Stay at least 150m behind vehicle when following
Never back up faster than
A slow walking speed
Backing left or right
Right- look over right shoulder
Left-look over left shoulder
(The front of the vehicle will swing in the opposite direction that the back end is going)
How far from the curb should you be when parking
Within 50cm of the curb
Parking uphill with a curb
Turn front wheels left and make sure that your wheel touches the curb
Parking downhill with a curb
Turn front wheels right
Parking uphill without a curb
Turn wheels to the right
Parking downhill without a curb
Turn front wheels right
Preventable collision
one in which you failed to do everything that you reasonably could have done to prevent collision
defensive driving
Driving to prevent collisions in spite of the incorrect actions of others and adverse conditions
SAFER system of defensive driving
Space, attitude, foresight, eyesight, responsibility
Space
1 second for every 3m of length of your vehicle +2 seconds (drive with the intention of space)