money market
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
money market
nominal interest is the opportunity cost for holding money
money demand
asset demand for money —> the desire to hold wealth as an money instead of other assets,
transaction demand for money—> GDP = C +Ig +G + Xn
if asset demand or transaction increase/decrease
shift right/left
money supply
determined by actions of the central Bank and lending in the bank system
the money supply shifts to the right or shifts to the left
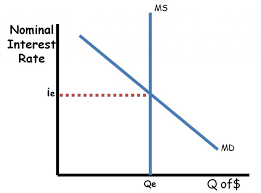
The Demand for Money:
Inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded
downwars sloping demand for money
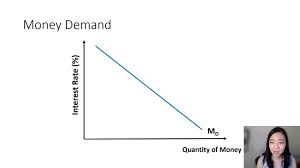
The demand for money
Transaction demand for money: people hold money for everyday transactions
asset demand for money: poeple hold money since it is less risky than other assets.
expansionary monetary policy
increase money supply —> increases interest rate —> increases investment —> increases AD
buy bonds, lower discount rate, lower reserve requirement
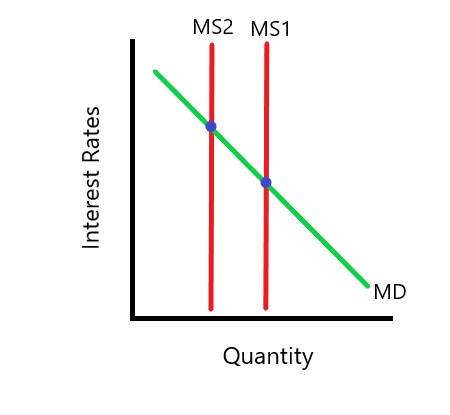
Contractionary monetary policy
decrease money supply, increase interest rate, decrease investment, decrease AD
sell bonds, raise discount rate, reserve requirement
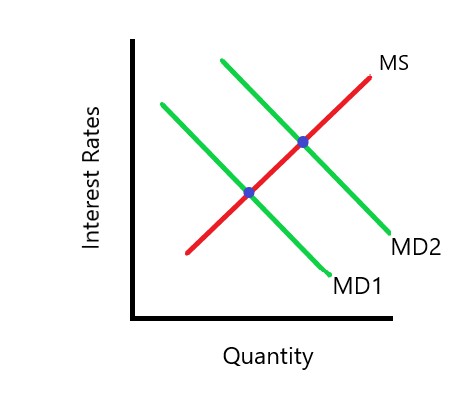
3 shifters of money supply
reserve requirement : reserve ration is the percent of deposits that banks must hold in reserve (the they can not loan out)
discount rate: the interest rate that the DEF charges commercial banks
open market operations: when the FED buys or sells government bonds (securities.)
1st money supply shifter
increased Reserve Req, —> Money supply decreased
decreased reserve req. —> increased money supply
2nd money supply shifter
increase discount rate —> money supply decreased
decreased discount rate —> money supply increased
3rd money supply shifter
FED Buys bonds —> money supply increase
FED sells bonds —> money supply decrease
federal funds rate
the interest rate that banks charge one another for one-day loans of reserves
FED influences them by setting a target and using open market operation to hit the target.
ample reserves
imply that banks have excess reserves beyond what is necessary to meet their reserve requirements and maintain liquidity.
raise administered rates or interest on reserves
contractionary policy
scarce reserves
imply that banks are operating with minimal excess reserves or even facing a deficiency of reserves relative to their obligations.
buy bonds, lower discount rate, lower reserve requirement