Movement Analysis in AQA GCSE PE
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Lever
A lever is a rigid structure (bone) that rotates around a fixed point (joint) to create movement.
Fulcrum (F)
The joint.
Load (L)
The weight/resistance.
Effort (E)
The force (muscle contraction).
1st Class Lever
F in middle (E-F-L); Example in Sport: Heading a football; Mechanical Advantage: Depends.
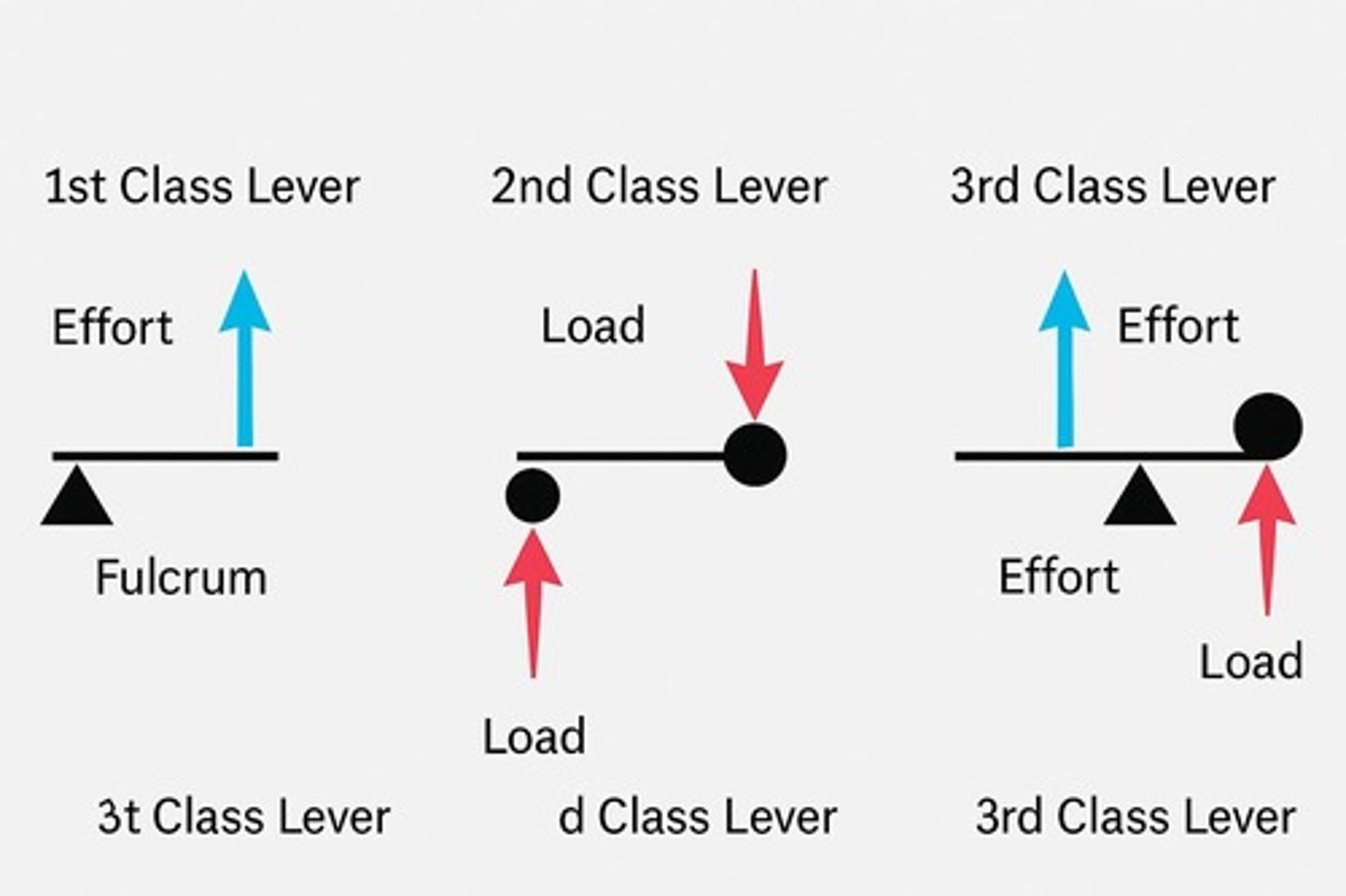
2nd Class Lever
L in middle (F-L-E); Example in Sport: Plantarflexion at ankle (tiptoe); Mechanical Advantage: Yes - powerful.
3rd Class Lever
E in middle (F-E-L); Example in Sport: Bicep curl / kicking ball; Mechanical Advantage: No - fast, large range.
Sagittal Plane
Divides body into left & right; Movement Types: Flexion/Extension; Sport Example: Sprinting, squat.
Frontal Plane
Divides body into front & back; Movement Types: Abduction/Adduction; Sport Example: Star jump, side lunge.
Transverse Plane
Divides body into top & bottom; Movement Types: Rotation; Sport Example: Tennis serve, golf swing.
Longitudinal Axis
Head to toe; Movement Direction: Rotational (twisting); Sport Example: Pirouette, ice spin.
Transverse Axis
Side to side; Movement Direction: Forward/backward; Sport Example: Somersault.
Frontal Axis
Front to back; Movement Direction: Side-to-side; Sport Example: Cartwheel.
Hinge Joint
Example: Knee, elbow; Movement Allowed: Flexion, extension; Sport Example: Sprinting, push-up.
Ball & Socket Joint
Example: Shoulder, hip; Movement Allowed: All directions (inc. rotation); Sport Example: Tennis serve, swimming stroke.
Pivot Joint
Example: Neck; Movement Allowed: Rotation; Sport Example: Looking left/right in football.
Condyloid Joint
Example: Wrist; Movement Allowed: Flexion, extension, circumduction; Sport Example: Netball pass.
Basketball Jump Shot
Lever: 3rd class (shoulder and elbow); Plane: Sagittal (elbow flexion/extension); Axis: Transverse (jumping vertically); Muscles: Triceps extend elbow, quadriceps extend knee.
Football Kick
Lever: 3rd class (hip and knee joints); Plane: Sagittal (hip/knee extension), Transverse (hip rotation); Axis: Longitudinal (rotation during kick); Muscles: Quadriceps extend knee; hip flexors bring leg forward.
Cartwheel (Gymnastics)
Plane: Frontal (side-to-side movement); Axis: Frontal (rotating over the side); Joint: Shoulder and wrist joints allow movement and balance; Muscles: Deltoids, triceps, core stabilisers.
What is a Lever in the Body?
A lever in the body is a bone that moves around a fulcrum (joint) when muscles apply effort (force) to move a load (resistance).
Memory Hack for Levers
1 - FLE; 2 - FLE; 3 - FEL; That's the order of Fulcrum, Load, Effort in each lever.
1st Class Lever
Heading a football
Fulcrum (1st Class Lever)
Neck joint
Effort (1st Class Lever)
Neck extensor muscles
Load (1st Class Lever)
Weight of the head
2nd Class Lever
Taking off for a jump
Fulcrum (2nd Class Lever)
Ball of the foot (ankle)
Load (2nd Class Lever)
Body weight
Effort (2nd Class Lever)
Gastrocnemius (calf muscle)
3rd Class Lever
Bicep curl
Fulcrum (3rd Class Lever)
Elbow joint
Effort (3rd Class Lever)
Biceps contracting
Load (3rd Class Lever)
Dumbbell in hand
Mechanical Advantage (MA)
Formula: MA = Effort Arm ÷ Load Arm
Efficient power (2nd class levers)
If MA > 1
Less efficient, but faster movement (3rd class levers)
If MA < 1
Flexion
Decreasing angle at a joint
Extension
Increasing angle at a joint
Abduction
Moving a limb away from the midline
Adduction
Moving a limb towards the midline
Rotation
Circular movement around a joint
Circumduction
Circular movement at ball & socket joints
Plantarflexion
Pointing toes (ankle movement)
Dorsiflexion
Lifting toes up
Sagittal Plane
Divides body into left and right
Frontal Plane
Divides body into front and back
Transverse Plane
Divides body into top and bottom
Frontal Axis
Runs front to back (side to side rotation)
Transverse Axis
Runs side to side (across the body)
Longitudinal Axis
Runs top to bottom (head to toe)