Module 1: Organic Chemistry - Part 10 - Alcohols, Alkyl halides, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic acid and Derivatives, Amines
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Mechanism of reaction of alcohol and alkyl halide.
a. Electrophilic addition
b. Electrophilic substitution
c. Nucleophilic addition
d. Nucleophilic substitution
d. Nucleophilic substitution
Qualitative test for alkyl halide.
a. Beilstein test
b. 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine test
c. Fehling's and Tollens test
d. Lucas test
a. Beilstein test
Qualitative test for alcohol.
a. Beilstein test
b. Grignard test
c. Hinsberg test
d. Lucas test
d. Lucas test
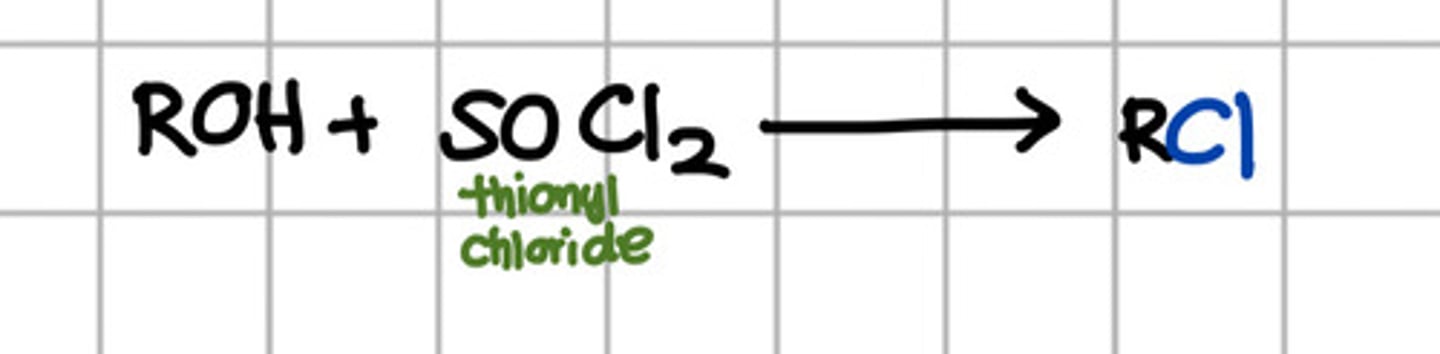
Reagent responsible for converting ROH to RCl.
a. SOCl2
b. PBr5
c. H2SO4
d. NaCl
a. SOCl2
Reagent responsible for converting ROH to RBr.
a. SOCl2
b. PBr5
c. H2SO4
d. HBr
b. PBr5

Reagent responsible for converting ROH to alkene.
a. SOCl2
b. PBr5
c. H2SO4
d. Base
c. H2SO4
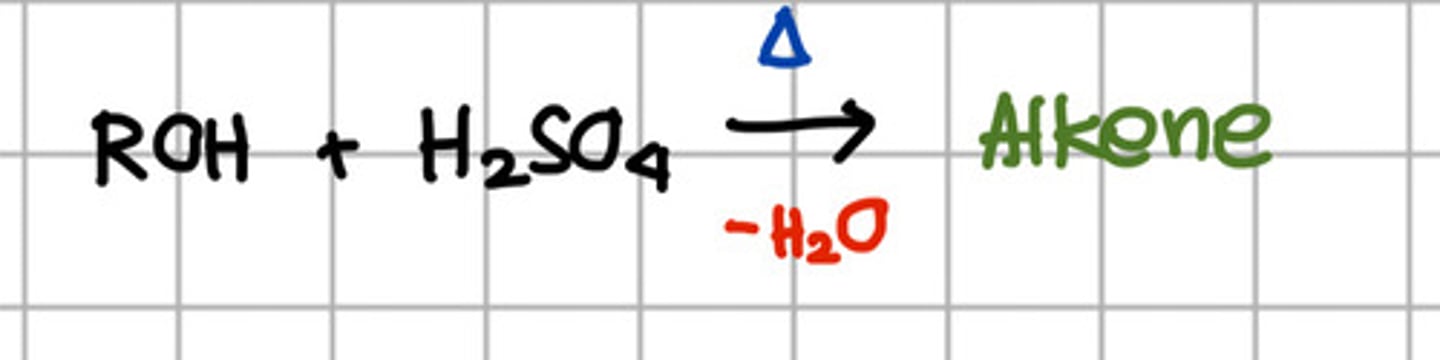
Converting ROH to alkene is through the reagent H2SO4 which involve what reaction?
a. Hydration
b. Dehydration
c. Dehydrohalogenation
d. Williamson synthesis
b. Dehydration
Reagent responsible for converting ROH initially to an alkoxide.
a. SOCl2
b. PBr5
c. H2SO4
d. Base
e. Alkyl halide
d. Base
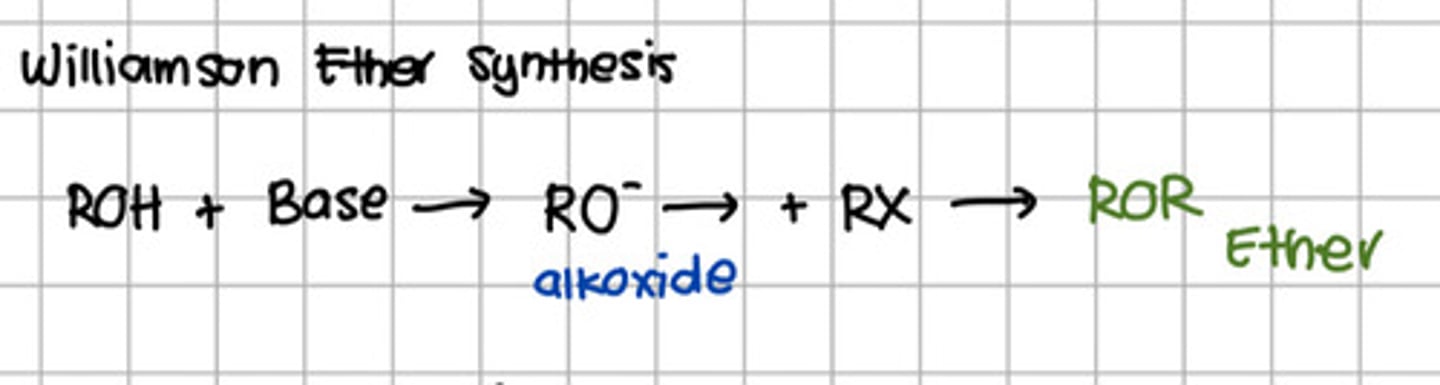
Reagent responsible for converting RO- to ROR.
a. SOCl2
b. PBr5
c. H2SO4
d. Base
e. Alkyl halide
e. Alkyl halide
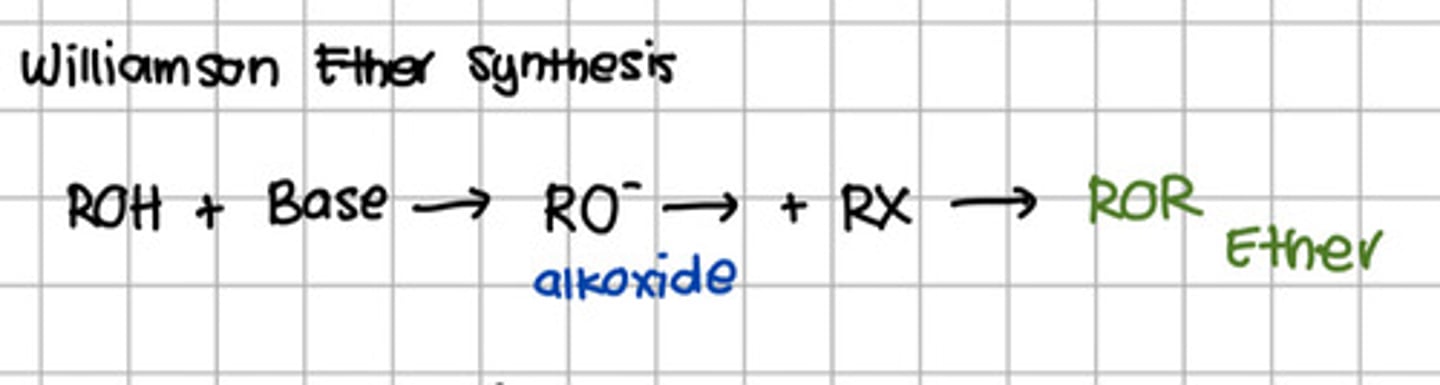
Reaction involved the conversion of alcohol to ether.
a. Hydration
b. Dehydration
c. Dehydrohalogenation
d. Williamson reaction
d. Williamson reaction - Williamson Ether Synthesis
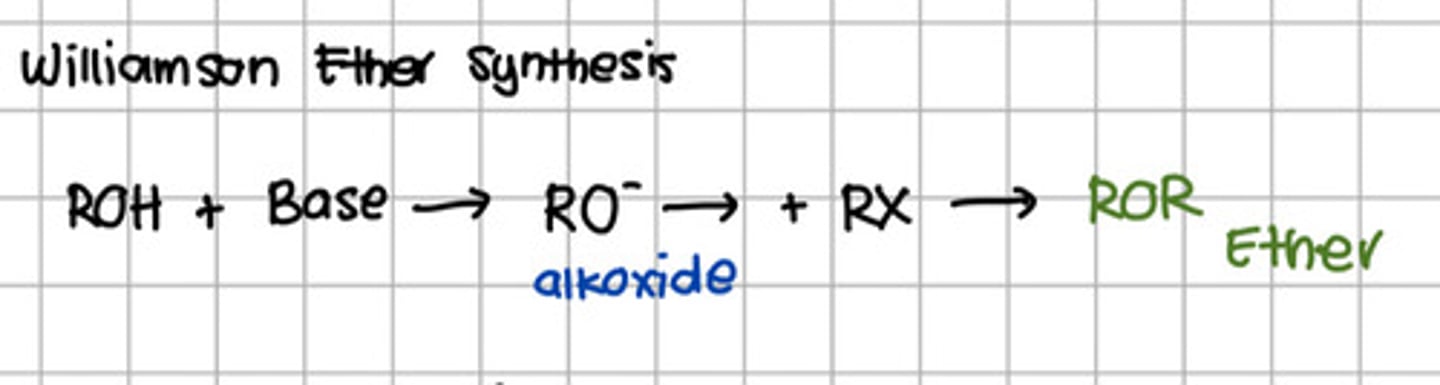
Product of reacting alcohol to a base and eventually a n alkyl halide.
a. Ester
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ether
d. Acyl halide
c. Ether - aka Williamson Ether Synthesis
What reaction will convert alkyl-halide to alkene?
a. Hydrogenation
b. Dehydrogenation
c. Dehydrohalogenation
d. Oxidation
c. Dehydrohalogenation
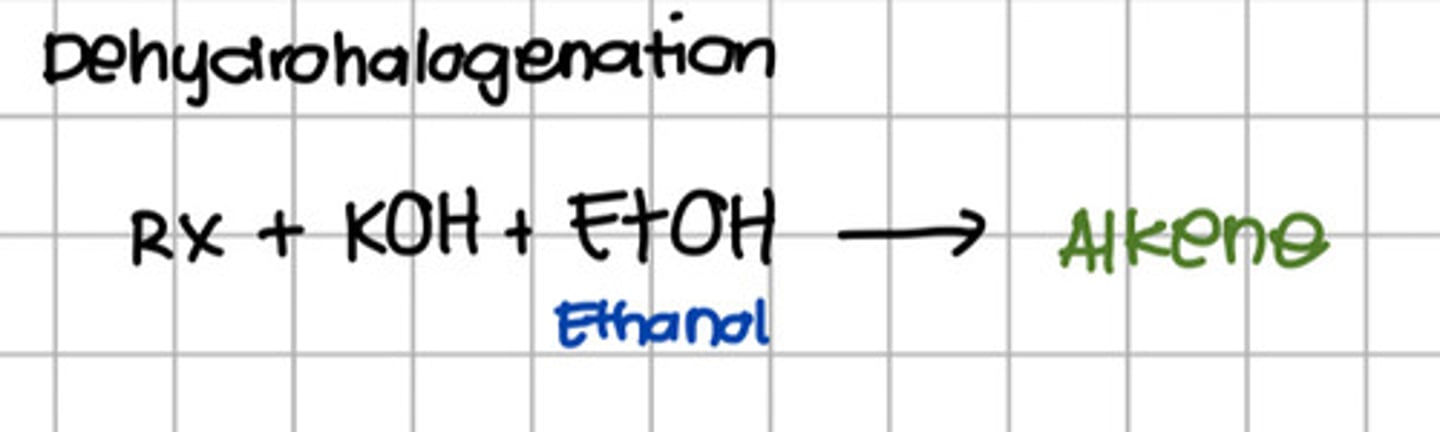
Reacting alkyl halide to which of the following will produce alcohol?
a. KOH
b. NaOH
c. Ethanol
d. a and b
e. a and c
f. All
b. NaOH
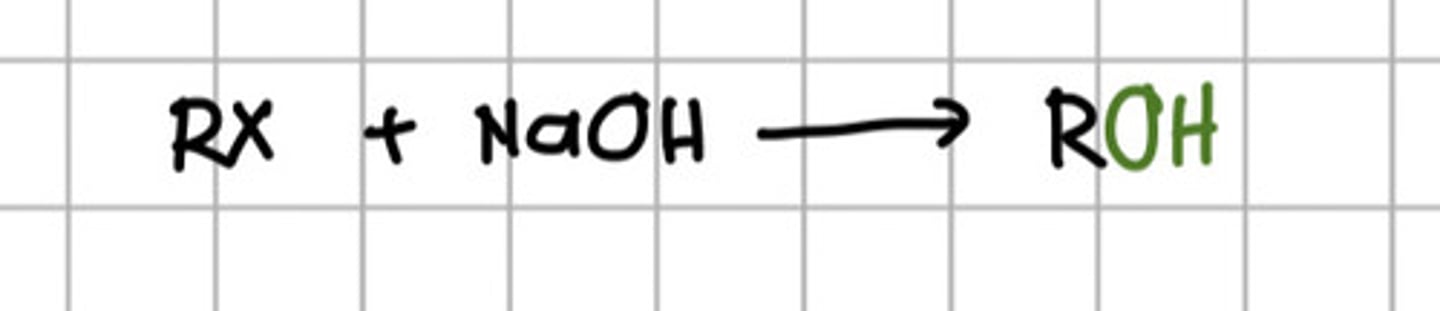
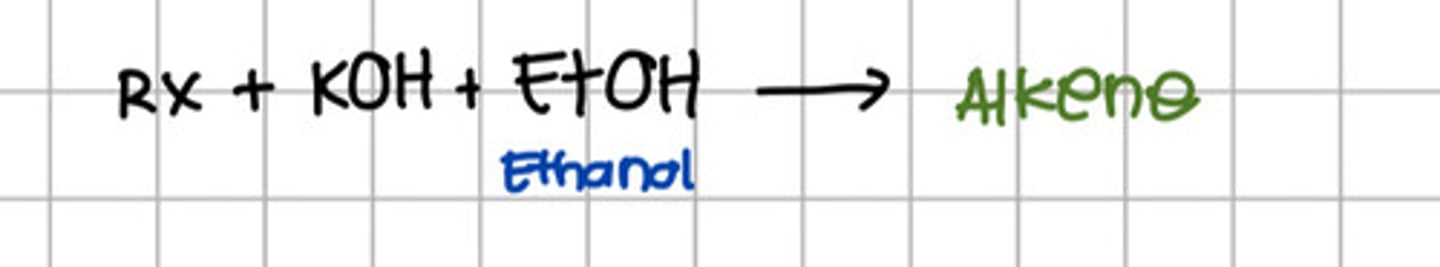
Reacting alkyl halide to which of the following will produce alkene?
a. KOH
b. NaOH
c. Ethanol
d. a and b
e. a and c
f. All
e. a and c - KOH and Ethanol
Initial product of oxidation of a primary alcohol.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
a. Aldehyde
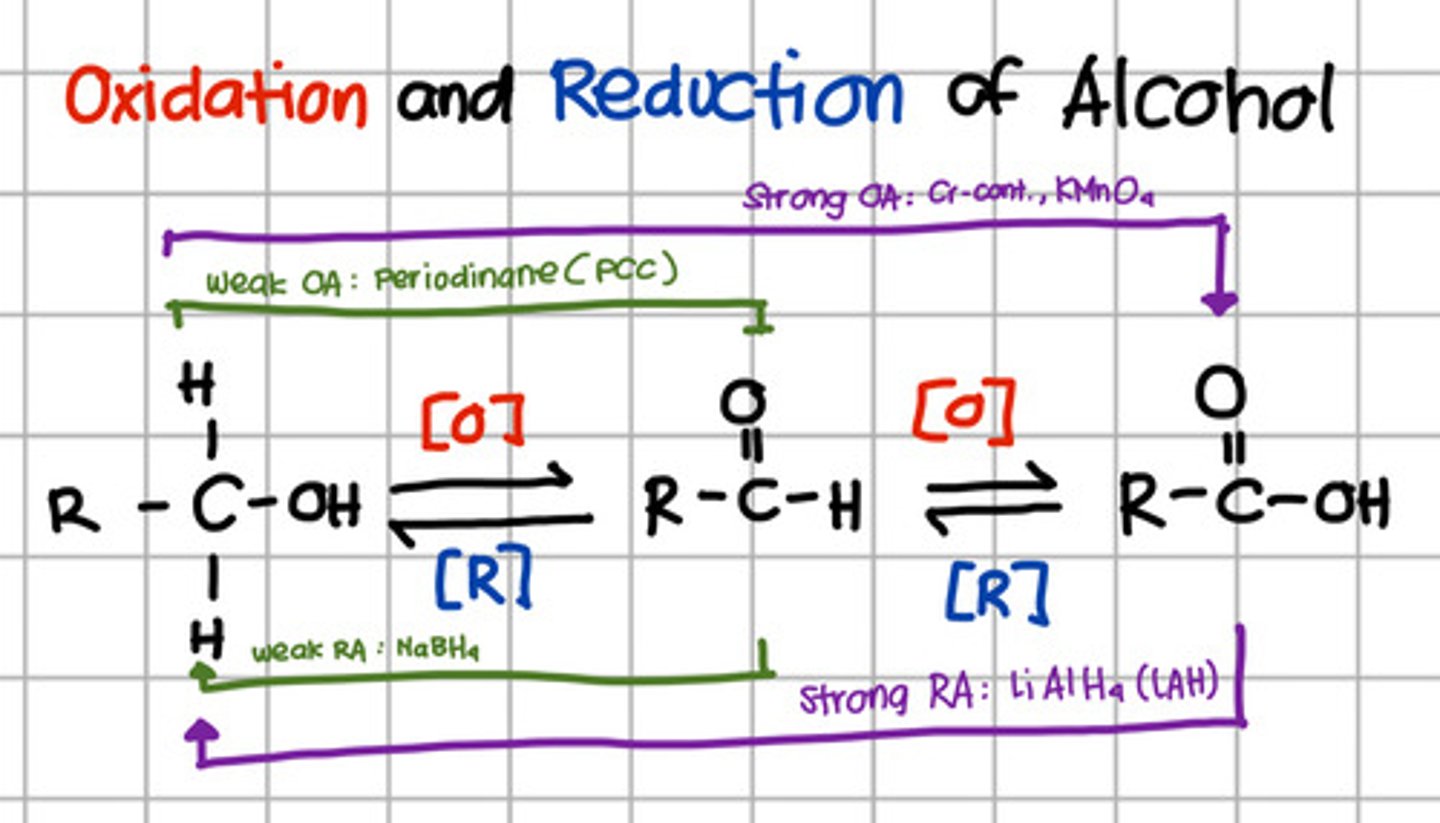
Product of complete oxidation of a primary alcohol.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
b. Carboxylic acid
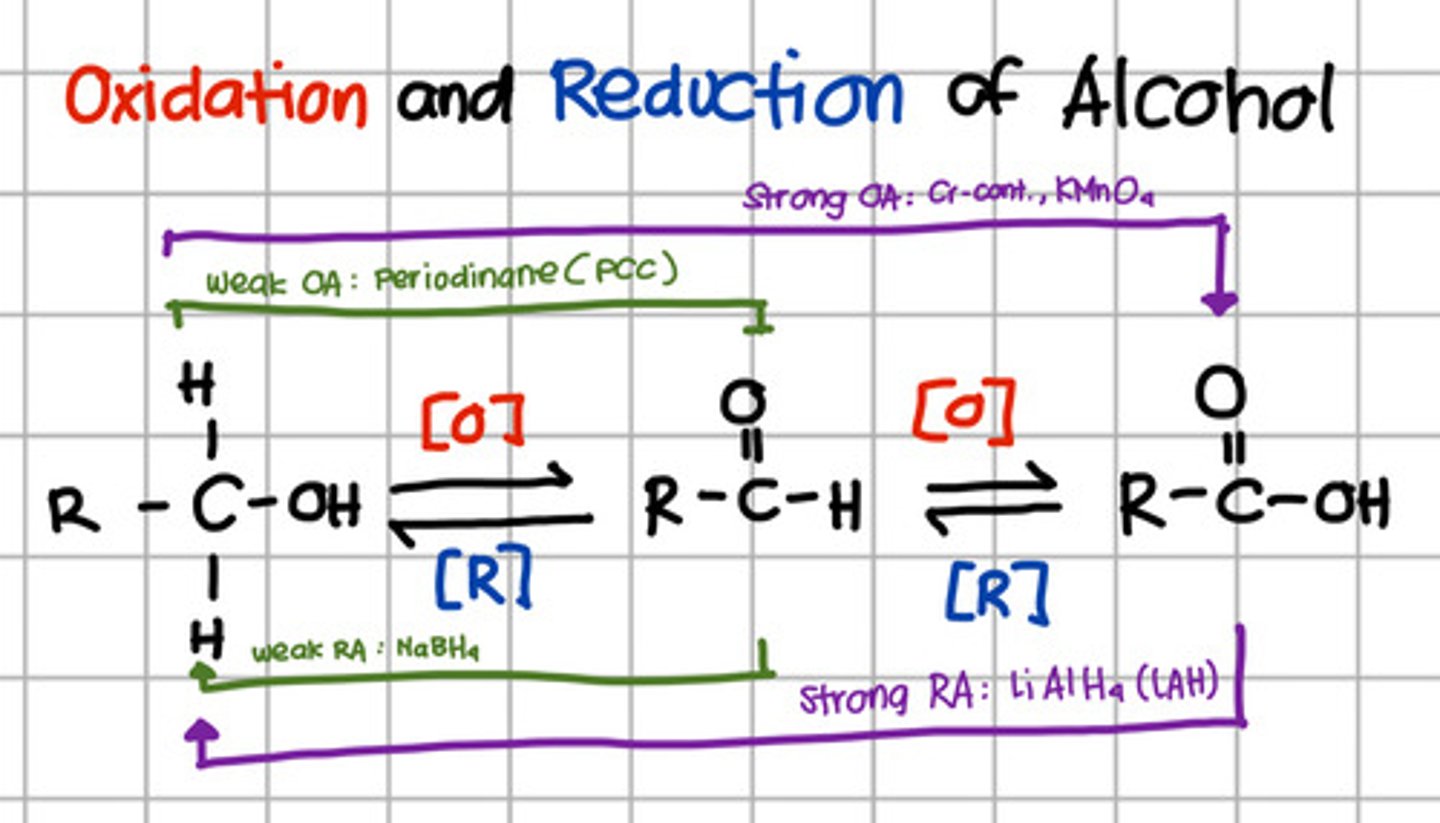
Product of oxidation of an aldehyde.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
b. Carboxylic acid
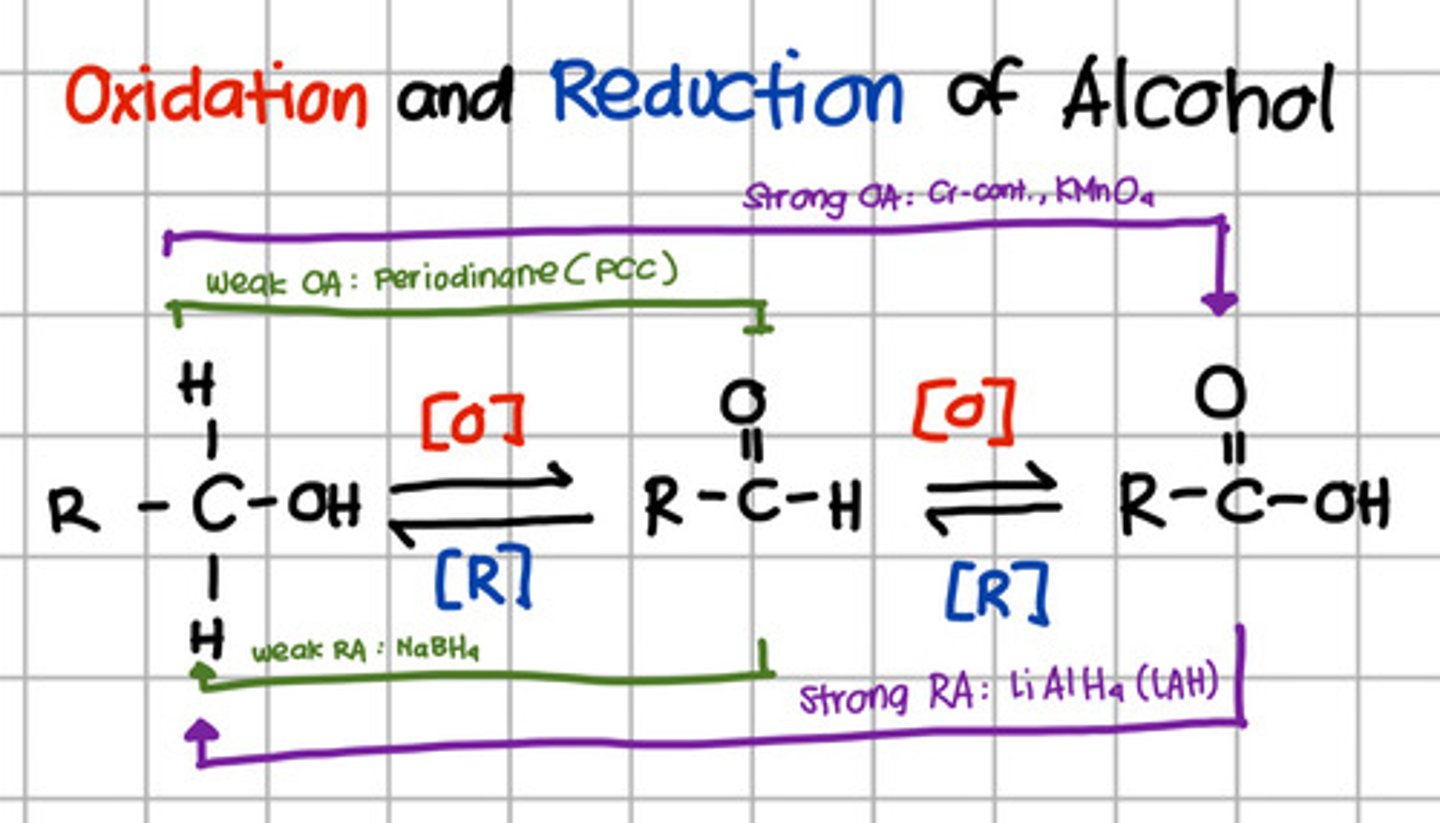
Intermediate product of reduction of carboxylic acid.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
a. Aldehyde
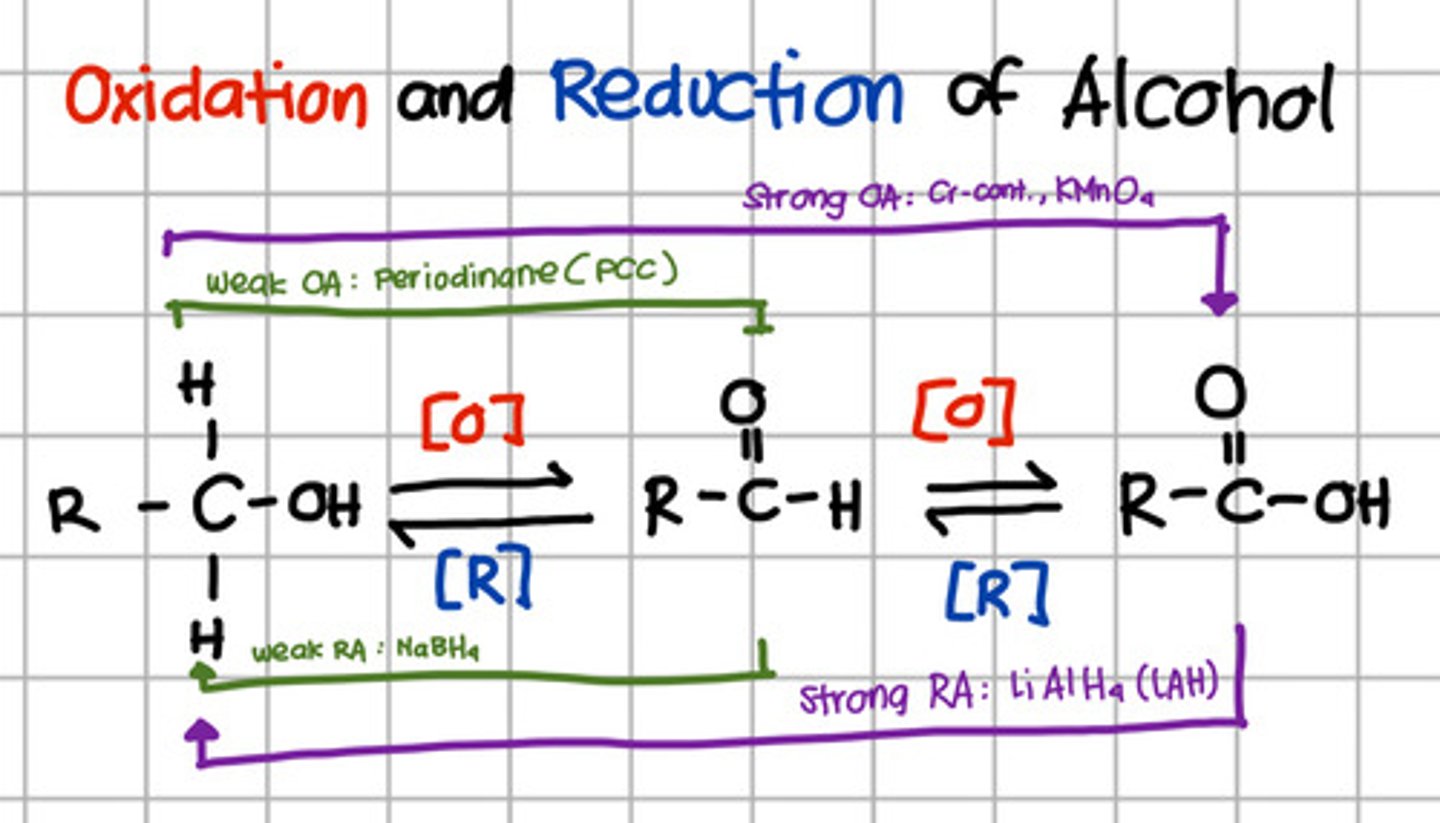
Product of reduction of aldehyde.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
d. Primary alcohol
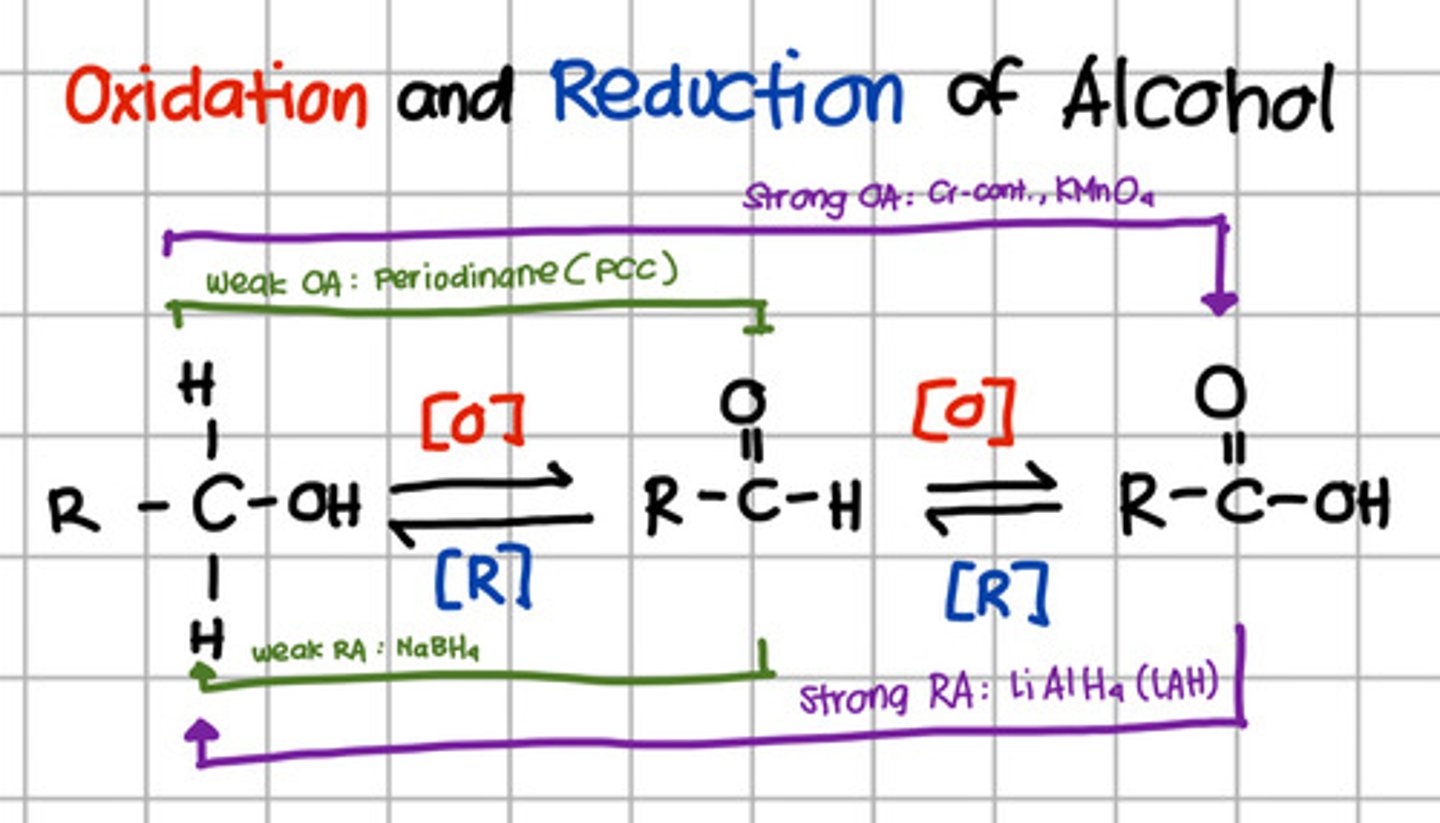
Product of complete reduction of carboxylic acid.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
d. Primary alcohol
Which will oxidize alcohol up to aldehyde only?
a. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
b. Chromium, KMnO4
c. LiAlH4
d. NaBH4
a. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) - also Periodinane which are weak oxidizing agents
Which will oxidize alcohol up to carboxylic acid?
a. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
b. Chromium, KMnO4
c. LiAlH4
d. NaBH4
b. Chromium, KMnO4 - strong oxidizing agents
Which will reduce carboxylic acid up to primary alcohol?
a. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
b. Chromium, KMnO4
c. LiAlH4
d. NaBH4
c. LiAlH4 - Strong reducing agents
Which will reduce aldehyde to primary alcohol?
a. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
b. Chromium, KMnO4
c. LiAlH4
d. NaBH4
d. NaBH4 - Weak reducing agent.
Which is a strong oxidizing agent?
a. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
b. Chromium, KMnO4
c. LiAlH4
d. NaBH4
b. Chromium, KMnO4
Secondary alcohol can be oxidize to:
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
c. Ketone
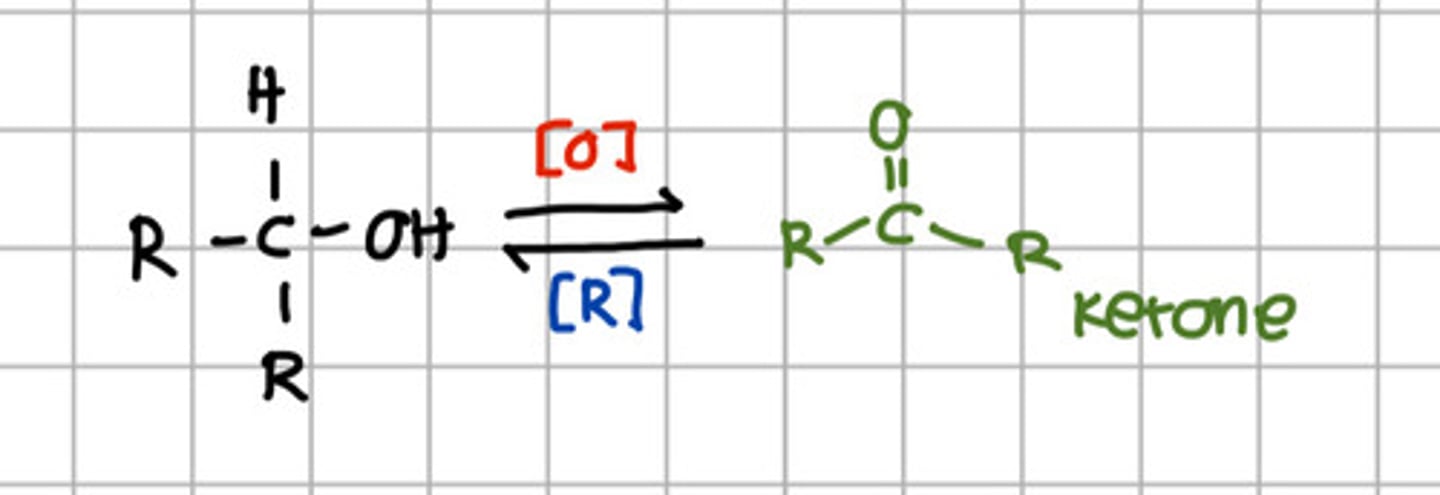
Ketone can be reduced to:
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
c. Ketone
d. Primary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
e. Secondary alcohol
Mechanism of reaction of aldehyde and ketone.
a. Electrophilic addition
b. Electrophilic substitution
c. Nucleophilic addition
d. Nucleophilic substitution
c. Nucleophilic addition
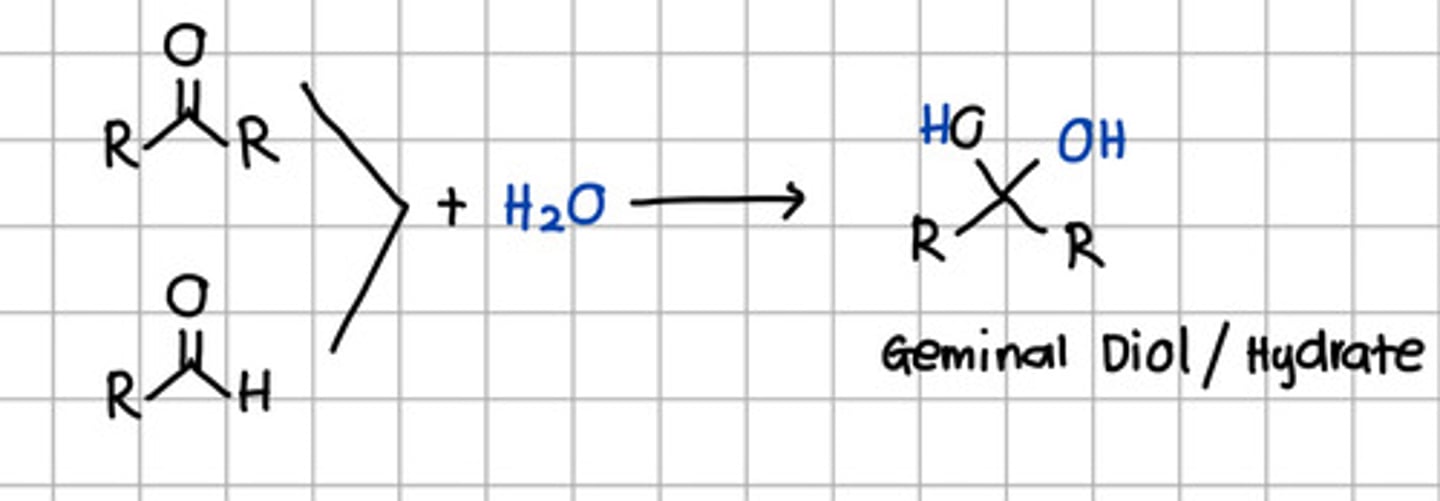
Product of nucleophilic addition of water to aldehyde and ketone
a. Geminal diol
b. Cyanohydrin
c. Tertiary alcohol
d. Secondary alcohol
e. Ketal
f. Imine
a. Geminal diol
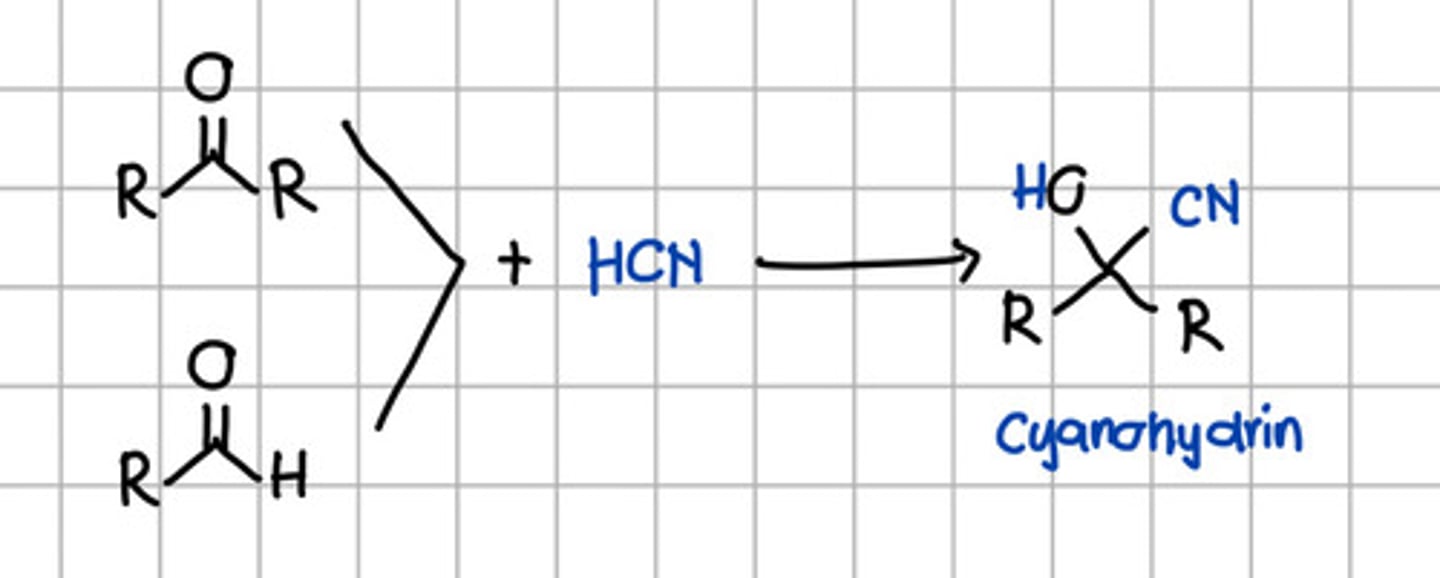
Product of nucleophilic addition of HCN to aldehyde and ketone.
a. Geminal diol
b. Cyanohydrin
c. Tertiary alcohol
d. Secondary alcohol
e. Ketal
f. Imine
b. Cyanohydrin
Addition of which to aldehyde or ketone is involved in Grignard reaction?
a. H2O
b. RMgX
c. ROH
d. RNH2
e. HCN
b. RMgX
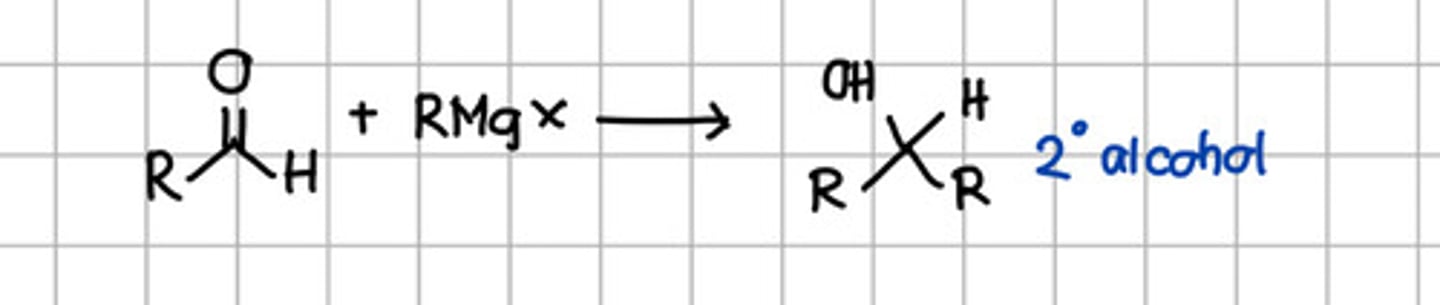
Product of Grignard reaction of aldehyde.
a. Geminal diol
b. Cyanohydrin
c. Tertiary alcohol
d. Secondary alcohol
e. Ketal
f. Imine
d. Secondary alcohol
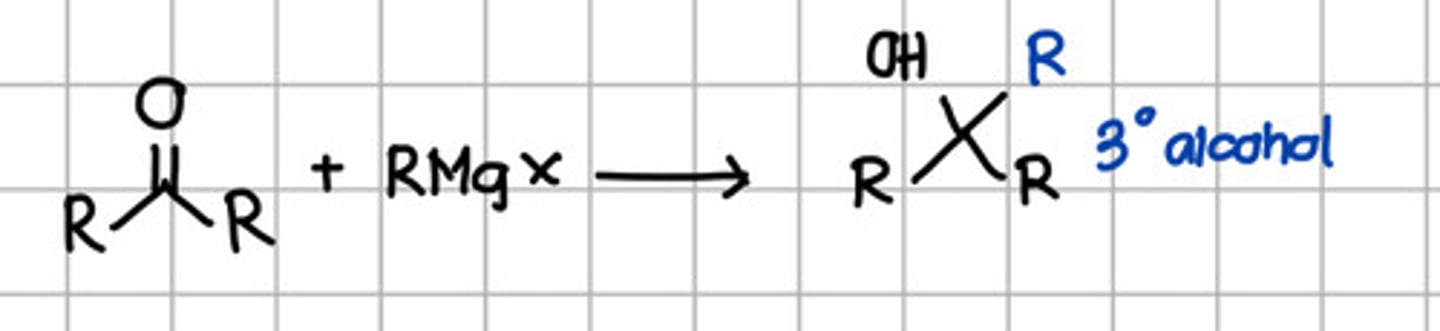
Product of nucleophilic addition of RMgX to ketone.
a. Geminal diol
b. Cyanohydrin
c. Tertiary alcohol
d. Secondary alcohol
e. Ketal
f. Imine
c. Tertiary alcohol
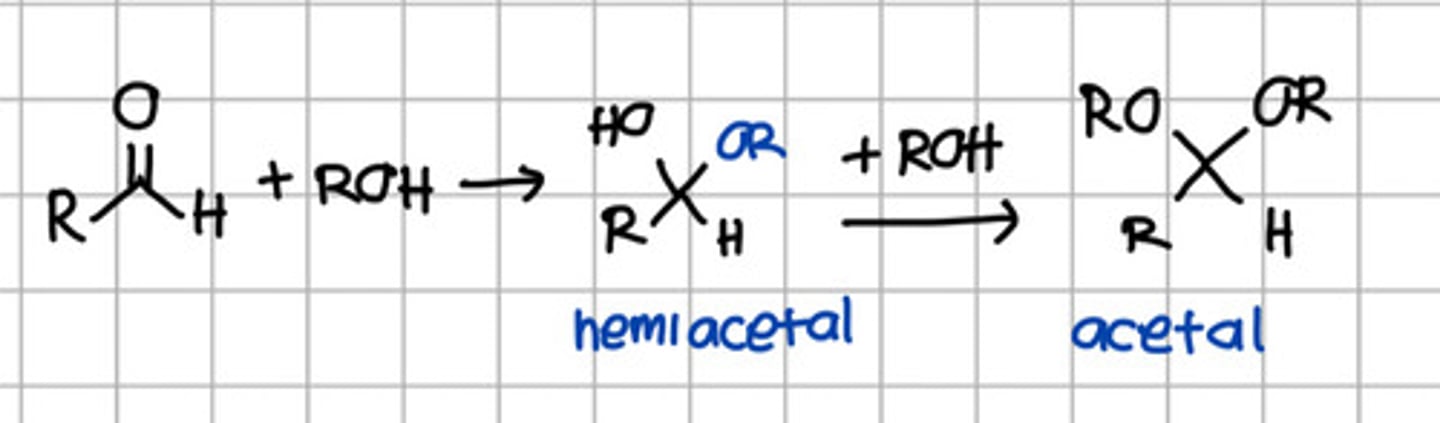
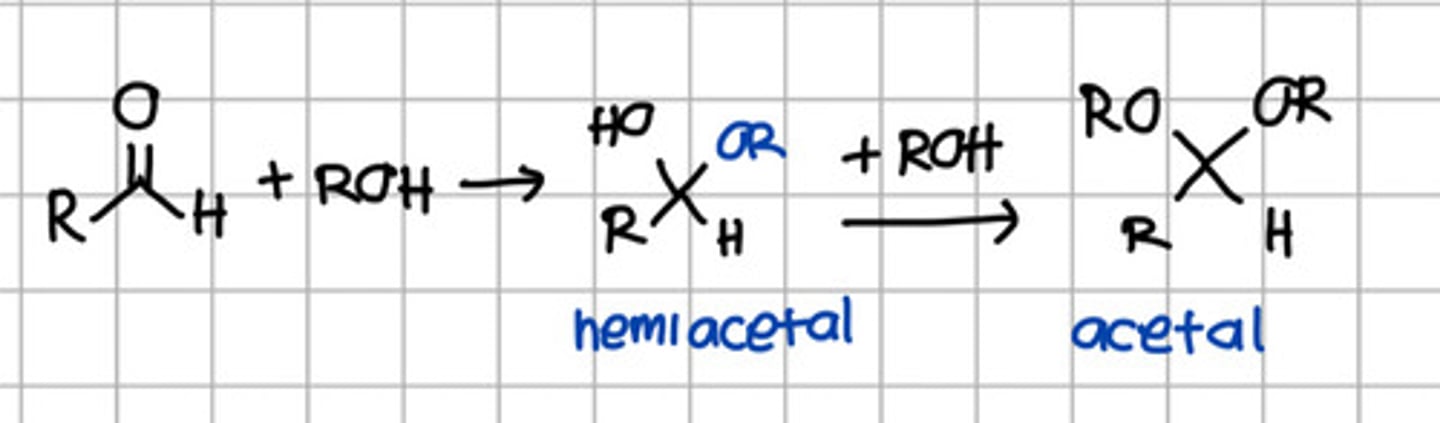
Product of initial nucleophilic addition of ROH to aldehyde.
a. Hemiketal
b. Hemiacetal
c. Ketal
d. Acetal
e. Imine
b. Hemiacetal
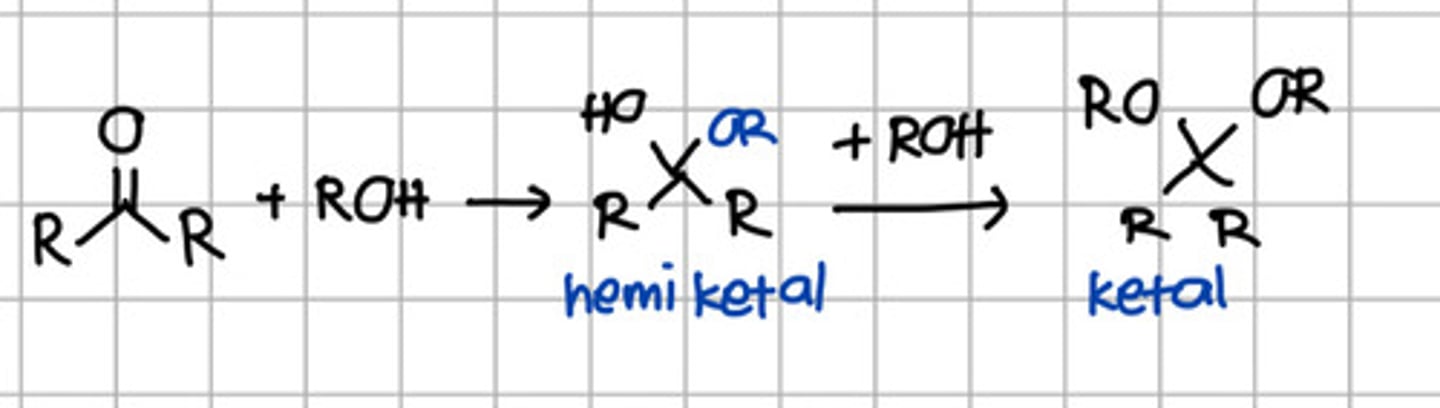
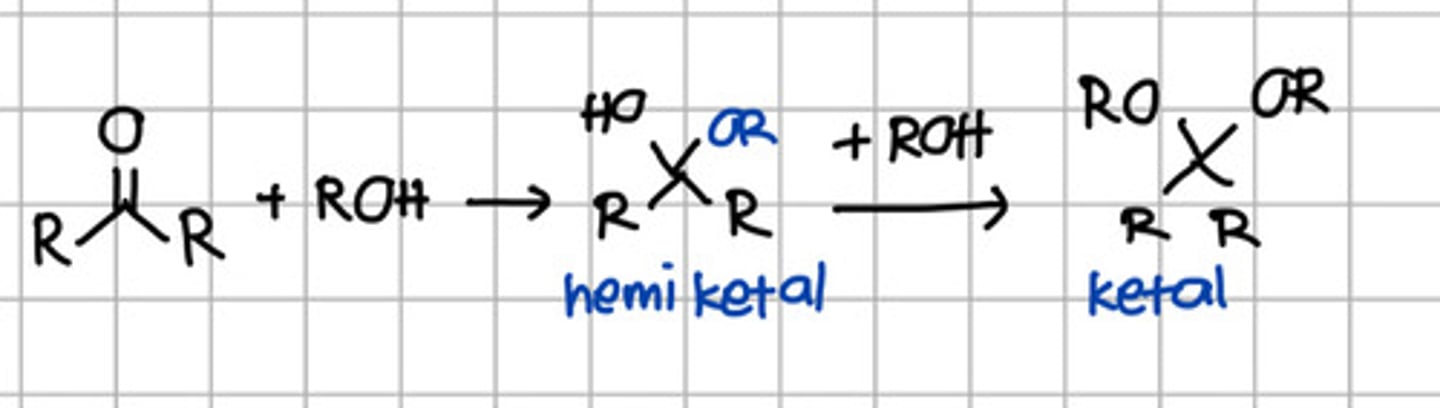
Product of initial nucleophilic addition of ROH to ketone.
a. Hemiketal
b. Hemiacetal
c. Ketal
d. Acetal
e. Imine
a. Hemiketal
Product of 2 rounds of nucleophilic addition of ROH to aldehyde.
a. Hemiketal
b. Hemiacetal
c. Ketal
d. Acetal
e. Imine
d. Acetal
Product of 2 rounds of nucleophilic addition of ROH to ketone.
a. Hemiketal
b. Hemiacetal
c. Ketal
d. Acetal
e. Imine
c. Ketal
Product of initial nucleophilic addition of RNH2 to aldehyde or ketone.
a. Hydroxylamine
b. Imine
c. Ketal
d. Acetal
a. Hydroxylamine
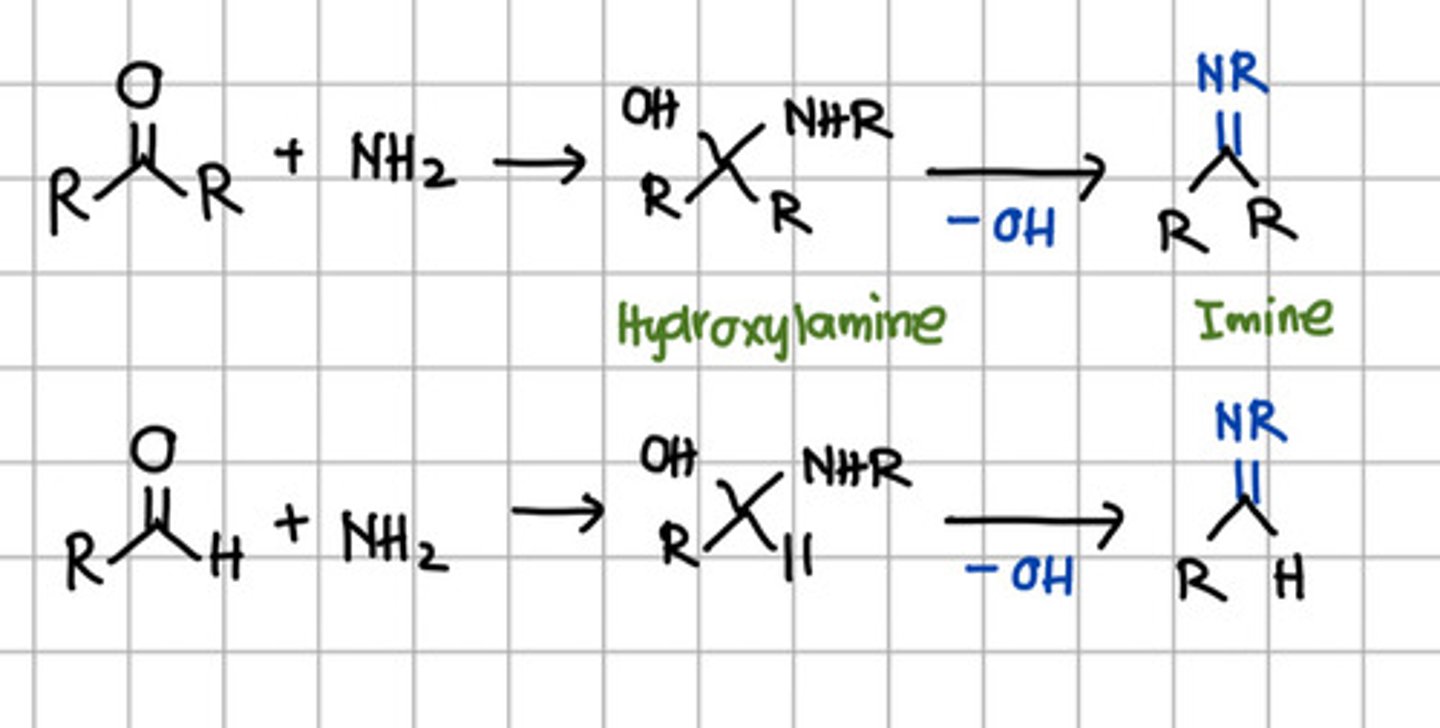
Product of complete nucleophilic addition of RNH2 to aldehyde or ketone.
a. Primary amine
b. Secondary amine
c. Tertiary amine
d. All
b. Secondary amine - aka Imine.
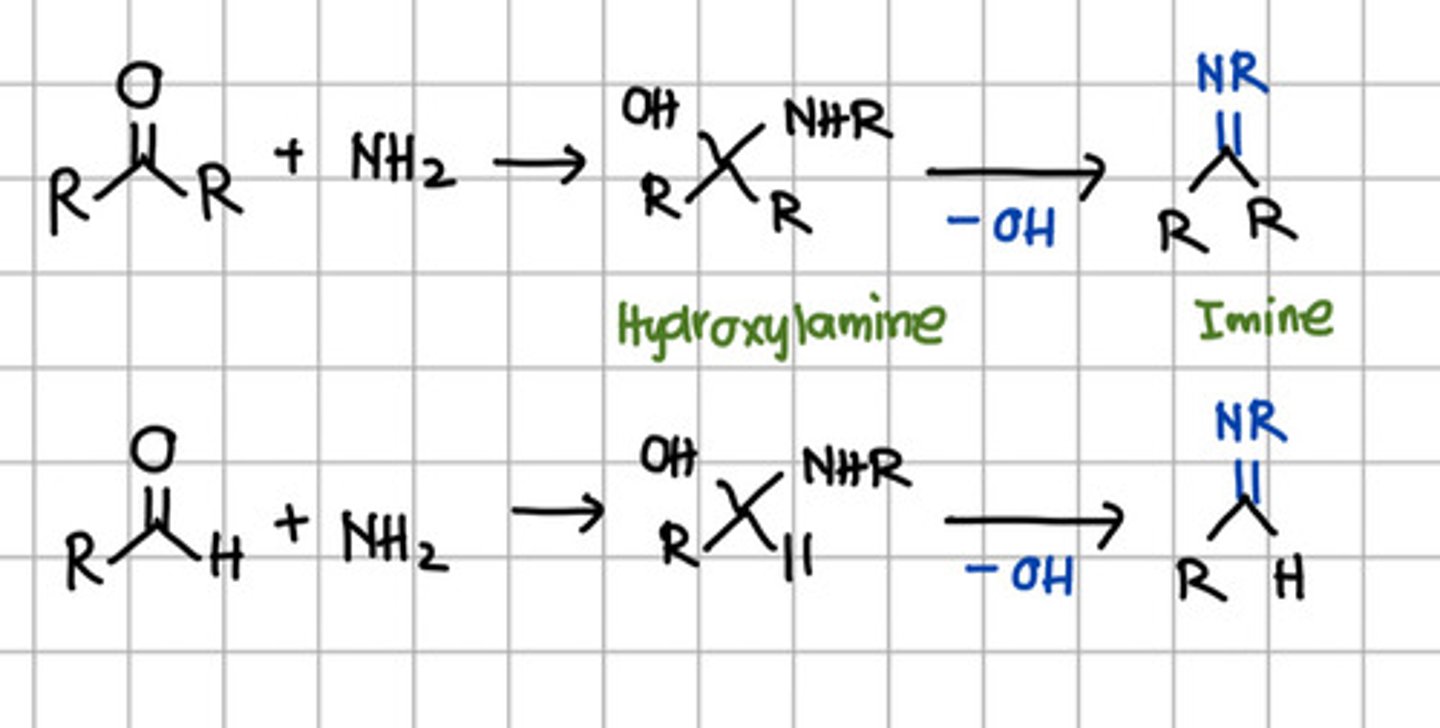
Qualitative test for both aldehyde and ketone.
a. Beilstein test
b. 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine test
c. Fehling's and Tollens test
d. Lucas test
b. 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine test
Qualitative test for aldehyde only.
a. Beilstein test
b. 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine test
c. Fehling's and Tollens test
d. Lucas test
c. Fehling's and Tollens test - These are tests for reducing substance thus to which aldehyde will yield positive result.
COOH derivatives except:
a. Ester
b. Amide
c. Acyl halide
d. Acid anhydride
e. None
e. None
Mechanism of reaction of carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. Electrophilic addition
b. Electrophilic substitution
c. Nucleophilic addition
d. Nucleophilic substitution
d. Nucleophilic substitution - or more specifically nucleophilic acyl substitution
Product of hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. RCOOH
d. RCOOR
c. RCONH2
d. RCONHR
e. RCOCl
a. RCOOH
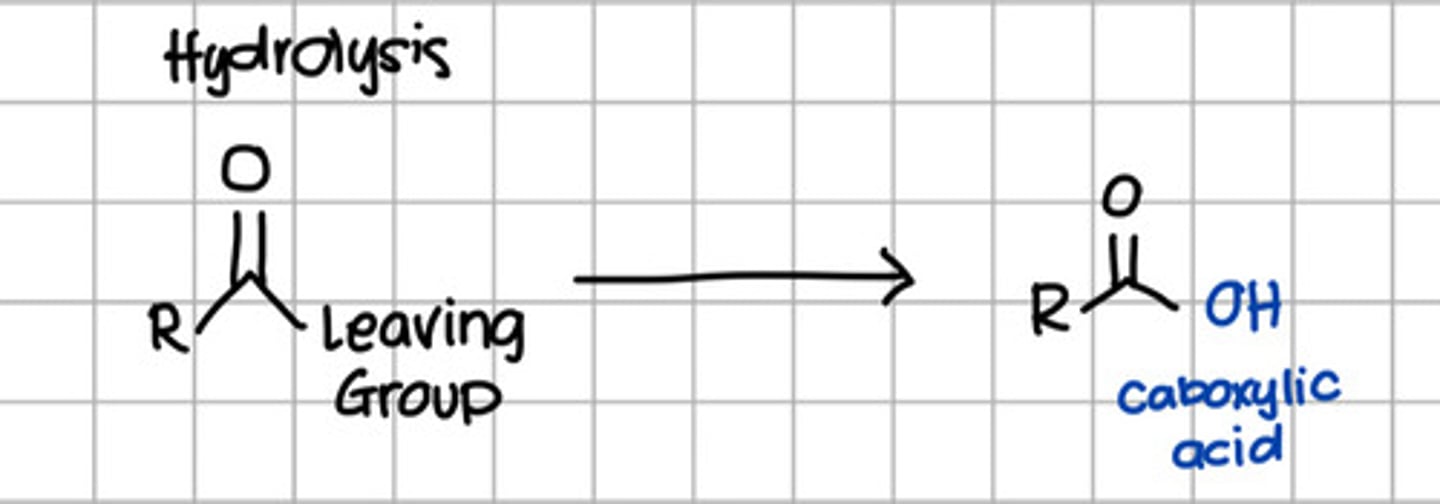
Product of nucleophilic substitution of carboxylic acid derivatives with ROH.
a. RCOOH
d. RCOOR
c. RCONH2
d. RCONHR
e. RCOCl
d. RCOOR - Thus also referred to esterification
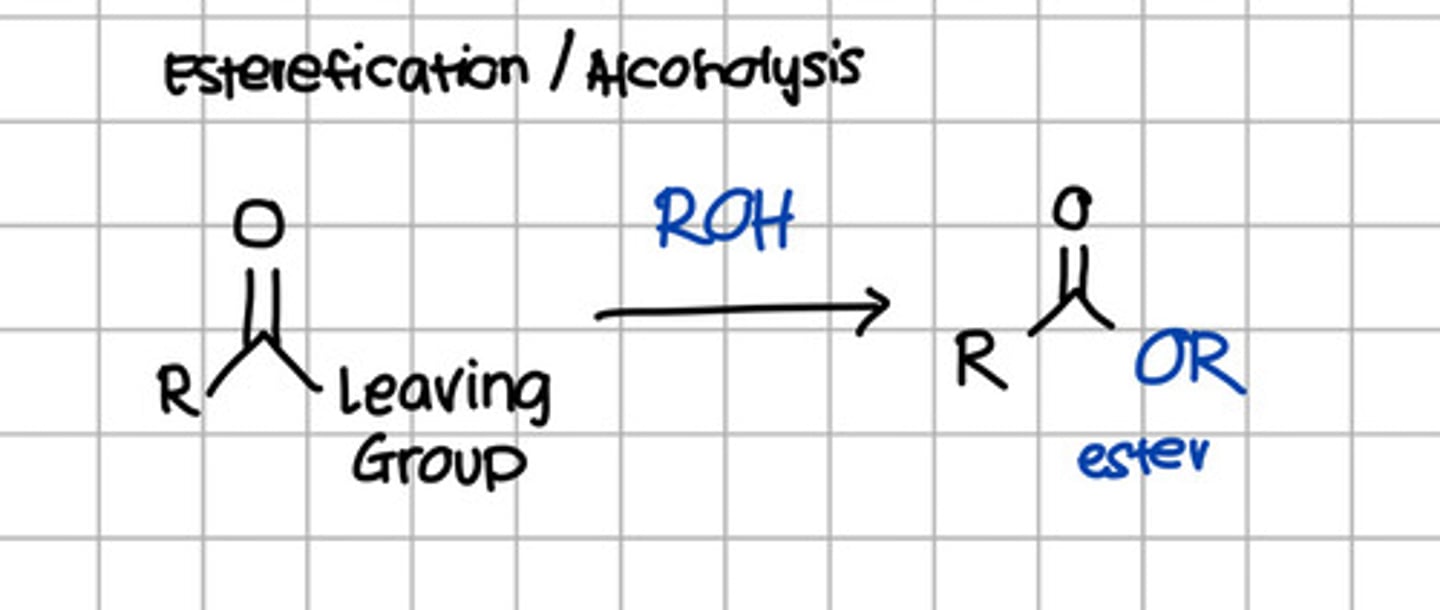
Product of alcoholysis of carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. RCOOH
d. RCOOR
c. RCONH2
d. RCONHR
e. RCOCl
d. RCOOR - Alcoholysis is also known as esterification
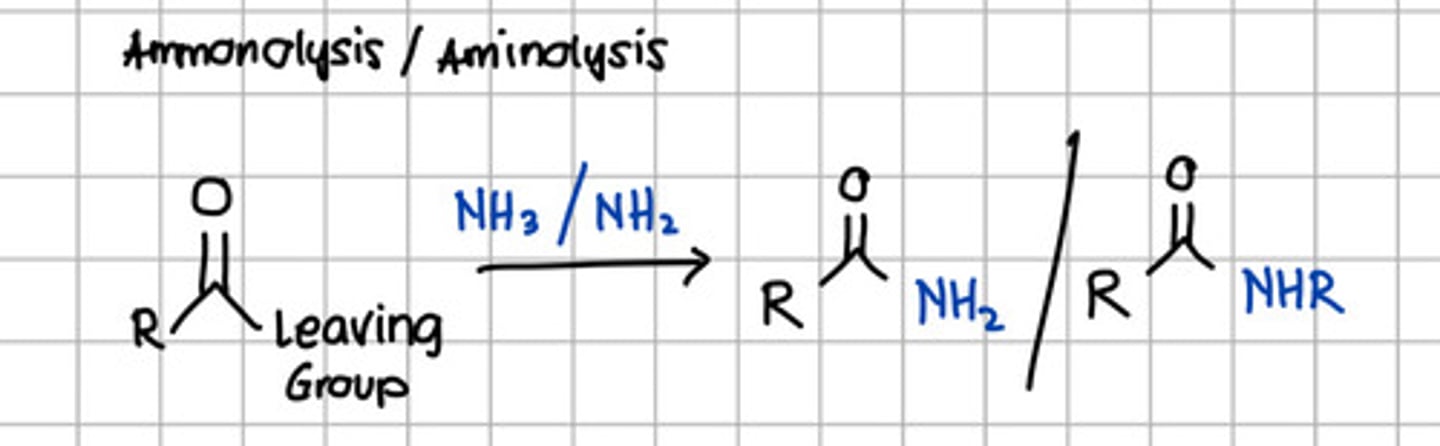
Product of ammonolysis or aminolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. Ester
d. Carboxylic acid derivatives
c. Amide
d. RCONHR
e. RCOCl
c. RCONH2 - through nucleophilic substitution with NH3, ammonia.
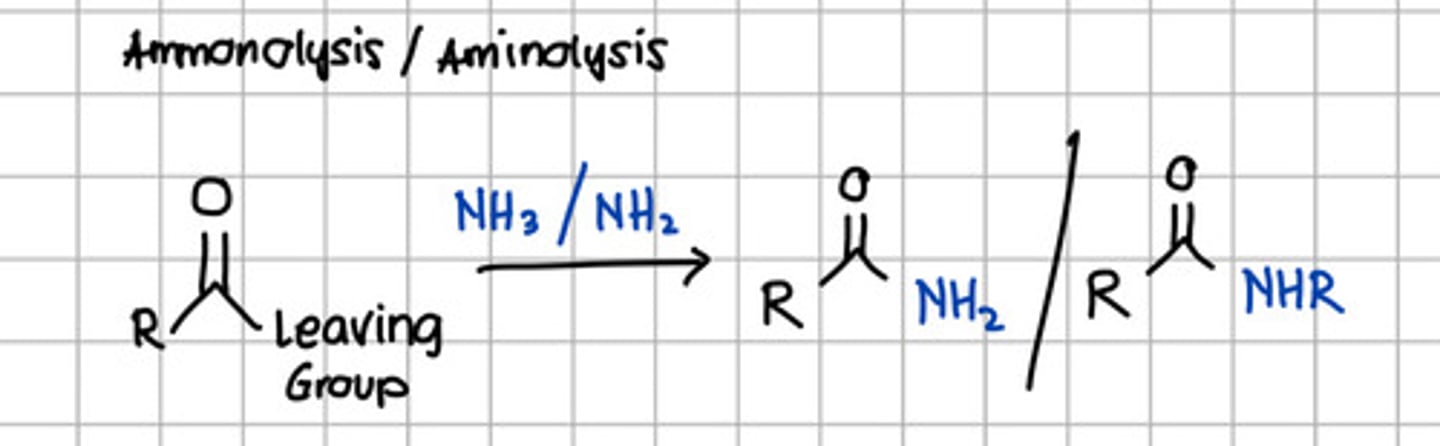
Product of ammonolysis or aminolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. Ester
d. Amide
c. Alcohol
d. Acyl anhydride
e. None of the choices
d. Amide
with NH3 - Ammonolysis
with NH2 - Aminolysis
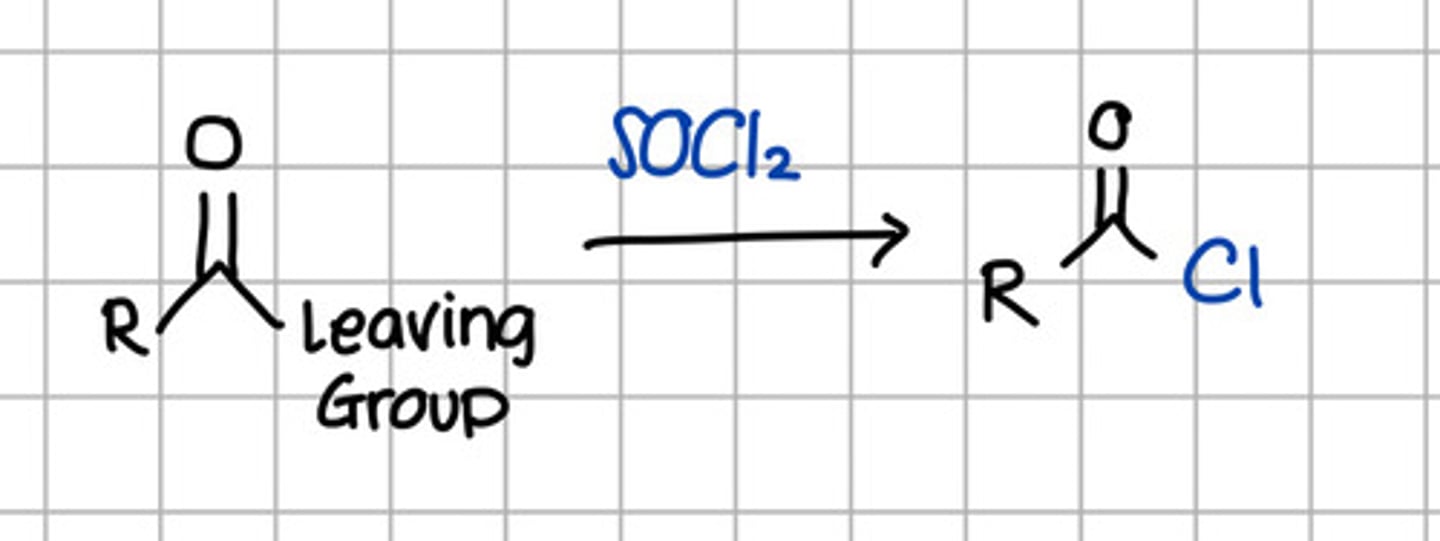
Product of nucleophilic substitution of thionyl chloride to carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. RCOOH
d. RCOOR
c. RCONH2
d. RCONHR
e. RCOCl
e. RCOCl
Qualitative tests for organic bases.
a. Beilstein test
b. Grignard test
c. Hinsberg test
d. Lucas test
c. Hinsberg test
Organic bases are the AMINES.
Arrange the different type of amines by increasing basicity.
a. 1° < 2° < 3°
b. 3° < 2° < 1°
c. 1° < 3° < 2°
d. 2° < 3° < 1°
c. 1° < 3° < 2°
Although 3° amine has the most electron donating groups (R group), it has less basicity because of steric strain that can be present between H of R groups.
Thus 2° amines are the most basic followed by 3° amines and 1° amines.