Chem 1050~Unit 2 Exam
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
what are the 3 subatomic particles that make up an atom?
protons, neutrons and electrons
what is the charge of a proton?
+1
what is the charge of a neutron?
0
what is the charge of a electron?
-1
where are protons found?
in the nucleus of each atom
where are electrons found?
orbiting the nucleus of an atom in distinct electron shells
where are neutrons found?
in the nucleus of each atom
what is the relative mass of an electron?
1/1840 amu (very small)
what is the relative mass of a proton?
1 amu
what is the relative mass of an neutron?
1 amu
what does the “atomic number” refer to?
number of protons in an element
Since the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom, the __________ will be the same as the number of electrons.
atomic number
what does the ‘mass number’ refer to?
number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
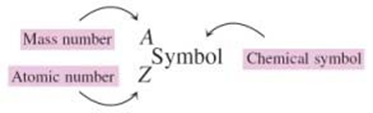
what is the complete chemical symbol notation?
the mass number is on the top and and the atomic number is on the bottom
What is an isotope?
Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons.
are ‘groups’ on the periodic table in rows or columns?
columns
are ‘periods’ on the periodic table in rows or columns?
rows
what is an example of describing an element on the periodic table?
group IVA period 3
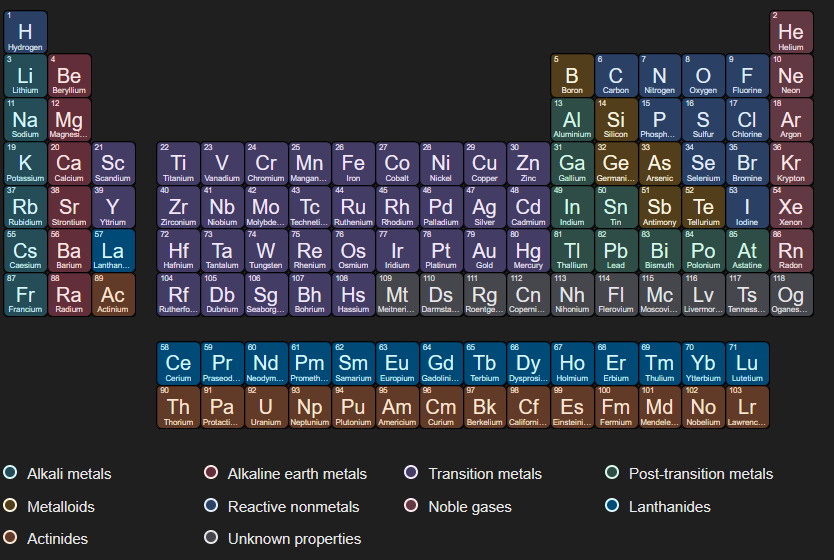
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the noble gases located?
VIIIA (8A)
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the halogens located?
Group VIIA (7A)

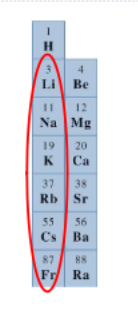
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the alkali metals located?
Group IA
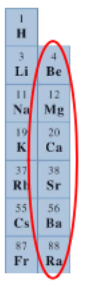
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the alkaline earth metals located?
Group IIA
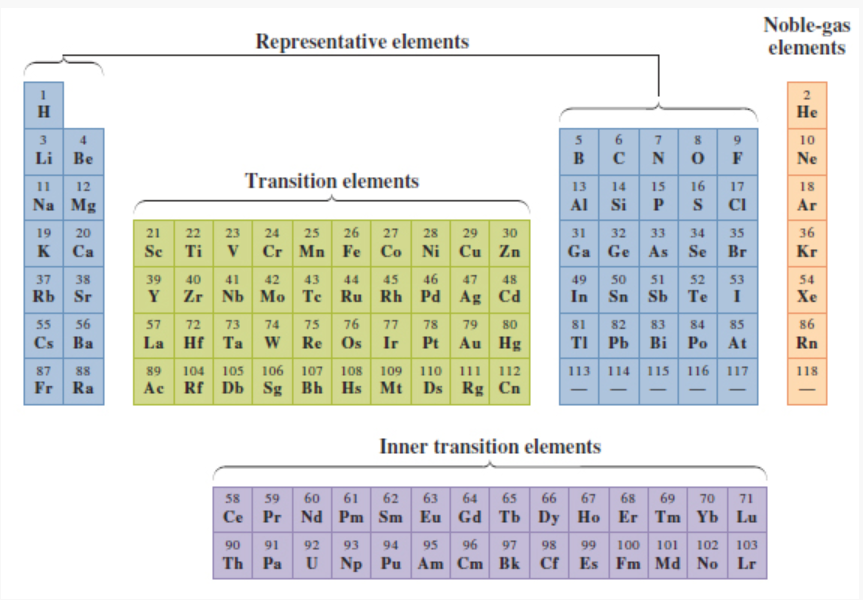
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the representative elements located?
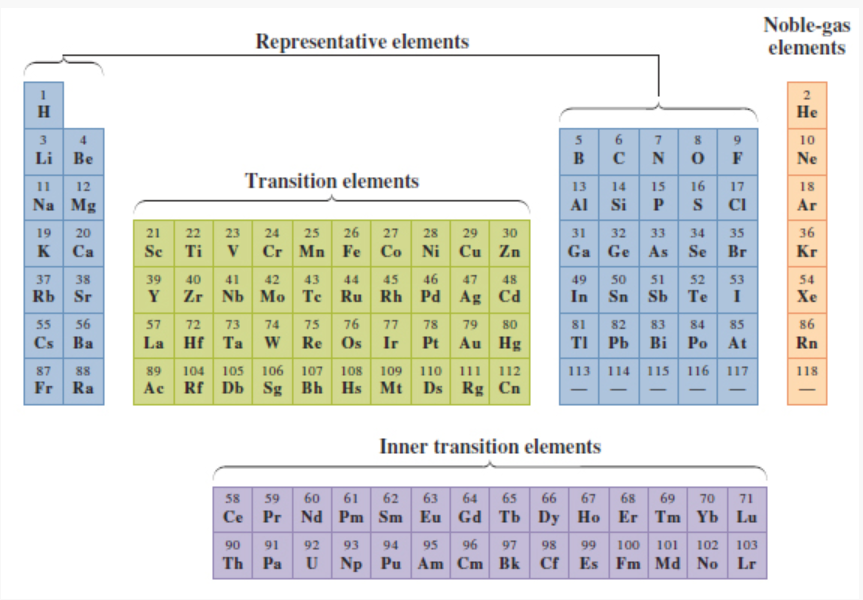
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the transition elements located?
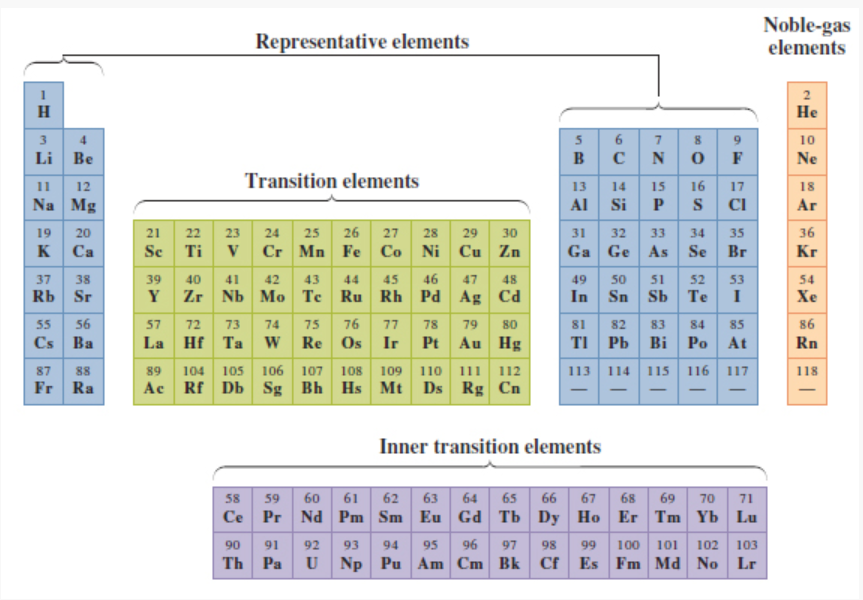
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the inner transition elements located?
how many elements are non-metal?
only 22 out of 118
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the Lanthanide elements located?
period 8
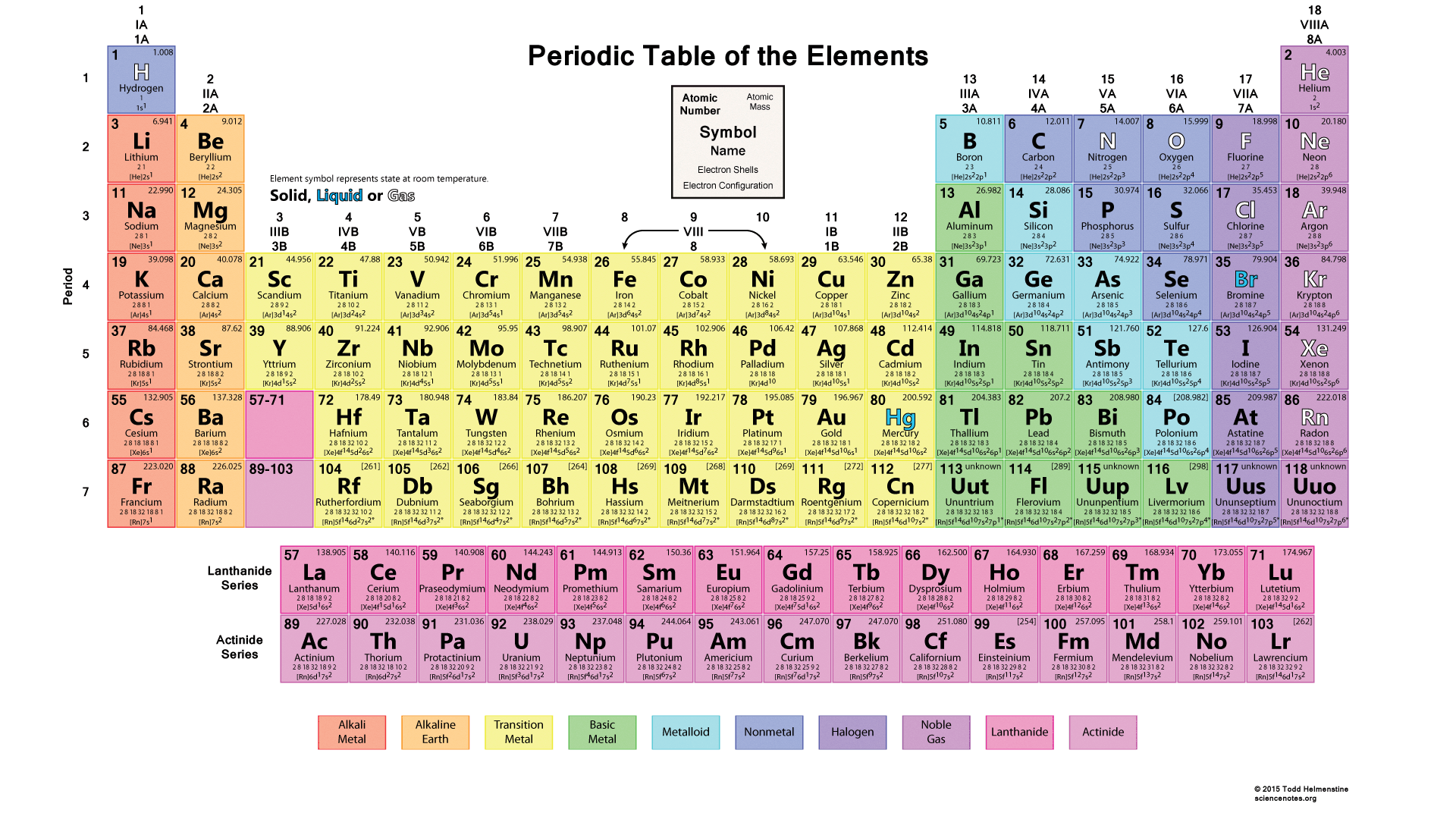
What elements/ where on the periodic table are the Actinide elements located?
period 9
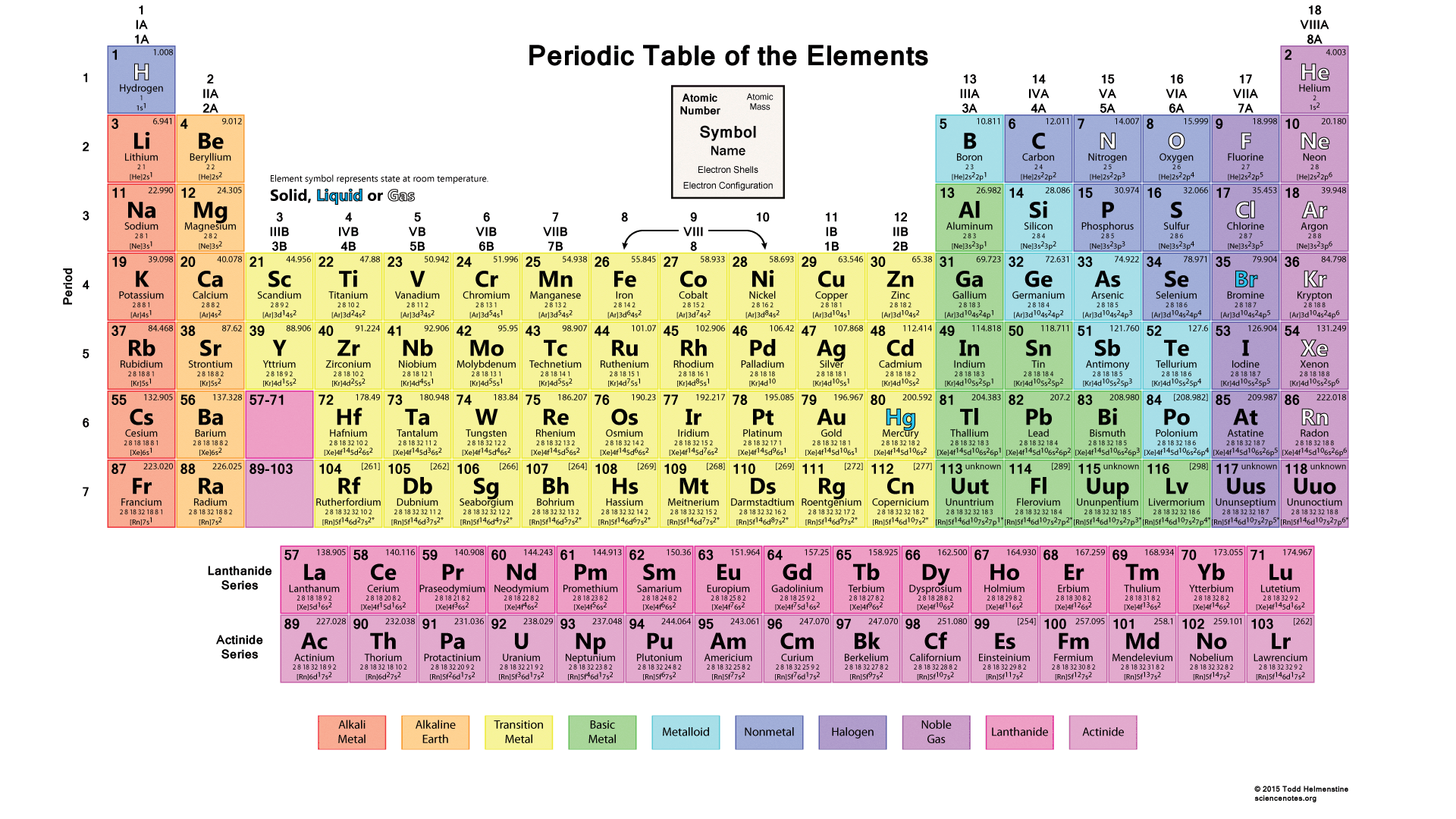
What are the properties of metal?
luster (shiny), malleable (sheets), ductile (wires), good conductors (heat & electricity), high melting points, dense. ALSO solid at room temp (other than Hg)
what are the properties of nonmetals?
dull, brittle, poor conductors, lower densities & melting points. Many are gases
bromine = only liquid at room temp
what is a trick to remember the metals on the periodic table?
Metals = left & center.
Nonmetals = upper right corner.
Zig-zag line = “stair-step” divider (metalloids lie along it).
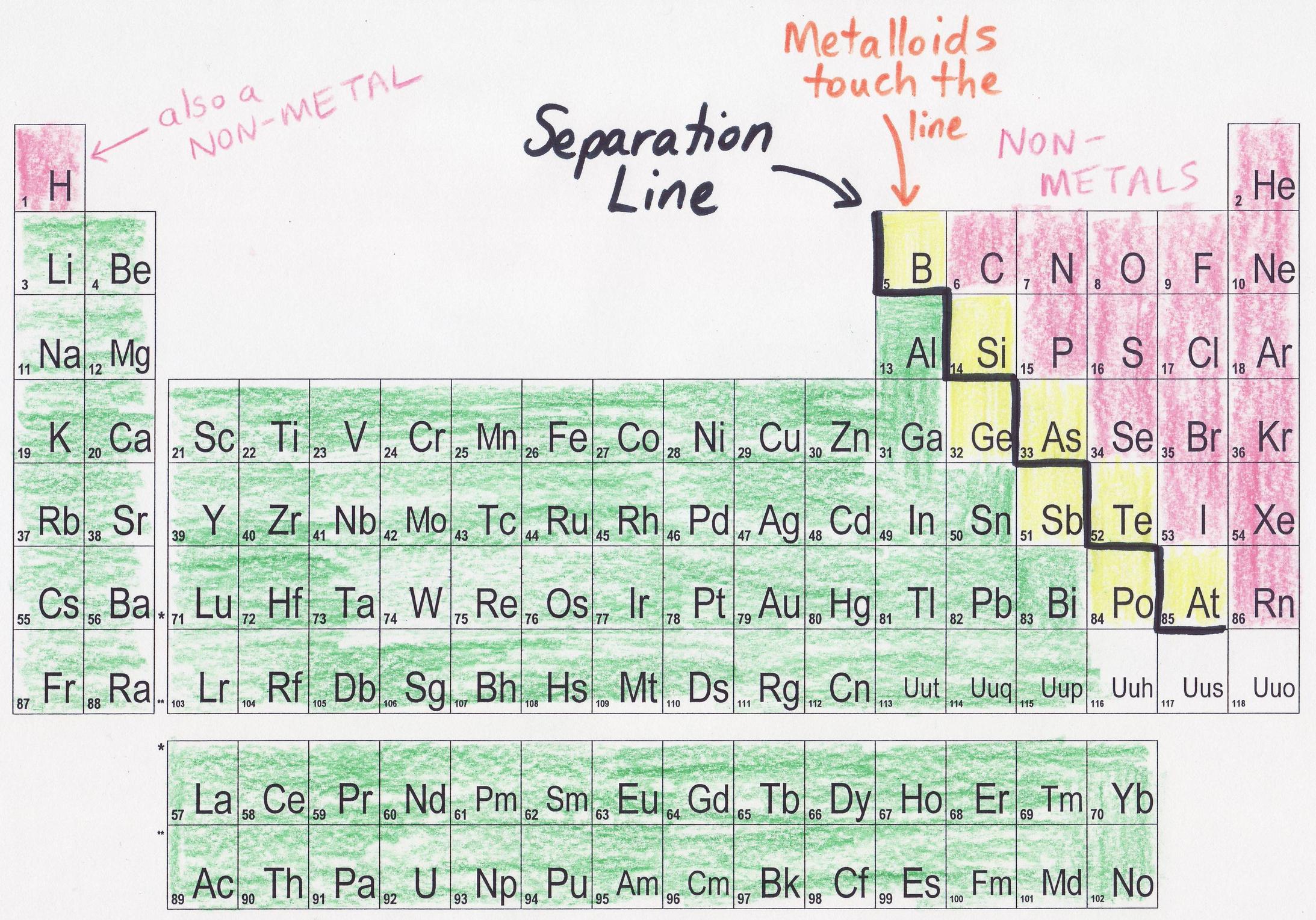
what are shells?
main energy levels (eg. shell 1, 2, 3..)
what are subshells?
s, p, d, f.
what are orbitals?
s = 1 orbital (2 electrons)
p = 3 orbitals (6 electrons)
d = 5 orbitals (10 electrons)
f = 7 orbitals (14 electrons)
What are the rules for electron configuration for orbital diagrams?
Aufbau principle- fill lowest energy orbitals first.
Hunds Rule- orbitals of equal energy get 1 electron each before pairing.
Pauli Exclusion Principle – max 2 electrons per orbital, opposite spins.
what kind of elements are involved with ionic bonding? like what kind of elements must be in an ionic bond?
a metal and a nonmetal
what is the definition of a chemical bond?
the attractive force that holds two atoms together in a more complex unit
what is the definition of an ionic bond?
a chemical bond formed through the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or group of atoms to another atom or group of atoms
what is the definition of a covalent bond?
A chemical bond formed through the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms
what is the definition of valence electrons?
An electron in the outermost electron shell of a representative element or noble gas element (the electrons involved in bonding).
what do the dots on a lewis symbol represent?
valence electrons
what is the octet rule?
In forming compounds, atoms of elements lose, gain, or share electrons in such a way as to produce a noble-gas electron configuration for each of the atoms involved. (to get to 8 electrons in each element).
AKA
Atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve 8 in their outer shell (noble gas configuration).
How many electrons is in a stable element (other than Hydrogen)
8
what is the definition of an ion?
Atom with electrical charge from gaining or losing electrons.
how are ions formed?
gaining or losing electrons
which elements form negatively charged ions (anions)
Elements in Groups VIIA, VIA, and VA
which elements form positively formed ions (cations)
elements in groups IA, IIA and IIIA
what is the relationship between where an element is located on the periodic table and the number of electrons gained or lost?
group 1A loses 1 electron so its charge is +1
group 2A loses 2 electrons so its charge is +2
group 3A loses 3 electrons so its charge is +3
group 5A gains 3 electrons so its charge is -3
group 6A gains 2 electrons so its charge is -2
group 7A gains 1 electrons so its charge is -1
group 8A is already stable so it gains/loses 0 electrons and its charge is 0 (other than helium)
what is the electron configuration all elements have when they have formed an ion?
the electron configuration of the nearest nobel gas
how are ionic bonds formed?
in the rules of chemical nomencature, what is given first?
the full name of the metallic element
in the rules of chemical nomencature, what suffix is added to the nonmetal element?
-ide
which metals have a fixed charge on the periodic table?
what elements have a variable charge on the periodic table?
what are the 6 polyatomic ions we need to know?
hydroxide, nitrate, sulfate, carbonate, phosphate, ammonium
what is the name of this chemical formula:
OH⁻
Hydroxide
what is the name of this chemical formula:
NO₃⁻
Nitrate
what is the name of this chemical formula:
SO₄²⁻
Sulfate
what is the name of this chemical formula:
CO₃²⁻
Carbonate
what is the name of this chemical formula:
PO₄³⁻
Phosphate
what is the name of this chemical formula:
NH₄⁺
Ammonium
what is the chemical formula of this polyatomic ion:
Hydroxide
OH⁻
what is the chemical formula of this polyatomic ion:
Nitrate
NO₃⁻
what is the chemical formula of this polyatomic ion:
Sulfate
SO₄²⁻
what is the chemical formula of this polyatomic ion:
Carbonate
CO₃²⁻
what is the chemical formula of this polyatomic ion:
Phosphate
PO₄³⁻
what is the chemical formula of this polyatomic ion:
Ammonium
NH₄⁺
What is the charge of the following polyatomic ion:
Hydroxide?
-1
What is the charge of the following polyatomic ion:
Nitrate?
-1
What is the charge of the following polyatomic ion:
Sulfate?
-2
What is the charge of the following polyatomic ion:
Carbonate?
-2
What is the charge of the following polyatomic ion:
Phosphate?
-3
What is the charge of the following polyatomic ion:
Ammonium?
+1
what are the 2 types of chemical bonds?
ionic and covalent (molecular)