skills nmu part 2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
what are cognition and metacognition ?
• Cognition ( المعرفة (is a mental process: Memory, learning, problem solving, Attention, decision making
• Metacognition ( المعرفة وراء ما (is higher order cognitive thinking: A person has higher control of his cognition (thinking about thinking)
metacognition involves two key elements
1-knowledge of cognition
2-regulation of cognition
knowledge of cognition is done through 3 ?
• Awareness of factors that influence your own learning
• Choosing the appropriate strategy for the specific learning situation
• Identifying one’s own learning style (visual, auditory, kinesthetic..)
regulation of cognition is done through 2 ?
setting goals and planning
monitoring and evaluating your own learning
examples of setting goals and planning (regulation of cognition) ? 3
o Make a to-do-list
o Gathering and organizing study materials
o Arranging a study space and schedule
examples of monitoring and evaluating your own learning (regulation of cognition) ? 5
o Monitoring mistakes
o Evaluating task success: answer formative exam
o Assessing if the strategy you are using is working or not
o Making adjustments
o Trying something new
what is the MAIN sign of poor metacognition
One of the biggest pitfalls in learning (metacognitive bias and the illusion of knowing: Learners experience when they “feel” they have learned a concept, when in fact it is still primarily in their working memory. In reality, they have yet to do the hard work of establishing solid links to push that to long term memory
what are the 6 other signs of poor metacognition ?
• Won’t get started: requiring constant reminders to begin schoolwork
• Lacking study strategies: getting lost on homework assignments
• Gets stuck: failing to ask for help on schoolwork
• Unclear thinking process: unable to describe a plan for how to complete a task
• Lacks procedural knowledge: responding, “I don’t know?” when asked, ‘How will you do this?’
• Gets frustrated: giving up easily on schoolwork or homework
how to develop metacognitive skills ? 3
1-identify the needs
2-develop and implement a plan
3-monitoring and evaluating progress
بص معرفش دا ممكن يسال فيه ازاي

Gibbs’ reflective cycle steps ? 6
DFEACA
• Description of the experience
• Feelings and thoughts about the experience
• Evaluation of the experience, both good and bad
• Analysis to make sense of the situation
• Conclusion about what you learned and what you could have done differently
• Action plan for how you would deal with similar situations in the future, or general changes you might find appropriate.
في رايي اول كلمه اللي مهمه والباقي يستنتج منها
learning is ?
Changing behaviour of learner (Results in relatively permanent change in the way of thinking, feeling, and doing of the learner either Emotional Or Intellectual Allover Whole life span)
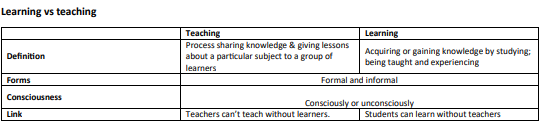
compare between teaching and learning
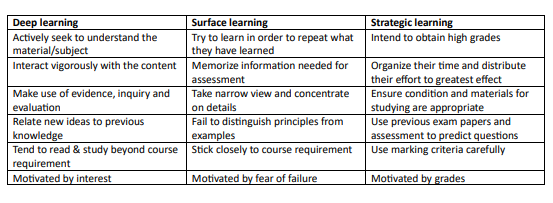
compare between deep, surface, strategic learning
kolb’s experiential learning cycle is ?
Describes the learning process whereby knowledge is created through experience Four-stage process (or cycle)
• Concrete experience
• Reflective observation
• Abstract conceptualisation
• Active experimentation
enumerate the 8 learning styles ?
عالاقل تبقي عارفهم
1-visual learners
2-auditory learners
3-kinesthetic learners
4-reading / writing
5-social learner
6-solitary learner
7-logical / mathematical learner
8-gustatory learner
visual learner is ? best way to learn ?
• individuals who prefer to take their information visually, maps, graphs, diagrams, charts, and others.
• The best way to present to visual learners is by showing them the relationship between different ideas visually.
• For instance, when explaining a scientific process, it can be done by using a flow chart.
auditory learners are ? best learn how ?
• individuals who learn better when information is heard or spoken.
• Auditory learners learn best when information is presented to them via strategies that involve talking, such as lectures and group discussions.
• They can benefit from repeating back the lessons, having recordings of the lectures, group activities that require classmates explaining ideas, etc.
kinesthetic learners are ? best way to learn is ?
• individuals who prefer to learn by doing. They enjoy a hands-on experience.
• The best way to present new information to a kinesthetic learner is through personal experience, practice, roleplaying, or simulations. For instance, they can remember an experiment by recreating it themselves.
reading / writing (learning style) is ?
how to get them engaged ?
• consume information best when it’s in words, whether that’s by writing it down or reading it.
• These individuals usually perform very well on written assignments.
• There are different ways to get a reading/writing learner to engage and understand a certain lesson. It would be best to have them describe charts and diagrams by written statements, take written quizzes on the topics, or give them written assignments.
social learners are ? best study how ?
• These types of learners favor educational lessons that include peer work or participation.
• Teachers can motivate these types of learners by using group activities, and encouraging student interaction (asking questions, sharing stories, etc.).
solitary learners are ? best way to study ?
• Best work alone.
• Making notes and reciting them back are useful activities when studying by yourself.
logical / mathematical learners are ? have what or special bcoz of what ?
• Refers to one's ability to use logic analyze cause and effect relationships, reason, solve problems,
• Skills to process words and numbers
• Find formulas and to do investigations scientifically
gustatory learners are ?
▪ Tend to chew or eat while they study.
• Making associations to food as they incorporate new knowledge with the old
thinking style is ?
It is a characteristic way of processing information. It involves how one acquires knowledge, organizes thoughts, forms views and opinions, applies personal values, solves problems, makes decisions, plans, and expresses oneself to others
enumerate the 5 types of thinking styles ?
SIPAR
synthesist
idealist
pragmatist
analyst
realist
a synthesist is ?
• creative thinker who perceives the world in terms of opposites.
• tend to be challenging and skeptical, even when there is no clear reason to be.
• open to argument and confrontation.
• like to speculate 'what if?'
idealist is ?
• believe in lofty goals and standards.
• respond to others in an attentive and receptive manner.
• avoid conflict.
• take a long view of things.
• focus on the whole.
pragmatist is ?
• look for immediate results.
• like to experiment and brainstorm.
• are good at convincing others of the validity of your ideas.
• have a willingness to agree with the ideas of others.
• are creative and innovative.
analyst is ?
• value accuracy, thoroughness, and attention to detail.
• thrive on data.
• break problems into their component parts.
• frequently write lists.
• value reason and rules
realist is ?
• like to get right at tasks and get them done.
• have a high reliance on your senses to learn about the world.
• like to deal with concrete things rather than abstract concepts.
• break down complex problems into simpler problems.
• have a poor tolerance for ambiguity.
what is the rarest combination of thinking styles ?
synthesist / realist
what are the most common thinking styles combination 3
1- analyst / realist
2-idealist / analyst
3-synthesist / idealist
how many % of people have peaks in two thinking styles ?
35%
the Myers Briggs personality type indicator is ?
It is a self-report inventory designed to identify a person's personality type, strengths, and preferences.
It has four different scales:
• Extraversion (E) – Introversion (I)
• Sensing (S) – Intuition (N)
• Thinking (T) – Feeling (F)
• Judging (J) – Perceiving (P)
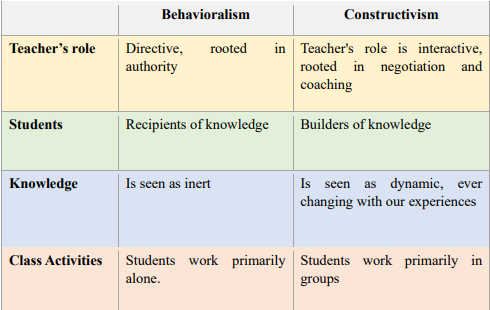
compare between behavioralism and constructivism
اعتقد مهمه فشخ
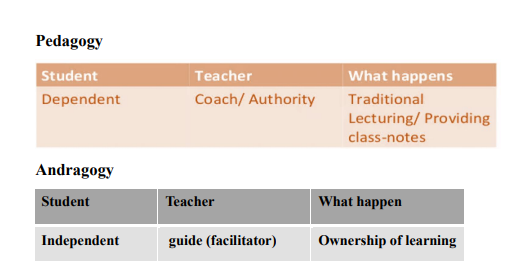
what is pedagogy ?

what is andragogy

compare between pedagogy and andragogy
knowles’ assumption of adult learning 6 ?
1- Problem Orientated: A problem or challenge is a learning opportunity → motivates adult to solve
2- Self -Directed: Adults are independent and self-directing
3- Readiness to learn: Social roles change overtime → learn new things & adapt to the changes in roles.
4- Motivation to Learn: Intrinsic motivation "I learn because I want to"
5- The Need to Know: Why do I need to know this?
6- Personal experience: Accumulation of a great deal of knowledge and experience
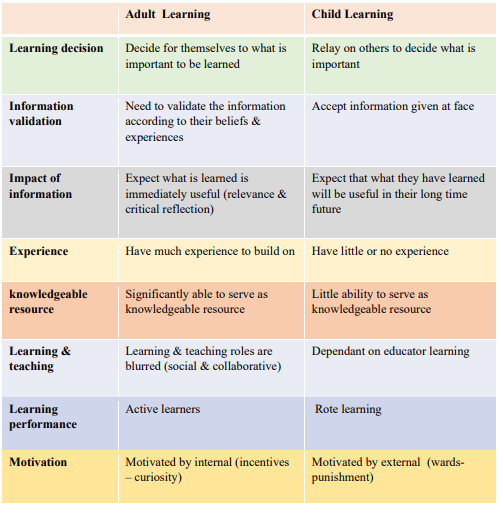
compare between adult learning and child learning
implication of learning theory 3 points
• Actively involve participants.
• Let them explore (Self-independent learner)
• Find out what the participants want to learn before designing the training
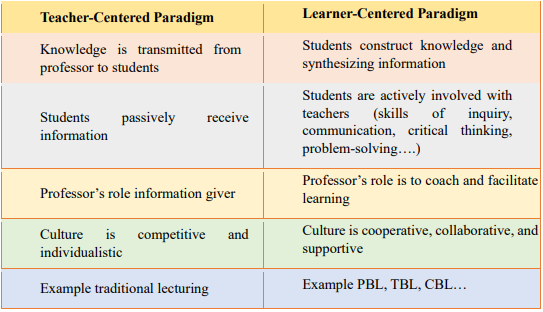
compare between teacher centered paradigm and learner centered paradigm
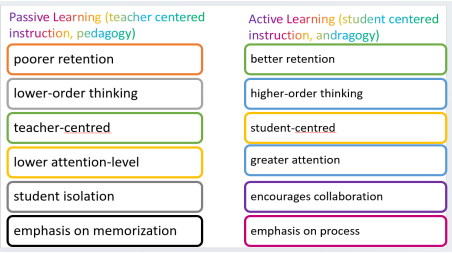
compare betwen passive learning and active learning
compare between teacher centered instruction and student centered instruction
compare between pedagogy and andragogy
كله نفس المعني
advantages of lecturing 5 ?
1. Delivery of large body of content
2. Addresses large audience group
3. Minimum time and resource utilization
4. Well structured and coherent
5. Empowerment and sense of control by teacher
disadvantages of lecturing 4 ?
1. Lack of active participation (attention span)
2. Lack of long-term effects (poor retention)
3. Limited suitability to cultivate higher order
4. Limited suitability for problem topics cognition
how to Improve retention: Memory ‐Based Lecturing? 4 points
• Link new knowledge to prior knowledge
• The more senses you use, the more durable memory
• Organize information in manageable "chunks
• Memories are like muscles: they develop with exercise: repeat repeat
how to Improve attention: interactive lecturing 2 points
• Add spice to your lectures with active learning!!
• Rather, adding small active learning strategies can make lecturing more effective for student learning.
to make learning interactive we adopt ? 8 ?
• Independent learning "Self-Directed / self –regulated learning"
• Course preparation assignment & Questions…”Brainstorm”
• Note taking
• Discussion
• Concept map & Mind map
• Peer Assisted learning
• Information technology learning
• Active learning methods as One- three-minute essay, think-pair-share
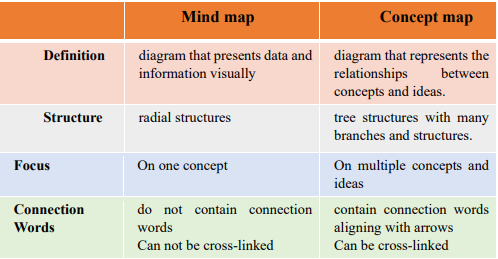
compare between mind and concept maps ?
peer assisted learning is ?
• People from similar social groupings who are not professional teachers helping each other (Students Become PAL tutors)
• lifelong learning and team-working competences.
information technology learning is ?
• An educational system that adopts interactive information and communication technology in providing educational or training programs
• May be synchronous method or Asynchronous
One- Three-minute Essay is ? 3 points
• This activity is meant to focus students on the day’s content as well as provide feedback to you as a teacher.
• This activity can be done at any time
• Students write a 1-2 min response to an open question
examples of one three minutes essay 5?
1- What is the most important thing you learned today?
2- Summarize today’s lecture in one sentence
3- What questions do you still have?
4- what remains unclear?
5- What would you like to know more about?
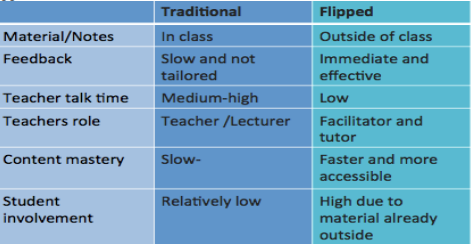
compare between traditional and flipped learning ?
collaborative learning is ?
Students: Active Learners
Teachers: “Guide on the Side”
it is A strategy in which students work together in small groups to perform a task or a specific project that meets their needs and interests, and is consistent with their strengths
The objectives of using cooperative learning groups are 3?
• Reducing the level of competition
• Increase students 'respect and understanding of others' abilities, interests and needs
• Improvement acquisition of social skills, increased academic achievement, and access to a high level of mental reasoning
integrated learning (problem solving) discuss it
• Scientific method of thinking
• Done by notifying and provoking learners thinking about a problem:
• Appropriate to their level
• Related to the subject of the lesson, and their living
• Cannot solve easily, but rather by researching and exploring the facts leading to the solution.
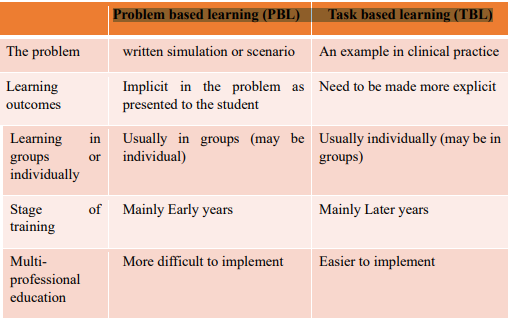
compare between Problem based learning (PBL) and Task based learning (TBL)
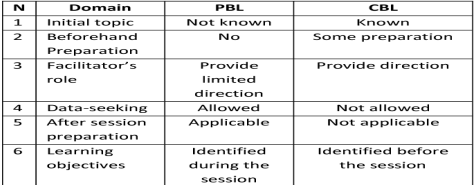
compare between problem based learning and case based learning
inquiry based learning depends on ?
• Using the principle of doubt and testing opinions
• In light of their previous knowledge
• In order to reach conclusions and knowledge away from prejudices.
• Overall goal is for students to make meaning.
• Teachers may guide the inquiry to various degrees (externally facilitated) and set parameters for a classroom inquiry
• True inquiry is internally motivated.
Experiential Learning: one learns from experience & test what we learn into new situation
5 points
• Learning from patients during clerkships, or residency for sustaining and enhancing their mastery of clinical practice
• Dissecting a cadaver
• Participating in a problem-based learning group
• Being instructed in a skills laboratory
• Project